Dynamically biased amplifier
A technology of amplifiers and operational amplifiers, applied in the fields of amplifiers, improving amplifiers to increase efficiency, and components of amplifying devices, etc., can solve the impossible, the bias circuit is not suitable for the use of high-frequency RF signals, and the difficulty of creating bias adjustment signals and other problems, to achieve the effect of linear increase and reduction of intermodulation distortion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] Throughout the drawings, the same reference numerals will be used for corresponding or similar elements.
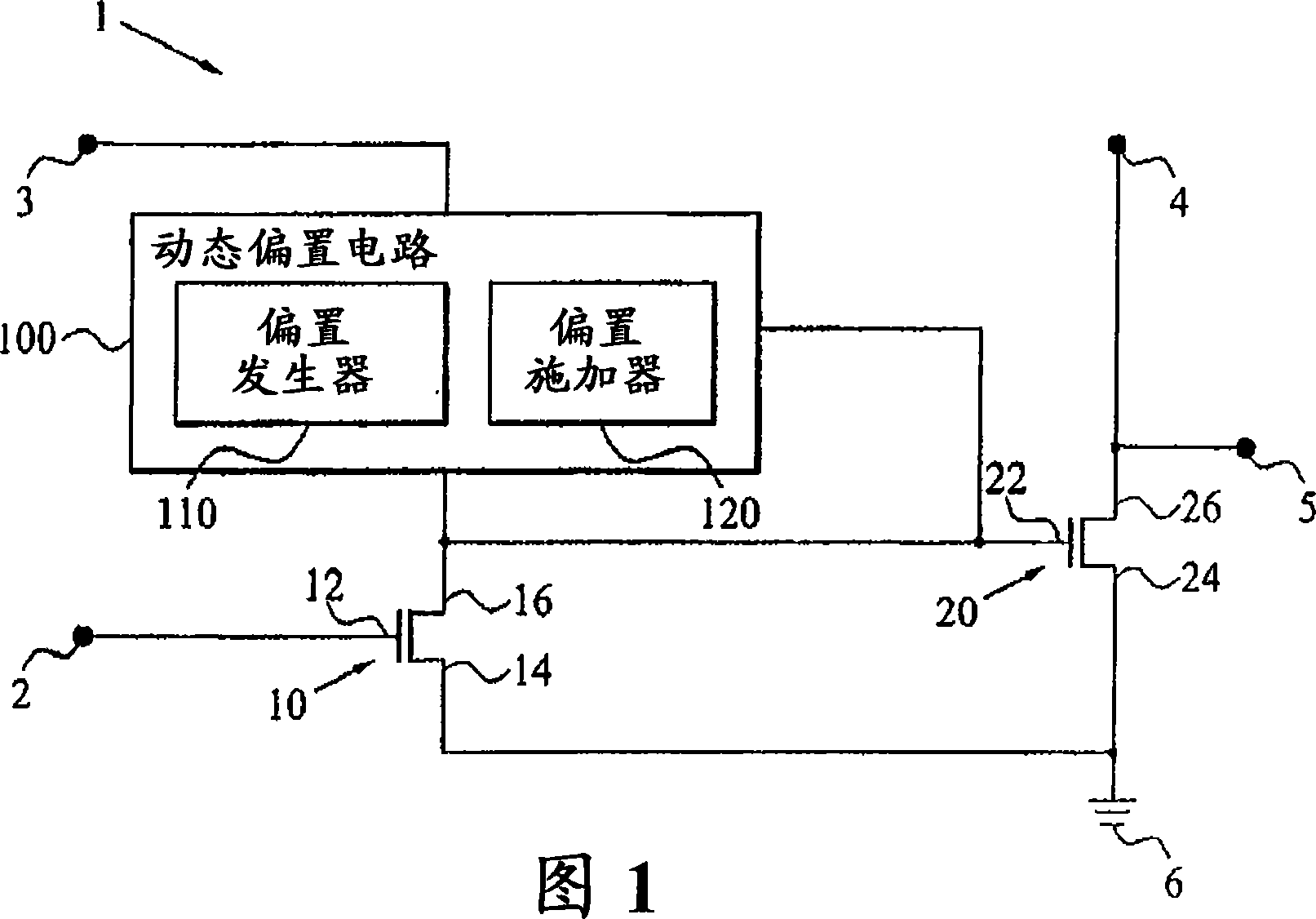
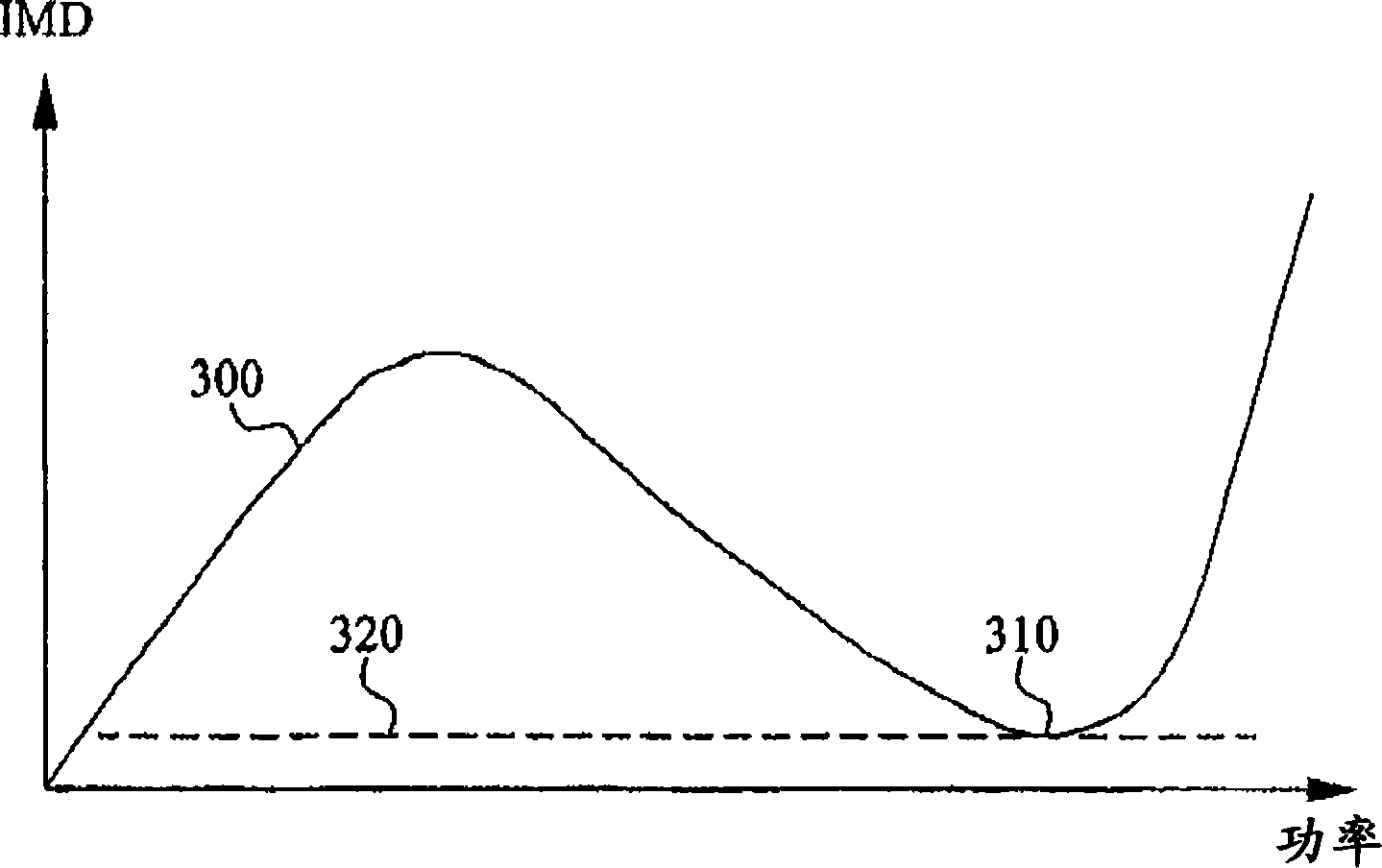
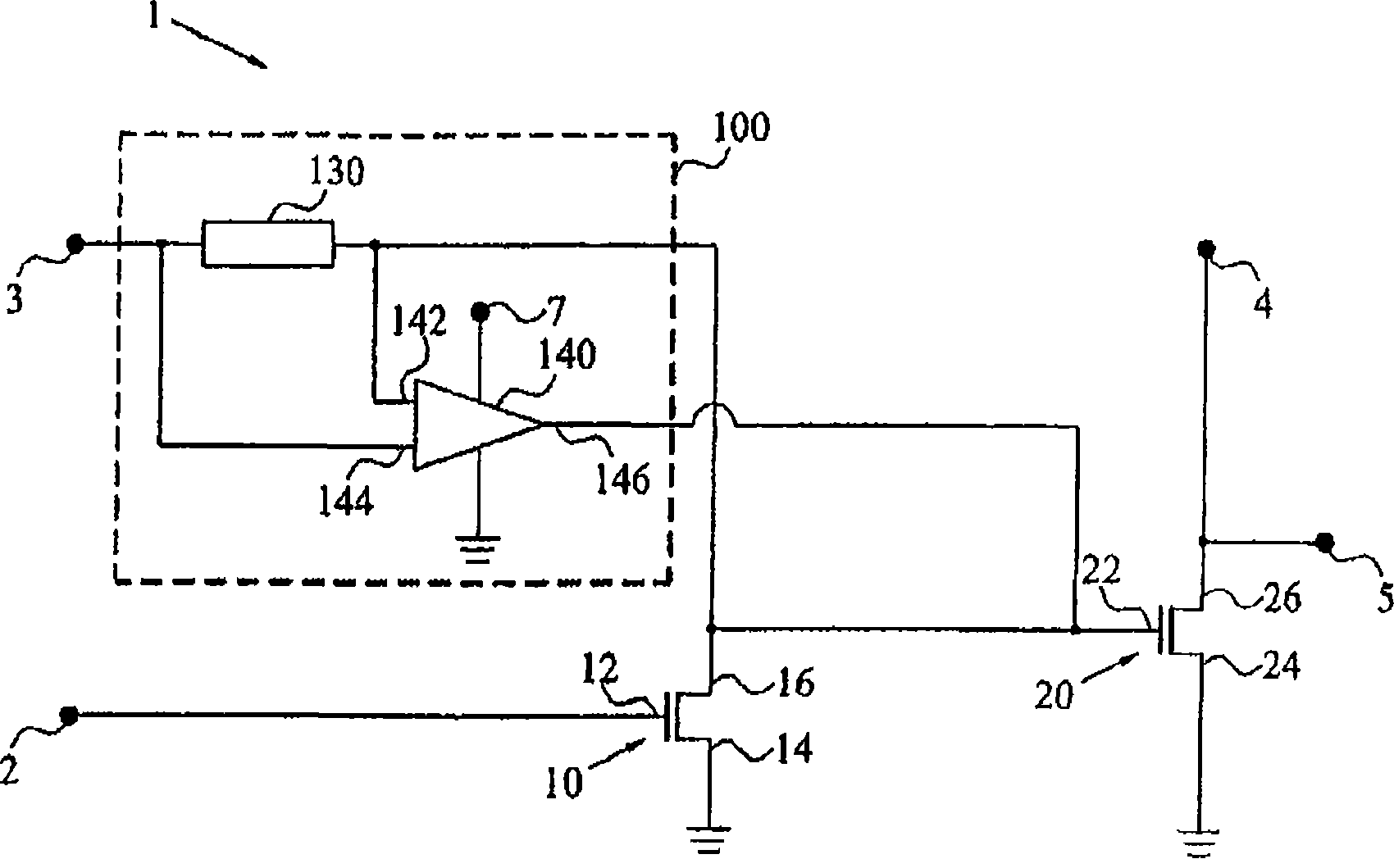
[0047] The present invention relates to dynamic biasing of transistors in amplifiers in order to reduce or suppress intermodulation distortion (IMD) and increase amplifier linearity.
[0048]In general, for a given output or input power level of the amplifier, a bias signal can be adjusted and applied in order to improve the IMD, ie reduce the IMD. Since output and input power are time-dependent, the bias signal should follow this power change. The present invention provides a dynamic bias circuit for use in an amplifier that is capable of generating a bias signal based on the input (and output) power level of the amplifier.
[0049] The dynamic biasing circuits and amplifiers described and disclosed herein are particularly useful in wireless communication applications. However, other applications are readily known to those skilled in the art.
[0050] Figure 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com