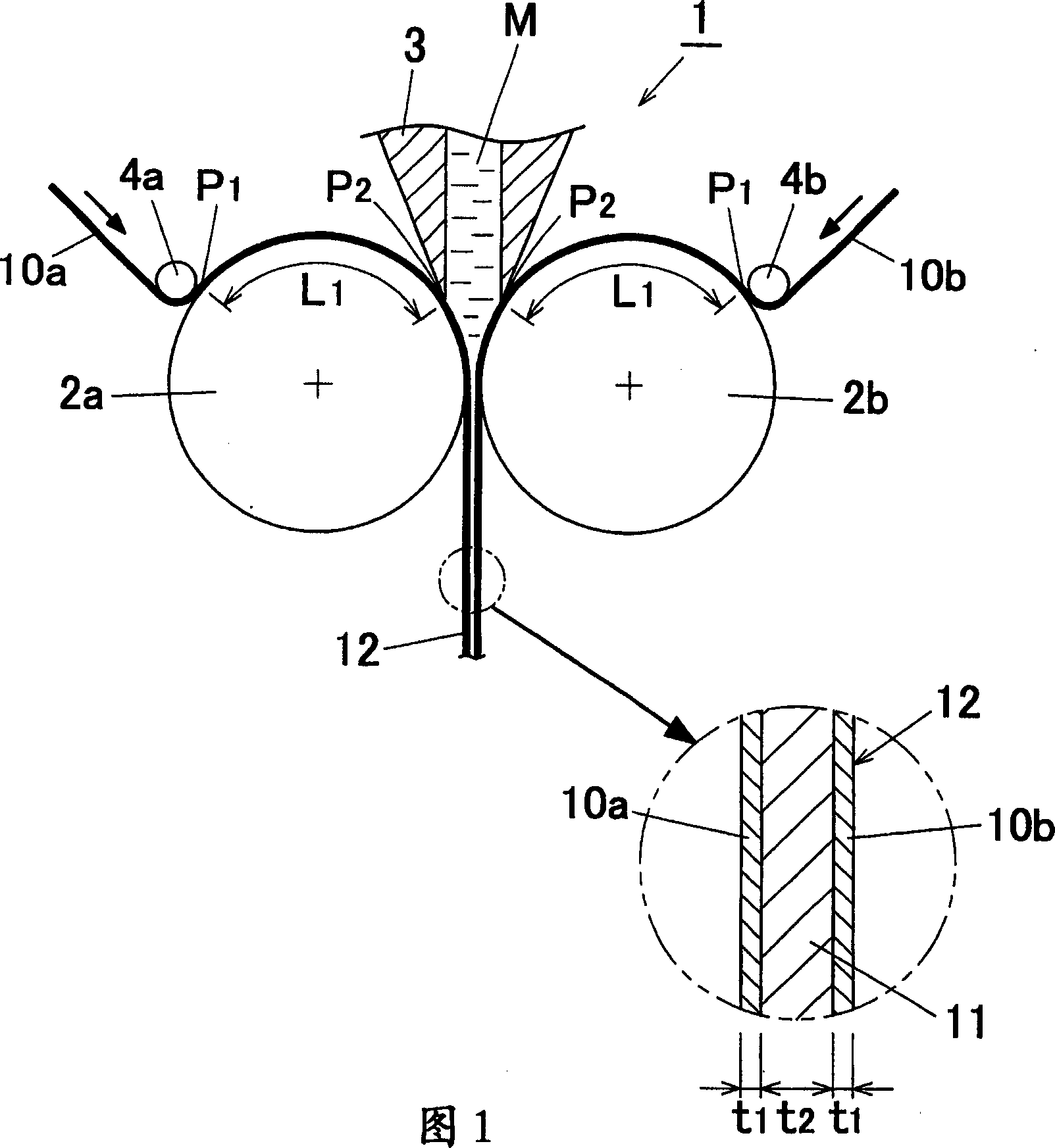
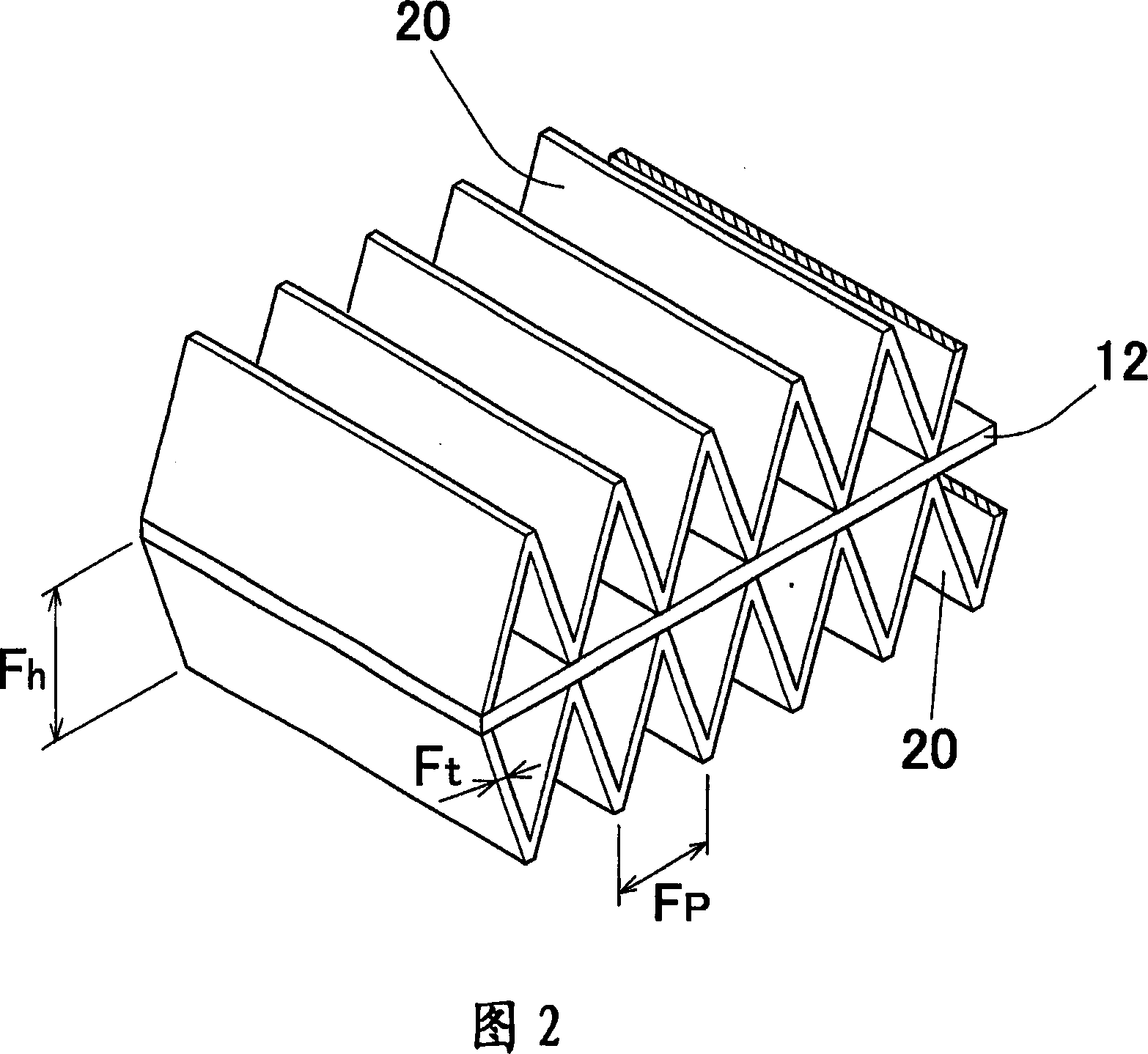
Clad material, method for manufacturing said clad material, and apparatus for manufacturing said clad material
A technology of layered materials and leather materials, applied in the field of manufacturing such composite materials, composite materials with very good high temperature strength, and devices for manufacturing such composite materials, can solve the problem of changes in roll surface characteristics, complex equipment structures, cracks, etc. and other problems, to achieve the effect of preventing change and deterioration, high cooling rate, and high cohesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0120] Example 1 is an example about the stability of the skin material and the texture of the core material under heat cladding conditions.
[0121]For skin materials 10a and 10b, ingots made of alloy Nos. (a), (c), (f) and (j) shown in Table 1 and manufactured using a semi-continuous casting method were subjected to hot rolling, Intermediate annealing at 370° C. x 4 hours, followed by cold rolling and intermediate annealing if necessary, to obtain a material with a thickness t1 of 0.20 mm.
[0122] For Inventive Examples Nos. 1 to 10 and Comparative Examples Nos. 11 to 19, 21 shown in Table 2 using the above-mentioned cladding material manufacturing apparatus 1, a skin material 10a coated on both surfaces of the core material 11 was produced. and 10b of the three-layer hot-rolled clad material 12 .
[0123] In detail, under the condition in which the skin materials 10a and 10b whose reference numbers are shown in Table 2 were set and rotated while contacting the peripheral ...
example 2
[0138] This example 2 is an example about the brazing performance and corrosion resistance of leather parts and skin materials.
[0139] For the skin materials 10a and 10b, the ingots produced with the alloy Nos. (m) to (r) shown in Table 1 using the semi-continuous casting method were subjected to hot rolling, intermediate annealing at 370° C. for 4 hours, and then if Cold rolling and intermediate annealing were carried out as necessary to obtain a material with a thickness t1 of 0.35 mm.
[0140] For Invention Examples Nos. 22 to 29 shown in Table 3 using an alloy having the composition shown in Table 1 as the molten metal M to be used as a core material, it was manufactured using the above-mentioned apparatus 1 for manufacturing the clad material of Example 1 A three-layer clad material 12 in which skin materials 10a and 10b are pressure-bonded on both surfaces of a core material 11 . At the time of manufacture, the target thickness of the core material 11 after hot rollin...
example 3
[0154] This Example 3 is an example of evaluation regarding the strength of the core material composition.
[0155] For skin materials 10a and 10b, ingots produced with alloy No.(t) shown in Table 1 using the semi-continuous casting method were subjected to hot rolling, intermediate annealing at 370° C. for 4 hours, and then cooling if necessary. Rolling and intermediate annealing to obtain a material with a thickness t1 of 0.25 mm.
[0156] For Invention Examples Nos. 30 to 35 shown in Table 4 using alloys having the compositions (u) to (z) shown in Table 1 as the molten metal M to be used as a core material, the above-mentioned according to Example 1 was used. The apparatus 1 for producing a clad material produces a three-layer clad metal 12 in which skin materials 10 a and 10 b are pressure-bonded on both surfaces of a core material 11 . At the time of manufacture, the target thickness of the core material 11 after hot rolling cladding was set to 5.0 mm. The contact dista...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com