Patents
Literature
506results about How to "Control tension" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Comprehensive tissue attachment system
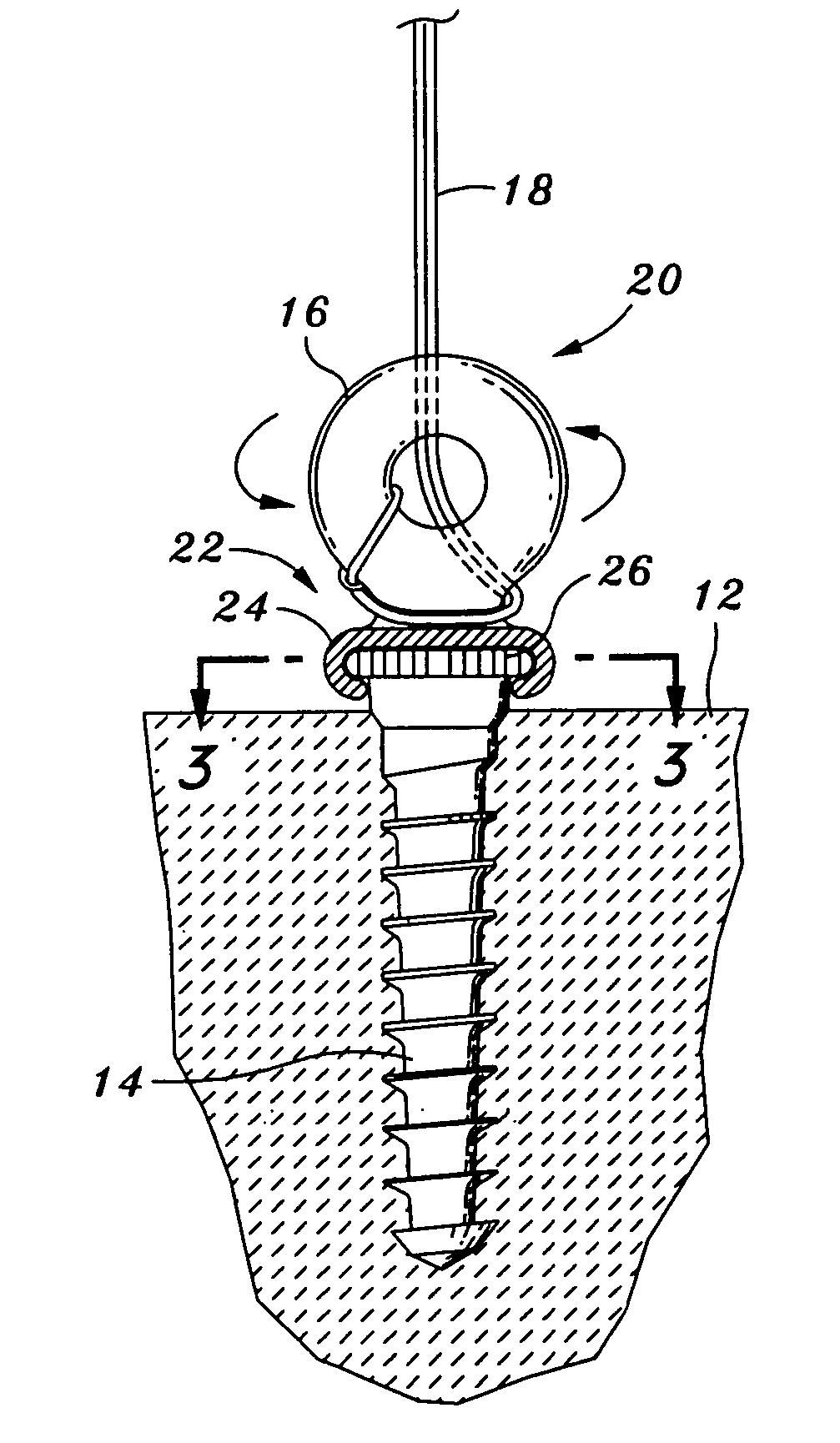
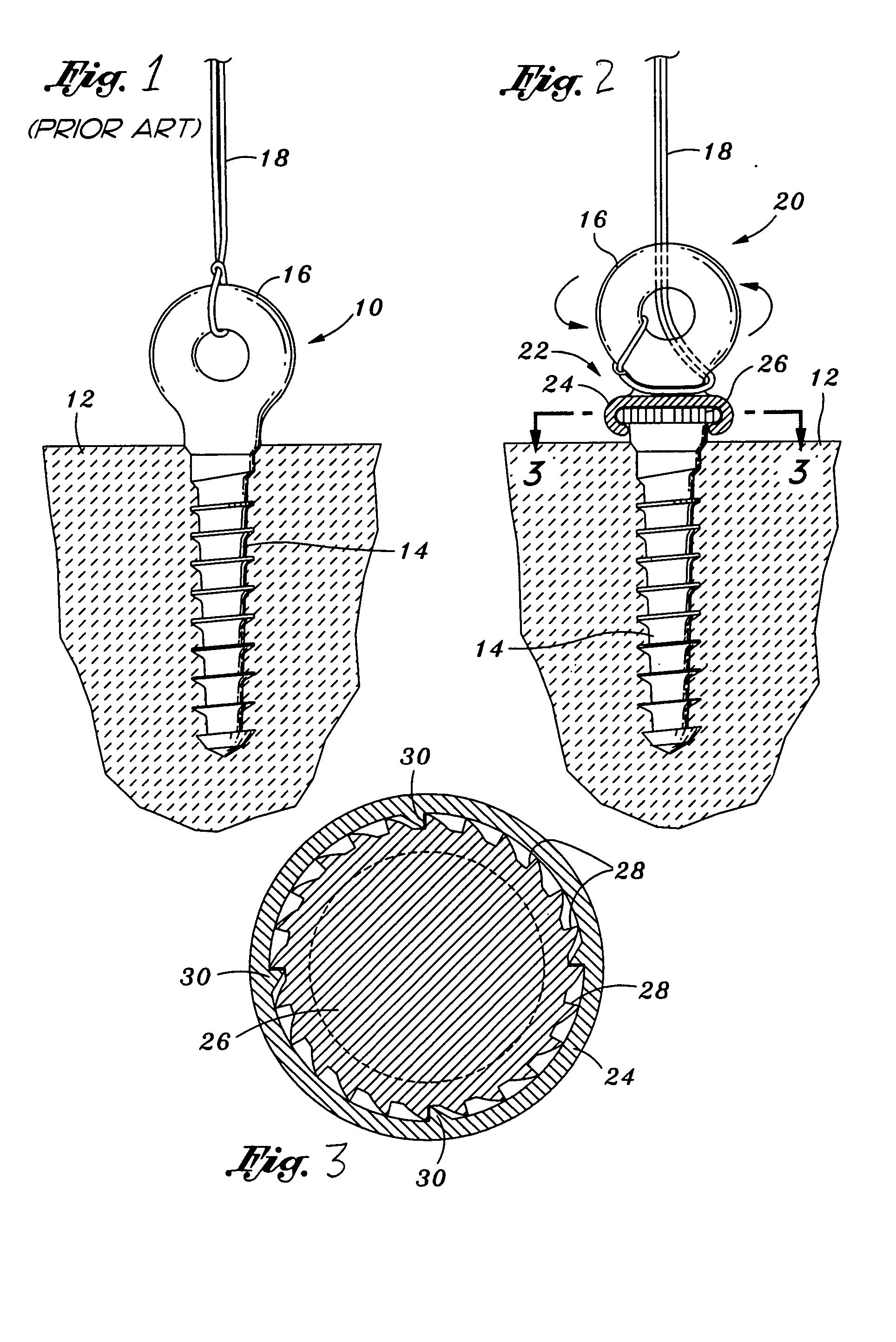
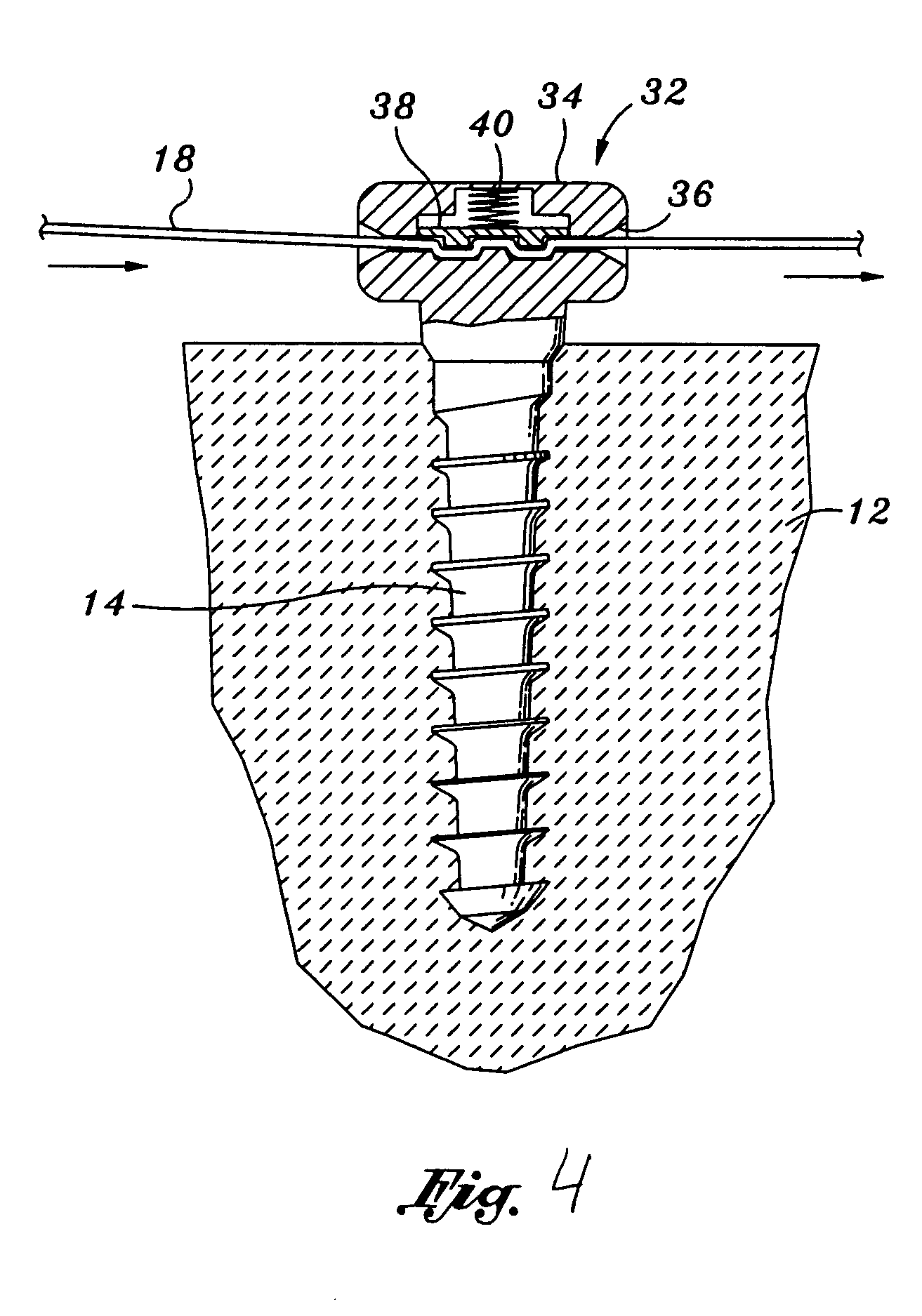
InactiveUS20050090827A1Precise level of tensionEasy constructionSuture equipmentsLigamentsAnatomical structuresLigament structure
Bone anchors, methods for deploying anchors, and systems for attaching ligaments and tendons to bone are disclosed. The bone anchors of the present invention are operative to remain firmly positioned within a target site of bone and provide means for selectively adjusting the degree of tension to one or more sutures secured thereto. The bone anchors are further operative to be utilized to connect tendons and ligaments directly to bone, as well as may be selectively utilized to adjustably position an implant or other anatomical structure held thereby. There is further disclosed methods for deploying a bone anchor utilizing a blind procedure that is expeditious, accurate and substantially less traumatic than prior art bone deployment techniques.
Owner:GEDEBOU TEWODROS
Ribbon feeder and printer
InactiveCN1914045AEliminate wrinklesUniform tensionPrinting mechanismsInking apparatusConductor CoilMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a ribbon feeder of printer. Ribbon tension detecting means (20, 21) each consisting of a plate-like lever body (35) are disposed upstream and downstream, respectively, of a ribbon path from a platen (7). The plate-like lever body (35) has first and second rollers (47, 48) disposed upstream and downstream of the ribbon path and swings around the axis of the rotary shaft of the second roller (48) according to the tension on the ribbon traveling as guided by these rollers (47, 48). When the amount of swing is above or below a fixed vale, a ribbon feed motor (18) or a ribbon winding motor (19) is driven. Further, the ribbon tension detecting means (20, 21) are each provided with a wrinkle eliminating member adapted to contact an ink ribbon (13) so as to eliminate wrinkles formed in the ink ribbon (13).
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
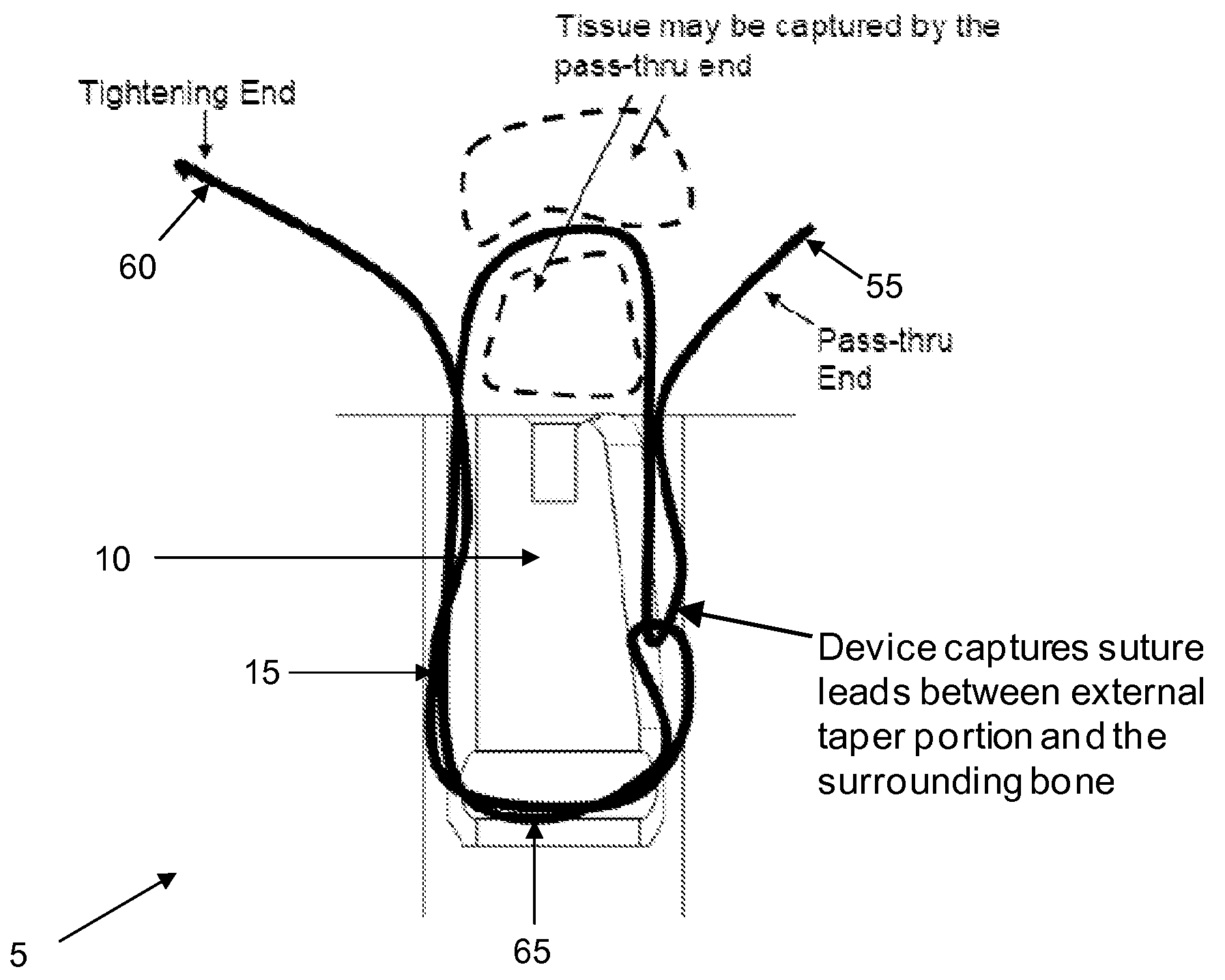
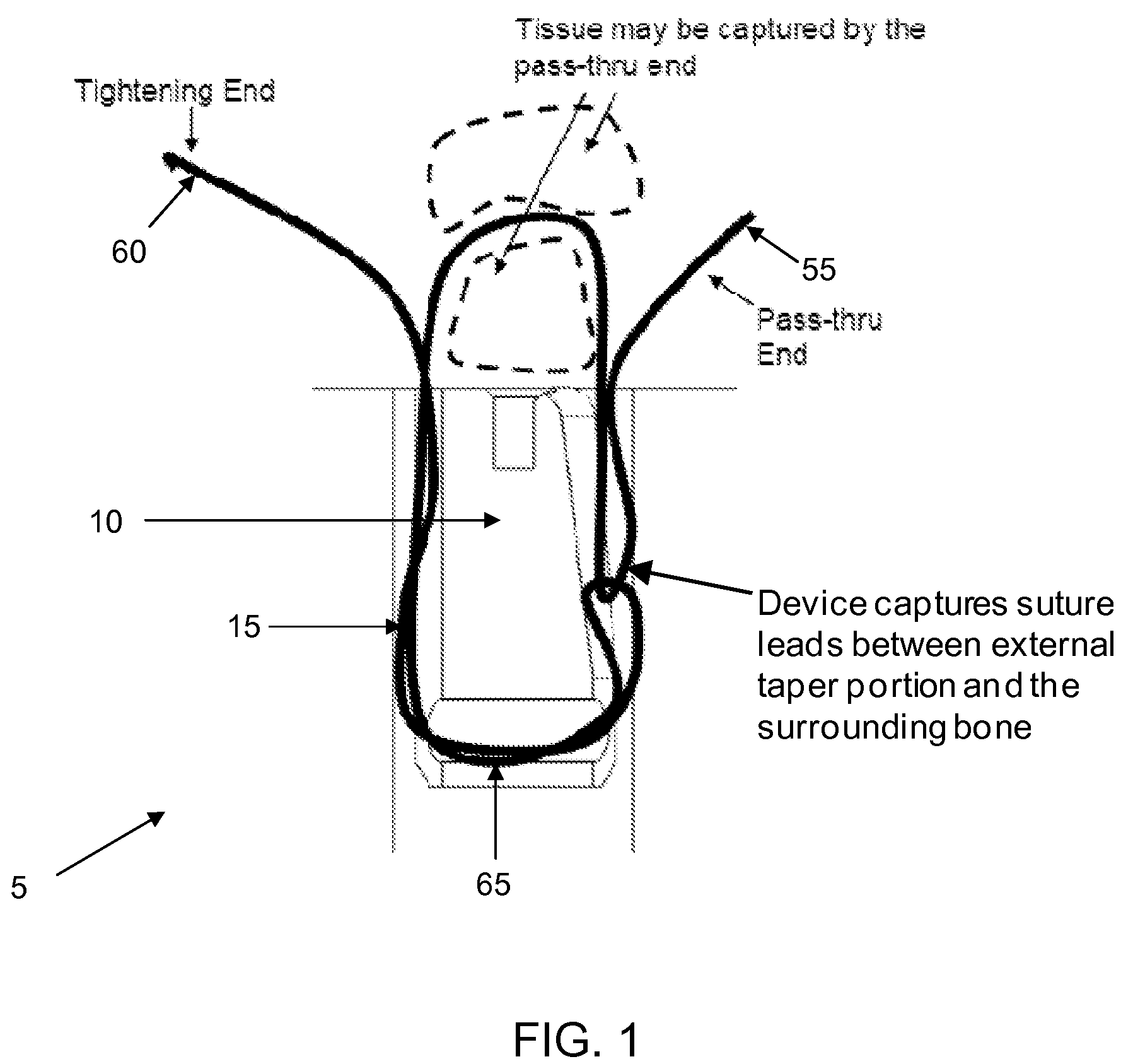
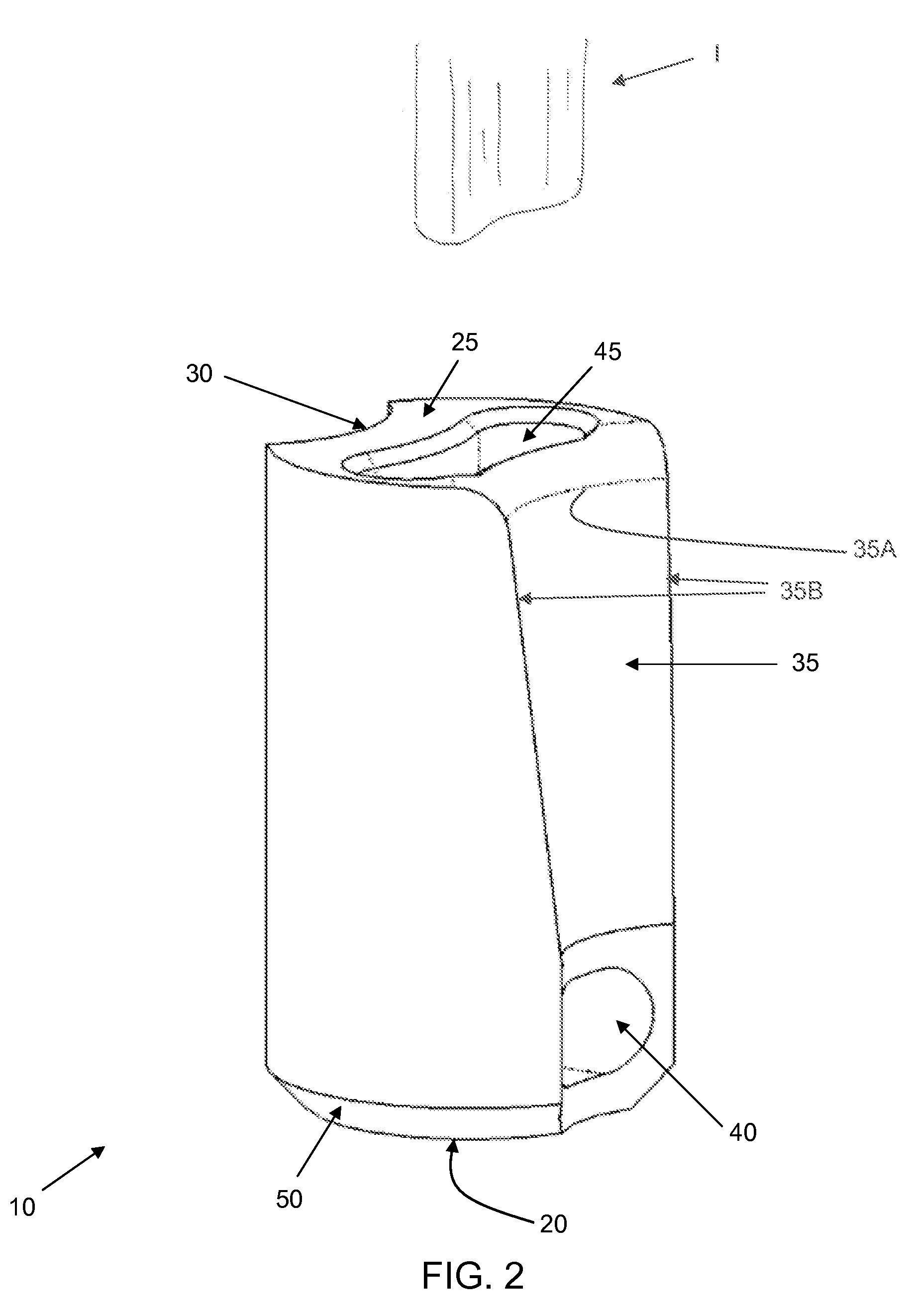
Method and apparatus for securing soft tissue to bone
Apparatus for securing an object to bone, the apparatus comprising:a suture anchor assembly comprising a suture anchor body and a suture;the suture anchor body being configured to be lockingly disposed within a hole formed in the bone, and having an opening formed therein for slidably receiving the suture therethrough;the suture having a first end, a second end and an intermediate portion extending therebetween;the suture extending through the opening in the suture anchor body so that the intermediate portion forms a loop on one side of the opening and the first and second ends are disposed on the other side of the opening, such that when the first end of the suture is passed through the loop and securingly engages the object, pulling on the second end of the suture draws the loop and a captured portion of the suture along a path toward the opening in the suture anchor body;the suture anchor body being configured so that when the suture anchor body is disposed in the hole in the bone, a tapered binding zone is established along the path followed by the loop and the captured portion of the suture when the second end of the suture is pulled, the tapered binding zone having a successively decreasing cross-sectional area such that continued pulling of the second end of the suture causes the loop and the captured portion of the suture to be jammed tightly in the tapered binding zone, whereby to bind the suture, and hence the object, to the suture anchor body, which is itself lockingly disposed within the bone.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Method and apparatus for winding a filter media pack
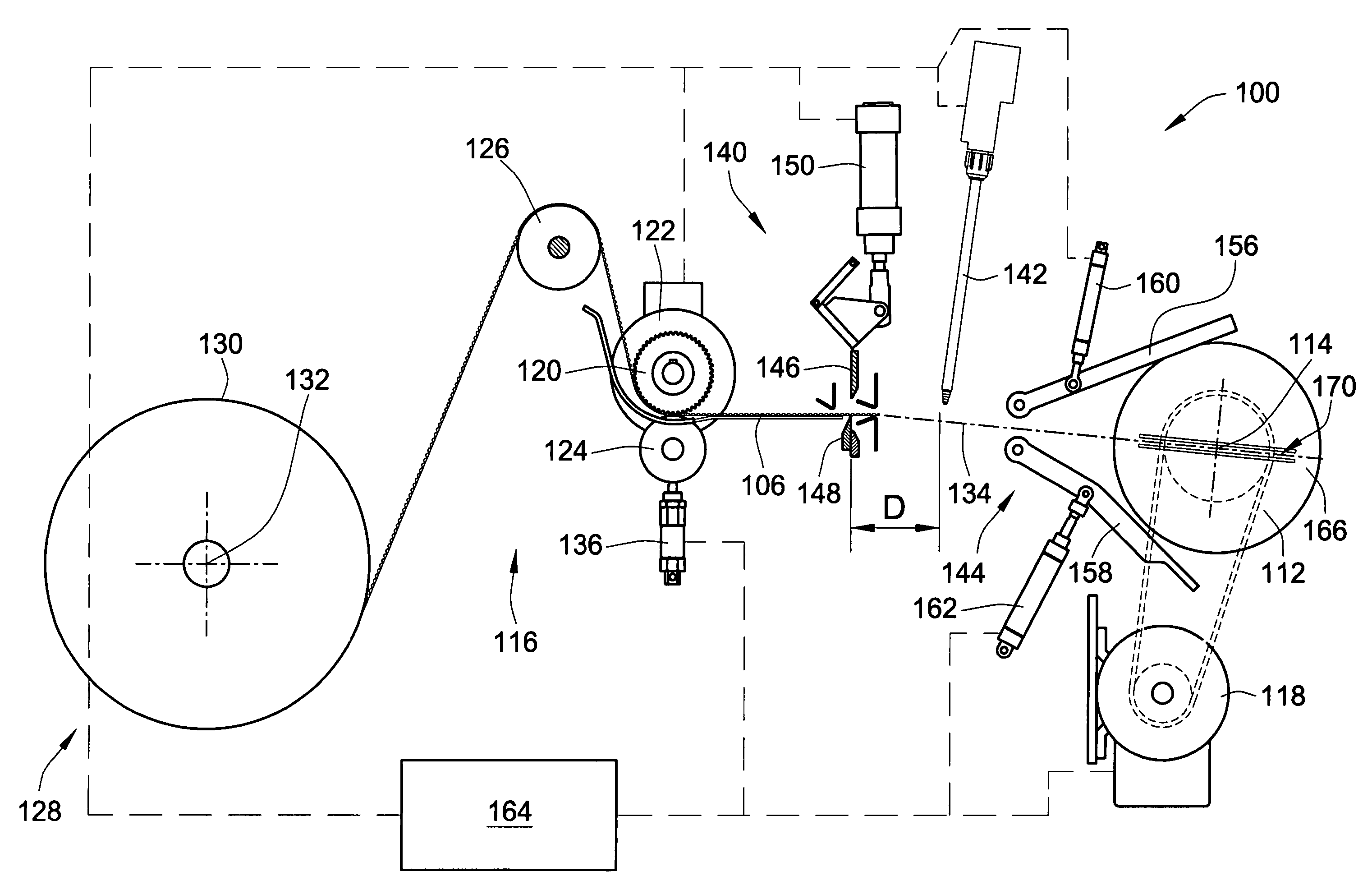
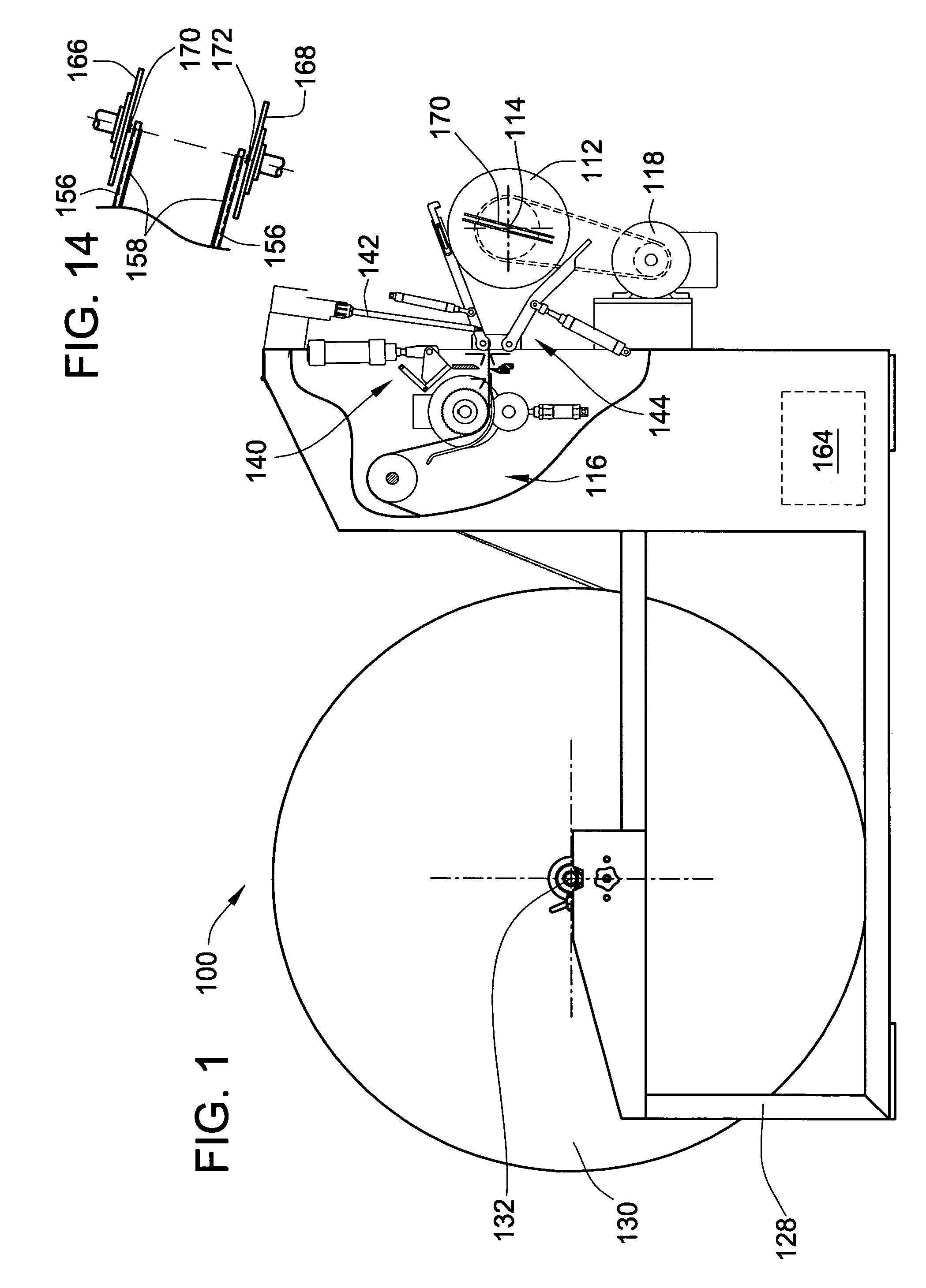
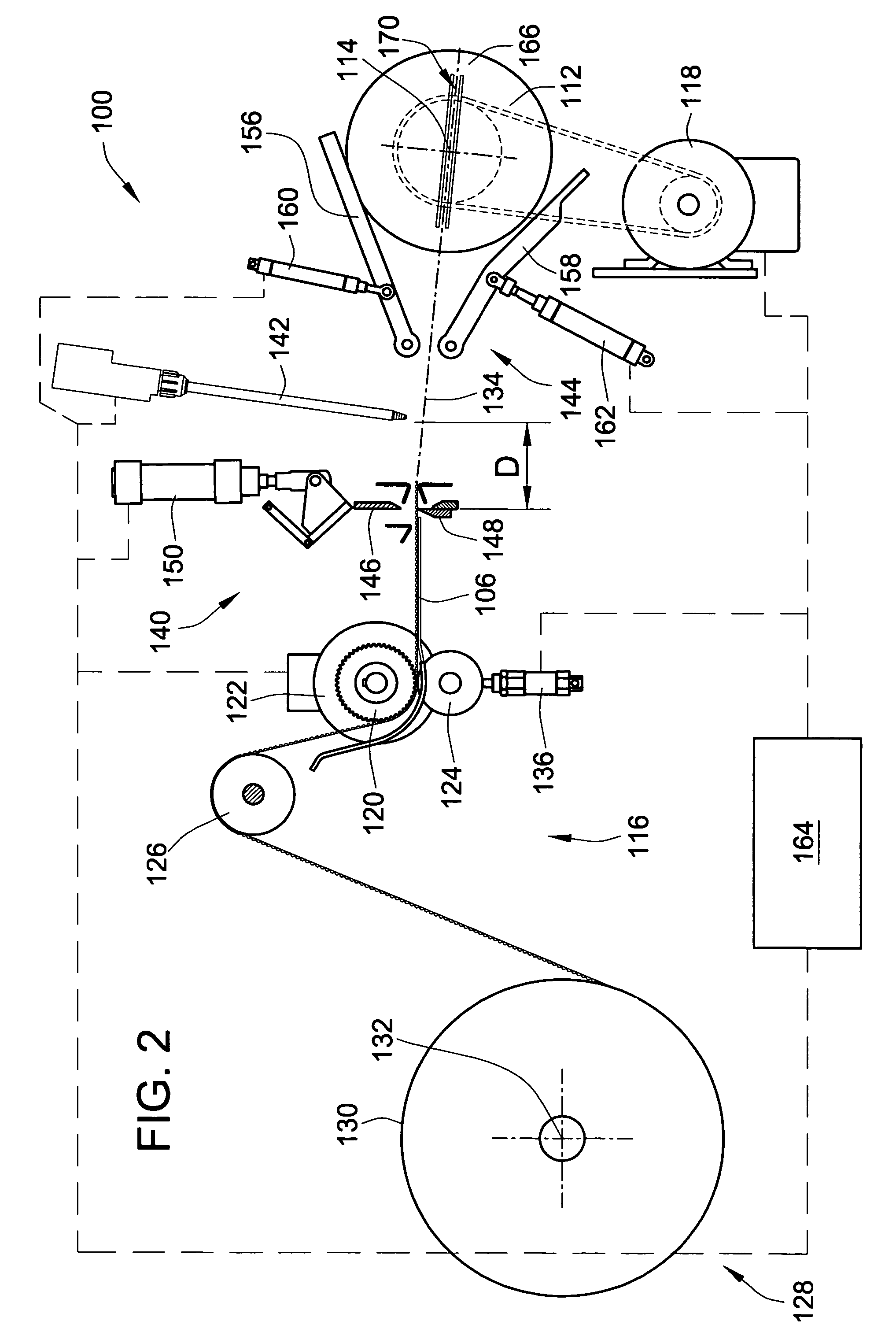
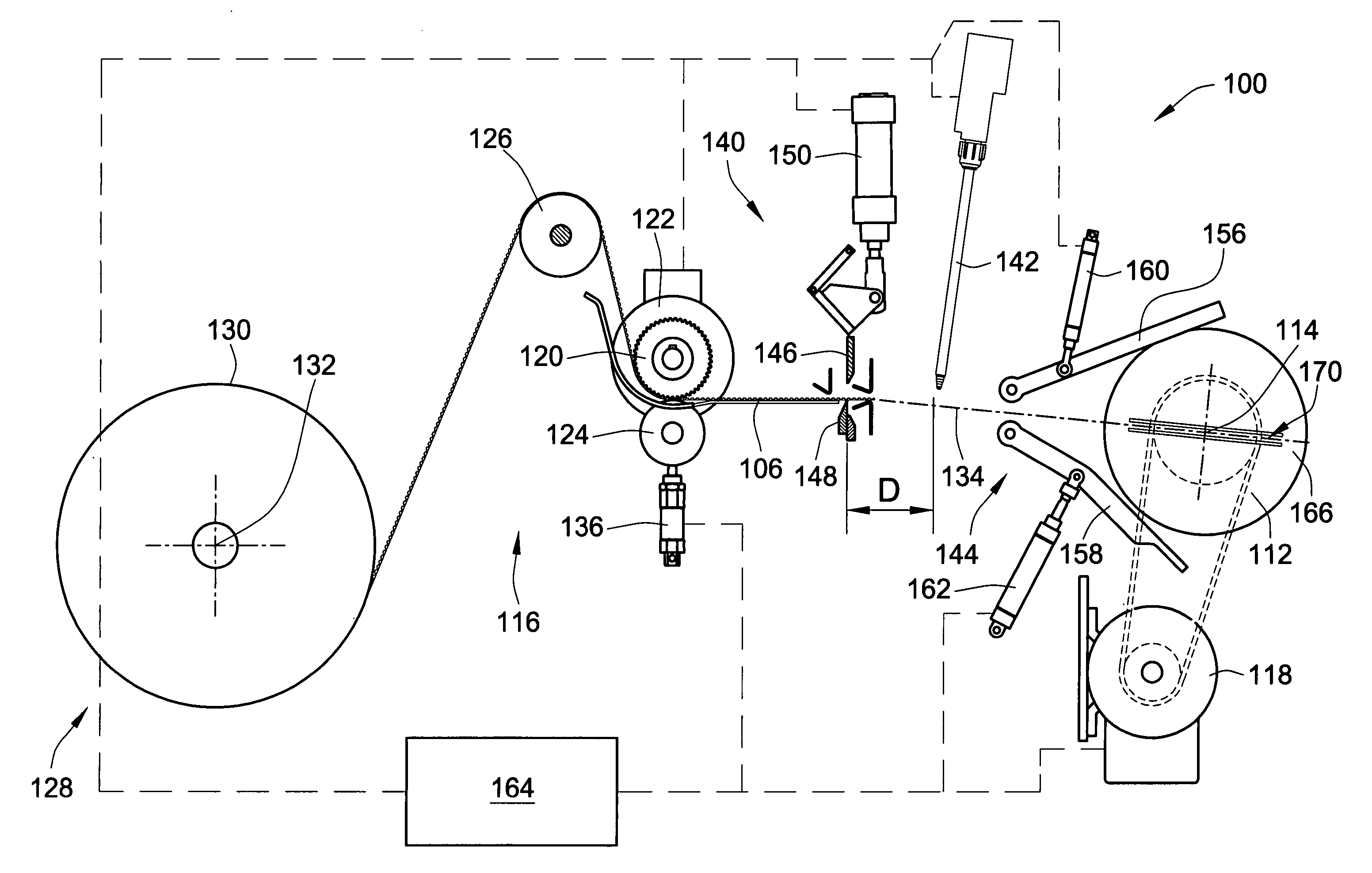
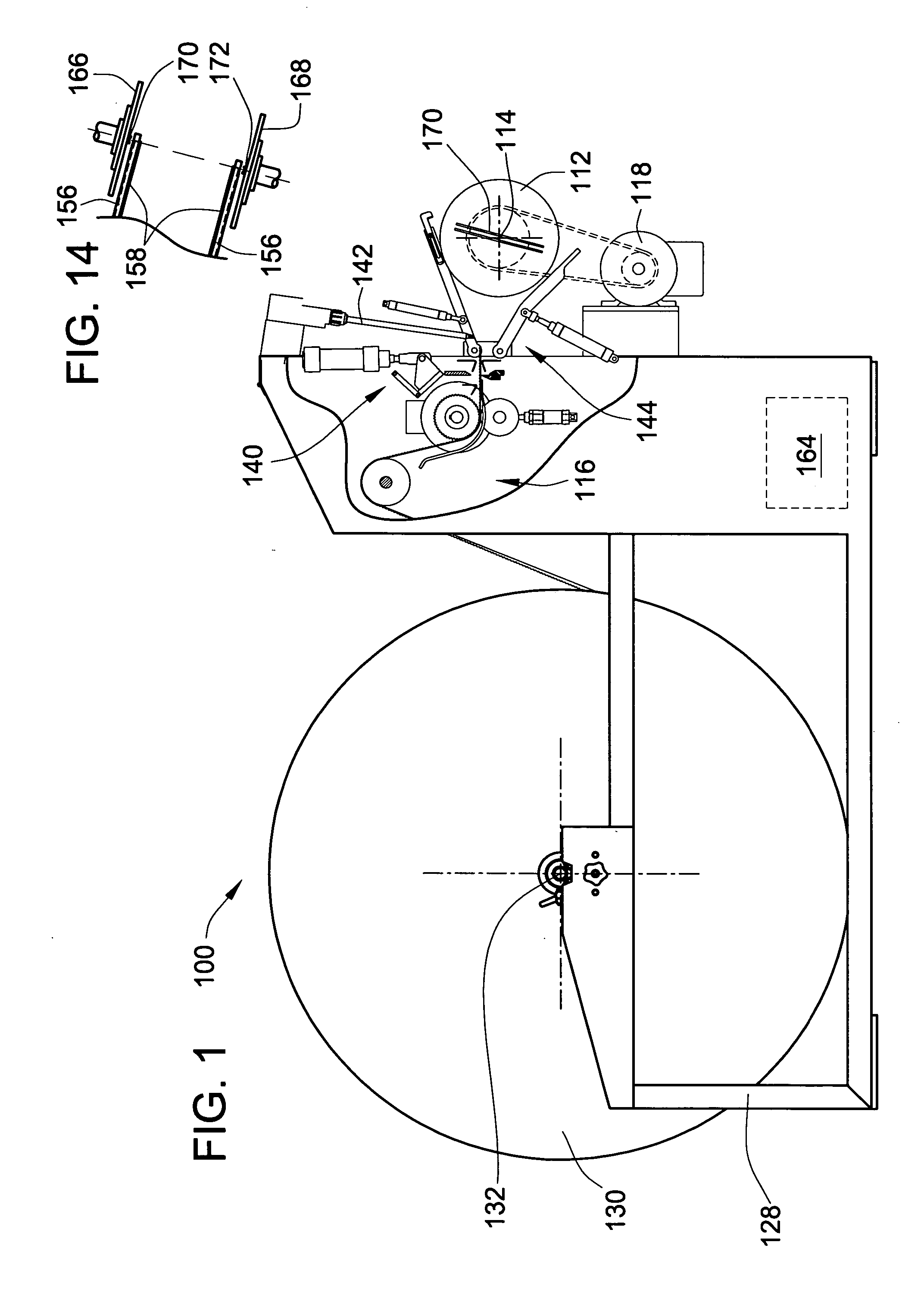
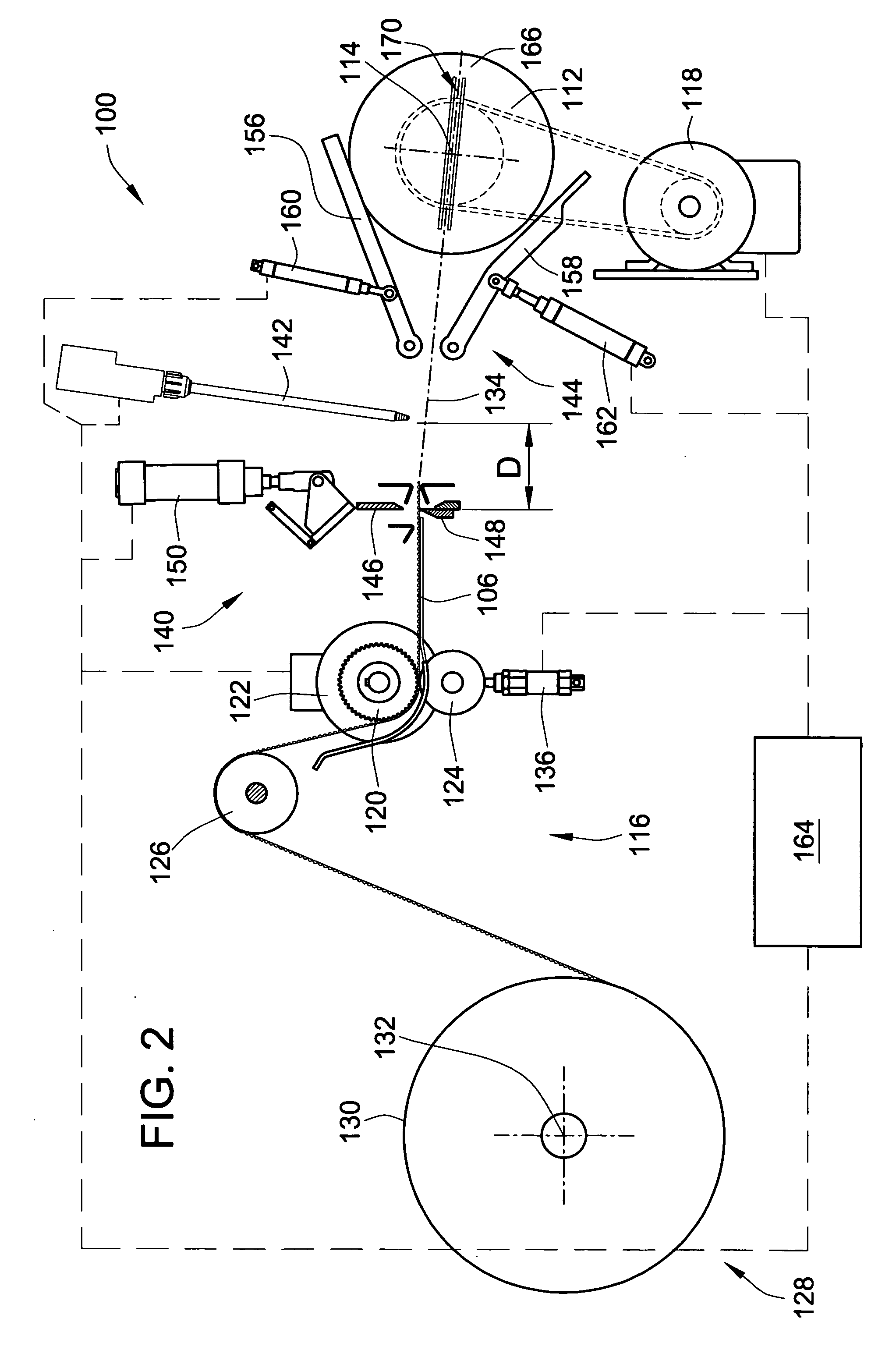
ActiveUS7255300B2Control tensionEasy to fillDispersed particle filtrationFilament handlingFilter mediaEngineering
A method and apparatus are provided, for forming a filter element including a media pack in the form of a coiled web of fluted filter media, by feeding the web of fluted filter media at a controlled linear speed onto a mandrel rotated by a winding motor providing a controlled driving torque to the mandrel, to thereby maintain a controlled tension on the web of fluted filter media as the web is wound onto the mandrel. The web may be fed at a substantially constant linear speed to the mandrel, and / or the winding motor may be controlled in a manner providing substantially constant driving torque to the mandrel for maintaining a constant tension on the web as a function of the constant driving torque. Coiled media packs having circular or non-circular cross sections, can be formed with either cored, or core-less construction.
Owner:BALDWIN FILTERS
Method and apparatus for making core-spun yarn of steple-fibre covered filament
The present invention is characterized by that on the spinning machine it utilizes addition of a yarn tension control device and simple renovation of guide wheel to spin the invented core-spun composition yarn whose yarn is covered with staple fiber, and its covering rate is high. Said composite core-covered yarn not only has the appearance style, hand property, fluffy property and other advantages of staple fibre, but also possesses the strength and elongation, conformal property and drapping property, etc. of yarn.
Owner:薛元
Method and apparatus for winding a filter media pack
ActiveUS20060151655A1Precise positioningFacilitate severingDispersed particle filtrationFilament handlingFilter mediaConductor Coil
A method and apparatus are provided, for forming a filter element including a media pack in the form of a coiled web of fluted filter media, by feeding the web of fluted filter media at a controlled linear speed onto a mandrel rotated by a winding motor providing a controlled driving torque to the mandrel, to thereby maintain a controlled tension on the web of fluted filter media as the web is wound onto the mandrel. The web may be fed at a substantially constant linear speed to the mandrel, and / or the winding motor may be controlled in a manner providing substantially constant driving torque to the mandrel for maintaining a constant tension on the web as a function of the constant driving torque. Coiled media packs having circular or non-circular cross sections, can be formed with either cored, or core-less construction.
Owner:BALDWIN FILTERS
Strand-reinforced composite material
InactiveUS7316840B2Control tensionSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationElastomer compositesComposite laminates
Elastomeric composites and elastomeric composite laminates including reinforcement strands incorporated into an elastomeric adhesive film. The strands may vary in terms of levels of tension. Facing layers, such as nonwoven webs, can be laminated to both surfaces of the elastomeric composite to form laminates. A method of making such composites and laminates involves adjusting tension among various elastic strands while extruding the elastic strands and incorporating the elastic strands into the elastomeric adhesive film.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method And Apparatus For Winding A Filter Media Pack
ActiveUS20080011896A1Increase propensityPrevent unwinding and unravelingDispersed particle filtrationPaper/cardboard wound articlesFilter mediaEngineering
A method and apparatus are provided, for forming a filter element including a media pack in the form of a coiled fluted filter media, by winding the web of fluted filter media around a pair of tools of a mandrel. The tools engage the sides of the filter media. The tools define a major to provide the media pack with a oblong or elongated shape. The web may be fed at constant linear speed, and / or a motor may be controlled in a manner to provide constant driving torque to maintain a constant tension on the web. The winding apparatus and methods may include apparatus or methods to modify the feed path of the web to adjust the tension of the web as it is being wound. Further, the coiled media packs can be fixtured to prevent relaxation. A method may form various shaped media packs with the same apparatus.
Owner:BALDWIN FILTERS
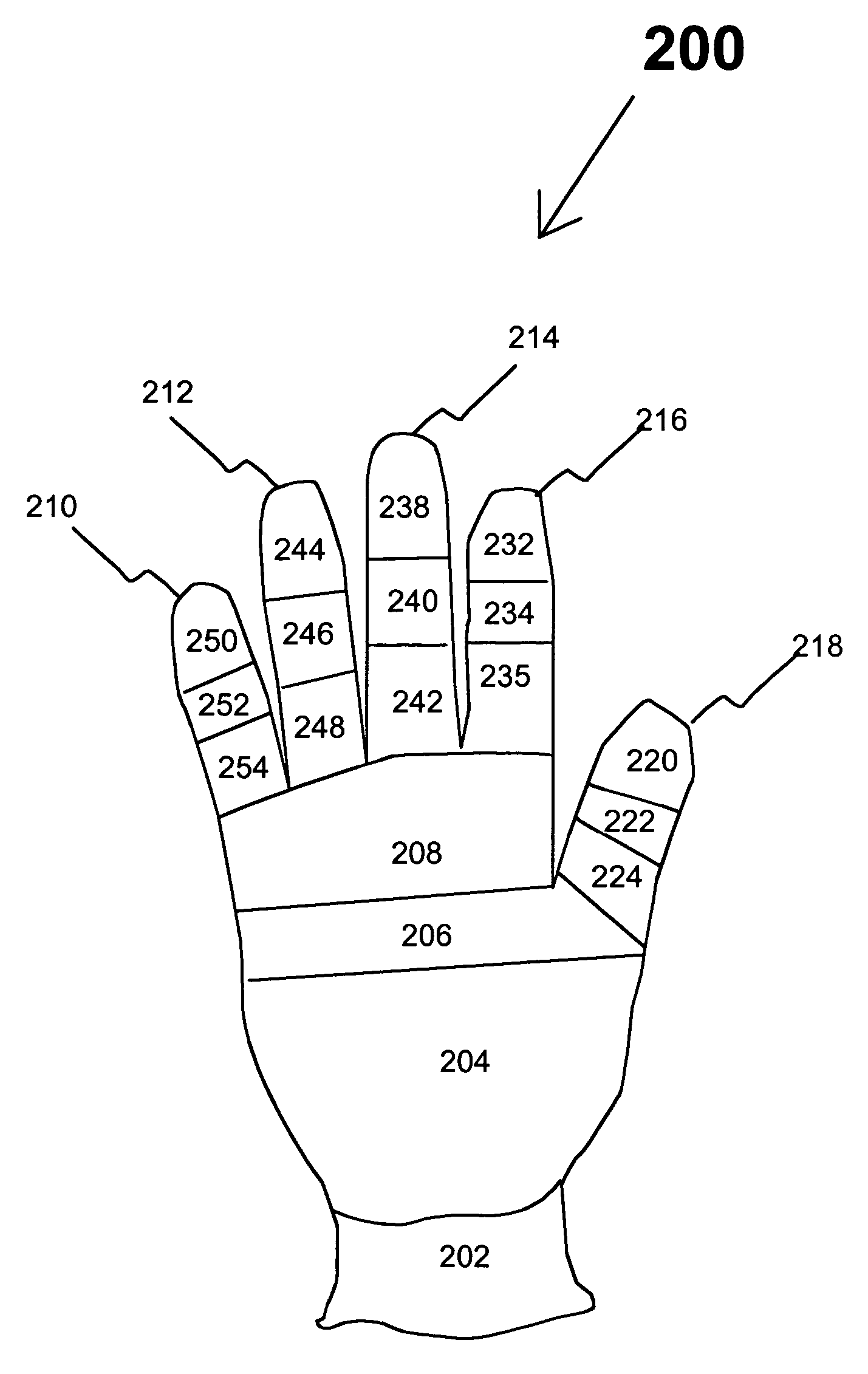
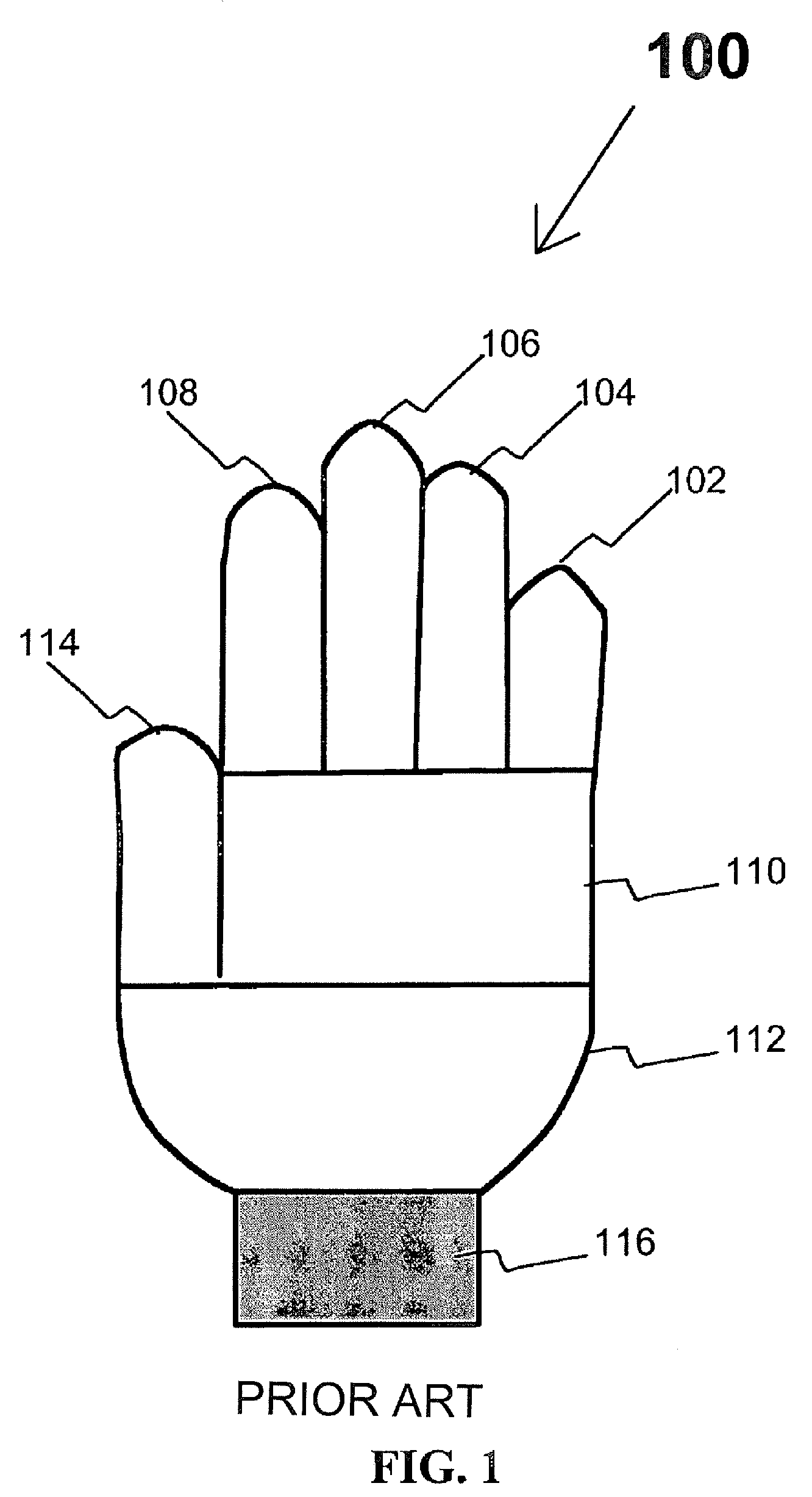
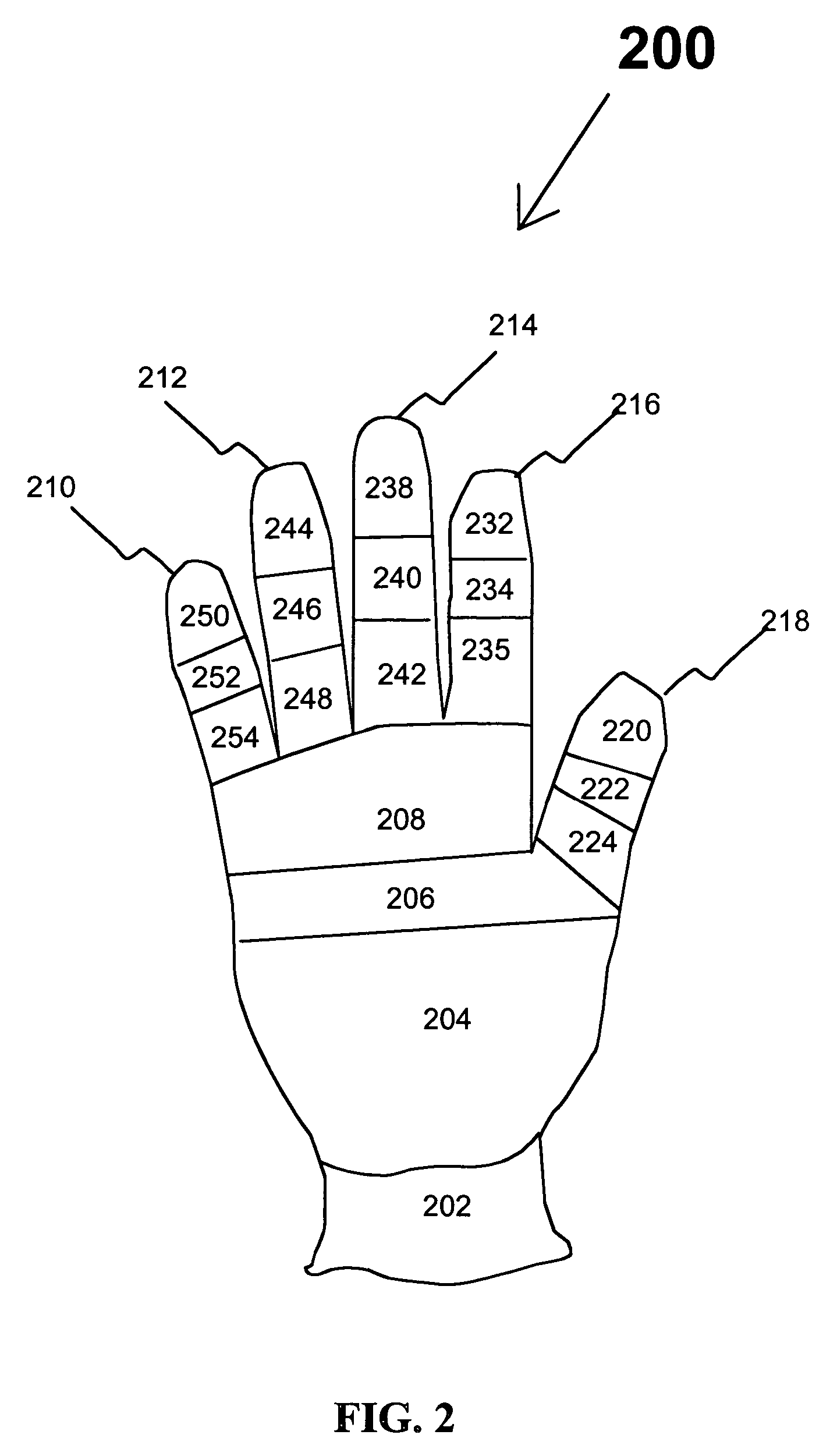
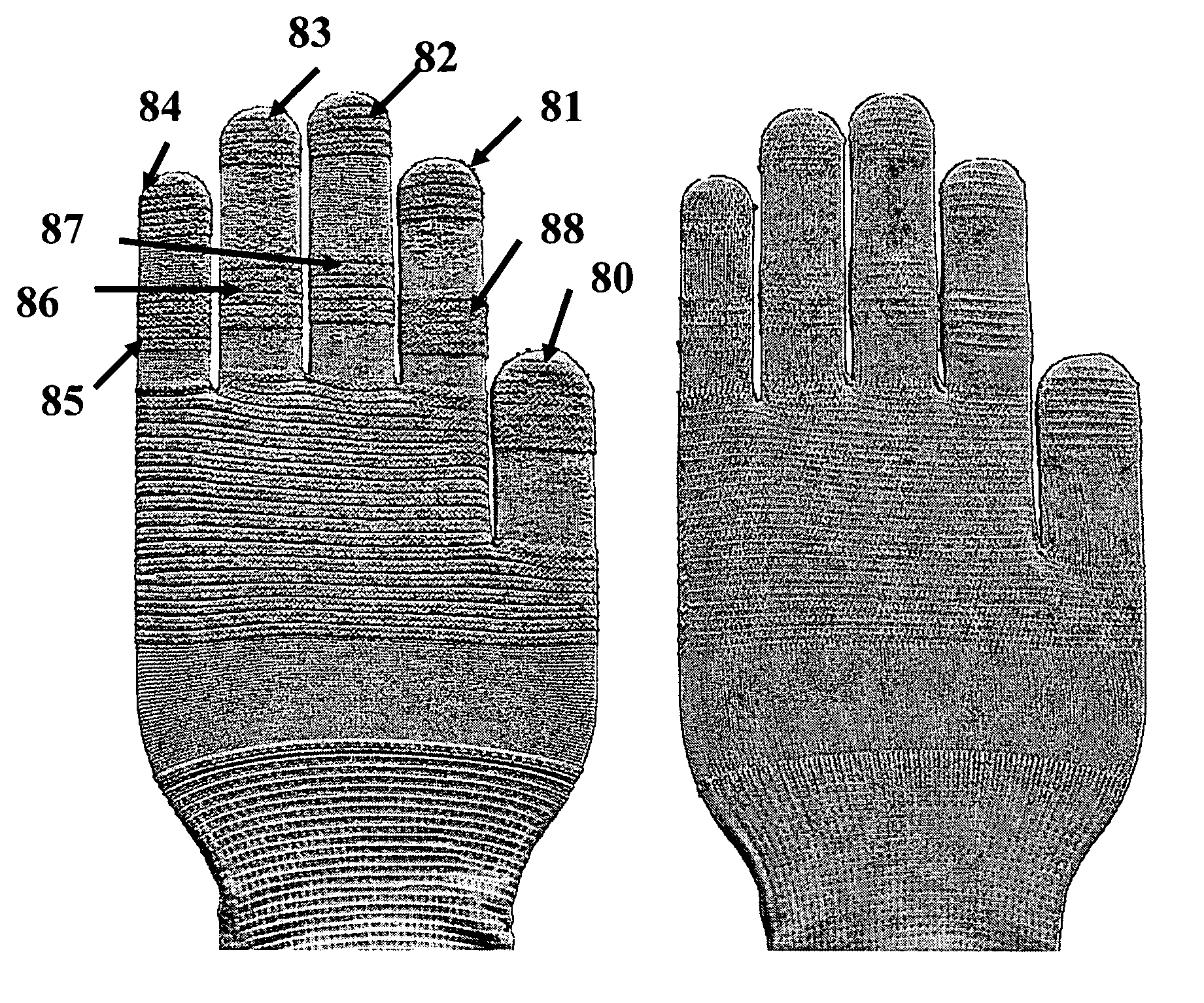
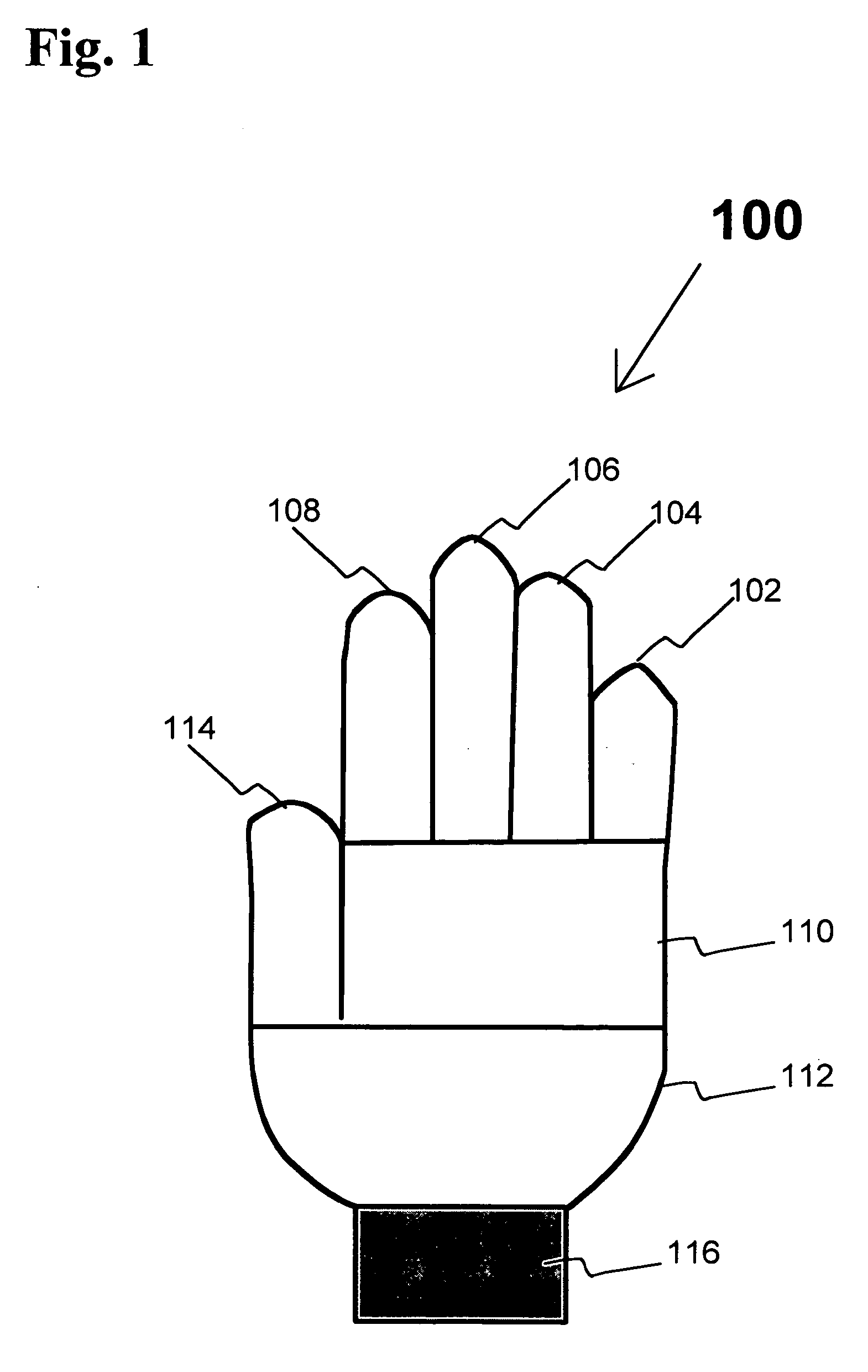
Knitted glove with controlled stitch stretch capability
ActiveUS7213419B2Improve tensile propertiesComfortable glove feelOrnamental textile articlesGlovesYarnDepth of penetration
A knitted glove made by creating each of the sections of the glove using a separate knitting course on a flat knitting machine providing variable stitch dimensions. Each of these sections provides its own designed stretch characteristics so that the glove fits tightly, yet provides flexibility and ease of movement. The variable stitch dimension is achieved by 1) varying the depth of penetration of a knitting needle into a fabric being knitted by a computer program, 2) adjusting the tension of yarn between a pinch roller and a knitting head by a mechanism controlled by a computer, and 3) casting off or picking up additional stitches in a course. The glove includes a plurality of finger components made from at least ten separately knitted sections, two palm components, each of which is made from at least two separately knitted sections, and a wrist component made from at least one knitted section.
Owner:ANSELL HEALTHCARE PRODS
Mounting assembly with adjustable spring tension and pivoting lock lever
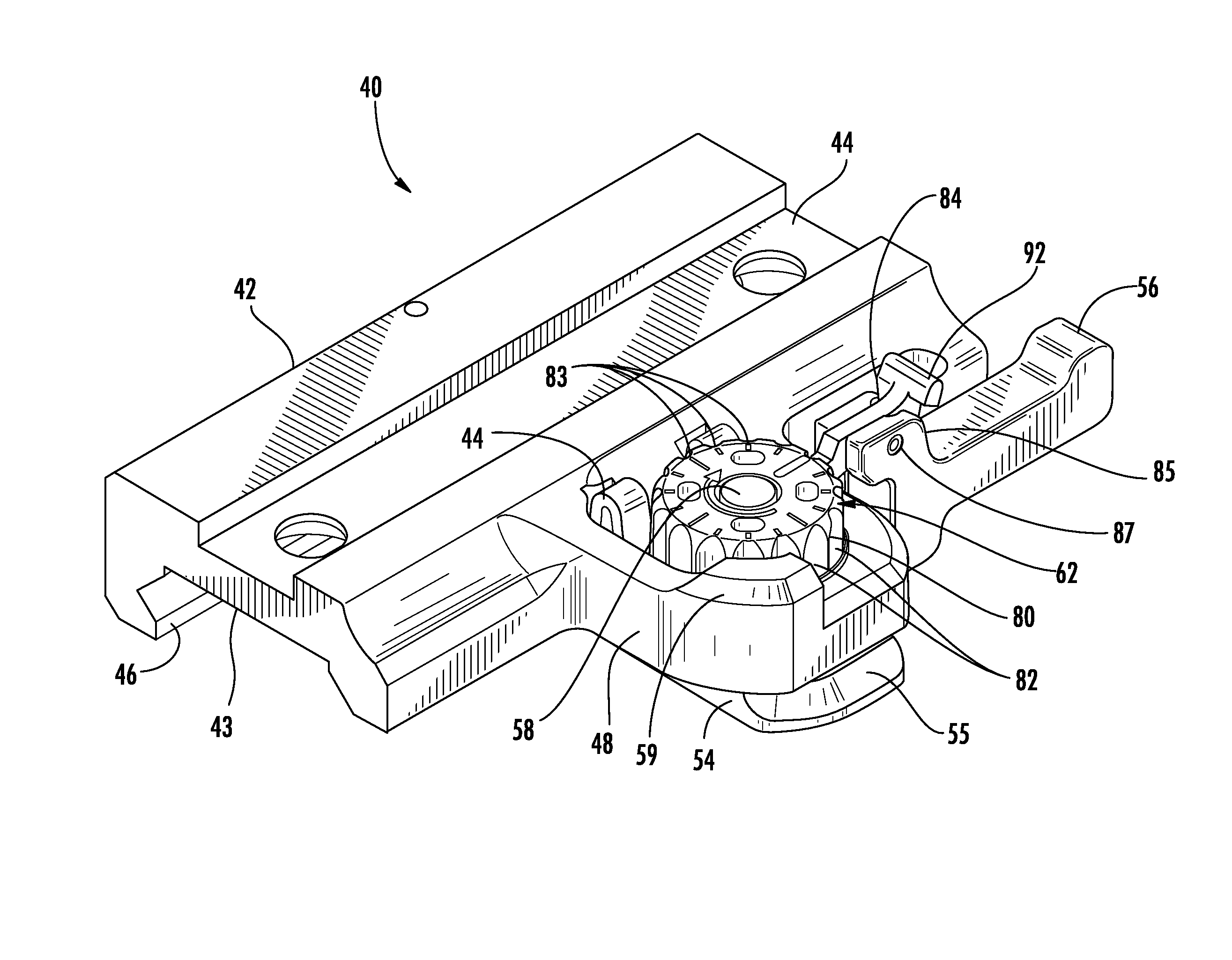
InactiveUS8112933B1Easy to installControl tensionSighting devicesRod connectionsRail profileEngineering
An improved mounting assembly is provided that is configured to be releasably attached to a standard dovetail rail profile, wherein the initial clamping tension of a clamping assembly is adjustable. The mounting assembly includes a main body having a lower portion that is configured to engage a standard dovetail and an upper portion accessory receiving formation. The lower portion of the mounting assembly has a first engagement member extending downwardly along one side thereof for engaging one side of the dovetail rail and a clamping assembly to engage the opposing side of the dovetail rail. At least one spring and a retention nut are provided as part of the clamping assembly such that retention nut controls the preset spring tension thereby controlling the clamping force applied by the clamping assembly. A lock lever connected to the actuator arm selectively locks the position of the retention nut on the threaded shaft.
Owner:SWAN RICHARD E
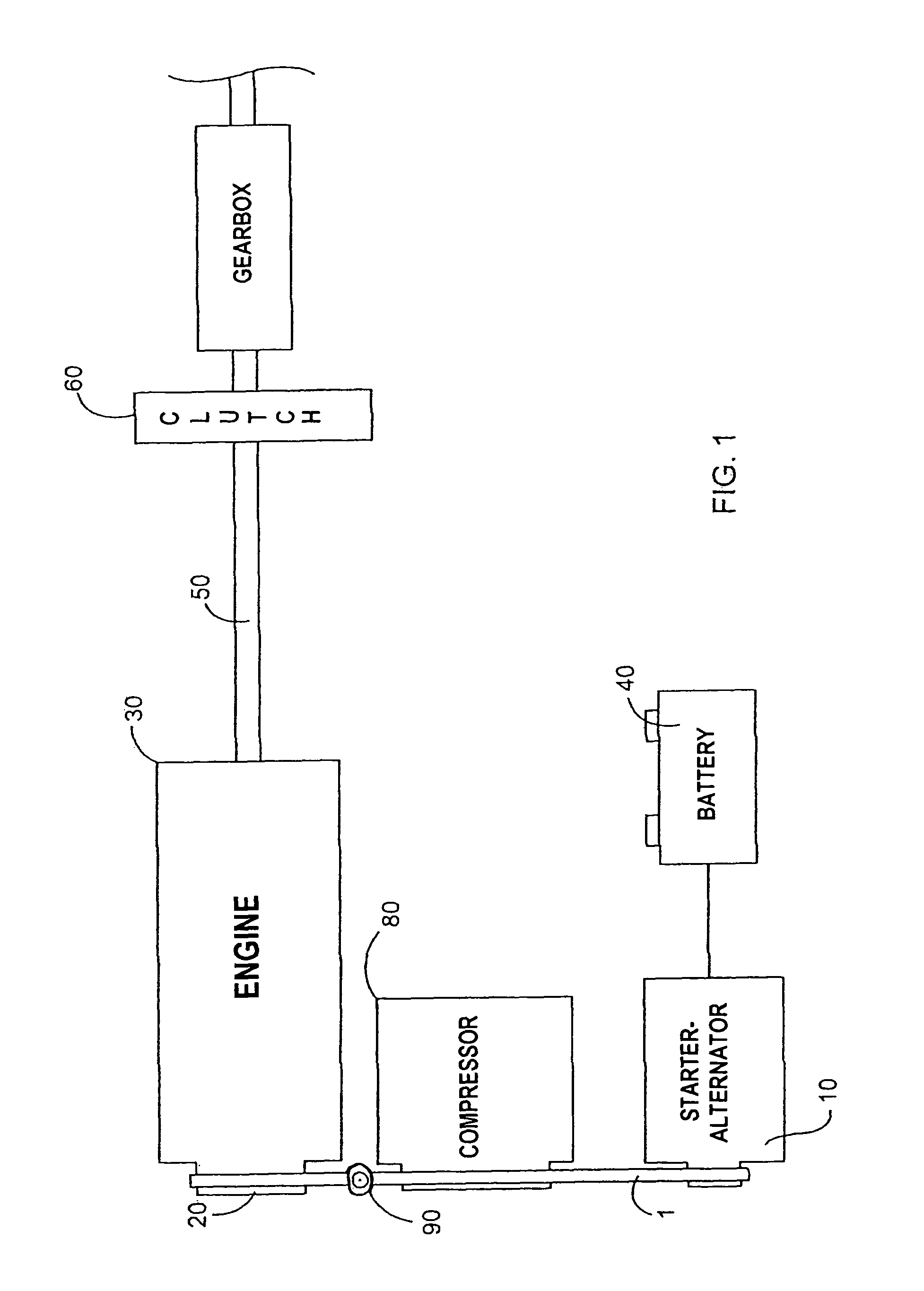
Pulley for a power transmission member, a separate starter-alternator fitted with such a pulley, and an engine drive system
InactiveUS7985150B2Control tensionControlling the riskRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingAlternatorDamping torque
The invention seeks to provide a transmission system, in particular for a starter-alternator, capable both of damping large variations in torque under starting conditions (drive from the alternator) and of providing effective decoupling under running conditions (alternator driven). In an embodiment, the decoupling located between a central hub and a rim over which a drive belt (not shown) is tensioned, is provided by at least one decoupler element designed to provide optimized stiffness. In addition, the decoupler assembly is associated with at least one deflection limiter having two components: a central plate secured to an outside face of the central hub and coupled to abutments that are regularly distributed around the periphery of an inside face of the rim, the abutments and the plate being shaped so as to come into deforming contact. The resilient assembly provides two stiffness values, whether in the drive direction or in the driven direction. The invention is applicable to starter-alternators, crankshafts, and other power transmission members (compressors, etc.).
Owner:HUTCHINSON SA
Surgical Instrument and Method for Tensioning and Securing a Flexible Suture
ActiveUS20100087837A1Reduce tensionEasy to separateSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEntire bonesBreast bone
A surgical instrument may be used to apply tension to a flexible suture to close and secure a broken or cut bone (e.g. a sternum following a sternotomy). The device preferably applies an adjustable tension to the flexible suture in order to secure the bone together. Multiple instruments may be used together to ensure the desired tension is applied to the entire bone structure being secured with the flexible sutures. Once the desired tension is achieved, the device preferably provides a mechanism to apply a uniform twist to the flexible suture to lock the flexible suture in place. The instrument preferably decreases the upward tension applied to the flexible sutures over the duration of the application of twisting.. The device may automatically cut the flexible suture, or the flexible suture may be cut by the surgeon once the twisting action has been performed.
Owner:KARDIUM
Knitted Glove
ActiveUS20090211305A1Enhanced and reduced stretch capabilityFeel tightGlovesCircular knitting machinesYarnEngineering
A knitted glove made by creating each of the sections of the glove using a separate knitting course on a flat knitting machine providing variable stitch dimensions. Each of these sections provides its own designed stretch characteristics so that the glove fits tightly, yet provides flexibility and ease of movement. The variable stitch dimension is achieved by 1) varying the depth of penetration of a knitting needle into a fabric being knitted by a computer program, 2) adjusting the tension of yarn between a pinch roller and a knitting head by a mechanism controlled by a computer, and 3) casting off or picking up additional stitches in a course. The glove includes a plurality of finger components made from at least ten separately knitted sections, two palm components, each of which is made from at least two separately knitted sections, and a wrist component made from at least one knitted section.
Owner:ANSELL HEALTHCARE PRODS
Screen printing screen, screen, screen frame, screen joining method, screen spreading method, painting canvas, advertisement sheet, and planer mirror
InactiveUS20050034614A1Easy to useControl tensionScreensLiquid surface applicatorsScreen printingTypes of mesh
The present invention relates to a screen for screen printing. More particularly, the structure of the screen can have different types of mesh or sheets joined together. The present invention also relates to a method of detachably spreading a screen to a screen frame.
Owner:KASUYA FURETABU
Method for improving teflon adhesive property and method for producing pressure-sensitive adhesive tape
The invention discloses a method for improving a teflon adhesive property. The method comprises the following steps of washing, wherein at least one kind of methyl alcohol, methyl alcohol, isopropanol, acetone and methylbenzene is adopted, and teflon base materials are washed through ultrasonic oscillation; normal-pressure low-temperature plasma processing, wherein a normal-pressure low-temperature plasma technology based on barometric pressure glow is used for carrying out the normal-pressure low-temperature plasma processing on the washed teflon base materials. The invention further discloses a method for producing pressure-sensitive adhesive tape. The method for improving the teflon adhesive property has the advantages that the adhesive property of the teflon base materials can be effectively improved, the contact angle of the surfaces of the processed materials is 86 degrees, and the adhesive strength is larger than 5.0MPa.
Owner:成都同明创新科技有限公司
Selective multiple yarn reinforcement of a knitted glove with controlled stitch stretch capability
ActiveUS20070022511A1Increasing and decreasing tensionReduce stretchOrnamental textile articlesGlovesYarnEngineering
A knitted glove made by creating each of the at least fifteen sections using a separate knitting course on a flat knitting machine providing variable stitch dimensions with one or two yarns. Each of these sections provides custom stretch characteristics using one or two yarns providing a tight glove that provides flexibility and ease of movement. The variable stitch dimension is achieved by 1) varying the depth of penetration of the knitting needle into fabric being knitted by a computer program, 2) adjusting the tension of yarn between a pinch roll and knitting head by a mechanism controlled by a computer and 3) casting off or picking up additional stitches in a course. The glove includes five finger components made from at least ten separately knitted sections, two palm components each made from at least two separately knitted sections, and a wrist component made from at least one knitted section.
Owner:ANSELL HEALTHCARE PRODS
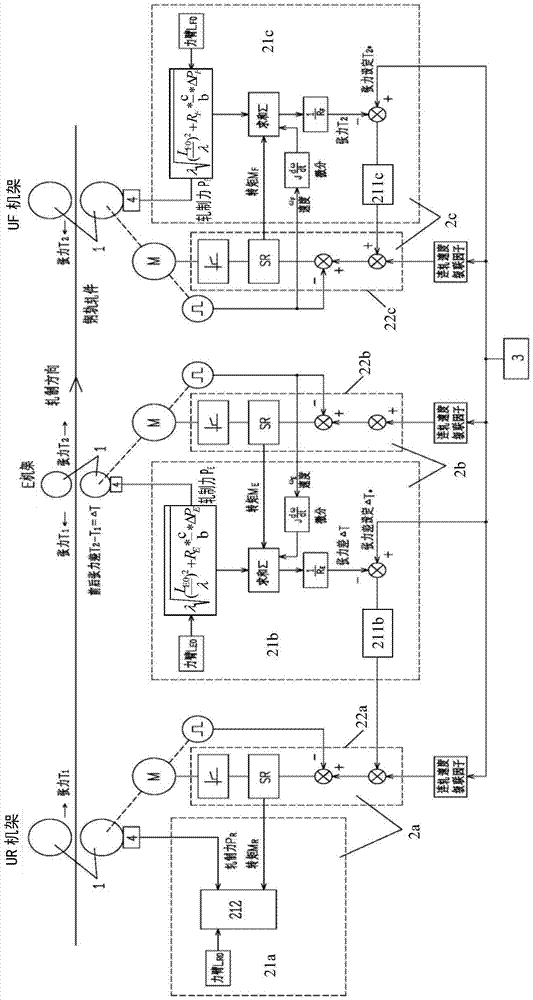
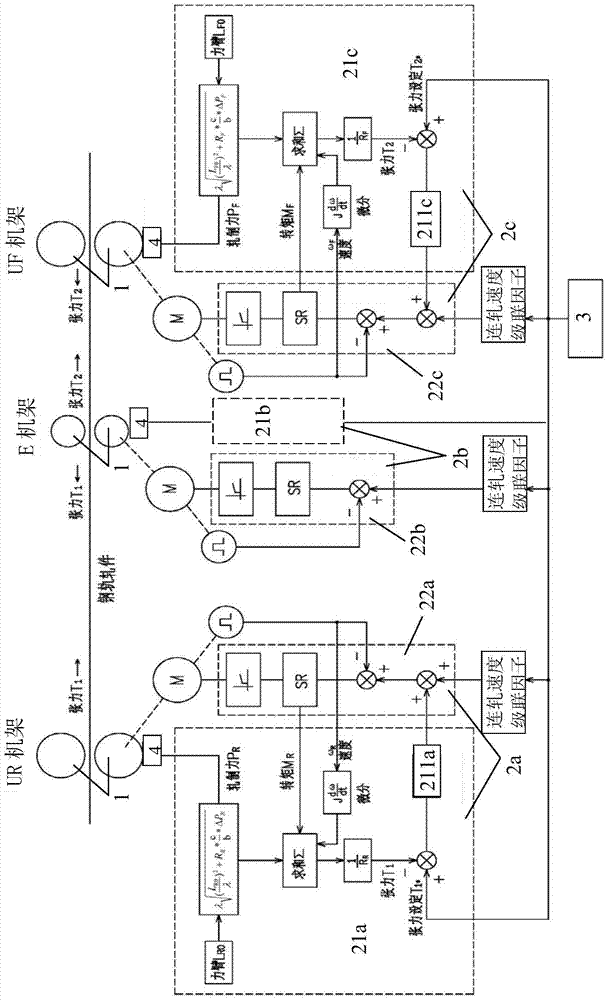
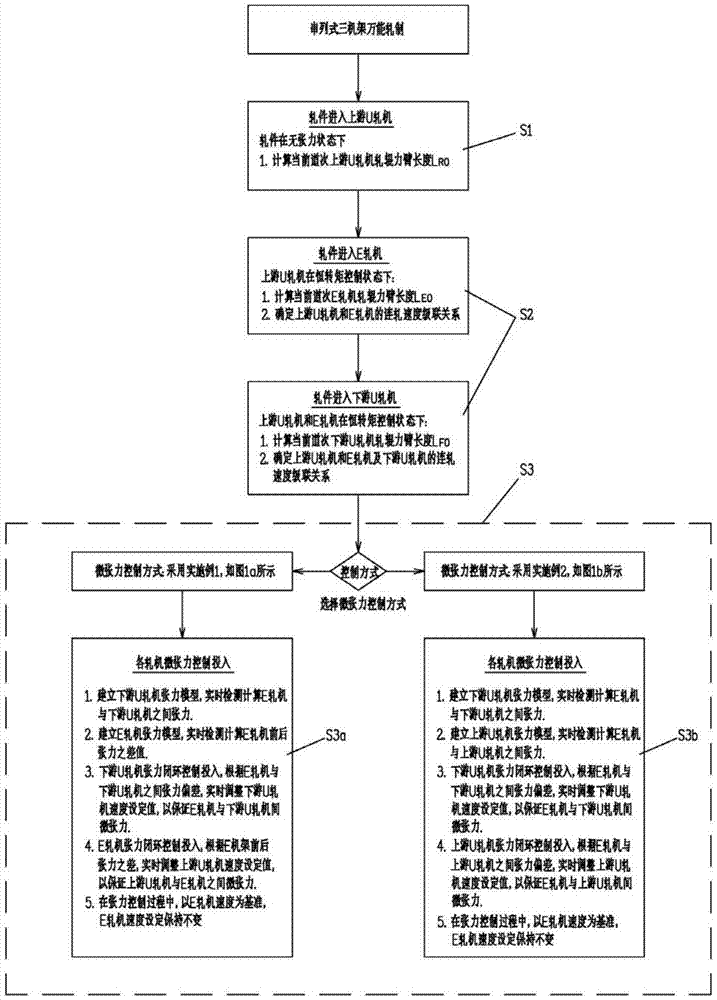
Micro-tension control system and method
ActiveCN103567230AGuaranteed tension control accuracyGeometry out-of-tolerance reductionMeasuring devicesTension/compression control deviceLoop controlClosed loop
The invention discloses a micro-tension control system and method. In the hot continuous rolling process, when a rolled piece enters a current machine frame and is stably bitten, the current machine frame is kept under speed control, speed control of main motors of machine frames on the upstream of the current machine frame is switched to constant torque control, on the basis, the torque and the rolling force of a main motor of the current machine frame are sampled to calculate the initial length of a rolling force arm, and the tension measurement calculating accuracy is improved. Each machine frame is provided with a pressure measuring head device to directly detect the rolling force, and consideration is given to the situation that the length of the rolling force arm is changed along with changes of the rolling force. Tension between the machine frames is obtained in real time through tension calculating models to form micro-tension closed-loop control to adjust the speeds of the machine frames so as to correct the tension deviations between the machine frames. As for a serial type universal rolling mill, the speed of the E machine frame serves as a standard, the rolling speed of the E machine frame is kept unchanged while speed set values of the other machine frames are adjusted, and real-time control is carried out on dynamic instantaneous values of the tension difference of the E machine frame before and after the adjustment process to guarantee micro-tension rolling of series universal rolling.
Owner:BERIS ENG & RES CORP
Mounting assembly with adjustable spring tension
InactiveUS7757423B1Prevents over tighteningPrevents loosening of the nut once installedSighting devicesRod connectionsRail profileActuator
An improved mounting assembly is provided that is configured to be releasably attached to a standard dovetail rail profile, wherein the initial clamping tension of the clamping actuator is adjustable. The mounting assembly generally includes a main body having a lower portion that is configured to engage a standard dovetail and an upper portion accessory receiving formation. The lower portion of the mounting assembly has a first engagement member extending downwardly along one side thereof for engaging one side of the dovetail rail and a clamping assembly to engage the opposing side of the dovetail rail. At least one spring and a retention nut are provided as part of the clamping assembly such that retention nut controls the preset spring tension thereby controlling the clamping force applied by the clamping assembly.
Owner:SWAN RICHARD E
Squat Bar for Fitness Machine
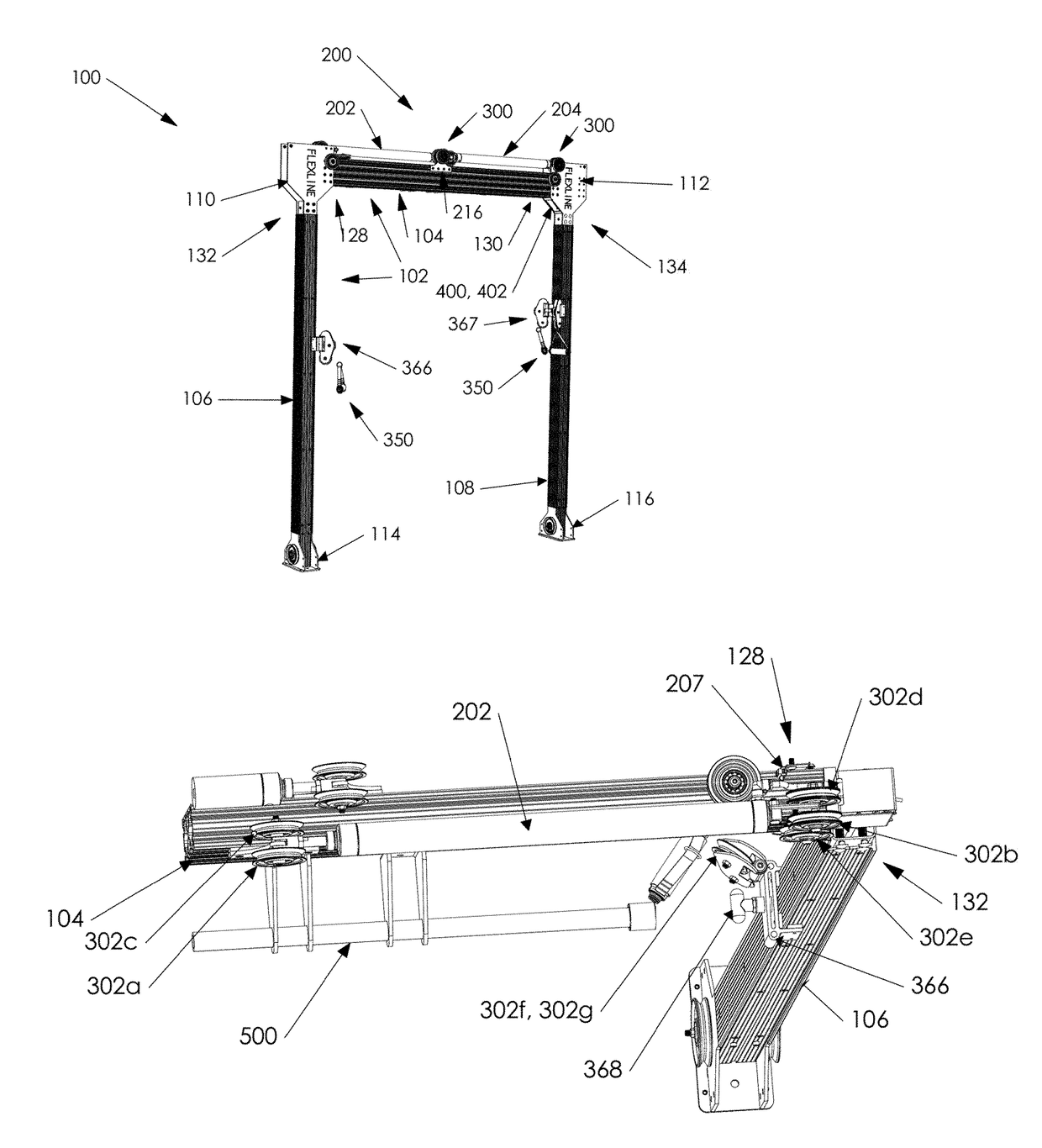
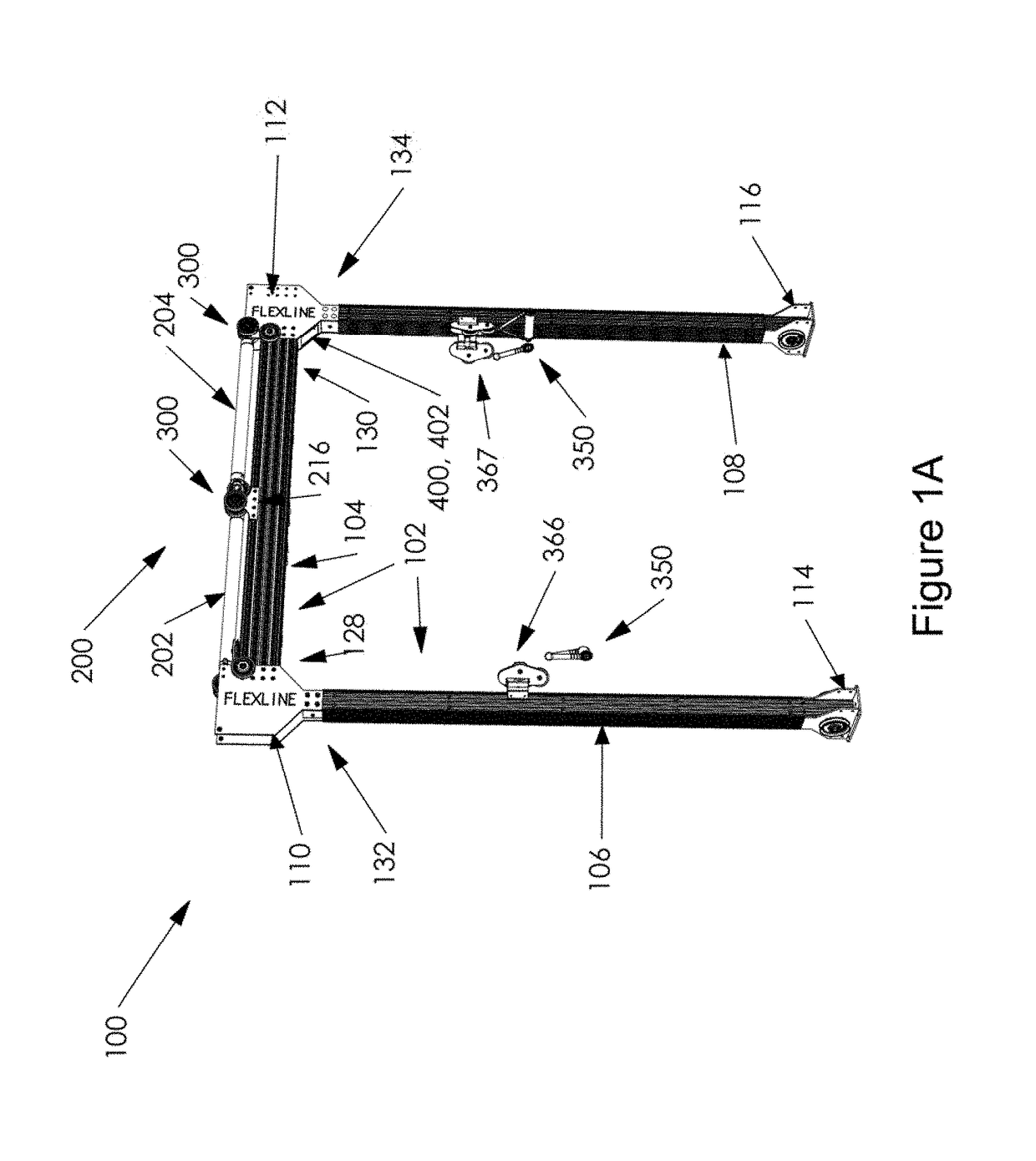
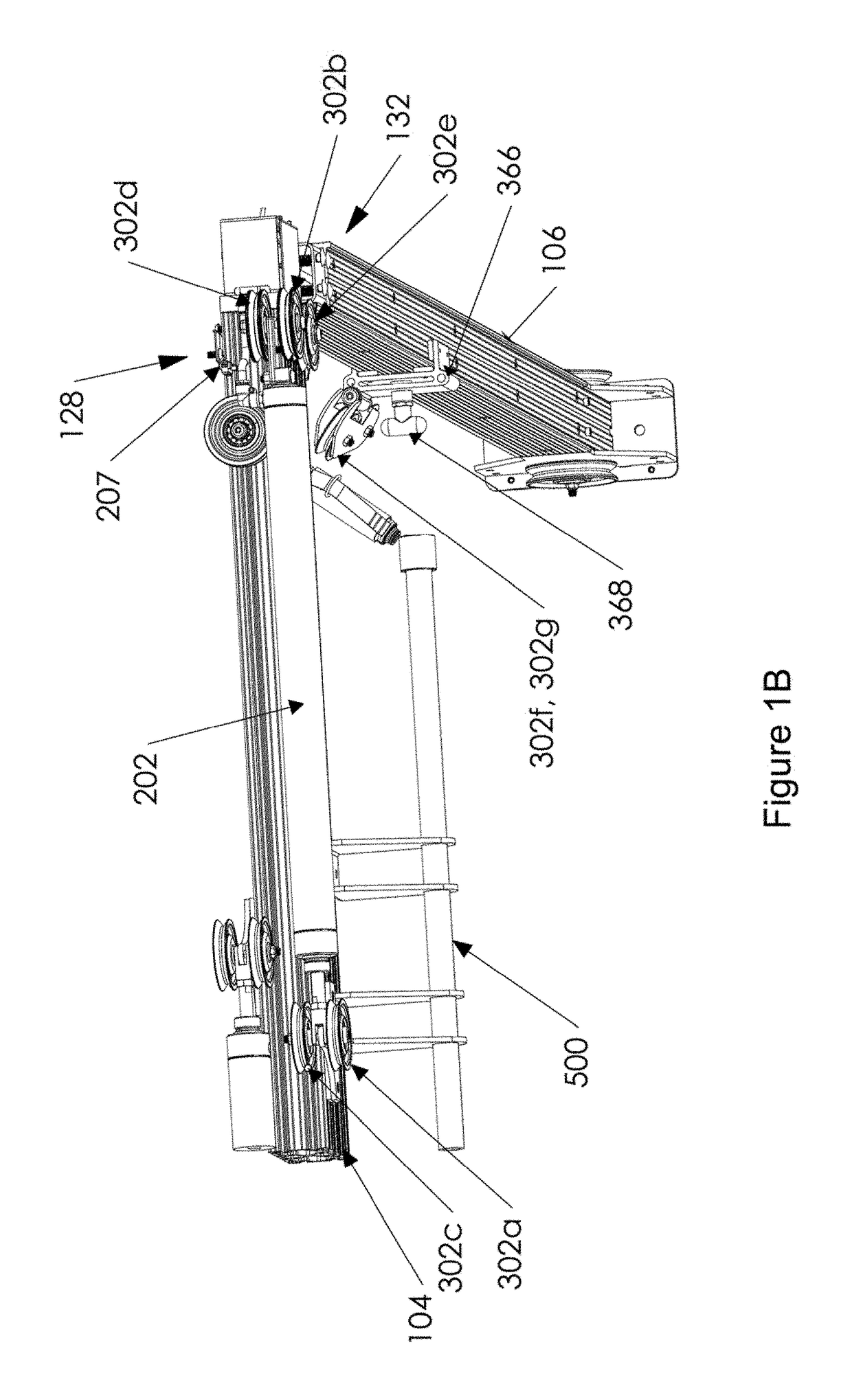
ActiveUS20180243600A1Individual control over the tension (resistance) of the machineSave spaceMuscle exercising devicesAccelerometerEngineering
A system and method of using an exercise system having a resistance structure of an exercise bar connected to cables, which cables are connected to at least one pneumatic cylinder that creates resistance, wherein the resistance is adjusted by the user via actuators in the exercise bar, so that the user does not need to release the exercise bar to adjust the resistance. The system may be supported by a frame, and the pneumatic cylinder may be connected to an equalizing tank that may be housed within or integrated into the frame. The system may include a monitor to visually display system parameters and other information to the user. The system may calculate resistance and work done by the user by measuring piston displacement and speed, as well as using accelerometers or other devices integrated into the exercise bar.
Owner:FLEXLINE FITNESS INC
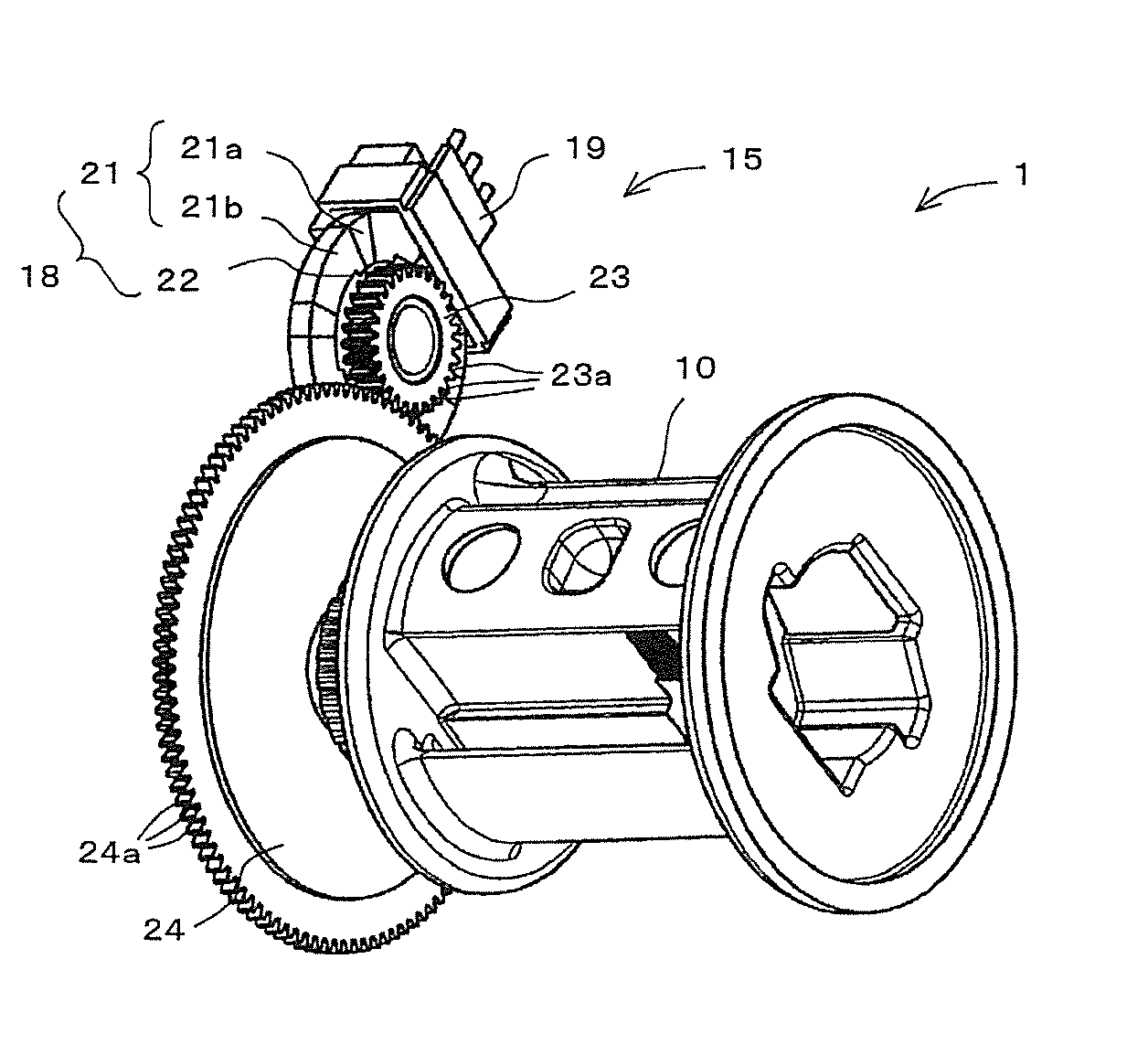
Position detector, seat belt retractor having this position detector, and seat belt apparatus having this seat belt retractor
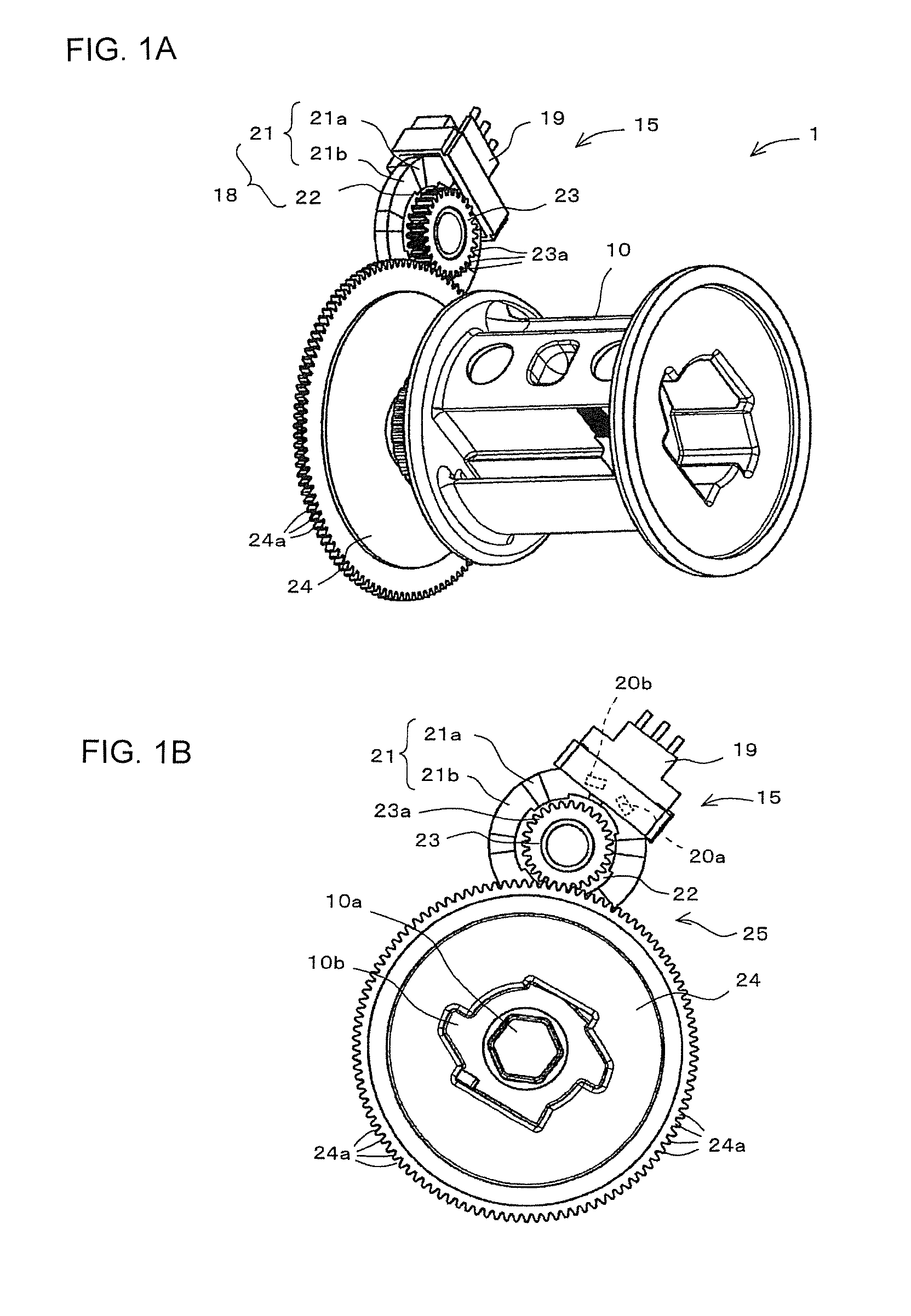
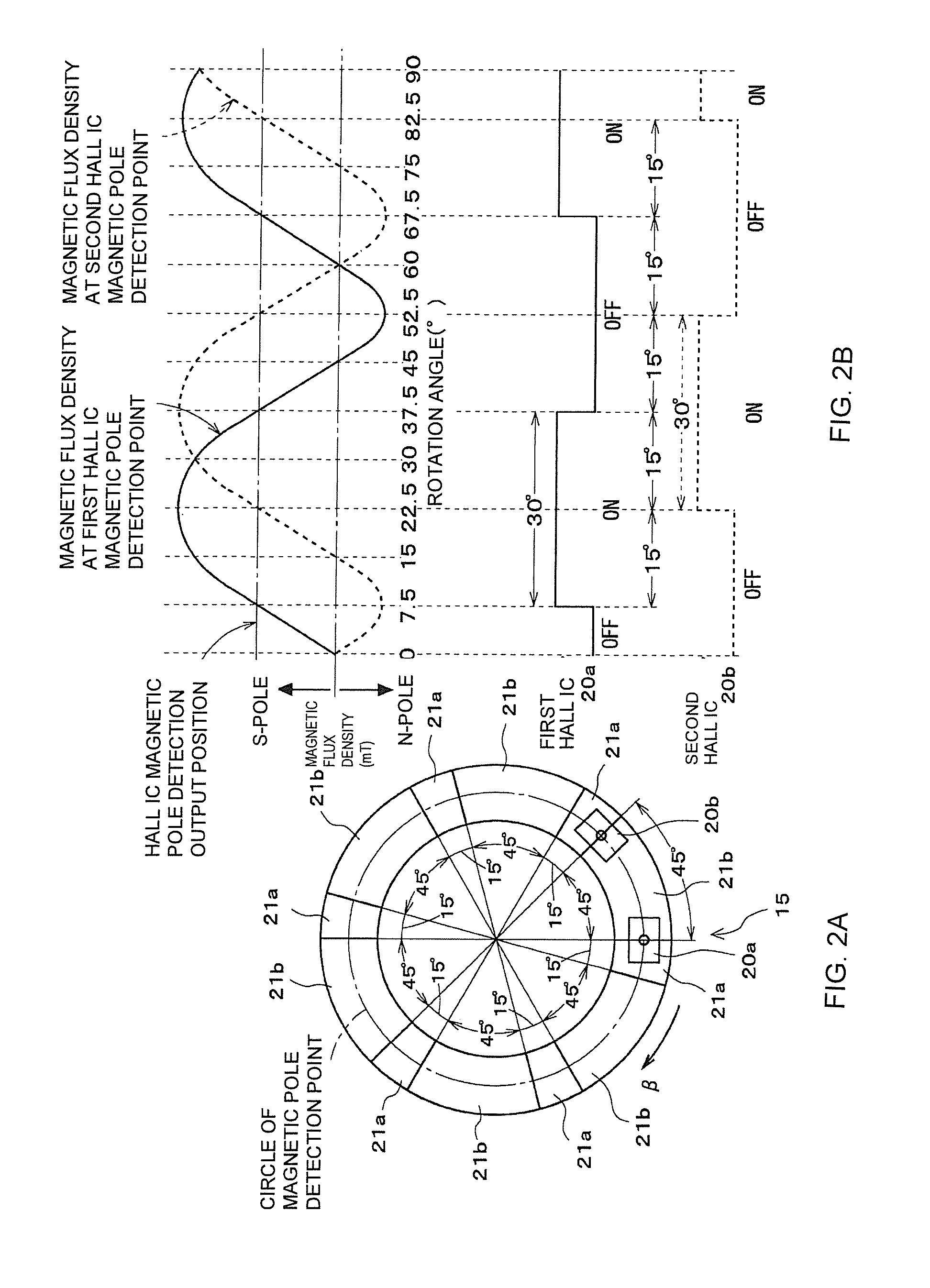
A position detector is provided that can detect the position of a moving member with a higher degree of accuracy. In one form, a rotation sensor includes a magnet in which N-pole magnets and S-pole magnets are arranged alternately and circularly and that rotates in conjunction with the rotation of a spool, and first and second Hall elements and that are disposed apart from each other in the circumferential direction of the magnet and detect the poles of the N-pole magnets and S-pole magnets. In that case, the first and second Hall elements and are both unipolar detection type Hall elements that detect only the S-pole. The magnetization width of the S-pole magnets is set large, and the magnetization width of the N-pole magnets is set small.
Owner:JOYSON SAFETY SYST JAPAN GK
Covered housing
ActiveUS20140140556A1Limit spatial controlControl tensionSingle transducer incorporationLoudspeaker screensEngineeringMechanical engineering
One embodiment of the invention is directed to a process for assembly of a covered housing comprising placing a first frame strip coupled with a fabric portion, under a shoulder on a first end of a housing, pulling the fabric portion toward a second end of a housing, placing a second frame strip coupled with the fabric portion, under a shoulder on the second end of the housing, placing a third frame strip coupled with the fabric portion, under a first main body shoulder of the housing, and placing a fourth frame strip coupled with the fabric portion, under a second main body shoulder of the housing.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
Linear guide track functional pulley group for bundle-like winding machine
A linear guide track functional pulley group for a bundle-like winding machine comprises a movable pulley used for guiding materials to be wound, and fixed pulleys which are arranged at two sides of the movable pulley; the movable pulley is arranged on a linear guide track and can reciprocate along the linear guide track; the movable pulley is connected with a displacement sensor connected with a control system; the control system controls the winding speed of the winding machine according to the displacement measured by the displacement sensor. The movable pulley is also connected with a forcing mechanism adopting any one from a spring, a cylinder or an oil cylinder, and the cylinder or the oil cylinder is connected with the control system. The linear guide track functional pulley group for the bundle-like winding machine is simple in structure, high in automation degree, safe and reliable in use, wide in application range, capable of fully meeting the demands of a production line and suitable for being promoted and used.
Owner:LUOYANG MINGWEI MACHINERY TECH
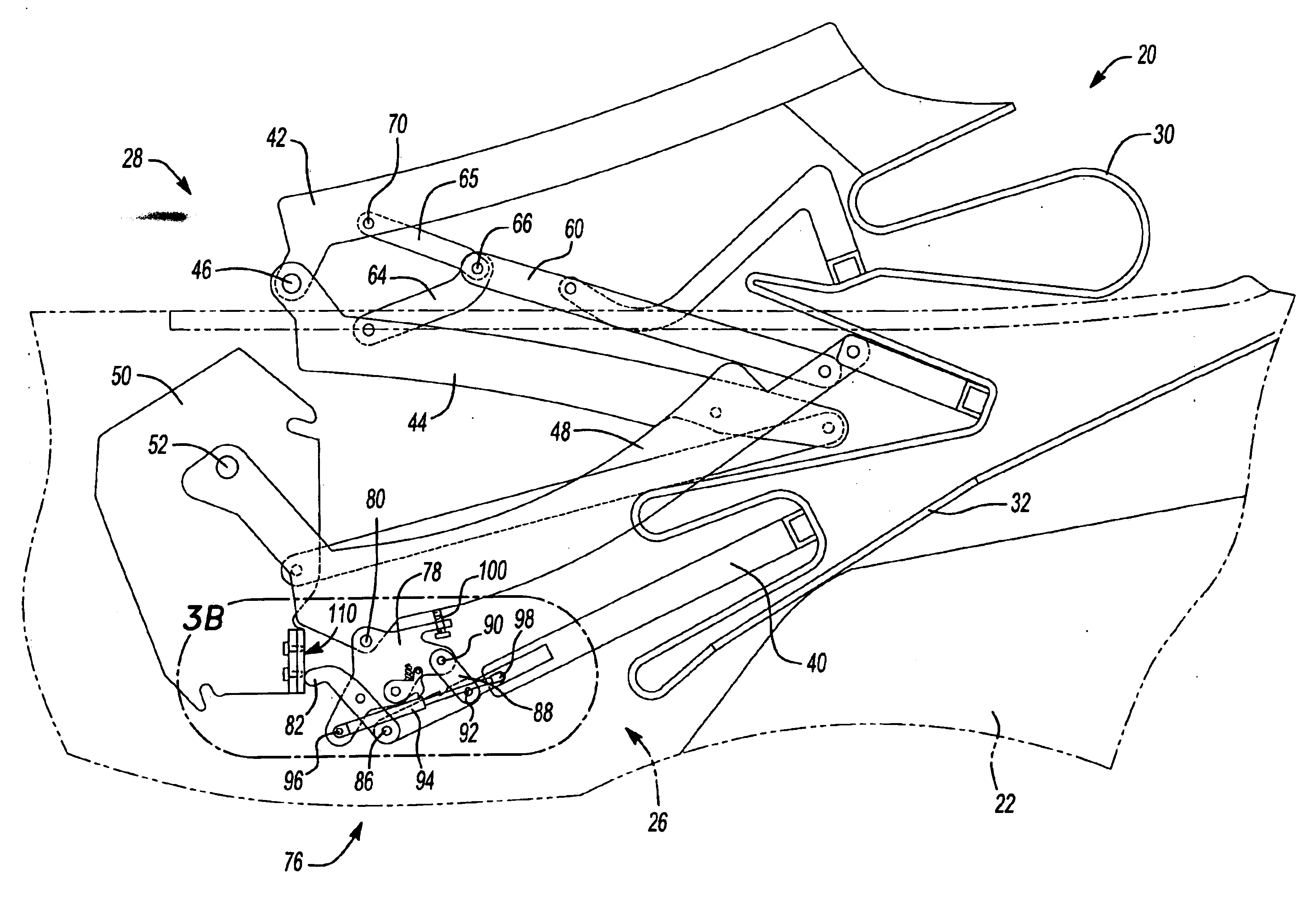
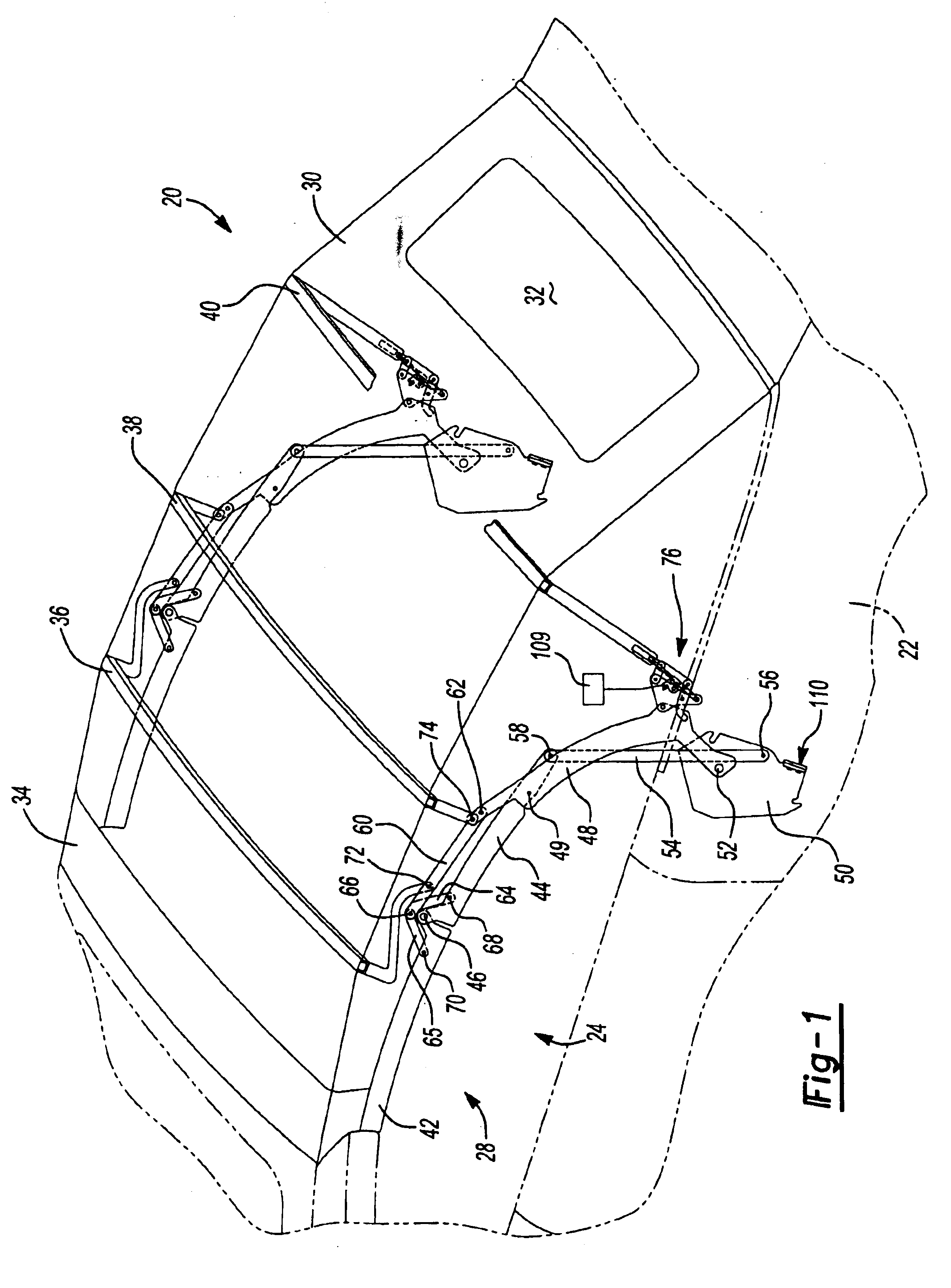
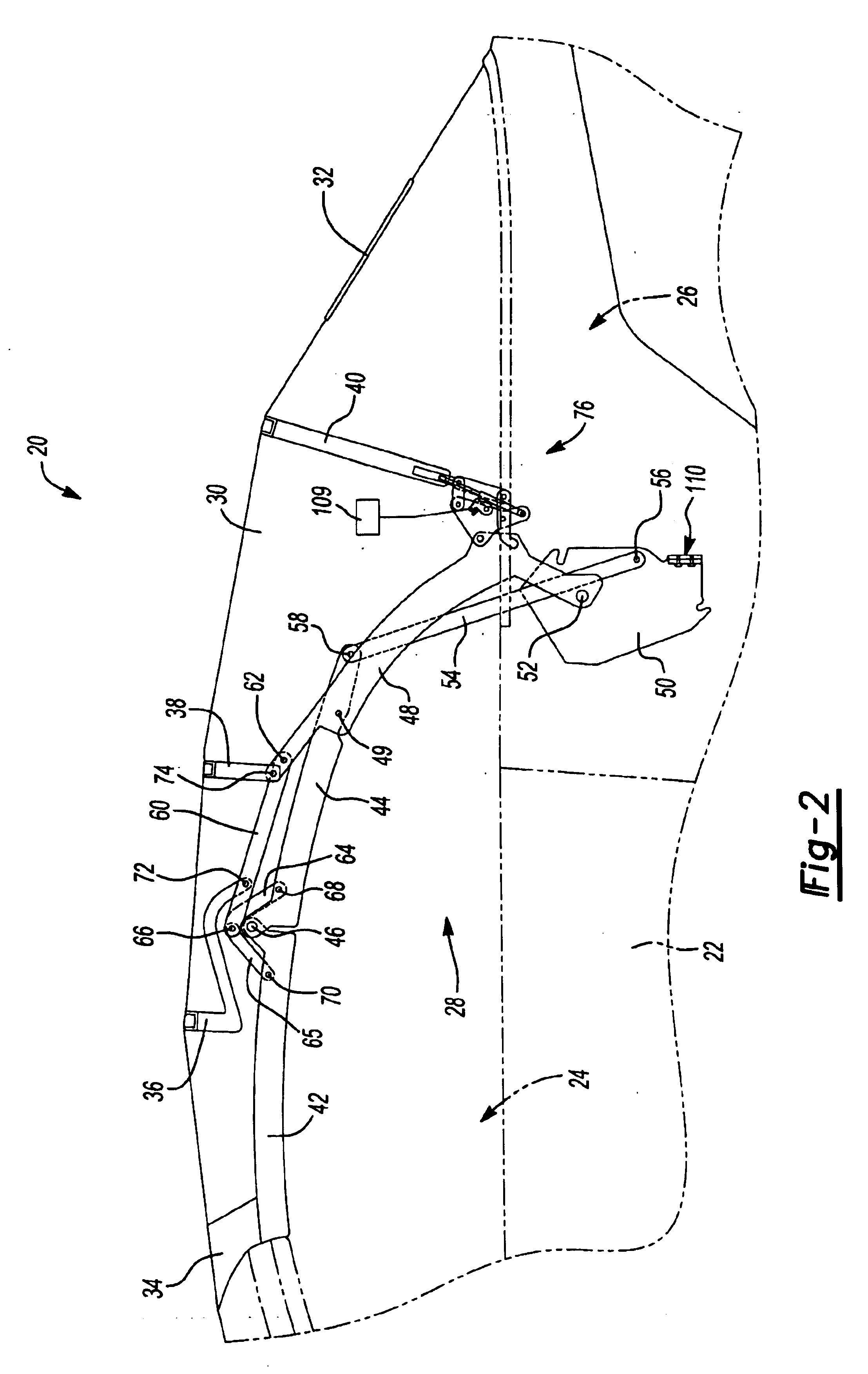
Vehicle convertible roof
InactiveUS6843522B2Acceptable pull-down forceSolve the lack of tensionEngine sealsVehicle sealing arrangementsMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
A convertible roof system for an automotive vehicle includes a roof bow that is operable between extended and retracted positions to vary tension of the roof cover and is actuated by a link that travels along a camming surface when the folding mechanism supporting the cover moves between the raised and stowed position.
Owner:SPECIALTY VEHICLE ACQUISITION
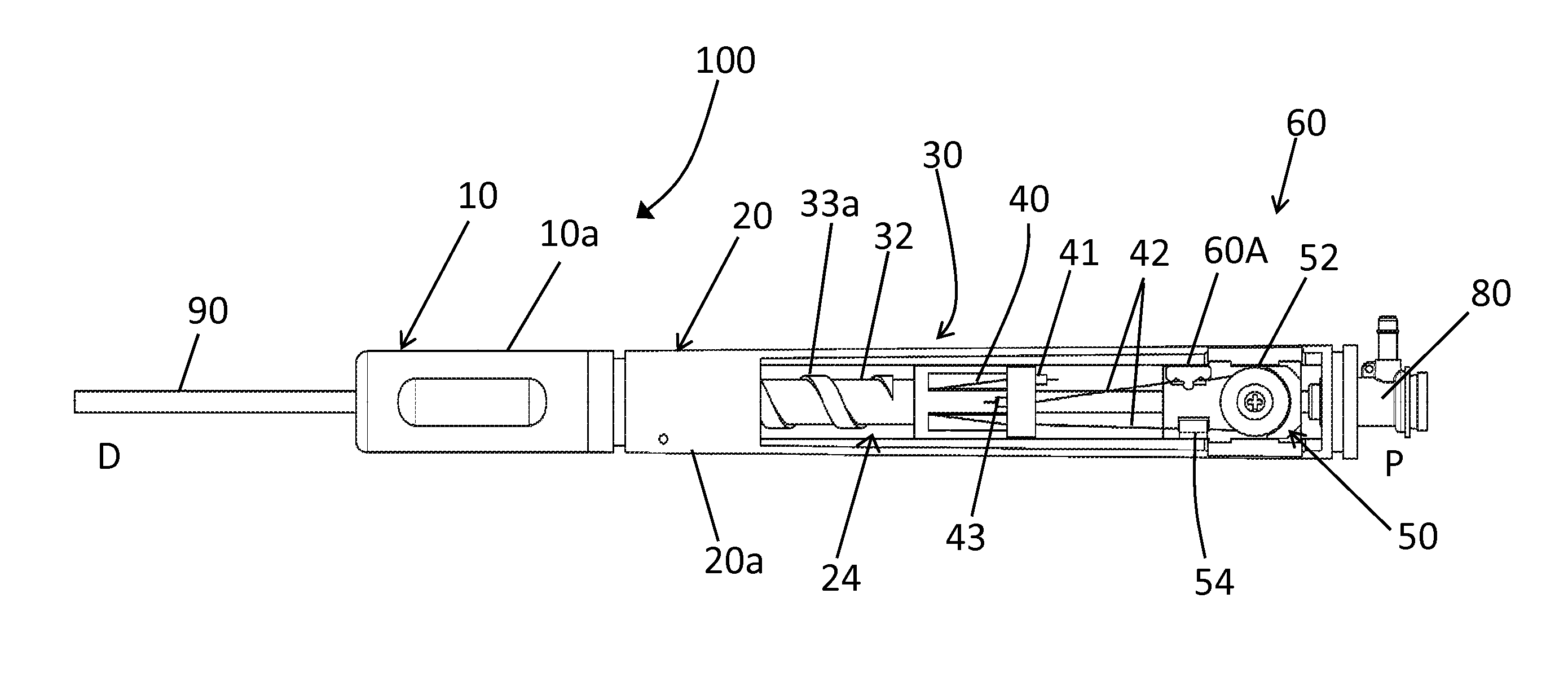
Steerable Medical Device Handle
A control system and method are provided for control of a steerable catheter, the catheter including at least two control wires, a distal end of each of the control wires being coupled to the catheter at a distal region thereof, the control system comprising: a housing coupled to the catheter; a slide assembly positioned within the housing and operable to translate linearly therein; a proximal portion of each of the at least two control wires being positioned through the slide assembly; and a control knob rotatably coupled to the housing for linearly translating the slide assembly, thereby enabling the slide assembly to separately manipulate each of said at least two control wires to effect a change in a deflection of said catheter. Rotation of the control knob in a first rotational direction causes distal movement of the slide assembly in a first linear direction causing the slide assembly to tension one of said at least two control wires thereby effecting a change in the deflection of said catheter in a first deflection direction and wherein rotation of the knob in a second rotational direction causes proximal movement of the slide assembly in a second linear direction causing the slide assembly to tension the other of said at least two control wires thereby effecting a change in the deflection of said catheter in a second deflection direction.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Film gauffer removing device, film tension adjusting method and film gauffer removing method
InactiveCN102024563AReduce involvementAvoid misalignmentThin/thick film capacitorStacked capacitorsEngineeringInjection air
Owner:NITTOKU ENG CO LTD
Method for automatic slip clutch tension on a reel
The method of preventing over tension to an umbilical wrapped on the spool of an offshore reel when the umbilical is being normally deployed or retrieved or when the umbilical is unexpectedly pulled from the spool on the reel, comprising providing a main disk, mounting the main disk on the spool of the reel with a slip connection which will be automatically controlled, connecting motor power for the reel to the main disk, connecting brakes to the main disk, such that when the diameter of deployment varies the slip connection torque will be automatically adjusted and prevent the umbilical from being subjected to tension higher than the desired amount.
Owner:REEL POWER LICENSING
Clad material, method for manufacturing said clad material, and apparatus for manufacturing said clad material
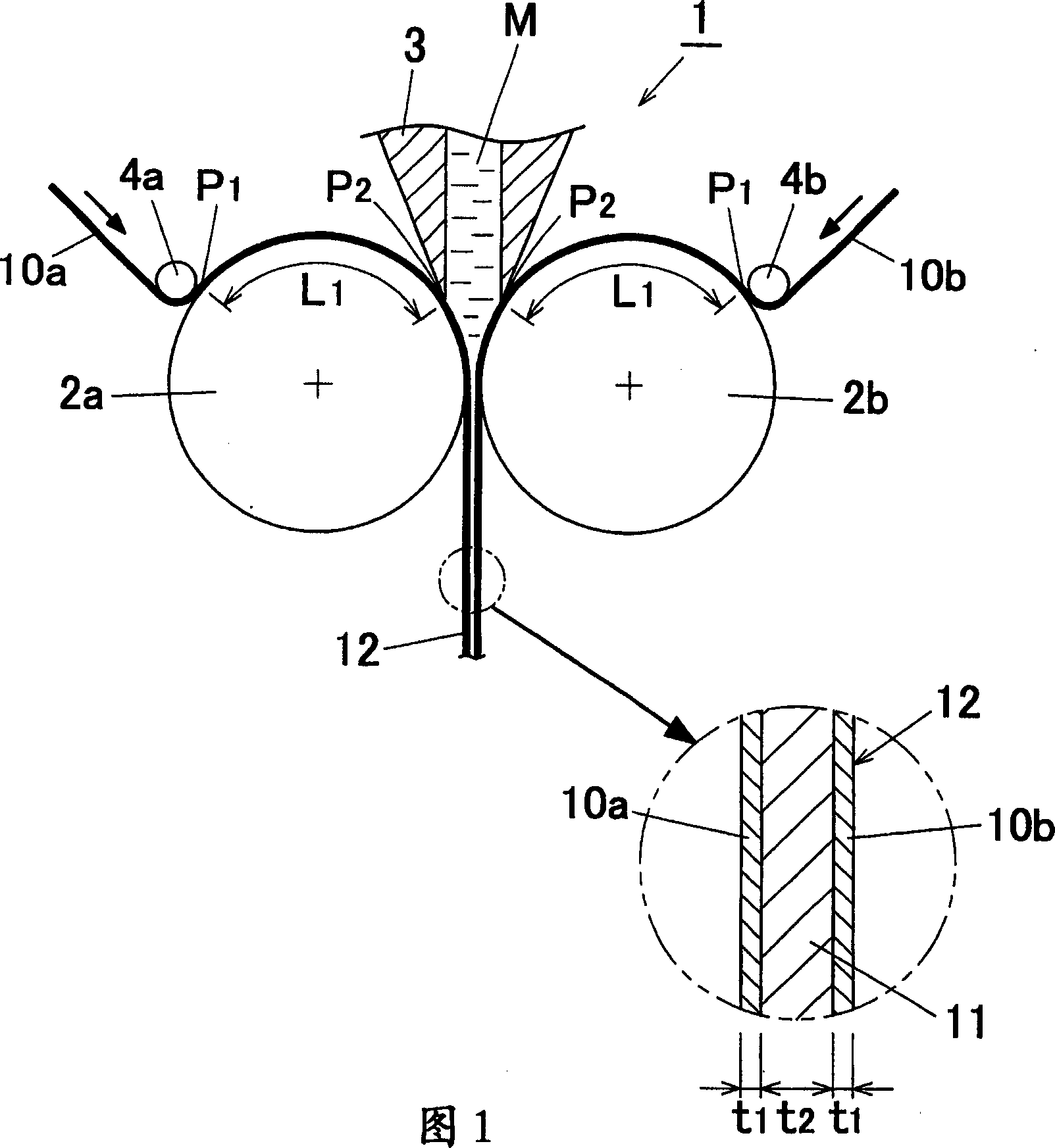
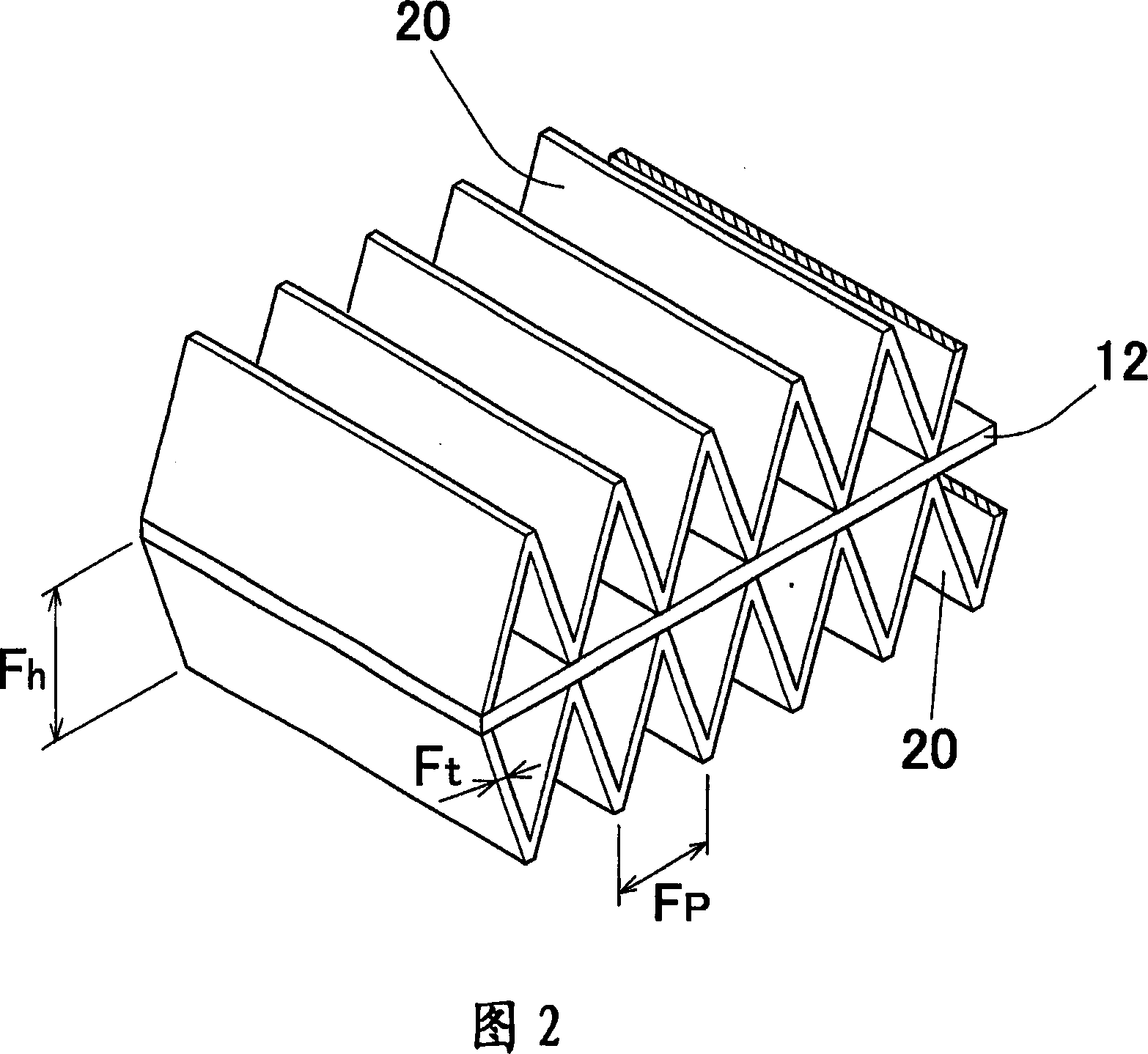
InactiveCN1933928AControl tensionIncrease cooling rateHeat exchange apparatusMetal rolling arrangementsMeeting placeMolten metal
A method for manufacturing a clad material in which a core material is cast and skin materials are pressure-bonded thereon aims to prevent deterioration of adhesiveness of the core material and the skin materials while keeping sufficient cooling rate of the core material, prevent thickness variation and / or breakage of the skin materials during the manufacturing process, and keep the surface property of the cooling rolls constant. The method for manufacturing a clad material (11) includes the steps of continuously supplying molten metal (M) into a gap between a pair of cooling rollers (2a) (2b) to cast a core material, and cladding skin materials (10a) (10b) on both surfaces of the core material with hot rolling by continuously supplying the skin materials on peripheral surfaces of the cooling rollers so that the skin materials prevent direct contact between the cooling rollers and the molten metal, wherein the skin materials are supplied so as to come into contact with the peripheral surfaces of the cooling rollers, and wherein a contact distance (L1) from a contact starting point (P1) where the skin material begins to come into contact with the cooling roller to a meeting point (P2) where the skin material begins to come into contact with the molten metal is set to 100 times or more of a thickness (t1) of the skin material.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
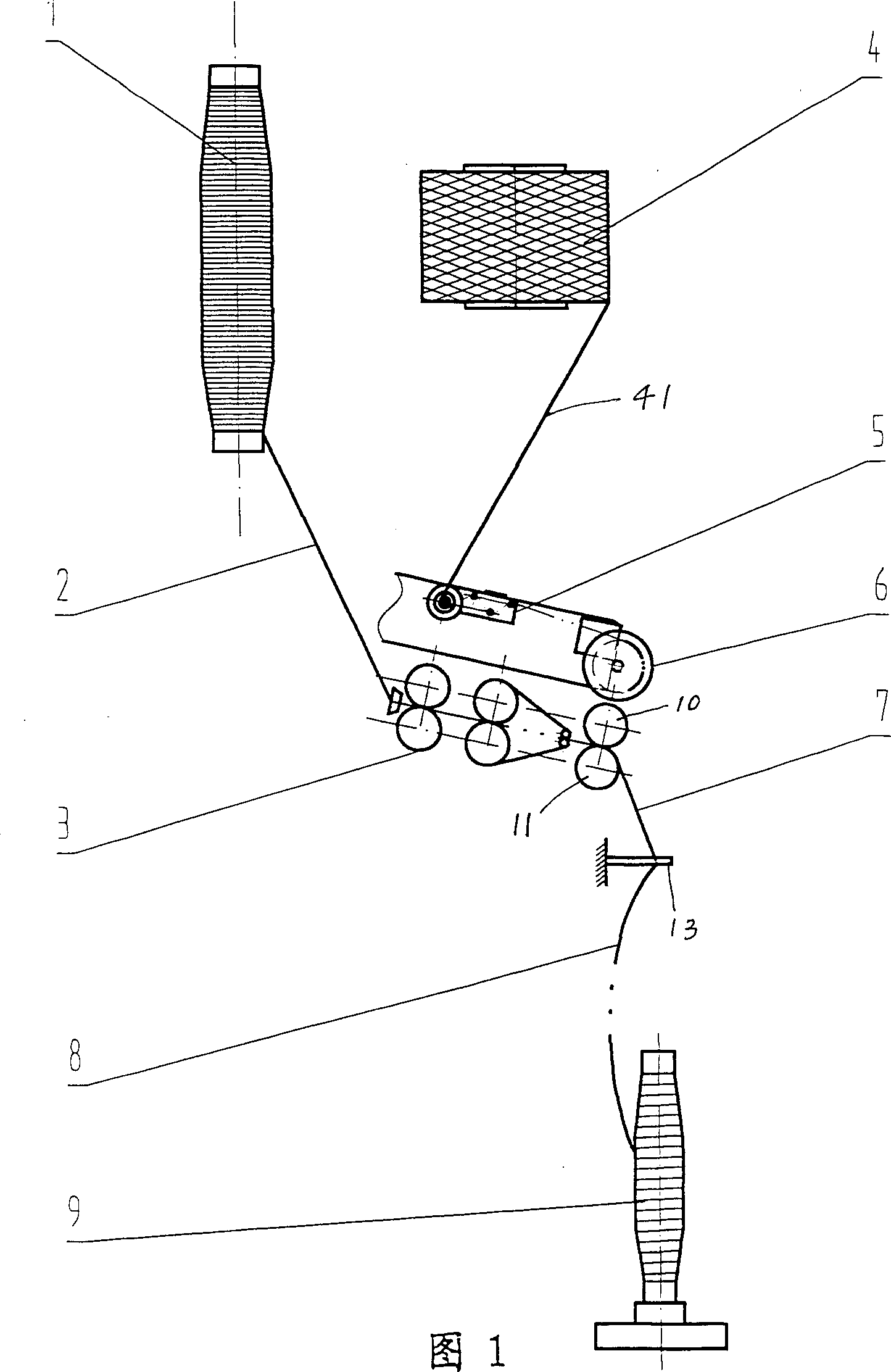
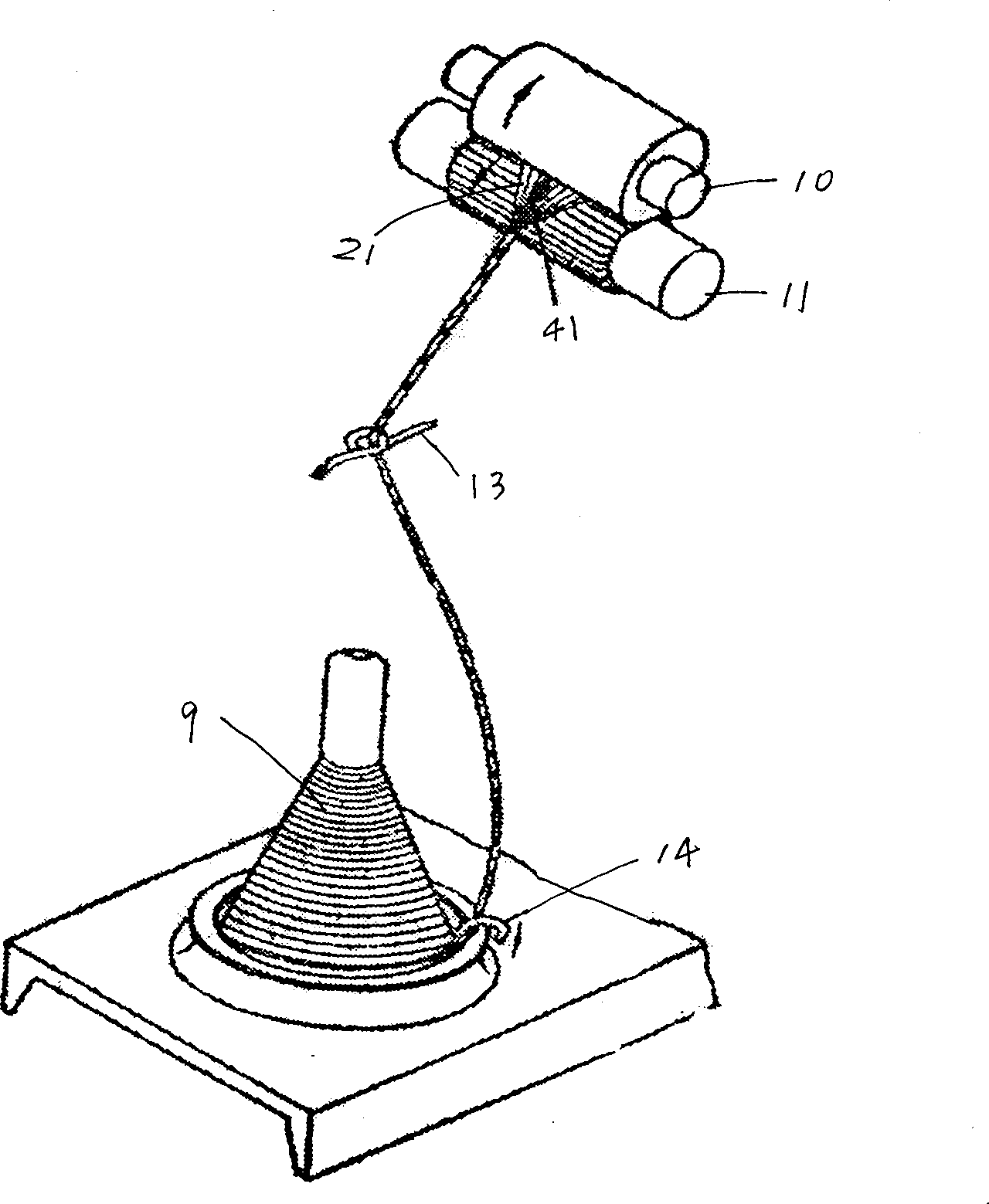
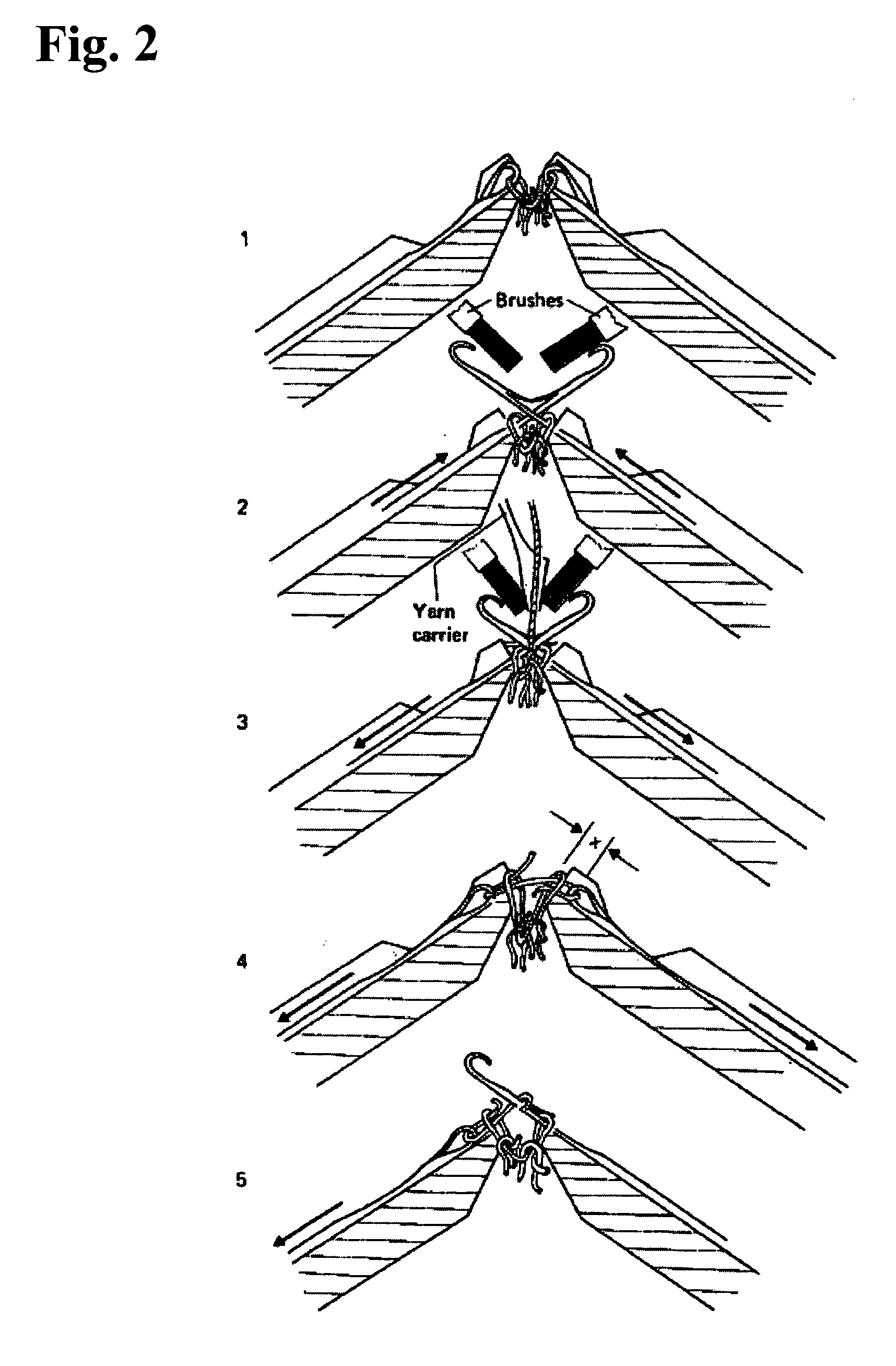
Spinning method and device for symmetrically covering rigid fiber filament by short fiber bundles
The invention provides a spinning method and device for symmetrically covering a rigid fiber filament by short fiber bundles. The spinning device comprises a ring spinning frame and is characterized by comprising a filament cylinder and a yarn guider, wherein one roller of a front roller pair of the ring spinning machine is a slotting roller, and a backing-off roll is arranged between the slotting roller and the yarn guider. By adopting the spinning device, under the drive of the front roller pair, a rigid fiber filament on the filament cylinder is fed into the backing-off roll through the yarn guider, enters a slot of the slotting roller and is output along the slot, the rigid fiber filament is fed into the front roller pair through a rear roller pair and a middle roller pair, and two strands of symmetrical short fiber bundles output by the front roller pair are converged at a convergence point; meanwhile, the short fiber bundles formed by rotary twisting are covered on the outer surface of the rigid fiber filament to form a composite yarn. According to the invention, the rigid fiber filament is produced into the softer and more comfortable composite yarn with the advantages of bending, shearing and torsion resistance and high wear resistance and multiple functions.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation method and application of heat-resistant titanium alloy wires
ActiveCN109355530ADifferent tensile strength matchingPlastic different matchingTitanium alloyHeat treated
The invention provides a machining and manufacturing method and application of heat-resistant titanium alloy Ti60 wires. The method comprises the steps that Ti60 titanium alloy ingot castings are smelted by adopting a vacuum consumable smelting technology; the smelted Ti60 titanium alloy ingot castings are forged into rods by adopting a free forging technology; the Ti60 titanium alloy rods are finish-forged into thick rod blanks by adopting a finish forging technology; the Ti60 titanium alloy thick rod blanks are rolled into straight strip wire blanks by adopting a hot rolling technology; surface treatment is conducted on Ti60 titanium alloy annealing wire blanks, and pre-oxidation oxidation film hanging treatment is conducted after defects on the surfaces of the wire blanks are removed; continuous high-temperature drawing deformation is conducted on the Ti60 titanium alloy wire blanks obtained after surface treatment by adopting a straight wire drawing machine; the drawn wires are straightened by adopting electric heating tension; and annealing heat treatment is conducted on the straightened wires, and finally centerless grinding is conducted. According to the machining and manufacturing method and application of the heat-resistant titanium alloy Ti60 wires, through combination of different heat machining and heat treating technologies, different matching combinations of the tensile strength, the plasticity and the shearing strength can be obtained, and the heat-resistant titanium alloy Ti60 wires can be used for manufacturing advanced aerospace fasteners such as rivets, bolts and nuts and are used in the temperature range of 600-650 DEG C.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for producing roll of microporous plastic film
InactiveUS20140014762A1Lower average tensionPrevent from being easily brokenHybrid capacitor separatorsCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersMicrocellular plasticSurface roughness
A microporous plastic film roll production method, comprising the steps of: conveying microporous plastic film having through-holes in its interior by using a plurality of conveyance rollers at least one conveyance roller of which has a surface roughness RzJIS (μm) of 0.3≦RzJIS≦30 and has a surface made of fluorine resin, silicone rubber, or a composite material containing one of them; and winding it up in a roll.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com