Process for producing roll of microporous plastic film
a microporous plastic and film production technology, applied in the direction of cell components, cell component details, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the production efficiency of the film, the difficulty of aforementioned methods alone to convey the film without causing either wrinkle or breakage, and the difficulty of preventing wrinkles and breakage. , to achieve the effect of preventing breakage and wrinkles, accelerating the stress concentration in the cut portions, and preventing wrinkles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
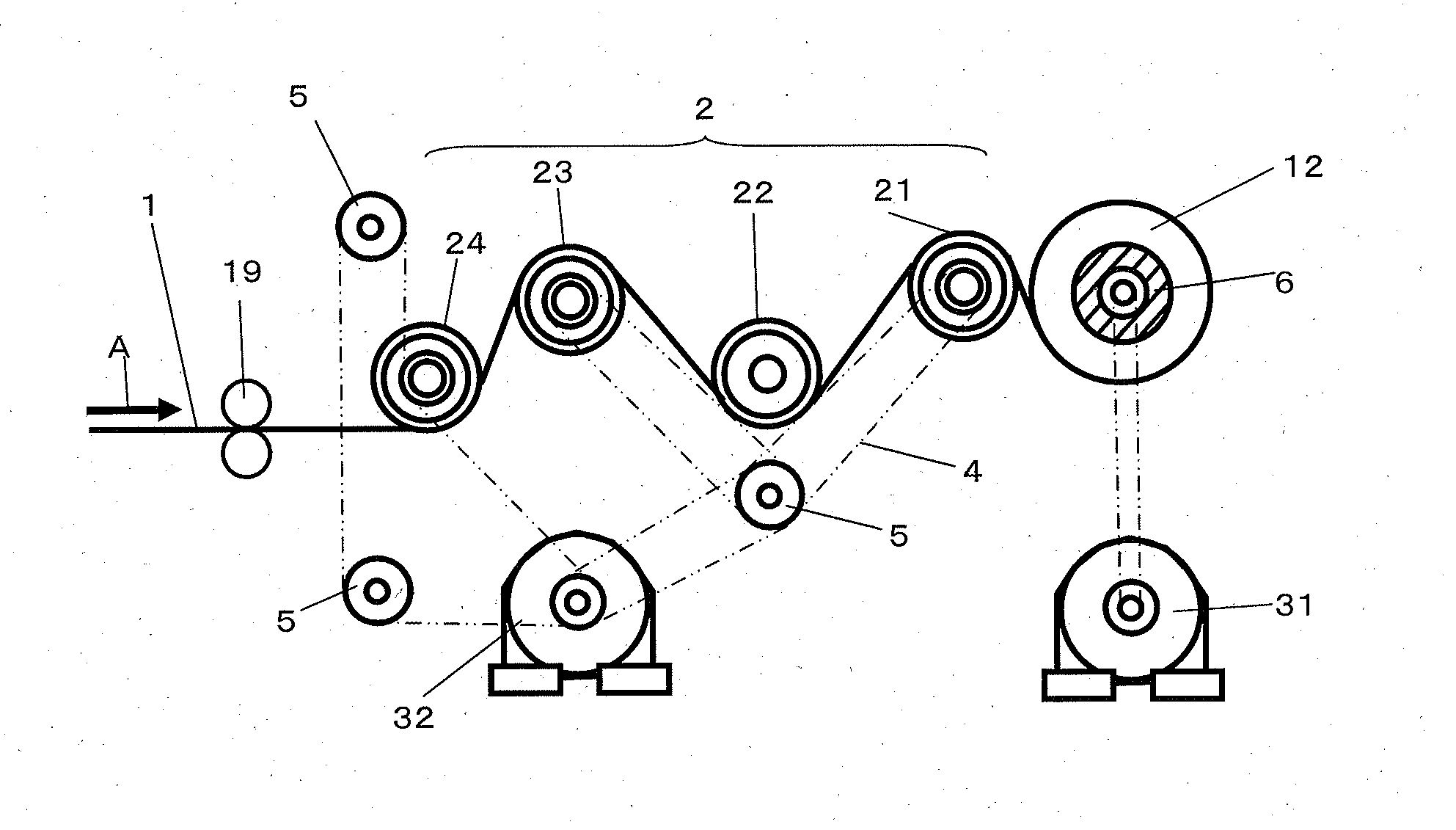
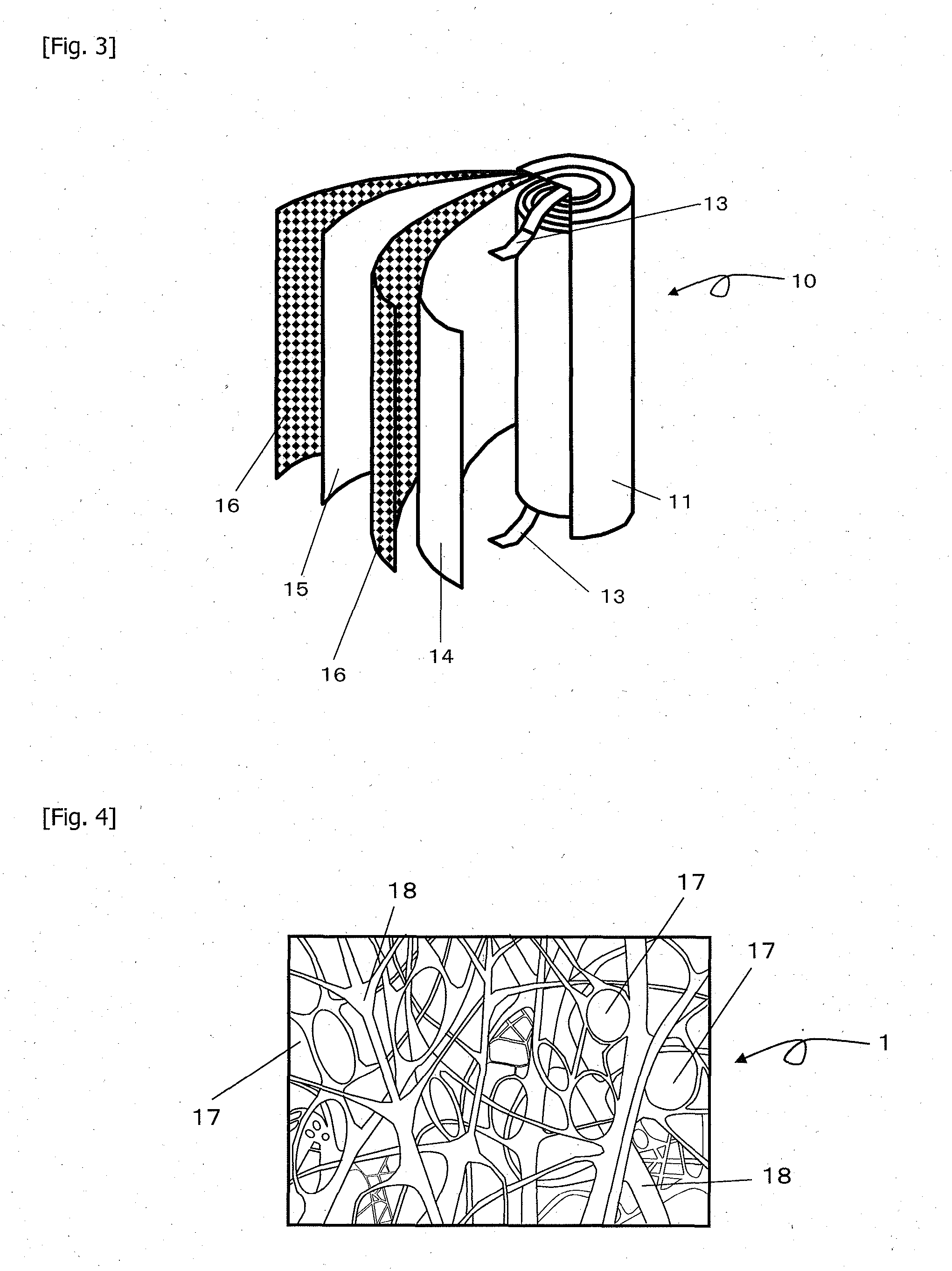
[0096]A microporous plastic film 1 of polypropylene in which through-holes as illustrated in FIG. 4 were formed by carrying out a biaxial stretching step while controlling the crystal structure of polypropylene was conveyed by a conveyance roller 2 as illustrated in FIG. 1 and wound up continuously on a core 6 to produce a microporous plastic film roll 12. The microporous polypropylene film had a Gurley air permeation resistance of 500 seconds per 100 ml, porosity of 70%, average pore size of 100 nm, and cushion rate of 17%. The film 1 had a width of 600 mm and thickness of 60 μm. The thickness was measured with an emitting / receiving type laser sensor, and the porosity was calculated by formula 6 from the measured thickness.
[0097]Here, the gas permeability is represented by the Gurley air permeation resistance (seconds per 100 ml) as specified in MS P8117 (2001). The Gurley air permeation resistance is defined as the time period required by 100 ml of air pressured under a constant p...
example 2
[0105]A film 1 with a thickness of 20 μm was wound up under the same conditions as in Example 1 to provide a microporous plastic film roll 12. The film had subsequently the same porosity as in the example, but its Gurley air permeation resistance was 100 seconds per 100 ml as a result of a smaller thickness.
example 3
[0106]The same procedure as in Example 2 was carried out except that a composite film of metal and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) was formed on the surfaces of the conveyance rollers 21 to 24 as illustrated in FIG. 2 so that the portions of the four rollers coming in contact with the film 1 had a coefficient of static friction of 0.5 or less. To represent the surface roughness of the roller surfaces, their ten-point average roughness was measured under the same conditions as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| micropore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com