Design method of composite sample store and its system
A design method and sample technology, applied in the field of high-efficiency experiments-high-throughput experiments, can solve problems such as lack of experience and knowledge without consideration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
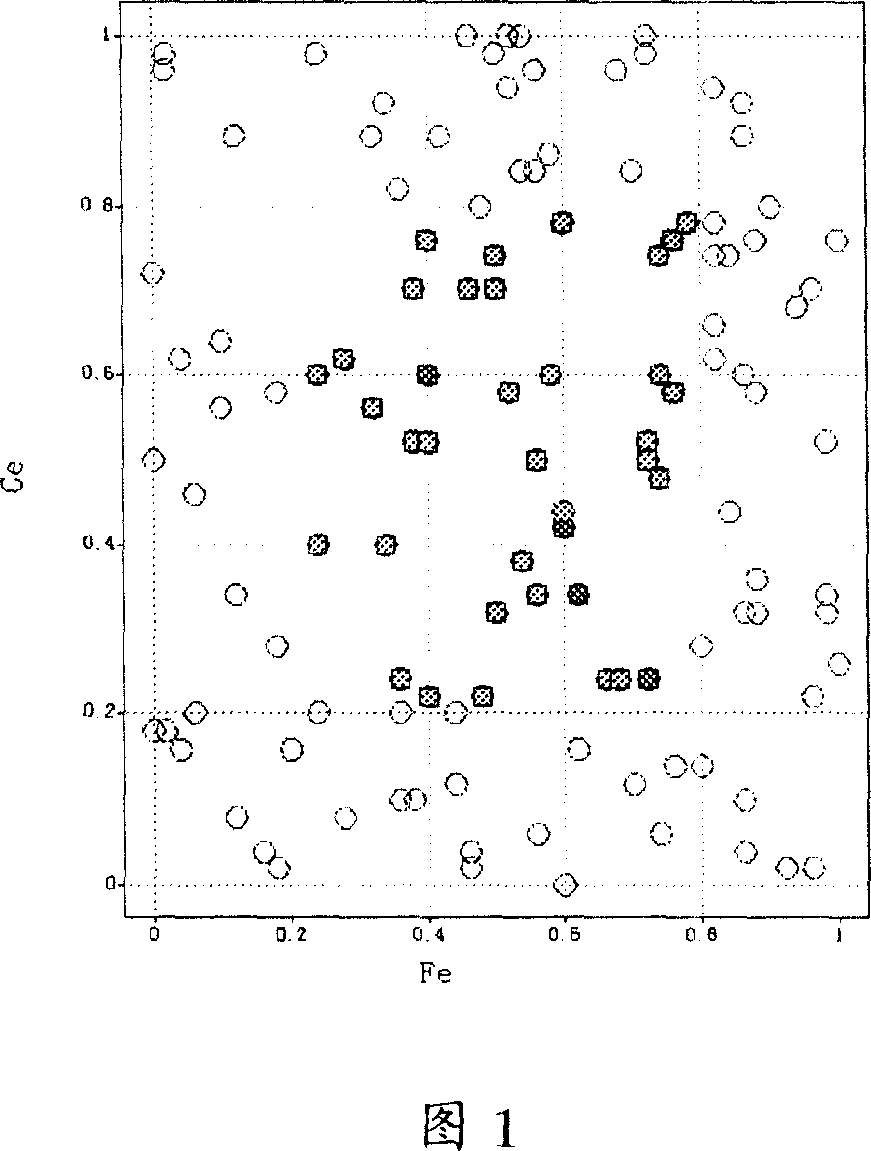
[0112] This example shows how to select qualified samples from pseudo-samples composed of two components (cerium and iron) produced by Monte Carlo simulation. Cerium variable V Ce Takes a value between 0 and 1, the iron variable V Fe It also takes a value between 0 and 1. The Monte Carlo simulation uses a uniformly distributed randomly generated V between 0 and 1 Ce and V Fe value to be carried out, the simulation in which V Ce A randomly generated value of V Fe The randomly generated values of are independent of each other. And in this simulation, V Ce and V Fe There are no mandatory limitations of any relationship or constraint. As a result of the Monte Carlo simulation, pseudo-sample populations are generated. The totality of points (including hollow, gray and dark colors) as shown in Fig. 1 constitute a set of pseudo samples.
[0113] We can use empirical knowledge to reduce the number of qualified samples by introducing constraints. The first constraint is de...
Embodiment 2
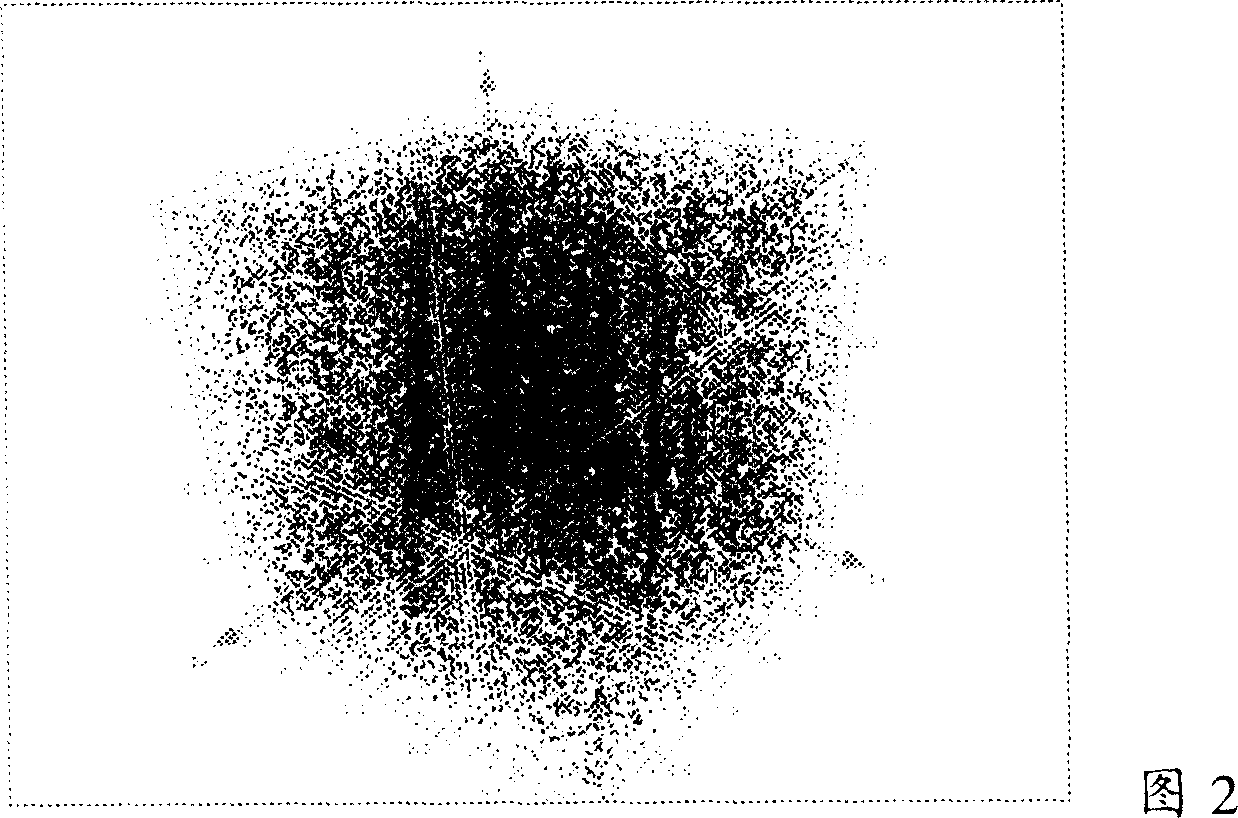
[0222] This example shows how to select qualified samples from pseudo-samples composed of four components (cerium, iron, tungsten and nickel) generated by Monte Carlo simulation. Variable V for cerium, iron, tungsten and nickel Ce , V Fe , V W , V NiBoth take values between 0 and 1. In the Monte Carlo simulation, we use uniformly distributed randomly generated values between 0 and 1 for each variable. The randomly generated values in this simulation are independent of each other and are not limited by any constraints. The result of the Monte Carlo simulation is a sample point (pseudo sample) in the four-dimensional space, and the projection of the four-dimensional sample point in the three-dimensional space is shown in FIG. 2 .
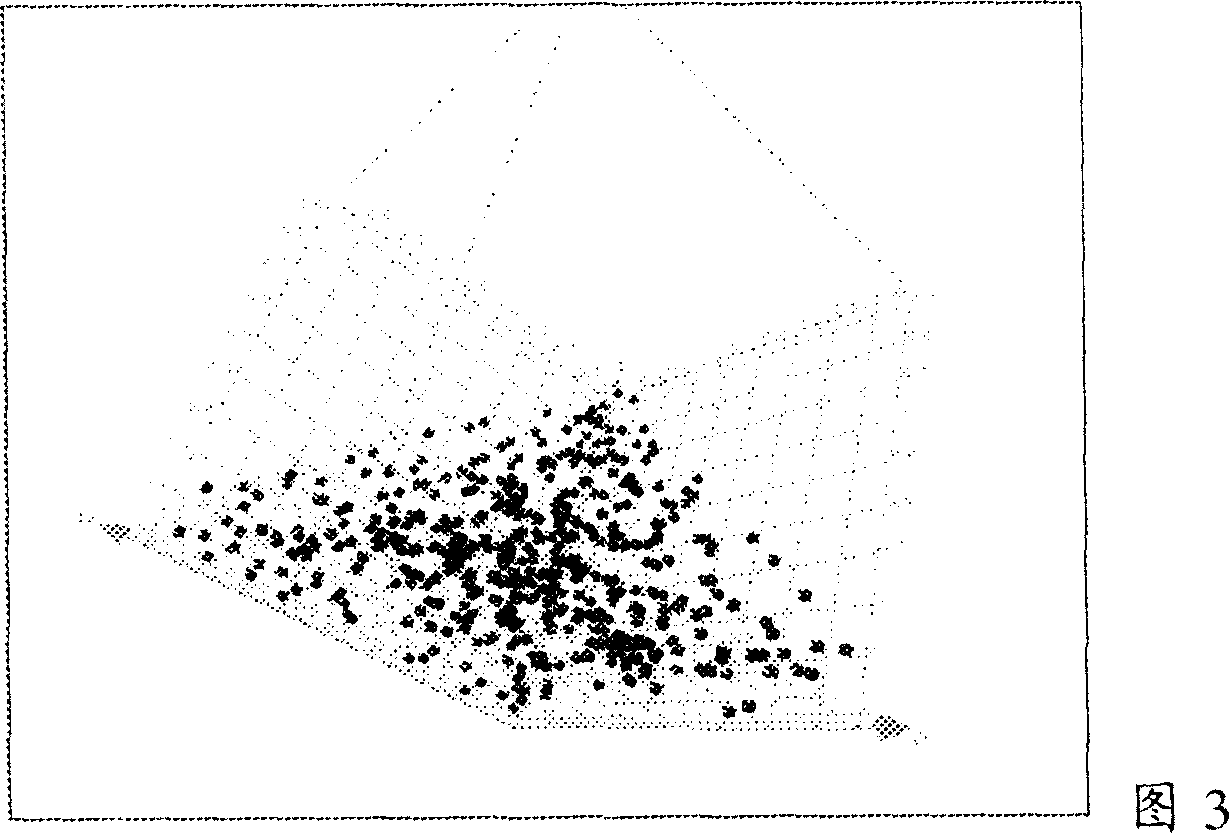
[0223] Here a first constraint is proposed for selecting samples corresponding to physically real, which is defined as V Ce +V Fe +V W +V Ni =1. When the first constraint is considered in the selection process, the selected set of pseud...
Embodiment 3
[0228] This example describes a computer program that allows a user to enter information through a graphical user interface and perform calculations and simulations, including Monte Carlo simulations, to design qualified sample libraries.
[0229] As shown in Figure 5, the graphical user interface allows the user to select the desired components for designing samples. For example, a sample composed of components A, B and C, component A can be any one from the element group consisting of vanadium (V), niobium (Nb) and molybdenum (Mo), the variable of component A (V a ) ranges from 0 to 1 (please refer to the range of 0.00 to 1.00 shown in FIG. 5 ), and the variable range is divided into 10 parts (10 segments as shown in FIG. 5 ). As a result, component A is assigned a variable (V a ) (please refer to Figure 6), similarly, components B and C are also given corresponding variables (V b and V c ) (please refer to Figure 6).
[0230] As a way to incorporate empirical knowledge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com