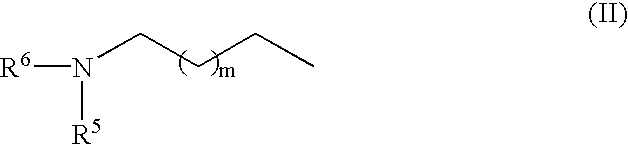
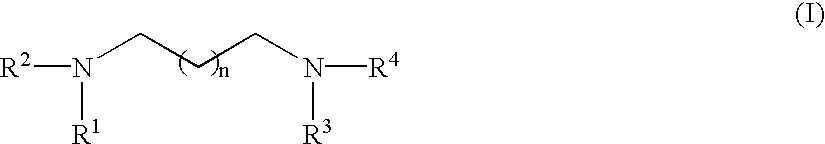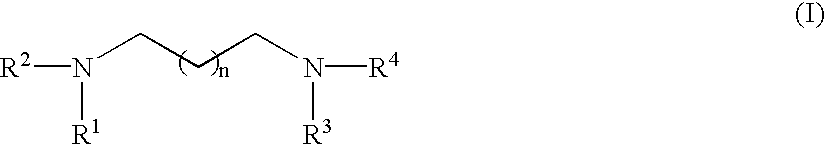RNA polymerase transcription promoter and nucleic acid sequencing method
a technology of transcription promoter and nucleic acid, applied in the direction of transferases, organic chemistry, biochemistry apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of et al having some problems, affecting the synthesis of rna or nucleic acid, and the evaluation method of a transcription promoting ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0087] Synthesis of 1,12-di(ethylamino)-4,9-diazadodecane HBr salt (5) 5
[0088] Diaminobutane as a raw material was reacted with tosyl chloride at room temperature for 3 hours to obtain N1,N4-di(p-toluenesulfonyl)-1,4-di-aminobutane. Using the obtained N1,N4-di(p-toluenesulfonyl)-1,4-diaminobut-ane and N-(3-bromopropyl)phthalimide as Chain A and Chain B, respectively, N1,N4,N9,N12-tetra(p-toluenesulfonyl)-1,12-diamino-4,9-diaz adodecane (3) was derived from the above Chain A and Chain B according to the known methods (Patent Documents 1 to 5 and References 6). Specifically, Compound 1 was synthesized, and then this Compound 1 was reacted with N.sub.2H.sub.4 in DMF at 70.degree. C. for 1 day to obtain Compound 2. The obtained Compound 2 was first treated with 2N HCl at 70.degree. C. for 1 hour, and then reacted with TsCl in pyridine in the presence of NEt.sub.3 at room temperature for four hours to obtain Compound 3.
[0089] Subsequently, a mixture of the above Compound 3 (0.17 g) anhyd...
example 2
[0090] Synthesis of 1,8-di(ethylamino)-4-azaoctane HBr salt (10) 6
[0091] 3-Bromopropylamine as a raw material was reacted with tosyl chloride at 0.degree. C. for 2 hours to synthesize N-(p-toluenesulfonyl)-3-bromopropylamine. Further, this was reacted with phthalimide at room temperature for 3 days to obtain N-(N3-p-toluenesulfonyl-3-aminopropyl)phthalimide. Using the obtained N-(N3-p-toluenesulfonyl-3-aminopropyl)phthalimide and N-(4-bromobutyl)phthalimide as Chain A and Chain B, respectively, N1,N4,N8-tri(p-toluenesulfonyl)-1,8-diamino-4-azaoctane (8) was derived from the above Chain A and Chain B according to the known methods (Patent Documents 1 to 5 and References 6). Specifically, Compound 6 was synthesized, and then this Compound 6 was reacted with N.sub.2H.sub.4 in DMF at 70.degree. C. for 1 day to obtain Compound 7. The obtained Compound 7 was first treated with 2 N HCl at 70.degree. C. for 1 hour, and then reacted with TsCl in pyridine in the presence of NEt.sub.3 at room ...
example 3.1
[0093] Synthesis of 1,14-di(ethylamino) -5,10-diazatetradecane HBr salt (15b) 7
[0094] Diaminobutane as a raw material was reacted with tosyl chloride at room temperature for 3 hours to obtain N1,N4-di(p-toluenesulfonyl)-1,4-di-aminobutane. Using the obtained N1,N4-di(p-toluenesulfonyl)-1,4-diaminobut-ane and N-(4-bromobutyl)phthalimide as Chain A and Chain B, respectively, N1,N5,N10,N14-tetra(p-toluenesulfonyl)-1,14-diamino-5,10-diazatetradecane (13b) was derived from the above Chain A and Chain B according to the known methods (Patent Documents 1 to 5 and References 6). Specifically, Compound 11a was synthesized, and then this Compound 11a was reacted with N.sub.2H.sub.4 in DMF at 70.degree. C. for 1 day to obtain Compound 12a. The obtained Compound 12a was first treated with 2 N HCl at 70.degree. C. for 1 hour, and then reacted with TsCl in pyridine in the presence of NEt.sub.3 at room temperature for 4 hours to obtain Compound 13a.
[0095] Subsequently, a mixture of the above Compo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com