Manufacture of carbon/carbon composites by hot pressing
a carbon/carbon composite and hot pressing technology, applied in the field of carbon/carbon composite manufacturing, can solve the problems of increasing weight, increasing cost, and increasing complexity of carbon/carbon composites, and achieves fewer densification and carbonization cycles and less processing steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Carbon / Carbon Composite Made by Dry Mixing of Precursor Materials
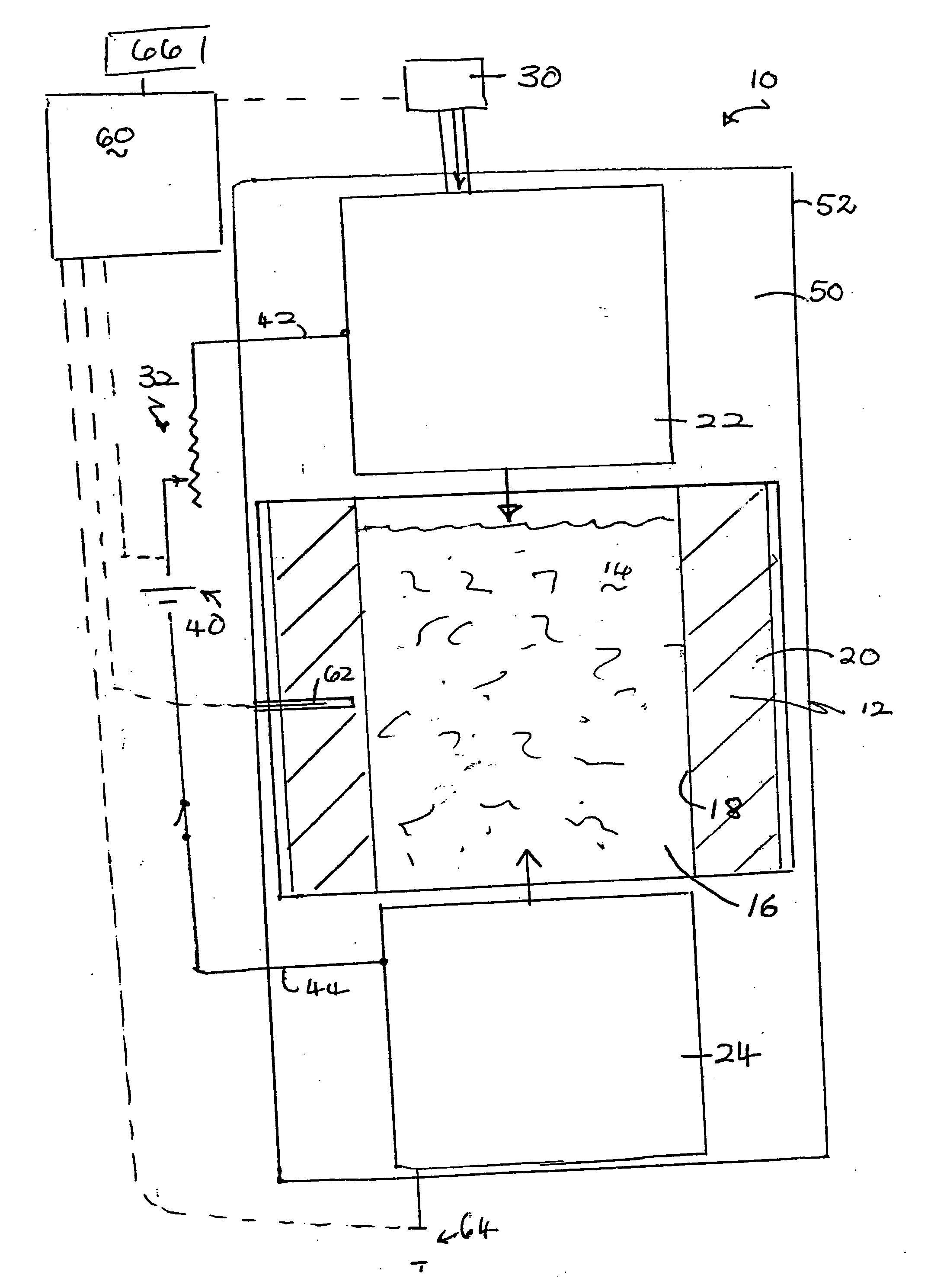
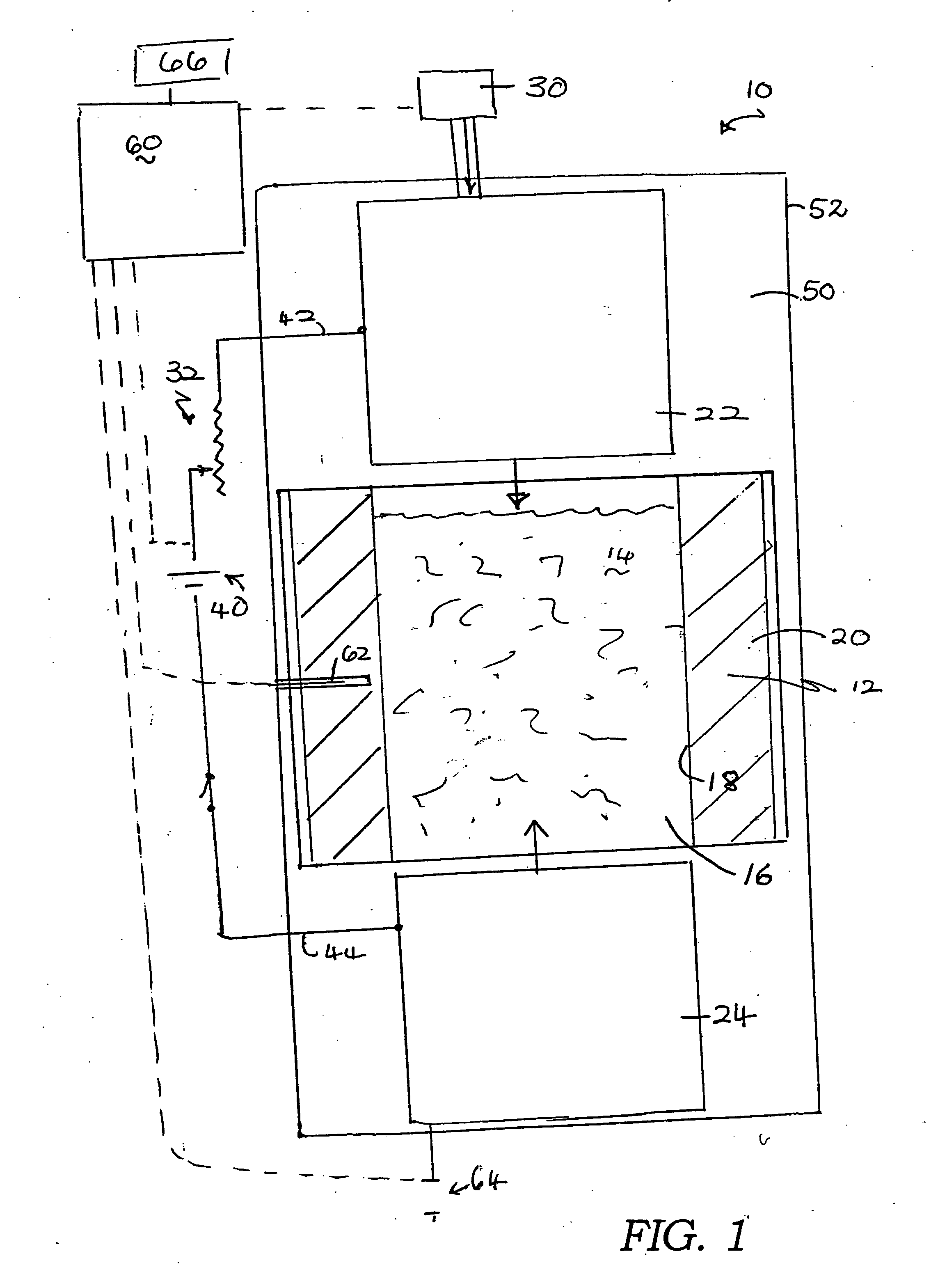
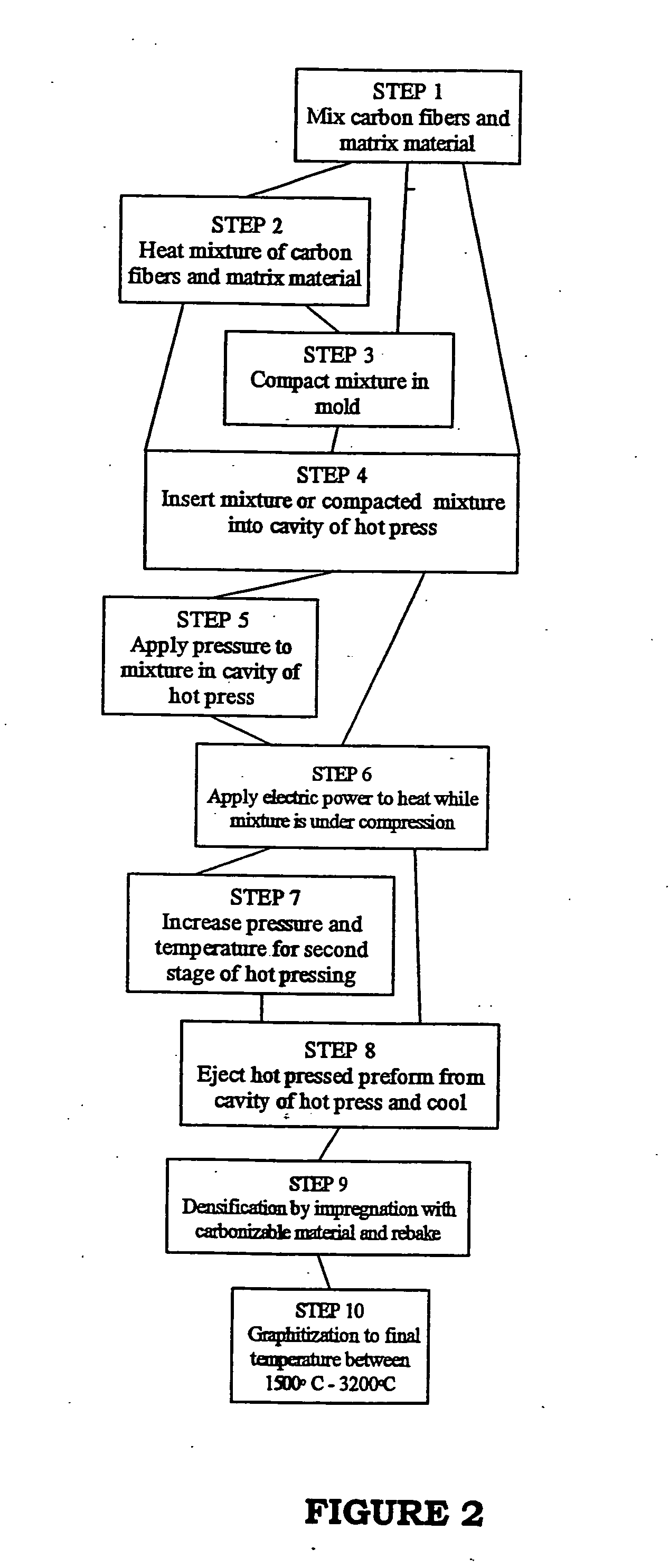
[0064] Mesophase pitch-based carbon fibers and a matrix material of milled pitch with 170° C. softening point and 70% coking yield were dry mixed at ambient temperature in a Sigma-type blender or similar type of mixer for about 5-15 minutes. The ratio of fibers to pitch matrix material was from 50-80 wt % fiber: 20-50 wt % pitch. The mixture was collected and charged into a mold box cavity (dimensions approximately 23×20 cm) of a hot press, as illustrated in FIG. 1. A pressure of up to about 140 kg / cm2 was applied to the mixture in the press. After pressing to compact the mixture, an electric current of about 1000-2000 amps (a power input of about 30-60 kW / kg) was passed through the mixture. The mix was held under the temperature and pressure conditions for about 5-10 minutes. The temperature of the mixture reached 800-900° C. This hot pressing process carbonizes and densifies the fiber / matrix mixture in a very short ...
example 2
Carbon / Carbon Composite Made by Hot Mixing of Precursor Materials
[0065] Various batches of mesophase pitch-based carbon fibers and a matrix material of milled pitch from Example 1 were hot mixed at a temperature of about 200° C. in a Sigma-type blender or similar type of mixer for about 30-45 minutes. The ratio of fibers to pitch matrix material was varied from about 50-80 wt % fiber:20-50 wt % pitch. During the hot mixing, the matrix material coated the fibers uniformly. The mixture was collected and charged into a mold box cavity of a hot press, and heated and pressed as described for Example 1. Alternatively, the mixture was compacted in a separate mold to a density of between about 0.5 and 1.0 g / cm3 prior to hot pressing.
[0066] A pressure of up to 140 kg / cm2 was applied to the mixture in the hot press. After pressing to compact the mixture, an electric current as high as 1500-2000 A (a power input of about 45-60 kW / kg) was passed through the mixture. The mix was held under the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com