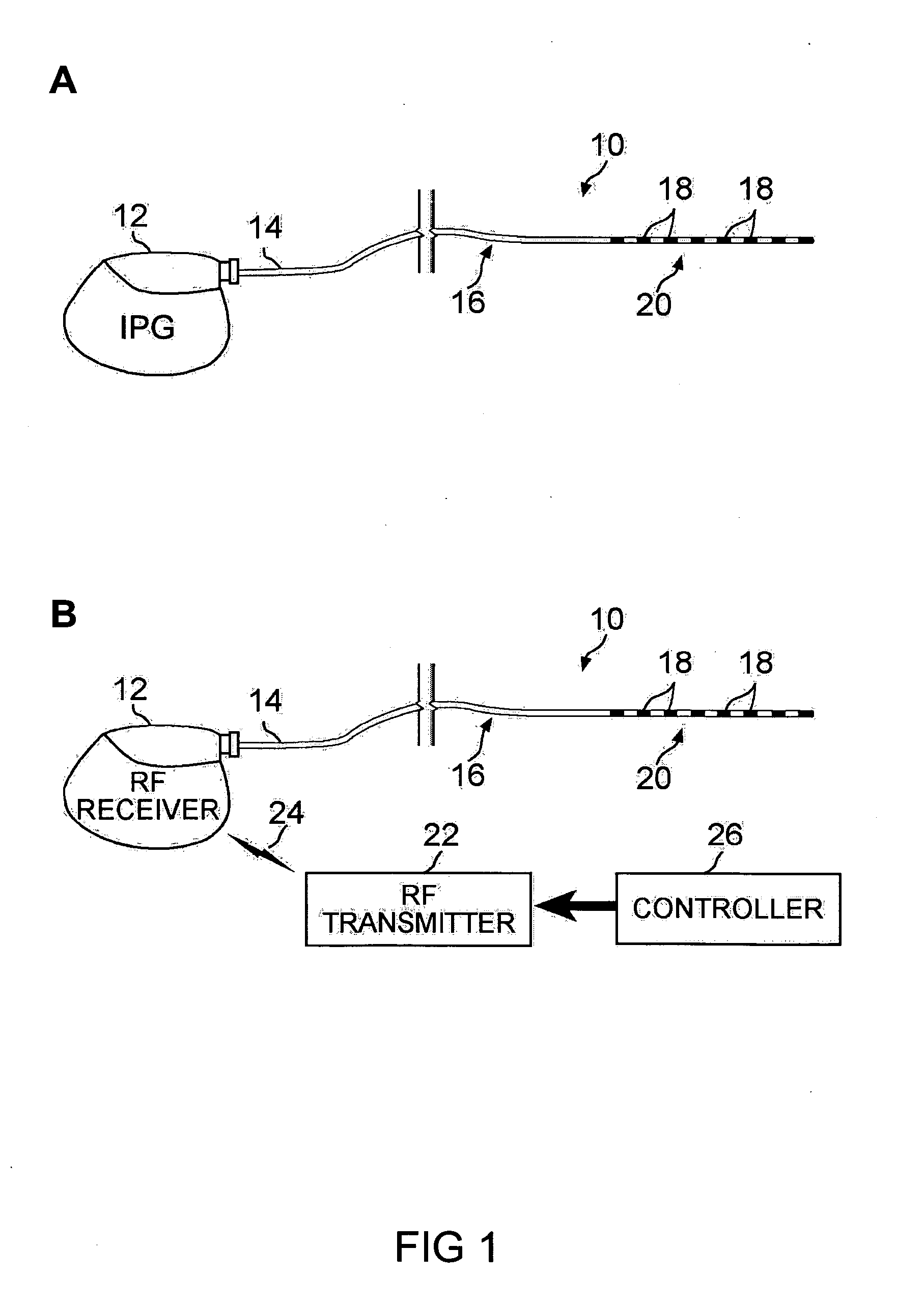
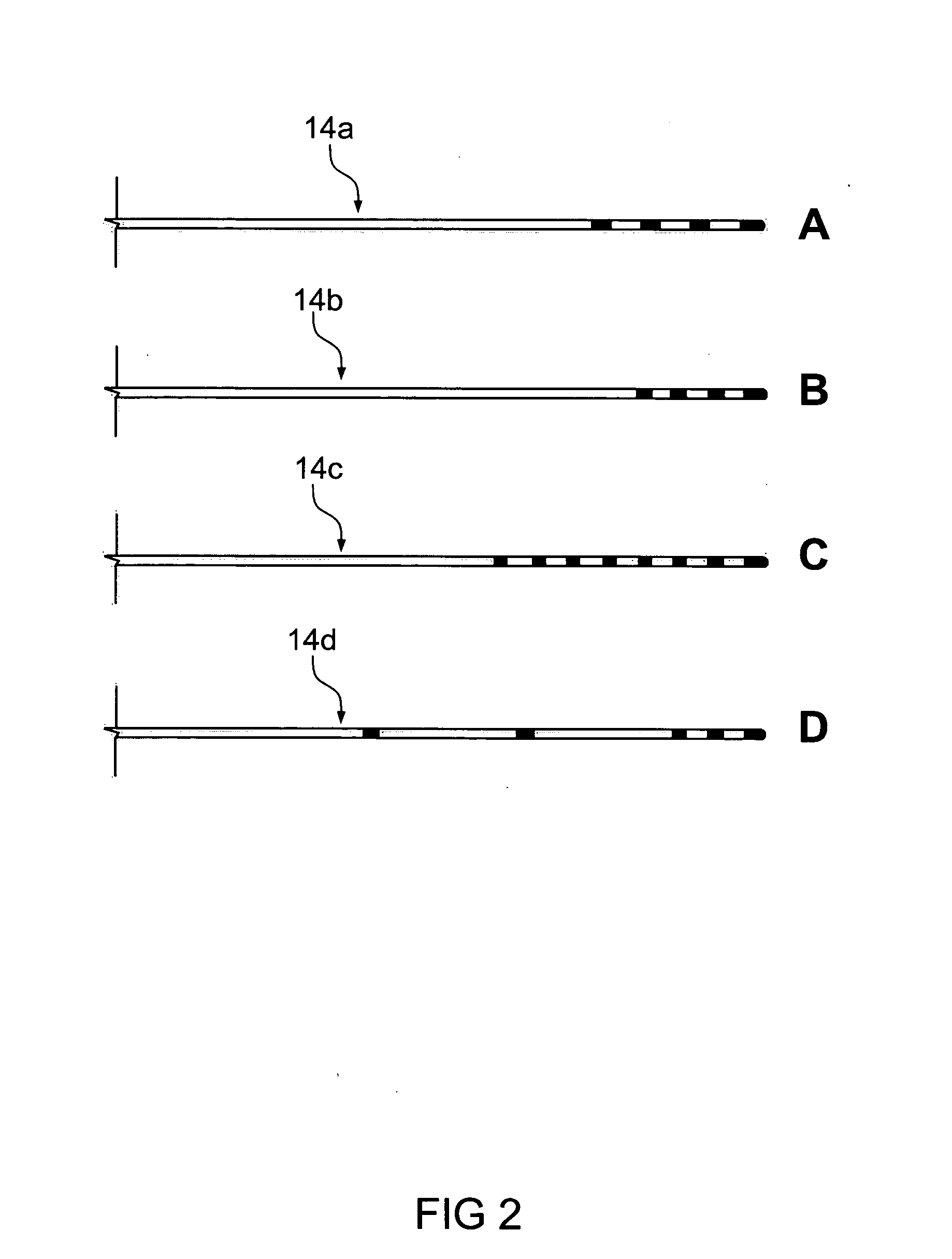
Method of treating depression, mood disorders and anxiety disorders using neuromodulation
a neuromodulation and depression technology, applied in the field of nerve tissue stimulation for treating depression, anxiety disorders and mood disorders, can solve the problems of chronically disabled, treatment-resistant depression has almost no alternative, major depression remains treatment refractory, etc., and achieves the effect of increasing the level of excitatory neurotransmitter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Patient Selection
[0096] Five patients were selected for electrical stimulation of the brain. Patients were selected based upon various demographics, family history of depression (FHx), age of onset, episodes of depression per year, the medications, other therapies, and the Hamilton rating score, as shown in Table 1. (Note “Dur yr” means duration in years).
[0097] As is known in the art, a score above 7 on the Hamilton 17 scale (“H17”) is an indication of depression. A 50% change in the H17 scale score of from the initial baseline score is considered a clinical response, while a score of less than 7 is considered clinical remission.
TABLE 1Patient DemographicAgeDurEpiPTSexAgeFHxonsetYrYrMedsECTCBTIPTH17dxAF48Y18202.51,2,4NNY29UPBF45Y212461,2,3,5YYY27UPCM37Y2017101,2YYY26UPDM48Y361251,2,5YYY24UPEM59N451531,2,3YNY20BPIIMean472818525
Meds: 1 = SSRI,
2 = bupropion,
3 = atypical antipsychotics,
4 = stimulates,
5 = other (benzo, and anticonvulsants).
example 2
Surgical Procedure
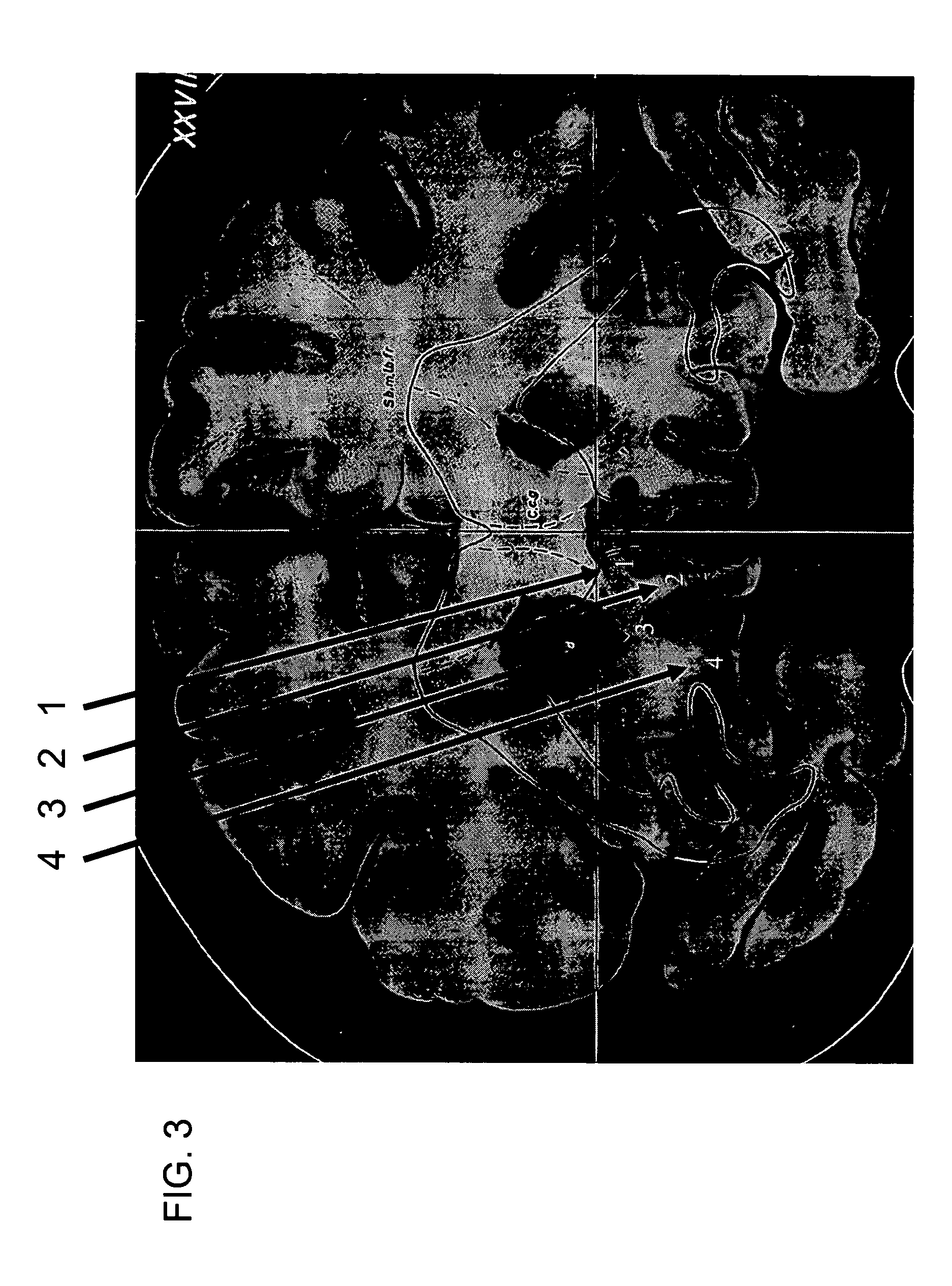
[0098] Under local anesthesia, a stereotactic frame was first placed on the patient's head, followed by acquisition of an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan to localize the target region. Patients were then taken to the operating room where, under local anesthesia, two burr holes were placed behind the hairline. Stereotactic coordinates were derived from the pre-op MRI. The coordinates of this target derived from the Schaltenbrand and Wahren Atlas plate 3 (FIG. 3) were 6-7 mm from the midline (range 2-14 mm), 29 mm anterior to the mid-commissural point range 20-40) and 5mm (range 0-10 mm) below the intra-commissural line.
[0099] Once the target sites were identified, two multi contact electrodes were delivered, one in each hemisphere. The electrodes were connected to a stimulating pulse generator.
[0100] With the patient's participation, each electrode contact was stimulated and acute changes in behavior was assessed using self report and mood rating scales, su...
example 3
Outpatient Programming and Clinical Follow-Up
[0102] Patients returned for generator device programming. There were several parameters that were tested, namely, which electrode contact was to be stimulated, the polarity of stimulation, the frequency and pulse width of stimulation, etc.
[0103] The electrode programming was done on an outpatient basis and involved a series of trials over the course of a week. Electrode contacts that produced acute behavioral changes or fMRI signal changes in the subgenual cingulate area (Brodmann area 25) were tried first. Once basic parameters were set, adjustments were made periodically until a stable program was established.
[0104] Once final stimulation parameters were established, psychiatric symptoms were monitored on a monthly basis. Clinical ratings were quantified using Beck, Hamilton, CGI, and Quality of Life Scales and Serial Neuropsychological Testing. Serial Neuropsychological Testing and PET studies were performed at 8 weeks and 6 months...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com