RAC-PK as a therapeutic agent or in diagnostics, screening method for agents and process for activating RAC-PK
a technology of rac-pk and therapeutic agents, applied in the field of rac-pk as a therapeutic agent or in diagnostics, screening methods for agents and processes for activating rac-pk, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory systems, disadvantageous use of such agents, and insulin not stimulating muscle cells and fat cells in the normal way
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
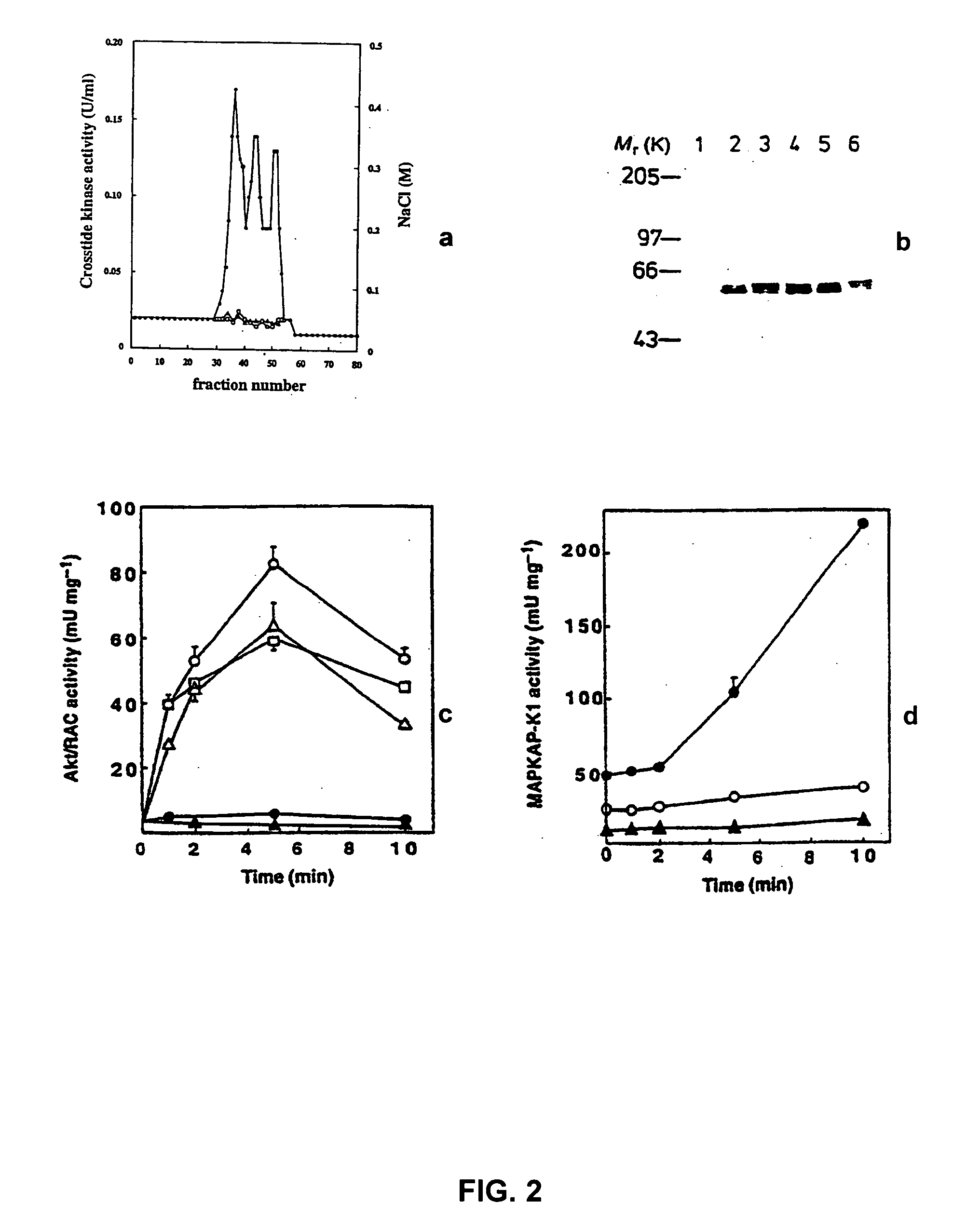
[0134] Specific Interaction of RAC-PK with IMPDH
[0135] a. Bacterial and Yeast Strains
[0136] All yeast strains and plasmids for two-hybrid experiments are obtained from Clontech (Palo Alto, Calif.) as components of the MATCHMAKER Two Hybrid System or from Dr. Nathans, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Baltimore, Md. Yeast strains SFY526, e.g., MATa, Ura3-52, His3-200, Ade2-101, Lys2-801, Trp1-901, Leu2-3, 112, canr, Gal4-542, Gal80-538 and Ura3::GAL1-lacZ; HF7c, e.g., MATa, Ura3-52, His3-200, Lys2-801, Ade2-101, Trp1-901, Leu2-3, 112, Gal4-542, Gal80-538, Lys2::Gal1-His3 and Ura3::(Gal4 17-mer)3-CYC1 -LacZ; and PCY2 [see Chevray and Nathans, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, Vol. 89, No. 13, pp. 5789-5793 (1992)], e.g., MATα, His3-200, Ade2-101, Lys2-801, Trp1-63, Leu2-3, Gal4-542, Gal80-538 and Ura3::Gal1-LacZ, are used to assay for protein-protein interactions. Yeast strain HF7c is used for library screening. SFY526 and PCY2 have the upstream activating sequence and TATA sequence of the GAL...
example 2
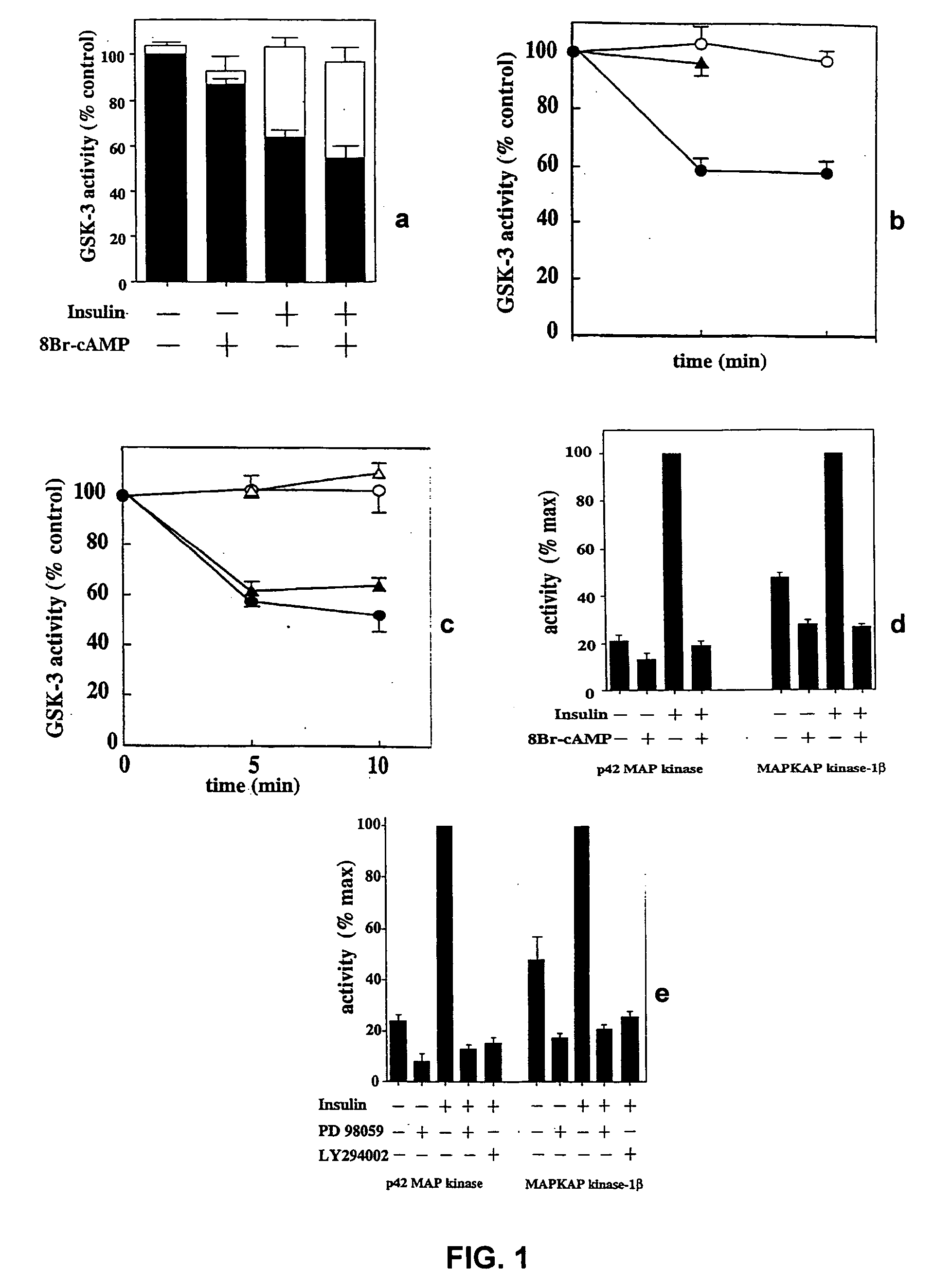
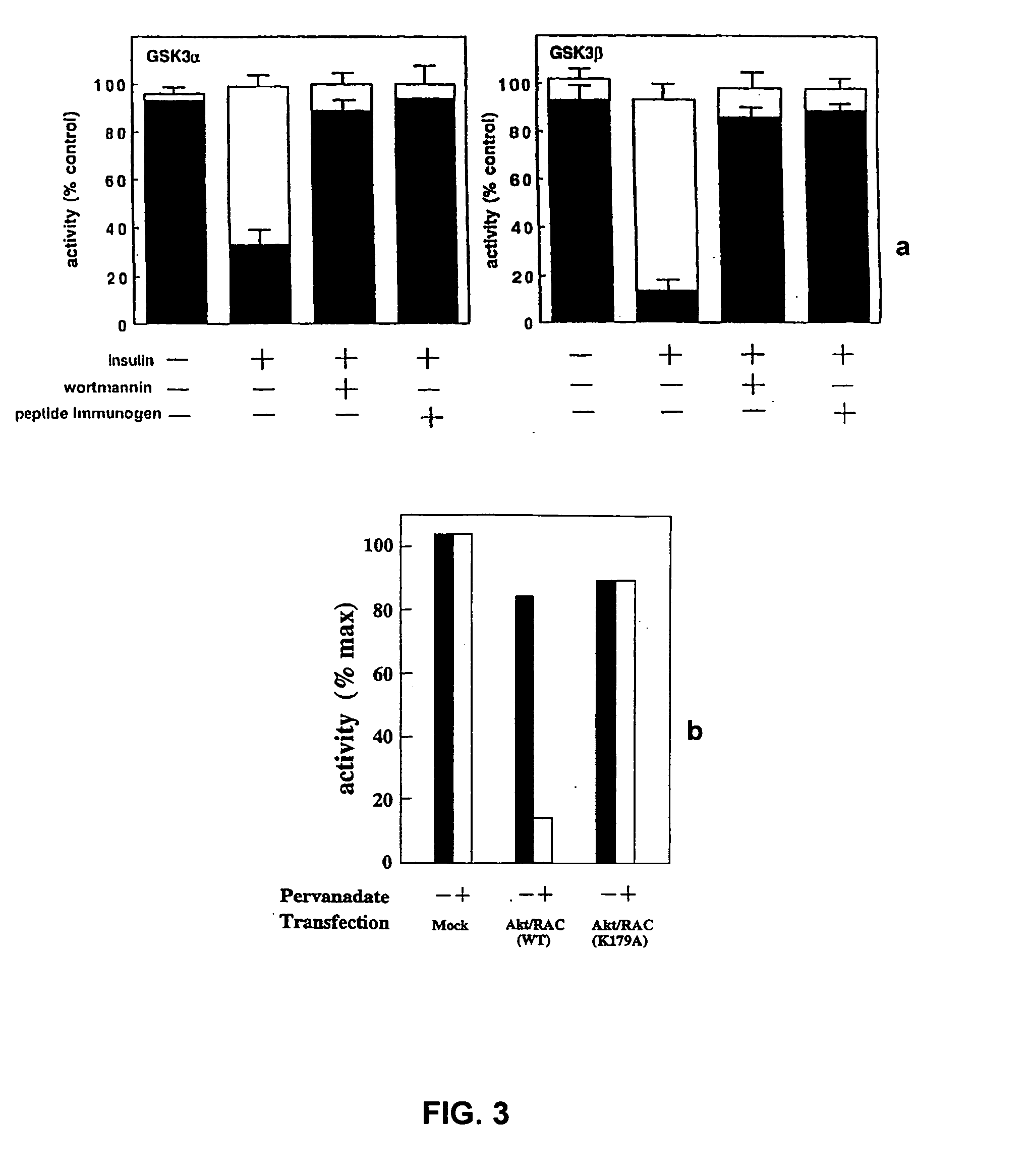
[0151] Inhibition of GSK3
[0152] Two major kinases known to be involved in regulating the insulin-dependent signalling pathways are MAPKAP kinase-1 and p70S6K. These kinases are respectively inhibited by PD98059 and rapamycin. Both of these agents fail to inhibit phosphorylation of GSK3, suggesting that the kinase responsible for GSK3 inactivation is not MAPKAP kinase-1 or p70S6K.
[0153] L6 myotubes are incubated with both compounds and the stimulated with insulin, as follows. Monolayers of L6 cells are grown in 6 cm petri dishes to the stage of myotubes, deprived of serum overnight and then incubated for 1 hour in 20 mM Hepes / NaOH, pH 7.4, 0.14 M NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 2.5 mM MgSO4, 1 mM CaCl2, 25 mM glucose (HBS buffer), in the presence or absence of 50 μM PD98059 or 100 μM LY294002. Two (2) mM 8-Br-cAMP or 0.1 μM rapamycin, when added, are included for the last 15 minutes. The cells are stimulated for 5 minutes with 0.1 μM insulin, or for time courses of up to 10 minutes. The medium is ...
example 3
[0161] To determine if RAC-PK's domain with its carboxyl-terminal extension could interact with other proteins we fused it to the Gal4 DNA binding domain and screened a HeLa cDNA library fused to the Gal4 transcriptional activation domain in the yeast reporter strain HF7c following the procedure of Example 1. Briefly, amino acids 147-480 of RACα are fused in frame to GST in the expression vector pGEX-2T (see Example 1). Appropriate BamHI-EcoRI fragment is then subcloned into the PstI-XbaI sites of yeast vector pPC62 (Dr. Nathans) using PstI-BamHI and EcoRI-XbaI linkers in order to create a Gal4 DNA binding domain-RAC-PK and C-terminal domain fusion. XhoI-XbaI fragments are then subcloned into pGBT9 (Clontech). The HeLa S3 MATCHMAKER cDNA library is used as before.
[0162] In our screen of 1.5×106 primary transformants, we identify 7 clones which show specific interaction with RAC-PK's domain plus the carboxyl-terminal extension, by activation of the reporters for His auxotrophy and La...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com