Adjustment of amplitude and DC offsets in a digital receiver
a digital receiver and amplitude technology, applied in the field of data communication, can solve the problems of signal spectrum, performance degradation, and inability to suppress dc which is 100 db above the level of the received signal, and achieves the effect of low gate count, fast adaption to changing dc levels, and low cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Notation Used Throughout
[0032] The following notation is used throughout this document.
TermDefinitionAFCAutomatic Frequency ControlAGCAutomatic Gain ControlAHDLAdaptive Hard Decision LogicAPSAdaptive PrescalerASICApplication Specific Integrated CircuitBERBit Error RateDCDirect CurrentDCOCDC Offset CompensationFPGAField Programmable Gate ArrayGFSKGaussian Frequency Shift KeyingHDLHardware Description LanguageIFIntermediate FrequencyPSPrescalerRFRadio FrequencyRSSIReceive Signal Strength Indicator
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
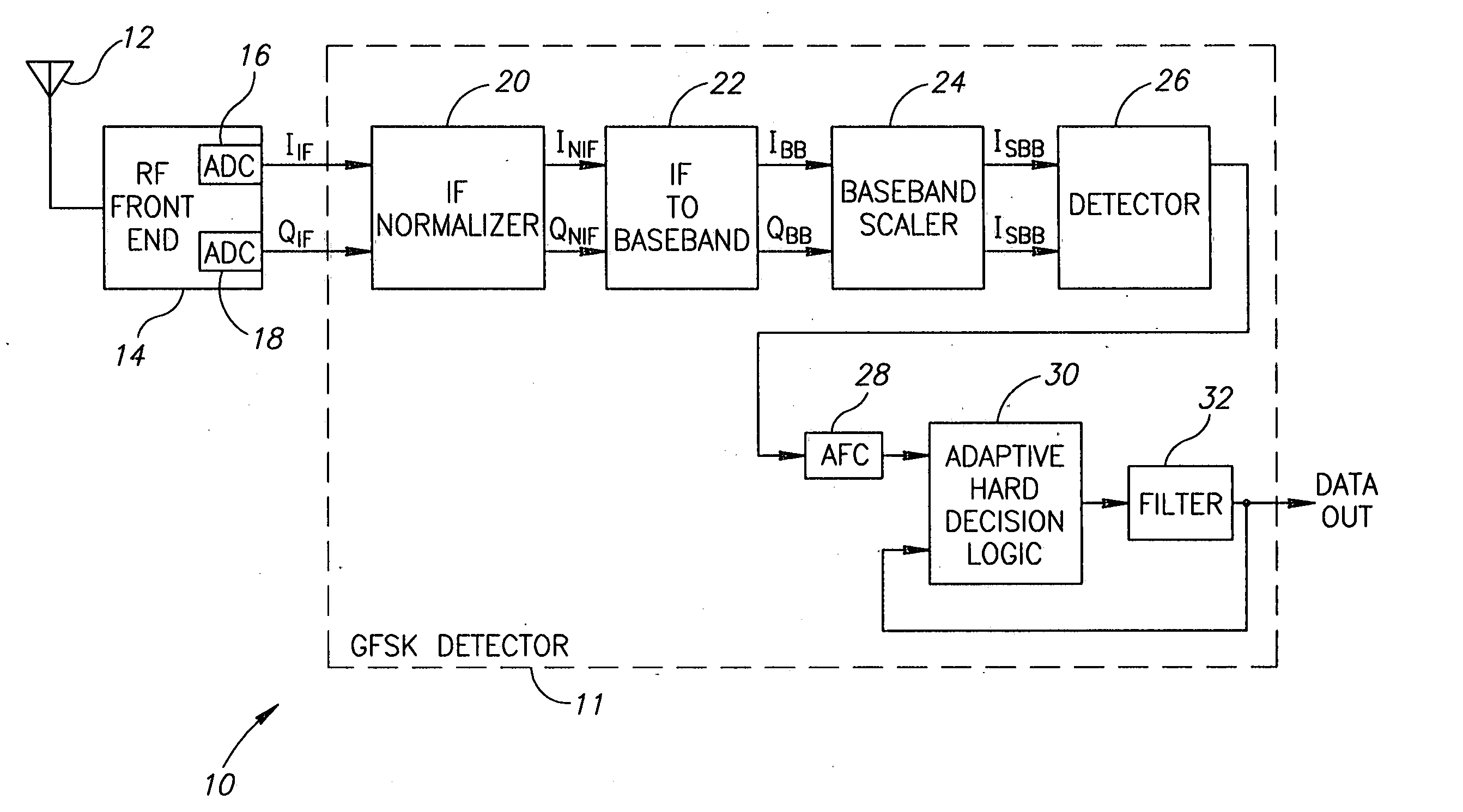
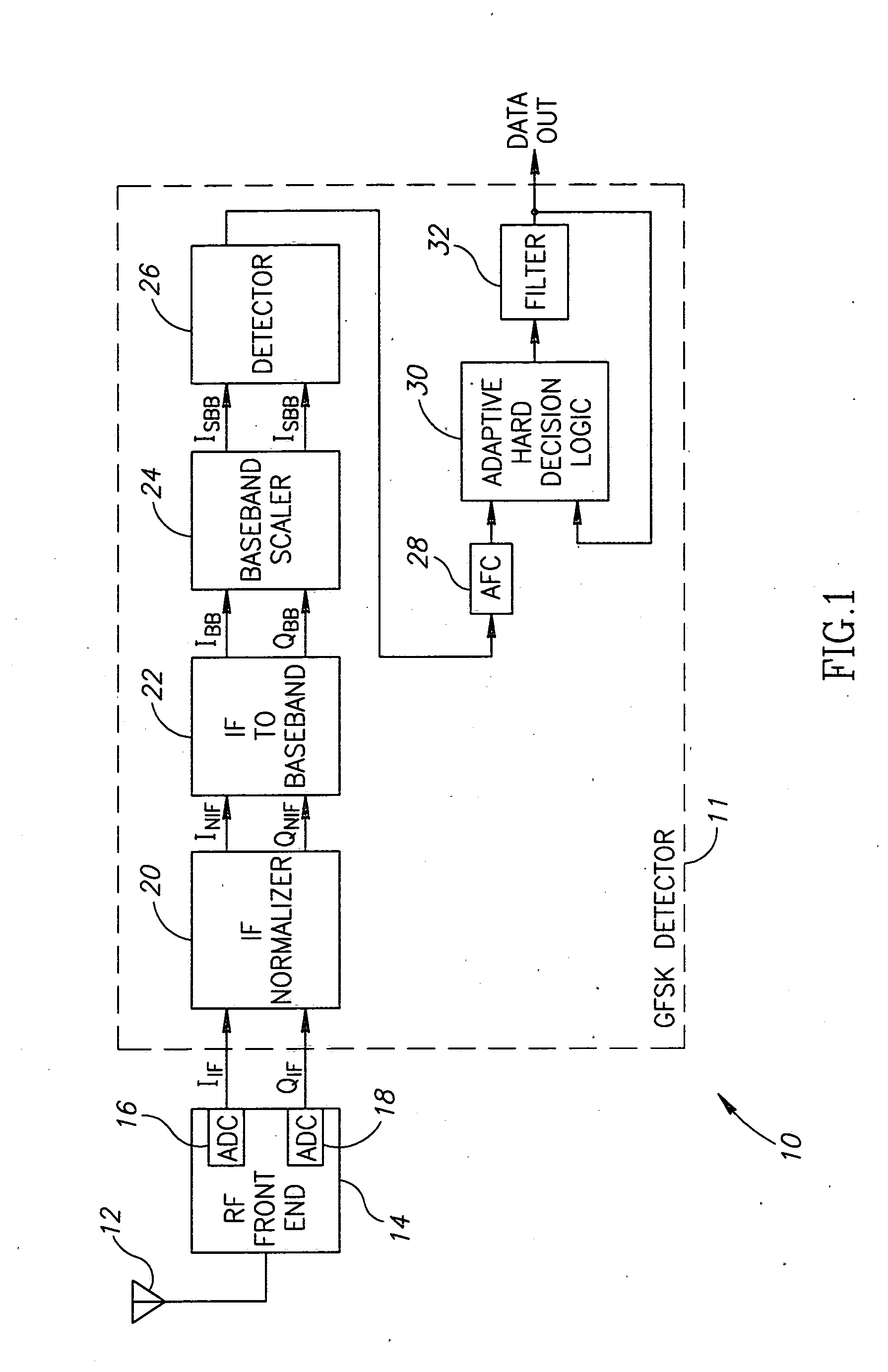
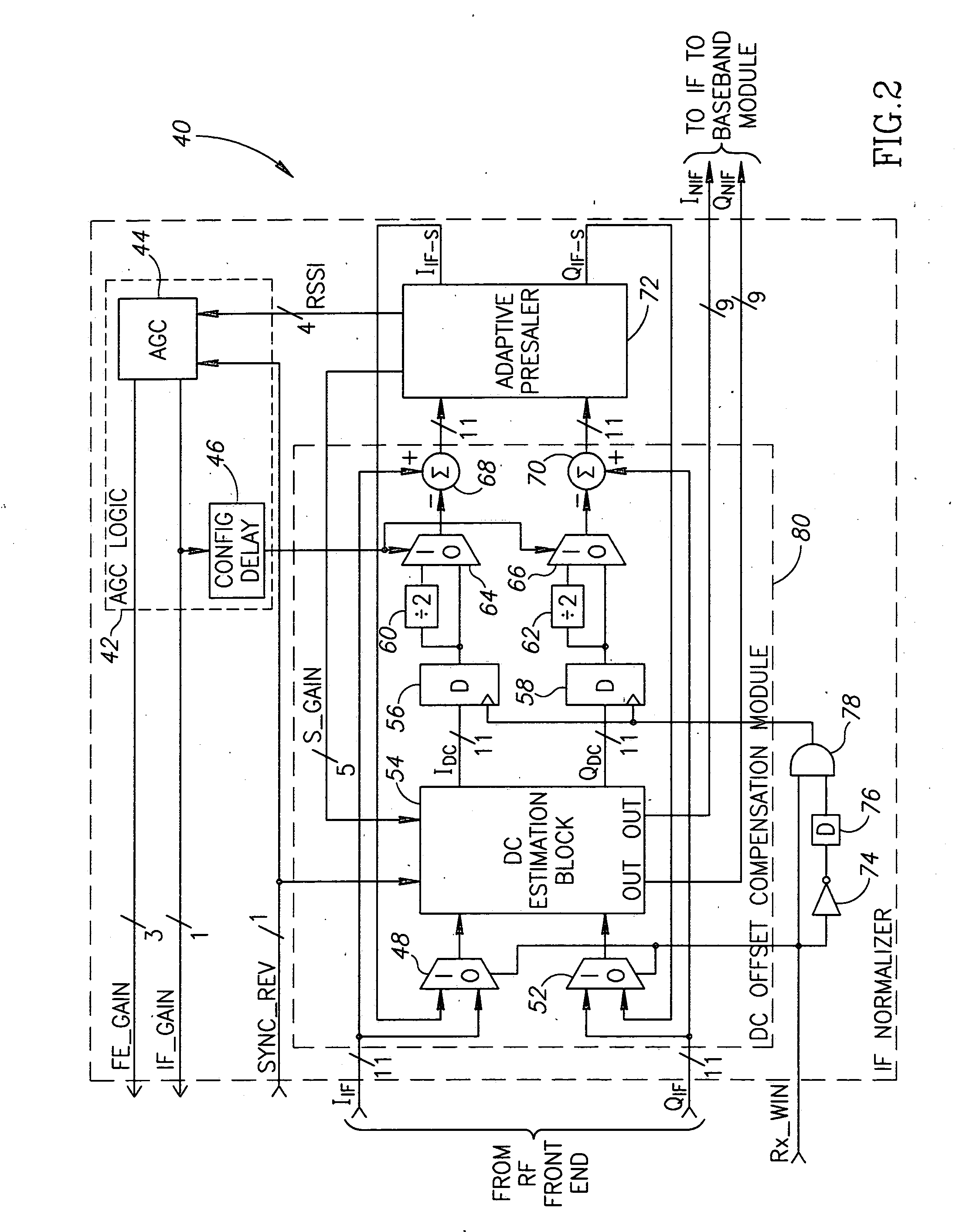
[0033] The present invention is a mechanism for amplitude adjustment and DC offset compensation. The mechanism functions to normalize the signal output from the RF front portion of a receiver before it is converted from IF to Zero-IF. The present invention is well suited for use in a digital receiver such as a Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying (GFSK) detector constructed according to the Bluetooth specification.
[0034] It is noted that the present invent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com