Left atrial access apparatus and methods
a technology of access apparatus and left atrial cavity, which is applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of serious injury or death of patients, complication of transeptal puncture, and inability to fully fully cover the aorta or the free wall of the atrium
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
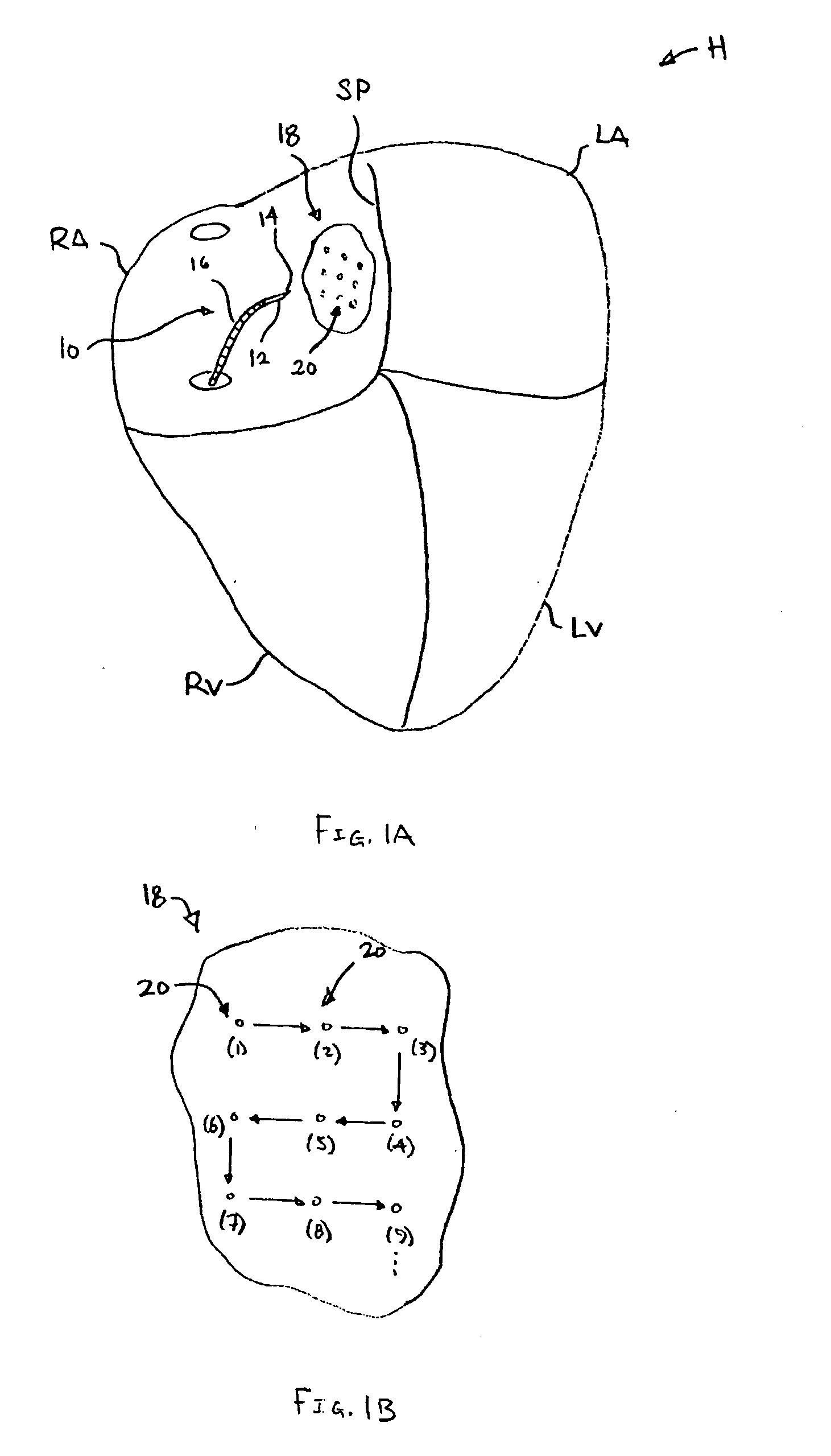
[0025] The left and right atria carry blood that varies in several physiological parameters. For example, the left atrium's blood oxygen saturation may reach 99% whereas the right atrium may only reach an oxygen saturation of 80% or lower. Another parameter includes pressure differences. The pressure in the left atrium is normally higher than the pressure in the right atrium, except in certain disease states. Also, the pressure wave forms have different amplitudes. Moreover, the wave forms also differ between the atria and other neighboring cardiac structures, such as the aorta (which has high velocity blood flow), and the intra-atrial septum or pericardium (which have no blood flow).
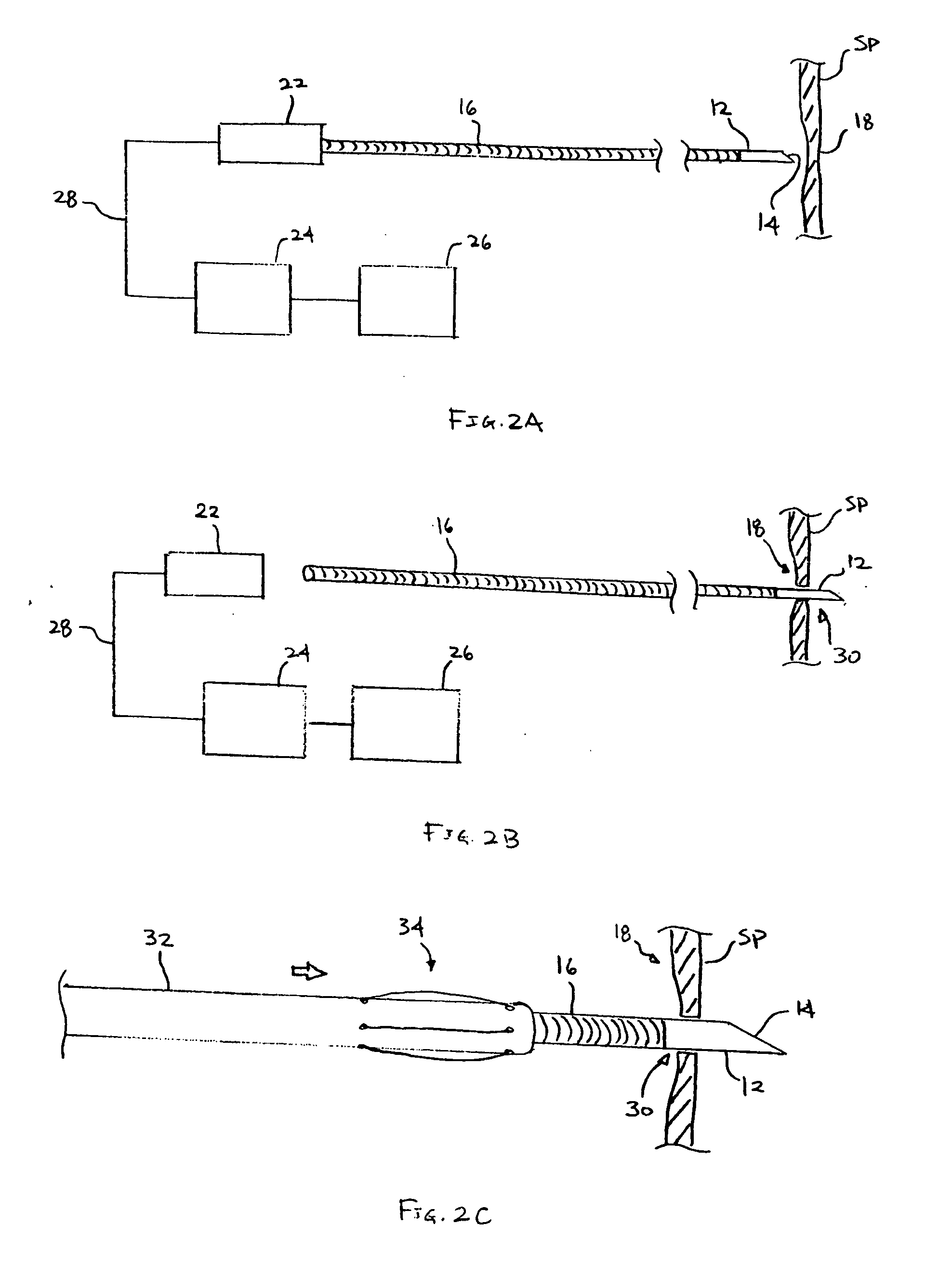
[0026] To gain access to the left atrium when performing a transeptal puncture, a clinician can perform a sounding procedure by utilizing any of the physiological parameter differences to detect a direct pathway. One method may be to utilize the oxygen saturation difference between the atrial chambers ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com