Method for analyzing a glycomolecule
a glycomolecule and structure technology, applied in the field of structure analysis of glycomolecules, can solve problems such as difficult analysis, and achieve the effect of facilitating access to glycomolecules and simplifying sample preparation and processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Comparative Glycomolecule Fingerprints of Desialized and Non-Desialized Glycoproteins
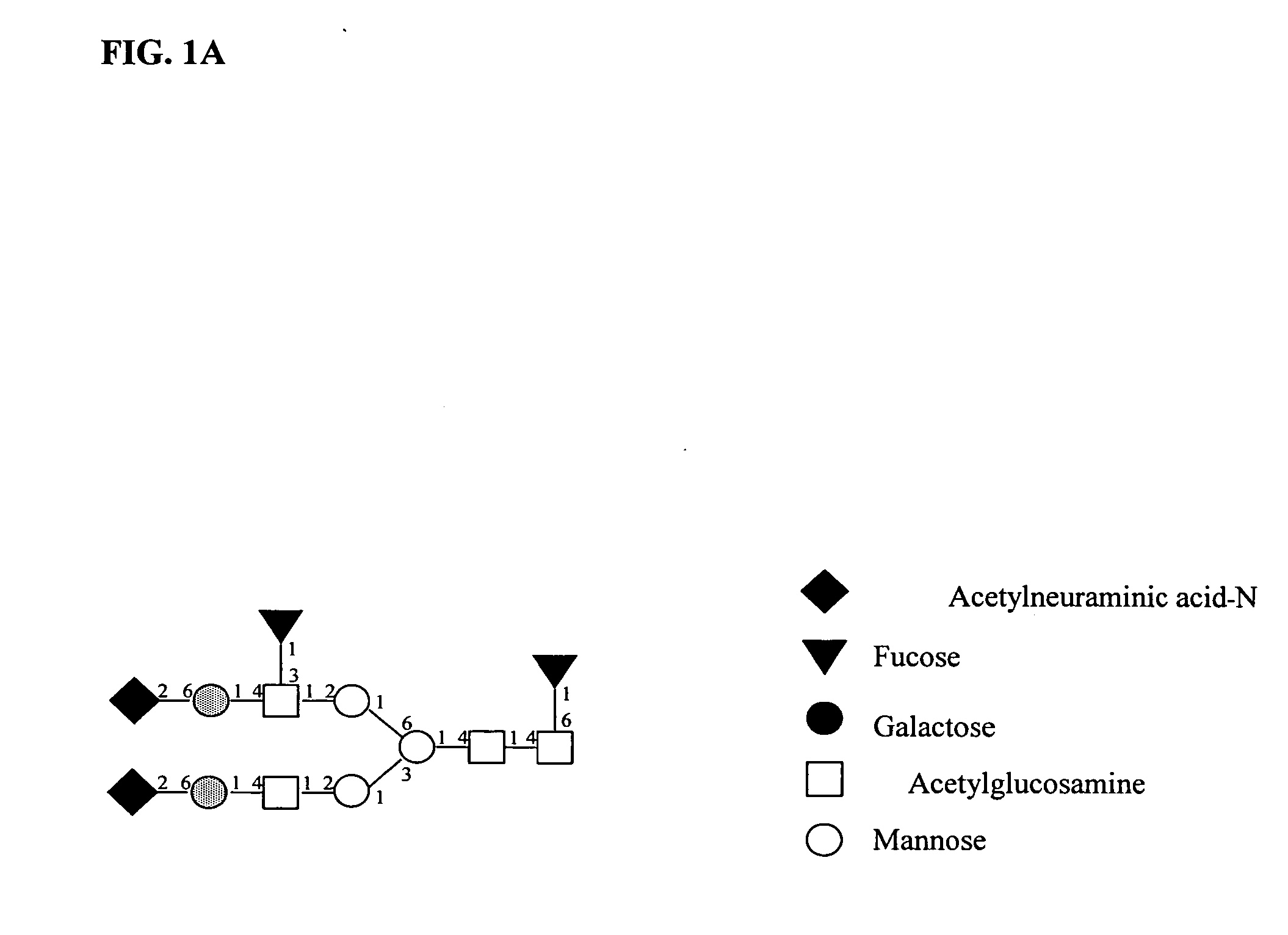
[0075] The glycomolecule fingerprint of human milk lactoferrin (hmLF) before and after disialyzation was examined. hmLF is a glycoprotein with a relatively simple glycosylation structure (Spik et al. Eur J Biochem. 1982;121(2):413-9). The hmLF structure includes two glycosylation sites that are occupied by any of 5 major glycans, resulting in 25 possible glycoforms. All of these glycans are of the complex bi-antennary type, containing a core fucose and differing in their levels of sialylation and the variable presence of antennary fucose (FIG. 1A). The various glycans differ in the presence of the (2,6) linked sialic acid residues and the (1,3) linked antennary fucose.
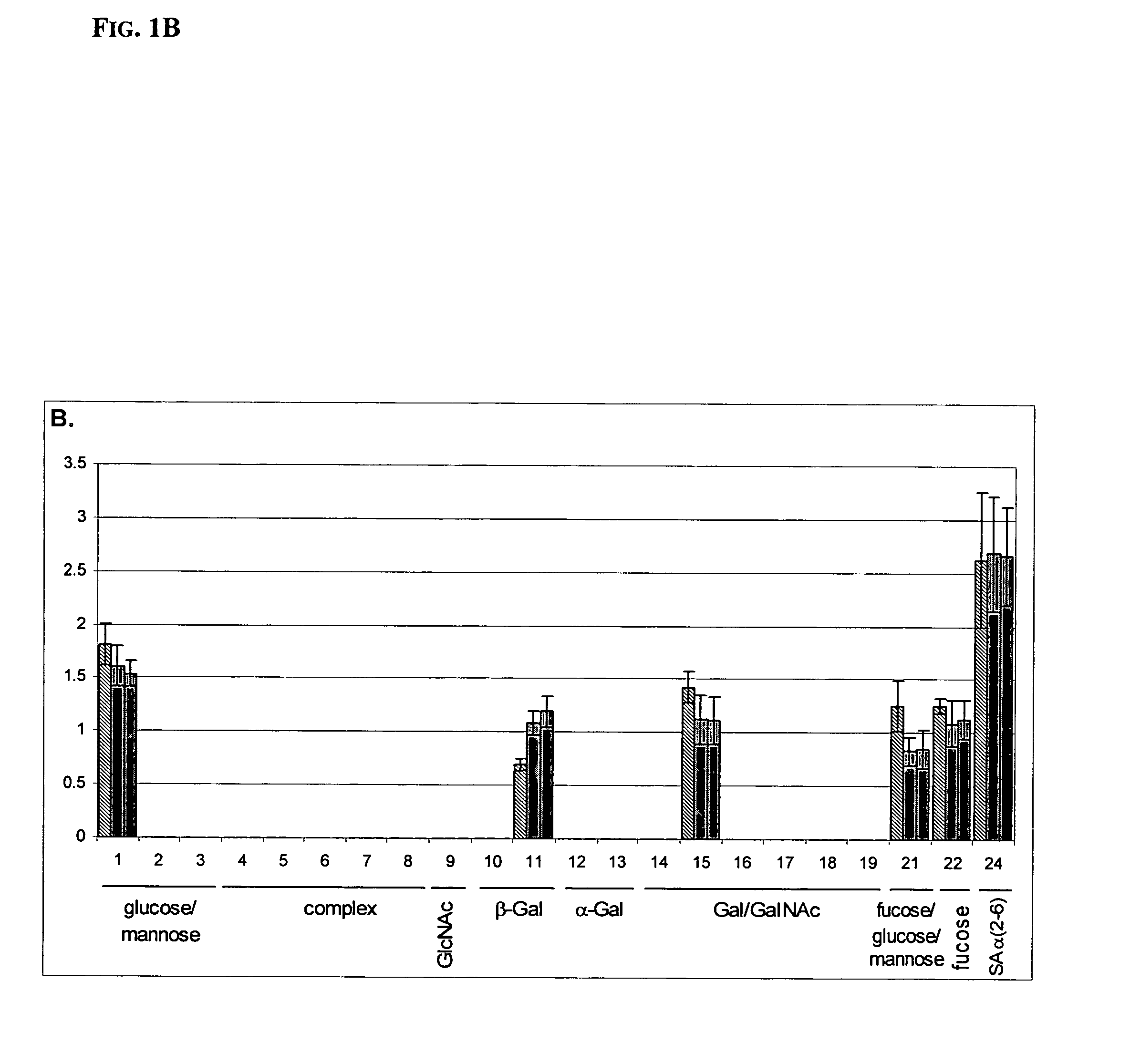
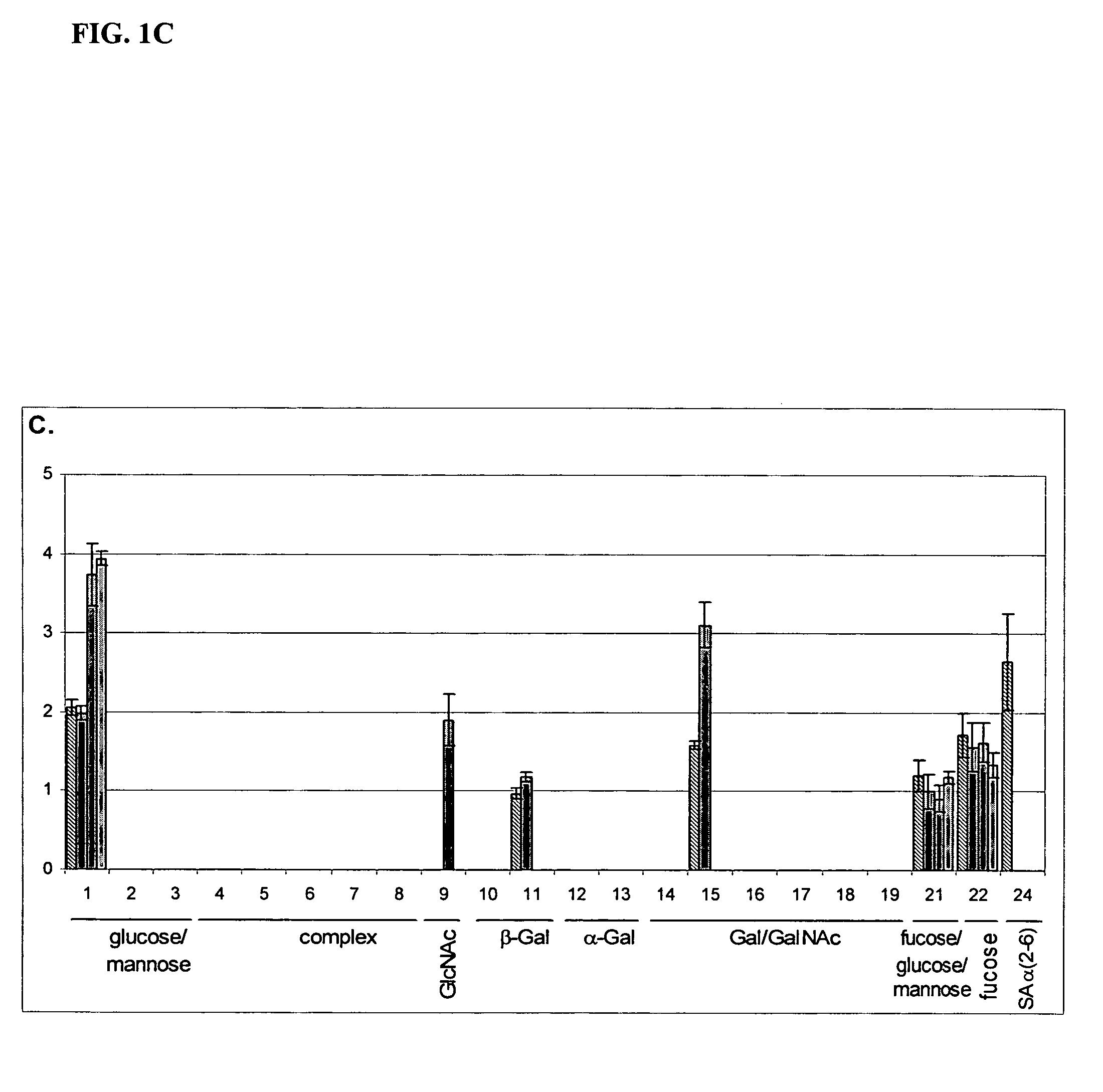
[0076] The fingerprints (FIG. 1B and FIG. 1C) were obtained by using a labeled anti-lactoferrin antibody as a probe. Twenty-four array-bound lectins were used and are grouped by their specificities on the abscissa. The group of compl...
example 2
Rule-Based Fingerprint Deconvolution
[0084] Deconvolution of the fingerprints is optimally performed by acquring a detailed understanding of lectin glycan recognition. This is complicated by the broadness of lectin specificities towards glycans, and by the fact that the affinities, both within and between the groups, differ markedly and are unknown. Measurement of these affinities are hampered by the inability to obtain a single-glycan-type glycoprotein for each glycan type. Mathematically, this translates into uncertainties in the conditional probabilities of observing a signal for a particular lectin, when the presence of a particular glycan is known. This limits the use of probabilistic-based algorithms.
[0085] An alternative approach using a rule-based expert system (Castillo et al., “Expert Systems and Probabilistic Network Models”—(Monographs in Computer Science) Springer-Verlag, New-York 1997) for fingerprint deconvolution was chosen. The rule base consists of lectin-glycan r...
example 3
Comparison of Glycomolecule Fingerprints Obtained Using Direct-Labeled Glycomolecules and Glycomolecule Fingerprints Obtained Using Labeled Lectins as Second Saccharide-Binding Agents
[0093] Fingerprint patterns obtained using direct labeling of the samples were compared to fingerprint patterns obtained using a labeled lectin to detect glycomolecules bound to a substrate.
[0094]FIGS. 2A-2C shows a fingerprints of a Bows melanoma cell-line derived tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). Fingerprints were obtained by direct labeling of the sample (FIG. 2A); labeling with a glucose / mannose recognizing lectin probe that recognizes both high-mannose and complex bi-antennary glycans (FIG. 2B); or with a glucose / mannose recognizing lectin probe that recognizes only high mannose type glycans (FIG. 2C). Since each of the fingerprints was obtained using a different probe, signals were corrected for the variation in fluorescence of the labeled probes (or sample, for the study shown in FIG. 2A), an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorescence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com