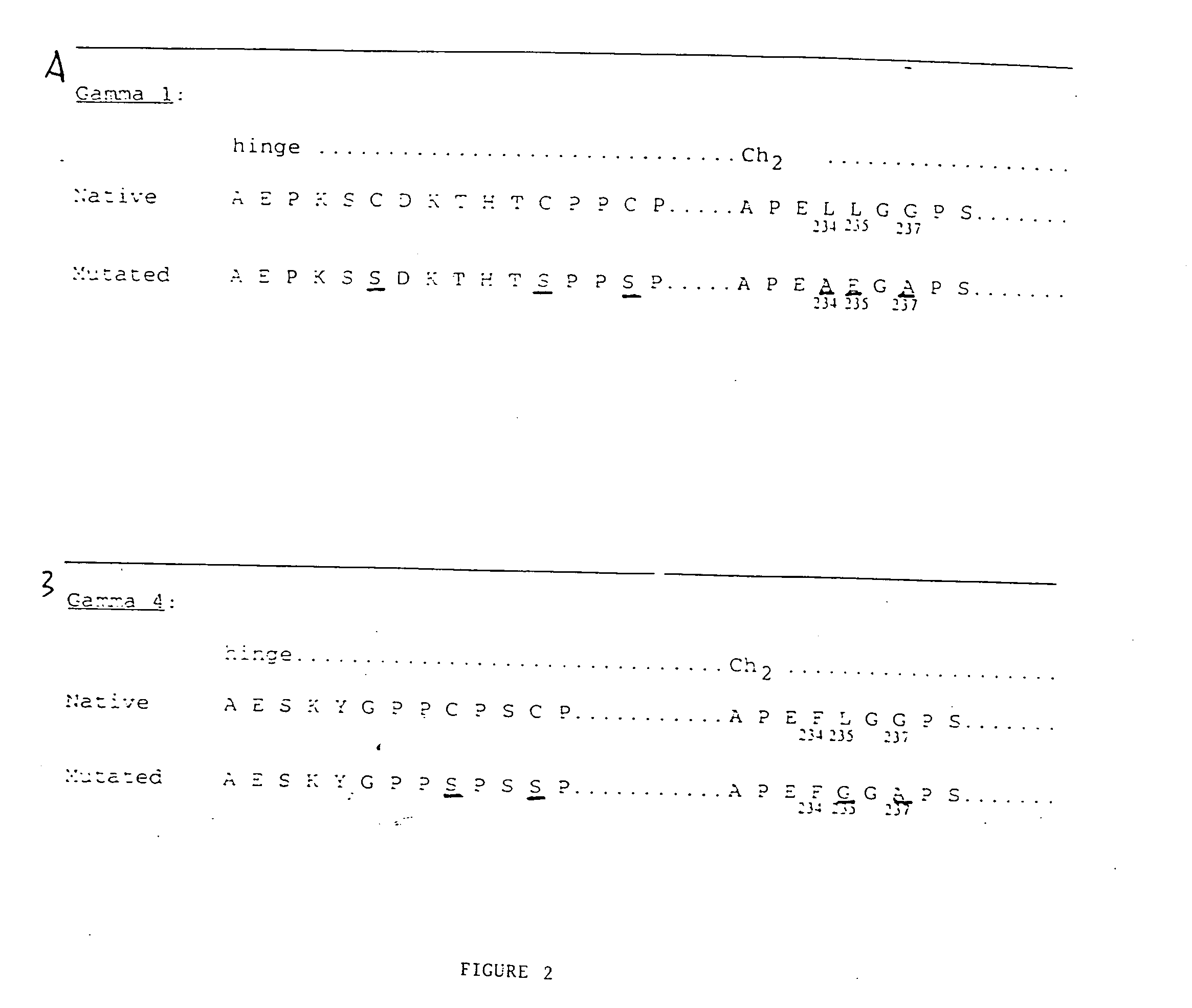CTLA4-Cy4 fusion proteins
a technology of fusion proteins and ctla4cy4, which is applied in the field of fusion proteins, can solve the problems of undesirable side effects and detrimental effects in the subject, and achieve the effects of suppressing cell-mediated immune responses, reducing complement activation ability, and provoking antigen-specific t cell toleran
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of CTLA4-Immunoglobulin Fusion Proteins with Reduced Effector Function
[0113] The extracellular portion of the T cell surface receptor CTLA4 was prepared as a fusion protein coupled to an immunoglobulin constant region. The immunoglobulin constant region was genetically modified to reduce or eliminate effector activity inherent in the immunoglobulin structure. Briefly, DNA encoding the extracellular portion of CTLA4 was joined to DNA encoding the hinge, CH2 and CH3 regions of human IgCγ1 or IgCγ4 modified by directed mutagenesis. This was accomplished as follows:
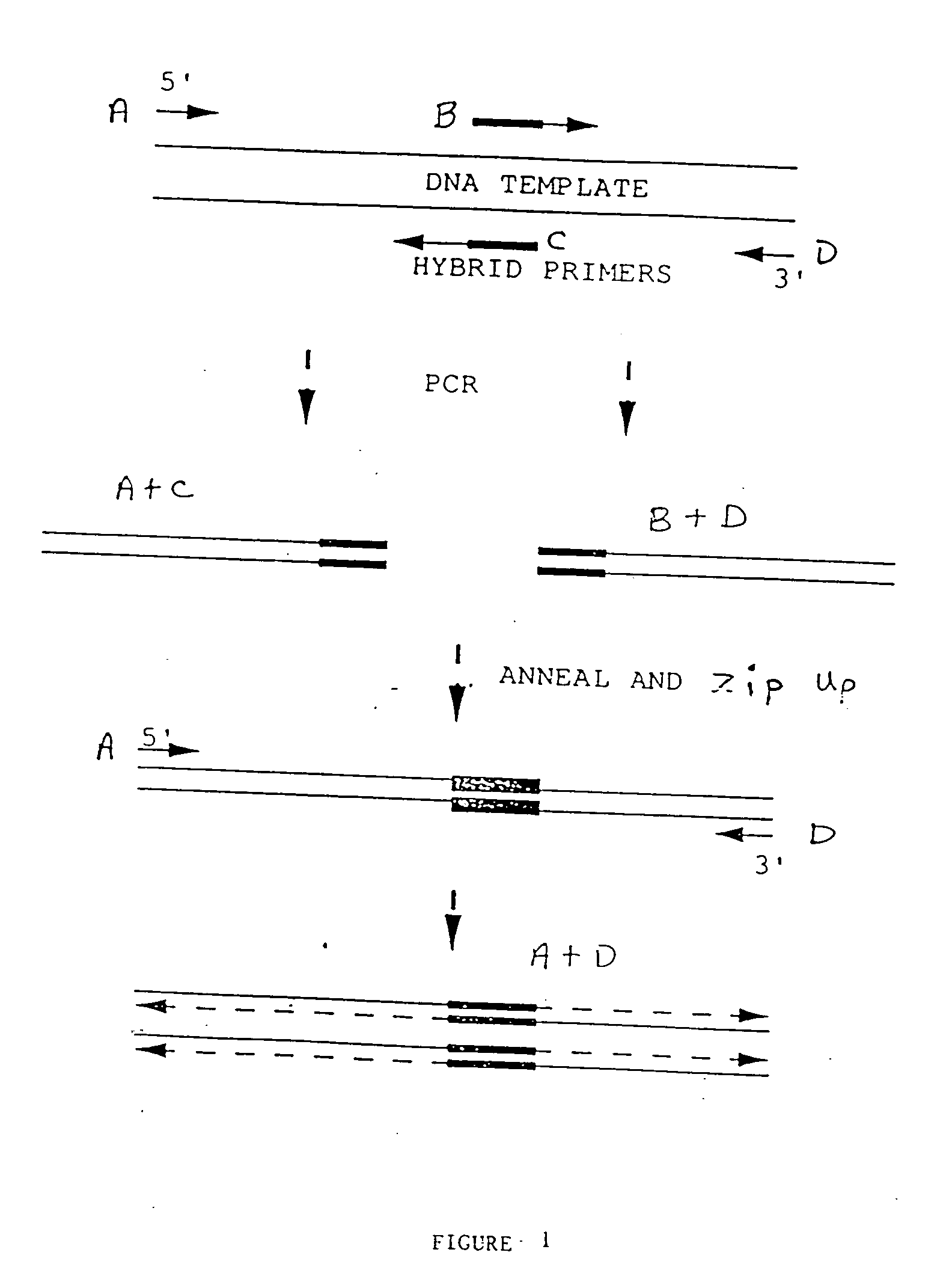
Preparation of Gene Fusions
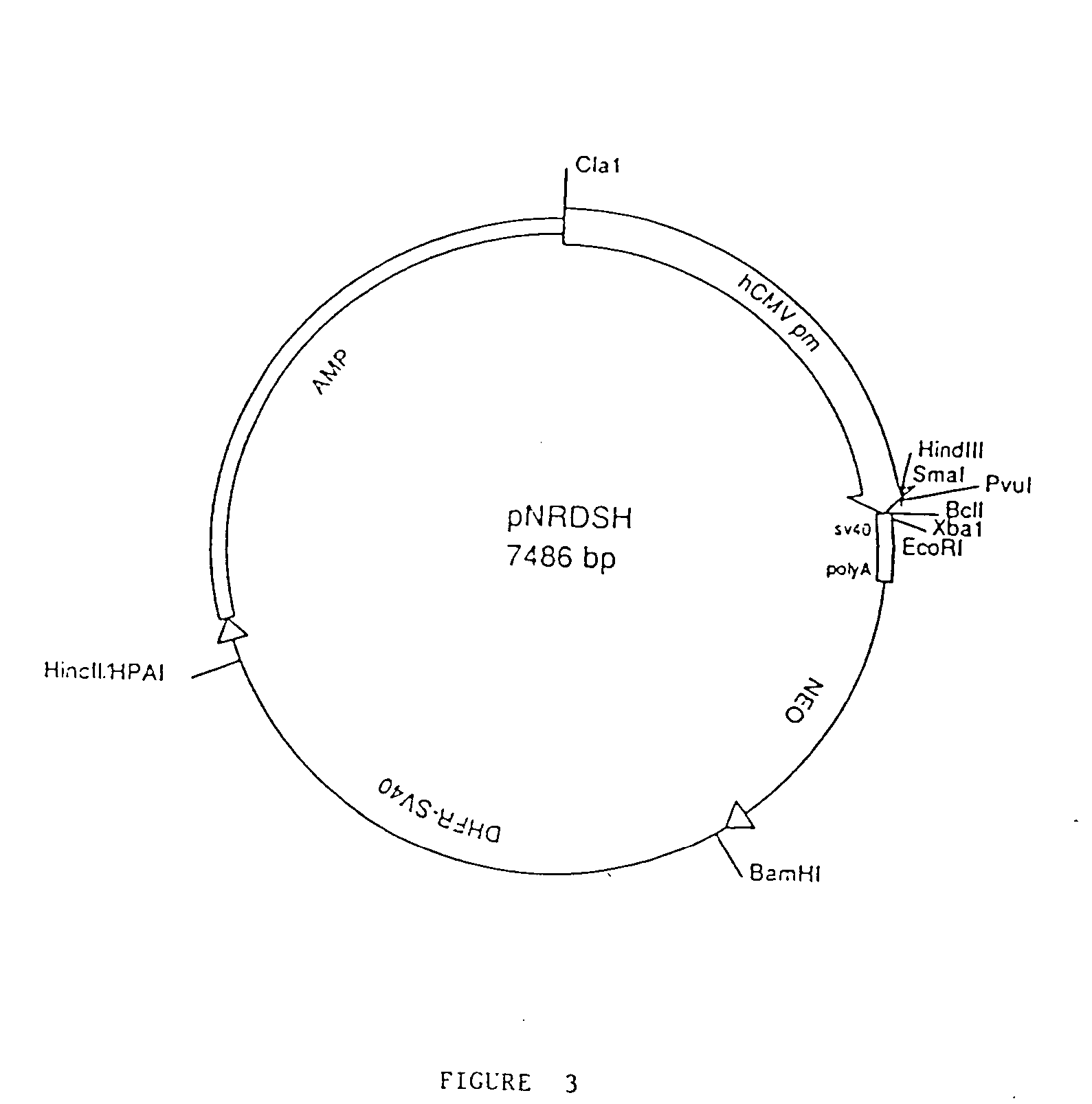
[0114] DNA fragments corresponding to the DNA sequences of interest were prepared by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using primer pairs described below. In general, PCR reactions were prepared in 100 μl final volume composed of Taq polymerase buffer (Gene Amp PCR Kit, Perkin-Elmer / Cetus, Norwalk, Conn.) containing primers (1 μM each). dNTPs (200 μM each), 1 ng of template DNA, and Ta...
example 2
Characterization of CTLA4 Fusion Proteins
[0143] The ability of the various CTLA4-Ig forms and CTLA4Ab to bind to their counter receptors B7-1 (Freeman, G. F., et al. (1988) J. Immunol. 143:2714-2722) and B7-2 (Freeman, G. F., et al., (1993) Science 262: 909-911) was demonstrated using the following assays.
A. Fluorescence Activated Cell Staining (FACS).
[0144] Purified preparations of the various recombinant CTLA4 forms were tested for their ability to bind to transfected COS cell transiently expressing hB7-1 or hB7-2 or transfected CHO cells stably expressing hB7-1 or hB7-2. The recombinant CTLA4 protein (10 μg / ml) was incubated with B7 expressing cells (2×106 cells) for 1 hr on ice in FACS wash solution (1% bovine serum albumin in PBS). The cells were washed 3 times with FACS wash solution. The cell bound CTLA4 was detected by reaction with anti-human Ig-FITC (Dako Corporation, Carpintera, Calif.) or protein A-FITC (Dako) for 30 mintues on ice in the dark. The cells were washed ...
example 3
Preparation of E. coli-Expressed Human CTLA4
A. Intracellular Expression of CTLA4 in E. coli
1. Cloning and Expression of CTLA4 Extracellular Domain
[0160] The extracellular domain of CTLA4 was expressed in E. coli after cloning into expression vector pETCm11a. This vector was derived from expression vector pET-11a (Novagen Inc., Madison Wis.) by cloning a chloramphenicol resistance gene cassette into the ScaI restriction site within the ampicillin resistance gene. The extracellular domain of CTLA4 was prepared from plasmid phCTLA4 by PCR amplification using oligonucleotide 5′GCAGAGAGACAT ATGGCAATGCACGTGGCCCAGCCTGCTGTGG-3′ (SEQ ID NO: 20) as forward primer and oligonucleotide 5′-GCAGAGAGAGGATCCTCAGTCAGTTAGT CAGAATCTGGGCACGGTTCTGG-3′ (SEQID NO: 21) as reverse primer. The forward PCR primer (SEQ ID NO: 20) contains an NdeI restriction site in which the ATG sequence in the NdeI restriction site is followed immediately by the codon for the first amino acid of mature CTLA4 (Dariavach, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com