Flow rate control valve
a flow rate control and valve body technology, applied in fluid pressure control, lighting and heating apparatus, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as complex construction, and achieve the effect of simple construction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
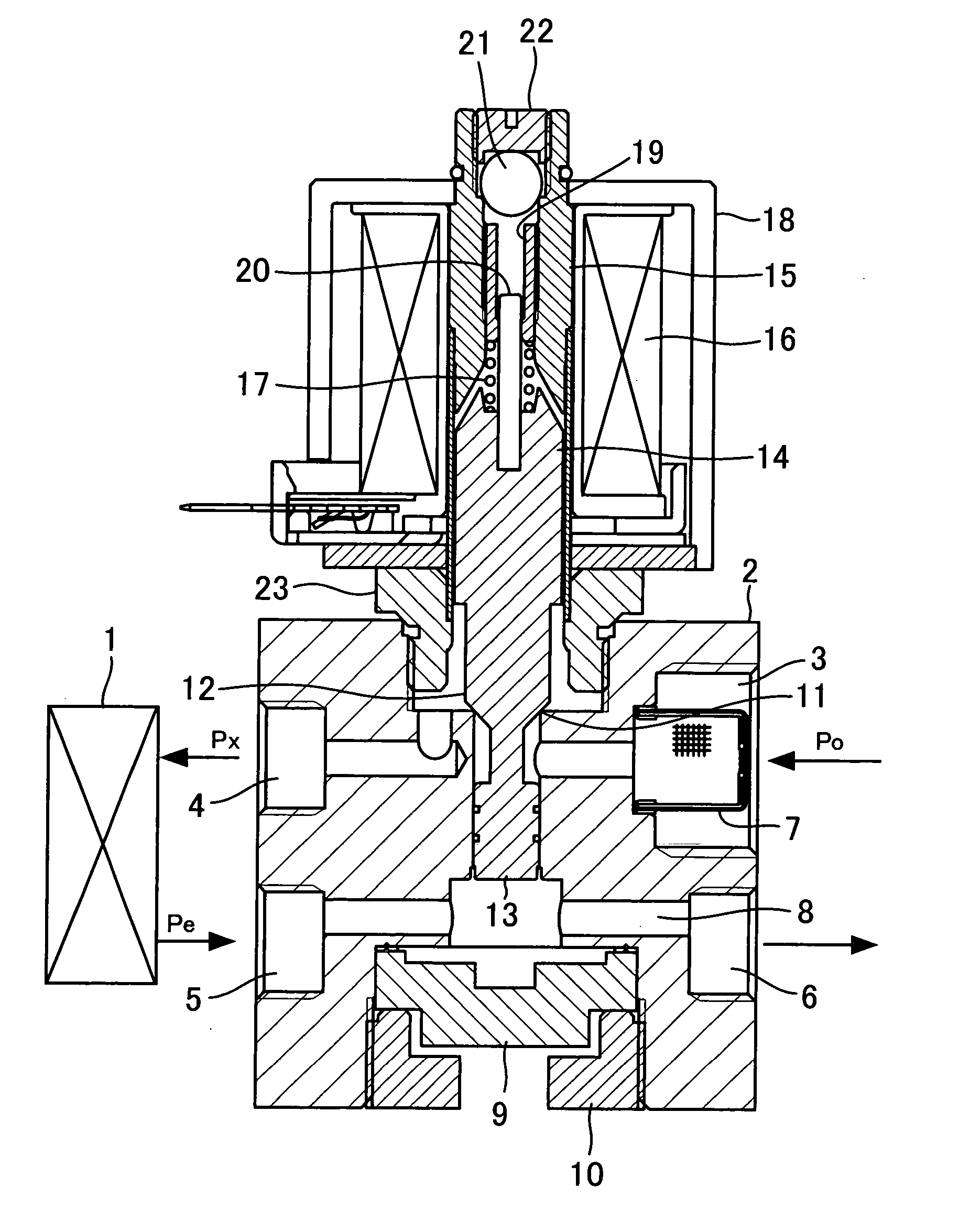
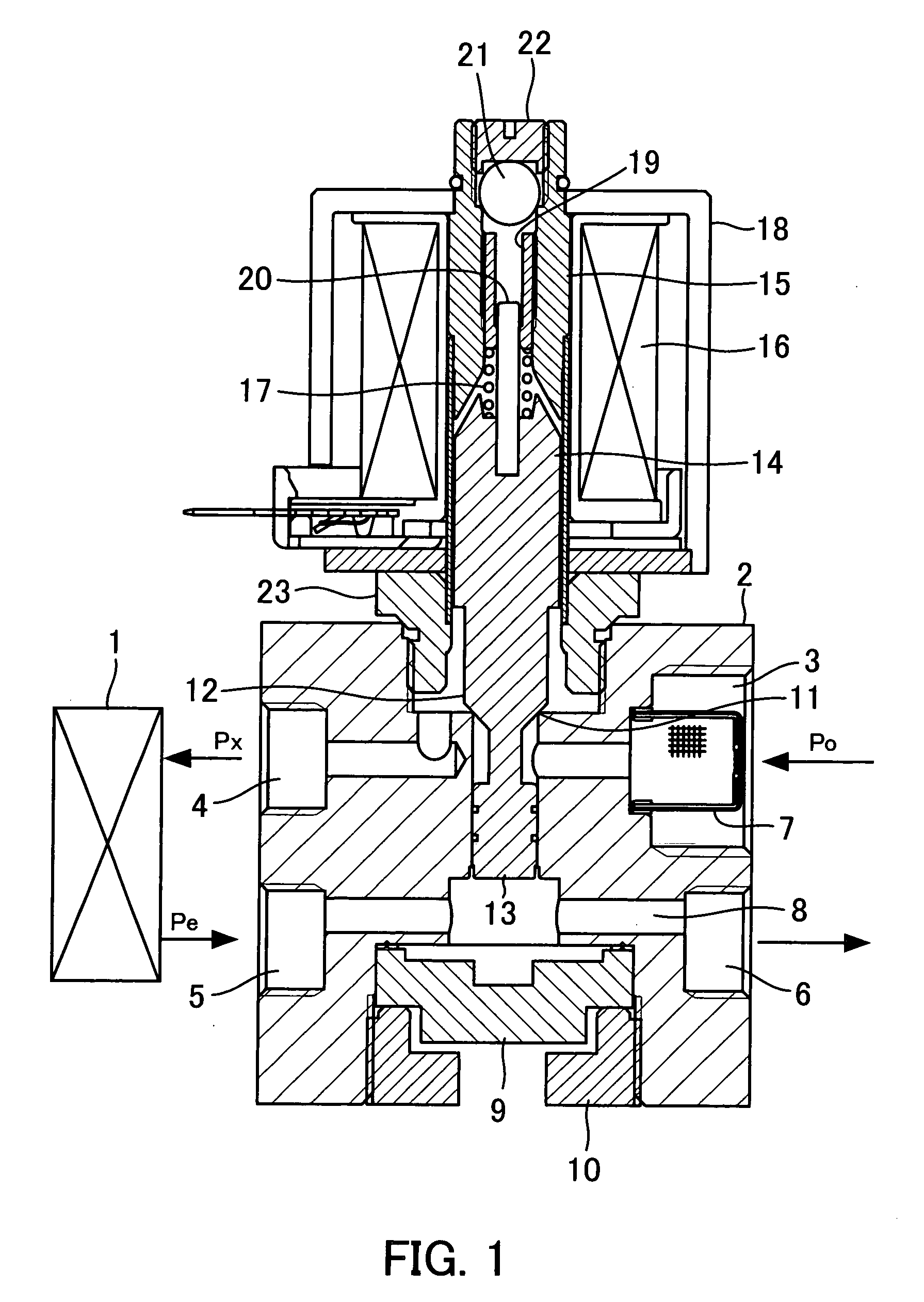
[0017]FIG. 1 is a central longitudinal cross-sectional view of the construction of a flow rate control valve according to the present invention.
[0018] The flow rate control valve is capable of performing constant flow rate control only after it is connected to an evaporator 1, and has a body block 2 provided with a high-pressure refrigerant inlet 3 to which refrigerant at pressure Po is supplied, a low-pressure refrigerant outlet 4 from which refrigerant is delivered to the evaporator 1 while being expanded, a return refrigerant inlet 5 to which refrigerant is returned from the evaporator 1, and a return refrigerant outlet 6 from which the returned refrigerant is delivered to a compressor. The high-pressure refrigerant inlet 3 has a strainer 7 disposed therein in a manner closing a passage formed therein.
[0019] The body block 2 has an upper portion thereof formed with a large-diameter hole, a central portion thereof formed with a cylinder concentric with the large-diameter hole and...
third embodiment
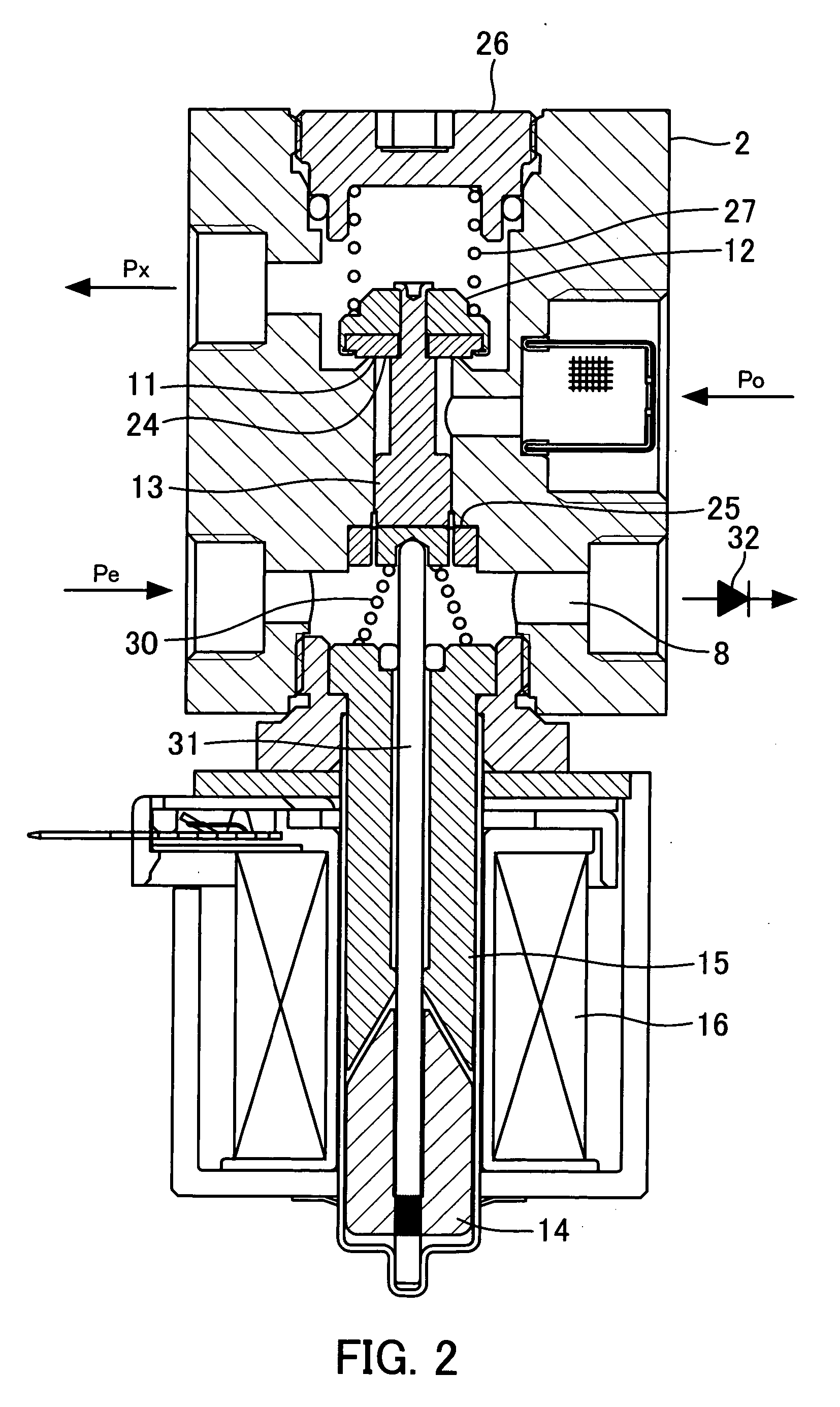
[0034]FIG. 4 is a central longitudinal cross-sectional view of the construction of a flow rate control valve according to the present invention. It should be noted that component elements in FIG. 4 identical or similar to those shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 are designated by identical reference numerals, and detailed description thereof is omitted.
[0035] The flow rate control valve according to the third embodiment is formed by providing the flow rate control valve shown in FIG. 1 with the internal leakage-preventing mechanism of the flow rate control valve shown in FIG. 2 and a backflow preventing mechanism for isolating the evaporator 1 from the refrigeration cycle during stoppage of the automotive air conditioner.
[0036] More specifically, the flow rate control valve according to the present embodiment is configured such that the valve element 12 is intimately seated on a valve seat-forming member 33 press-fitted in a passage between the high-pressure refrigerant inlet 3 and the low-pre...
fourth embodiment
[0039]FIG. 5 is a central longitudinal cross-sectional view of the construction of a flow rate control valve according to the present invention. It should be noted that component elements in FIG. 5 identical or similar to those shown in FIG. 4 are designated by identical reference numerals, and detailed description thereof is omitted.
[0040] In the flow rate control valve according to the fourth embodiment, the check valve 32 disposed in the return passage 8 is moved from the location toward the return refrigerant outlet 6 shown in FIG. 4 to a location toward the return refrigerant inlet 5.
[0041] Therefore, the flow rate control valve is responsive to the differential pressure obtained by adding the differential pressure across the evaporator 1 and the differential pressure across the check valve 32, received by the valve element 12 and the diaphragm 25, to control the differential pressure to be substantially constant, to thereby cause refrigerant to flow into the evaporator 1 at a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com