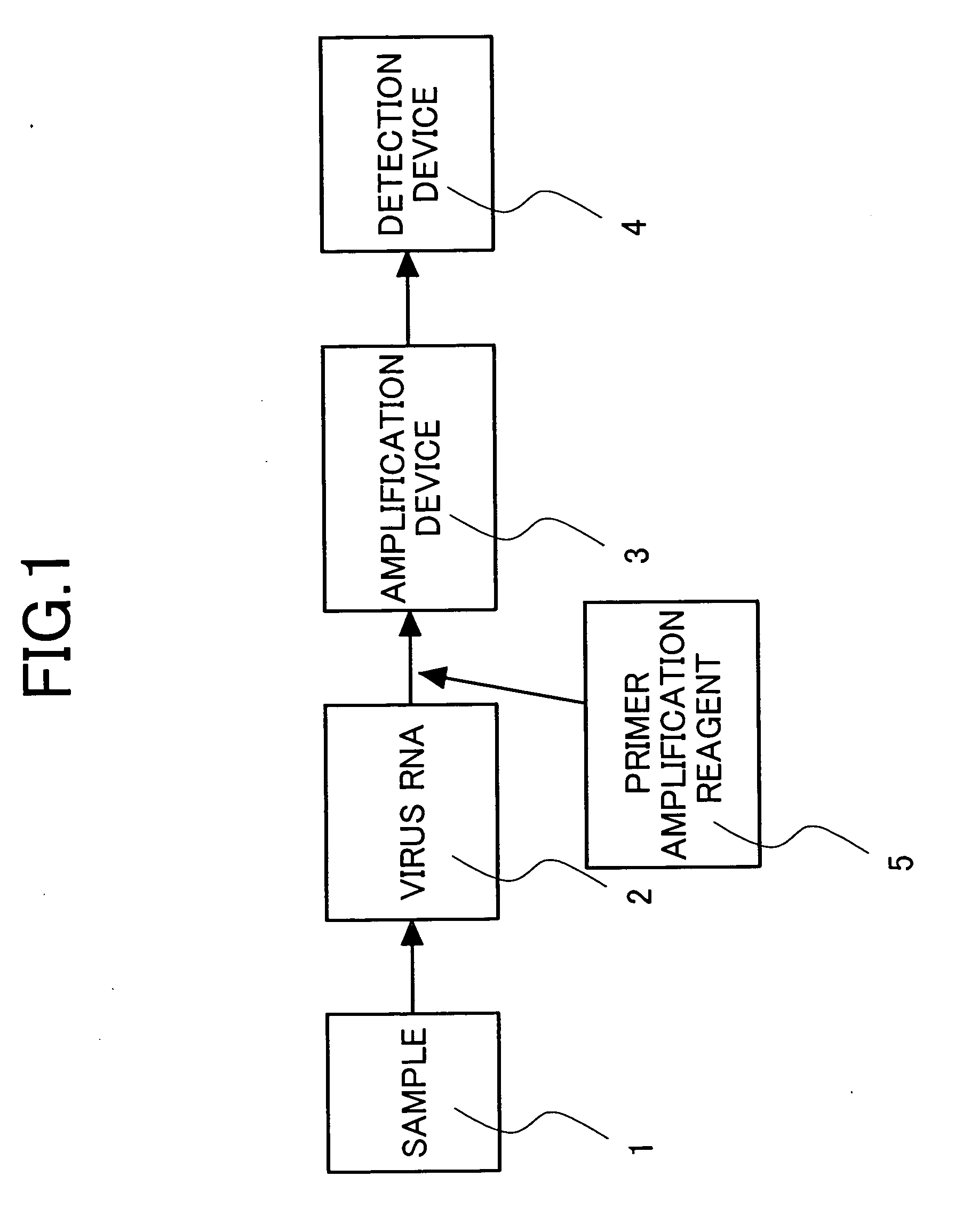
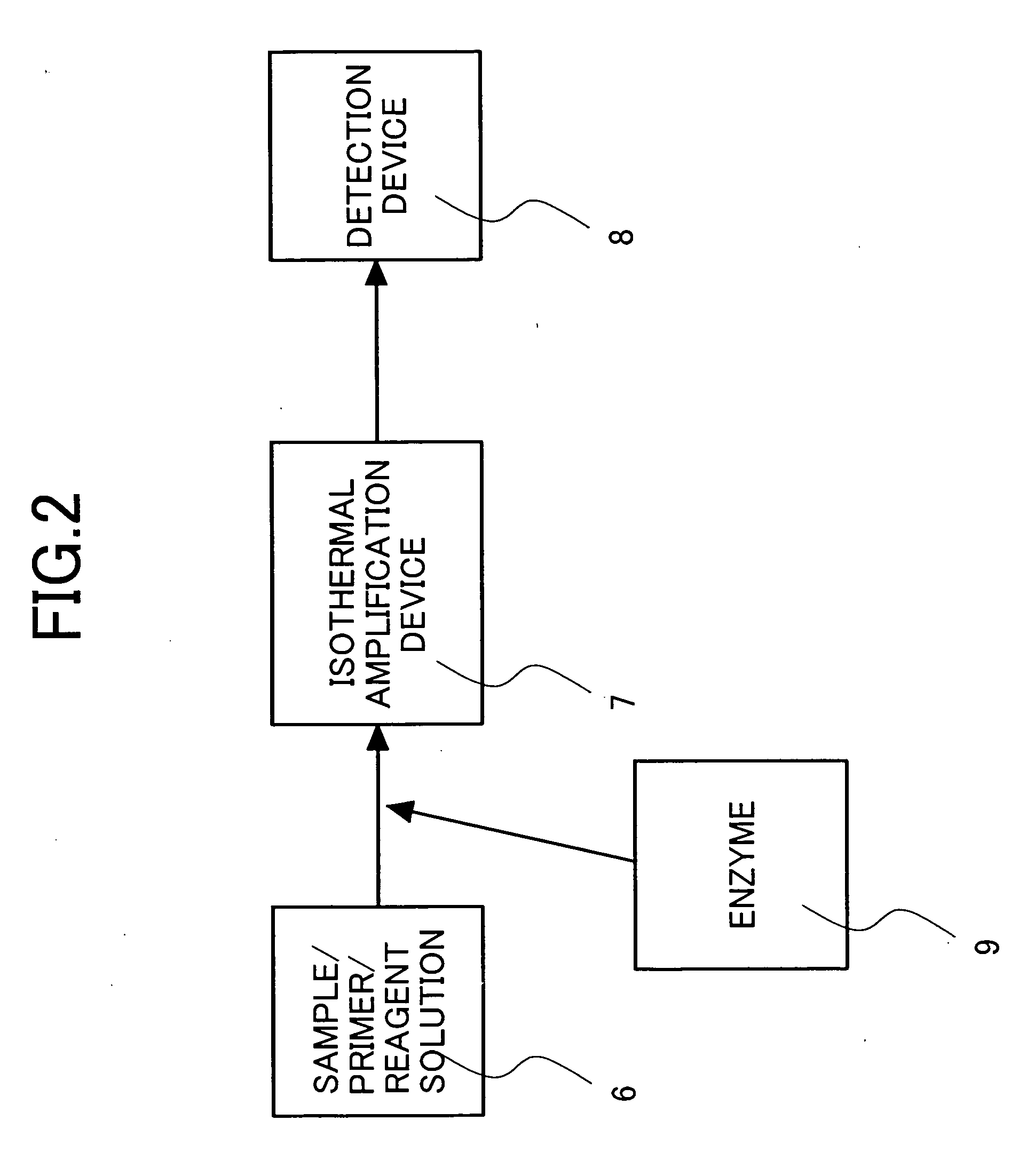
Primers for isothermal amplification of hepatitis C virus
a technology primers, which is applied in the field of primers for isothermal amplification of hepatitis c virus, can solve the problems of difficult design of specific primers capable of carrying out genotyping in the region, and the technique cannot determine the genotype of hcv gene, so as to achieve easy and rapid detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Screening of Primers Capable of Typing HCV Subtype 1a Gene by NASBA
[0053] An optimal pair of oligonucleotide primers for genotype-specific isothermal amplification by NASBA was determined by designing sense primers and antisense primers in regions in the core region of the HCV subtype 1a gene which are capable of highly specifically typing, setting pairs of the oligonucleotide primers in various combinations and subjecting the pairs of primers to NASBA. The sense primers are oligonucleotide primers of SEQ ID NOs: 1, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31 and 32, and the antisense primers are oligonucleotide primers of SEQ ID NOs: 11, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38 and 39 listed in Table 2. Each of the antisense primer further had a sequence (AATTCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGG: SEQ ID NO: 45) including a T7 promoter sequence at the 5′ end.
TABLE 2SEQPrimerSequence*location**ID NORefHCV1p2015′-GAGGTCTCGTAGACCGTGCACCA-3′(23bp)2-25bp24S1HCV1p2025′-CACCATGAGCACGAATCCTA-3′(20bp)21-40bp1S2HCV1p2O35′-TCAGAT...
example 2
Screening of Primers Capable of Genotyping HCV Subtypes 1b, 2a, 2b and 3a
[0064] Optimal pairs of oligonucleotide primers for genotype-specific isothermal amplification of HCV subtypes 1b, 2a, 2b and 3a genes by NASBA were determined by the procedure of Example 1.
[0065] (1) HCV Subtype 1b Gene
[0066] Primers listed in Table 4 were designed based on the sequence of a specific region capable of typing the core region of the HCV subtype 1b gene (SEQ ID NO: 41 corresponding to 1 to 325 bp of the core region of HCV subtype 1b). Different pairs of these primers were subjected to isothermal amplification by NASBA under the same conditions as in Example 1 using, as a template, a HCV subtype 1b gene sample, and the presence or absence of, and the position of amplified product were determined by electrophoresis. In addition, the presence or absence of, and the position of amplified product by NASBA using samples of the other HCV subtypes were determined on pairs of primers which yielded the ...
example 3
Genotyping of HCV Subtypes 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b and 3a Genes by NASBA
[0076] Genotyping of HCV was carried out by isothermal amplification according to NASBA and electrophoresis by the procedure of Example 1. More specifically, the sense primers used are oligonucleotide primers corresponding to SEQ ID NOs: 1, 3, 5 and 7, and the antisense primers are oligonucleotide primers corresponding to SEQ ID NOs: 11, 12, 13 and 14 each further having a sequence including a T7 promoter sequence at the 5′ end.
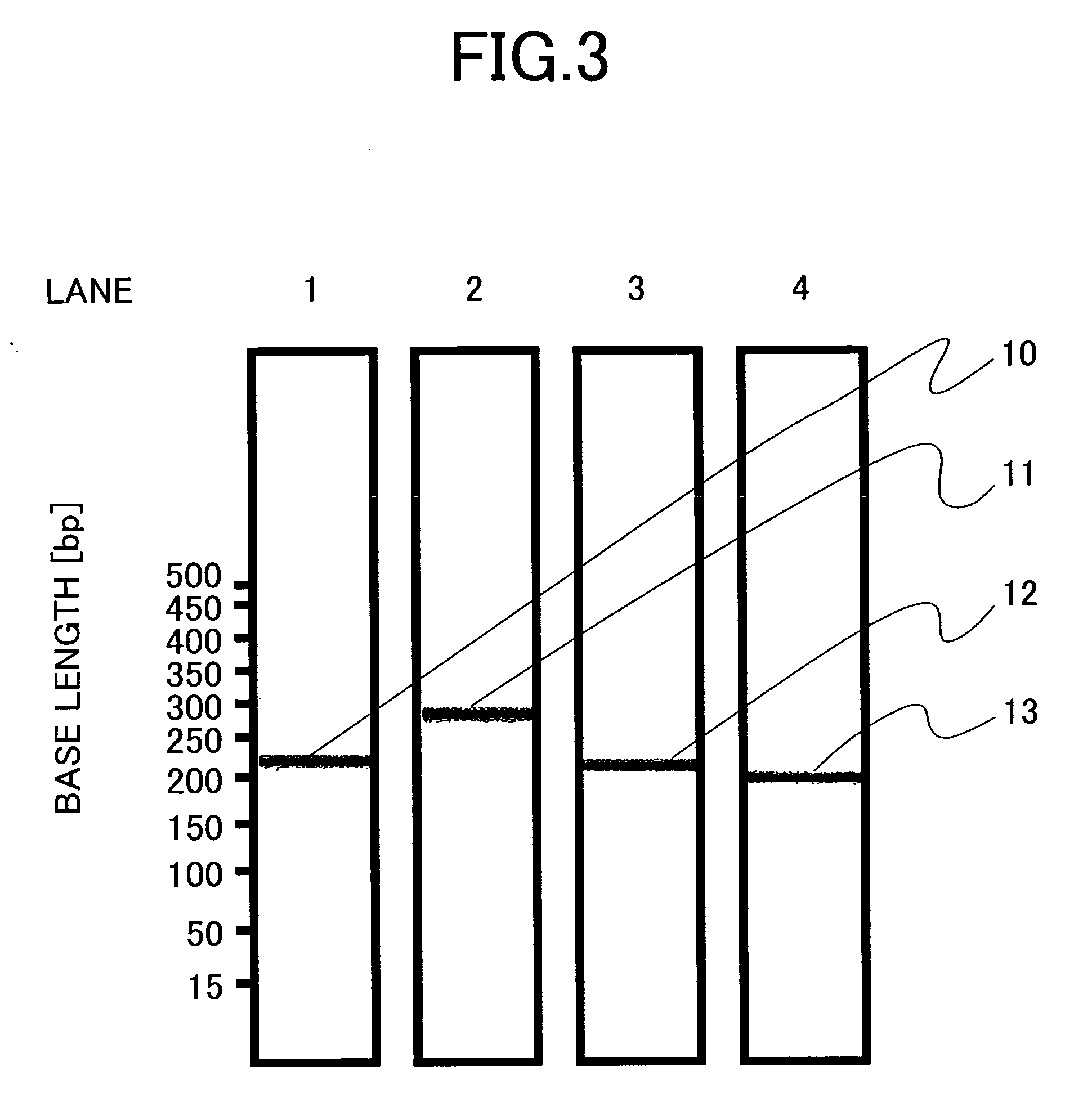
[0077] A pair of oligonucleotide primers corresponding to SEQ ID NOs: 1 and 2 was so designed as to yield an amplified product having a size of 217 bp as a result of the amplification of a sample HCV subtype 1a RNA. Likewise, a pair of oligonucleotide primers corresponding to SEQ ID NOs: 3 and 4, a pair of oligonucleotide primers corresponding to SEQ ID NOs: 5 and 6, and a pair of oligonucleotide primers corresponding to SEQ ID NOs: 7 and 8 were so designed as to yield amplified products having ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| secondary structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic acid sequence-based amplification | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com