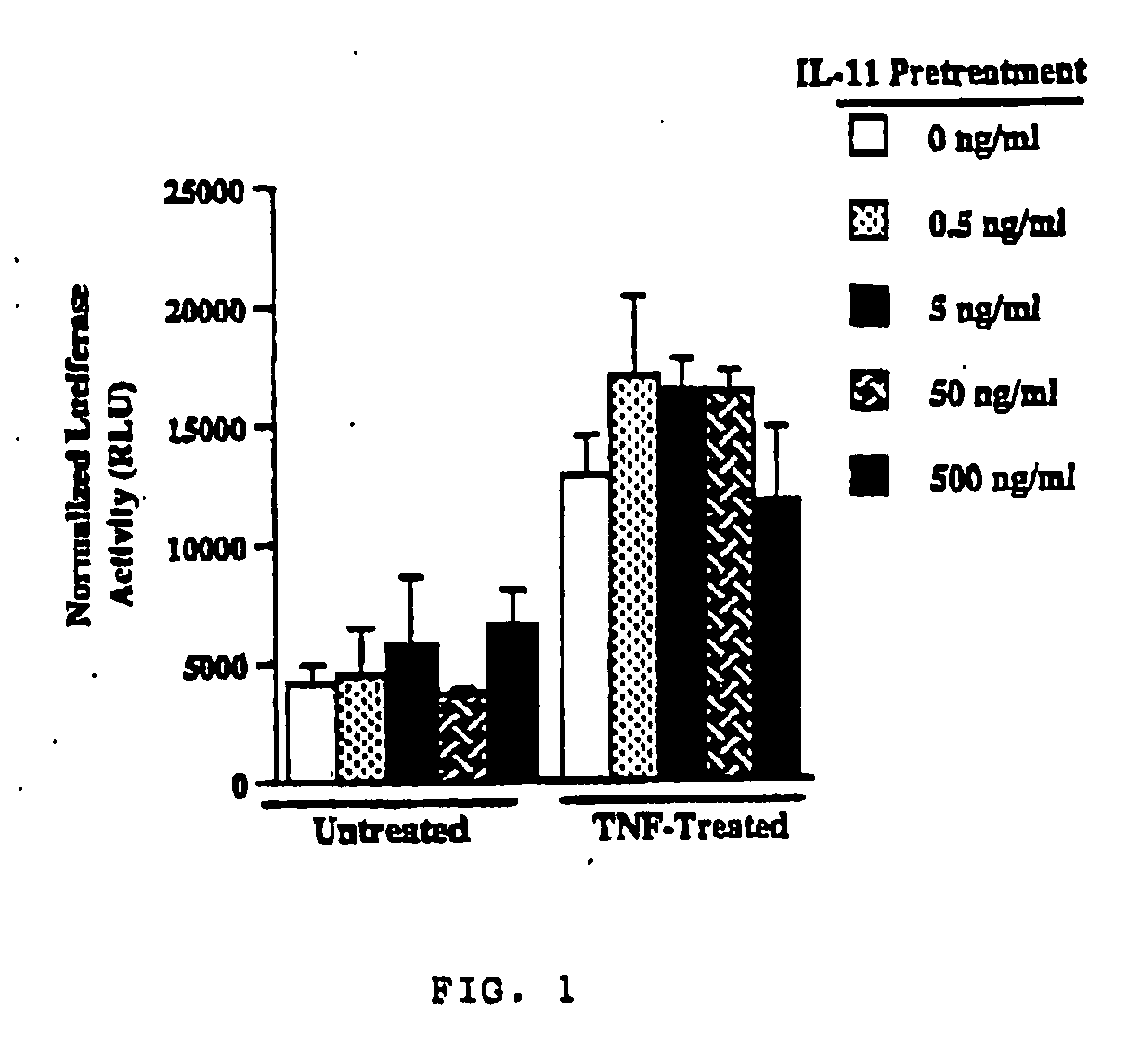
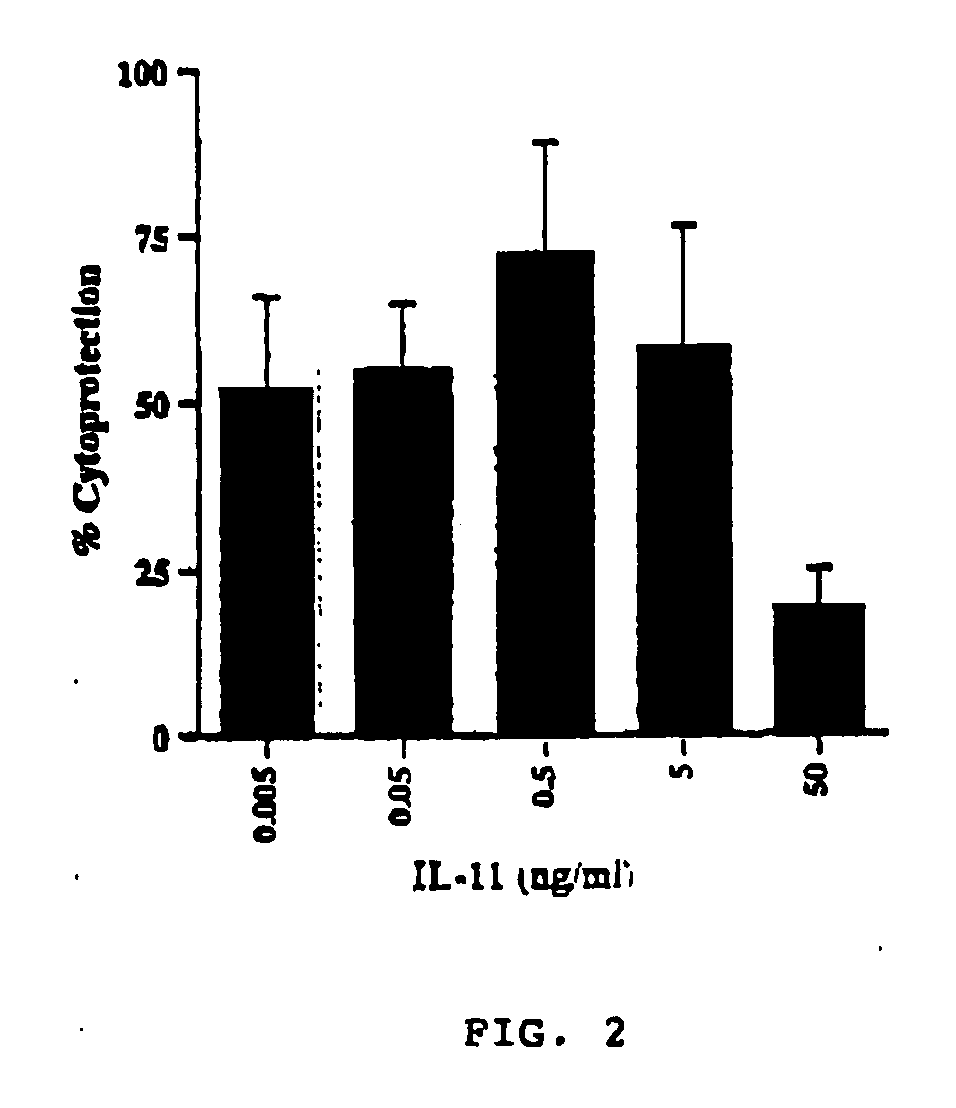
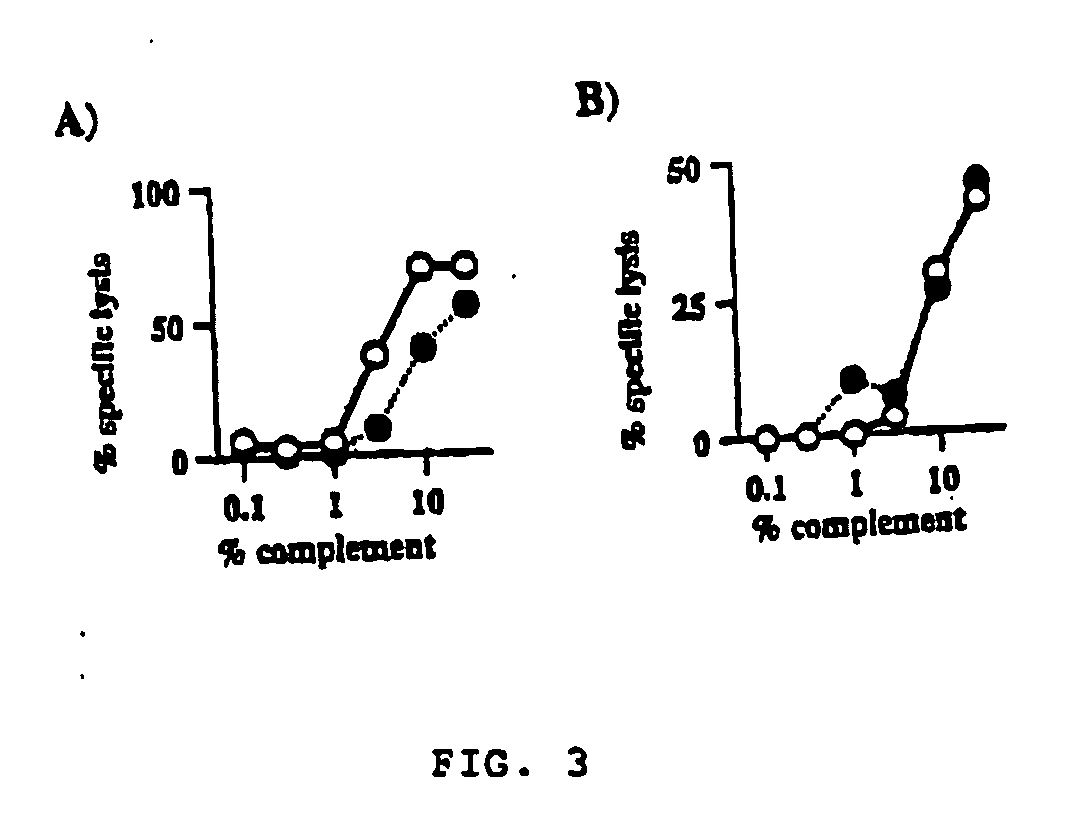
Use of interleukin-11 to prevent immune-mediated cytotoxicity
a technology of interleukin-11 and cytotoxicity, which is applied in the direction of immunological disorders, drug compositions, peptide/protein ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of depletion of bone marrow grafts, higher graft failure rate, and recipient at risk of graft-versus-host diseas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Dose and Time Dependent Phosphorylation by IL-11
[0060] 4 μg of total RNA from cultured HUVECs, CACO-2 or K562 cells was incubated over night with probes for human IL-11Rα chain and GAPDH genes. Samples were digested with RnbaseA / T1 and protected fragments (321 bp for IL-11Rα and 96 bp for GAPDH were resolved on a 6% acylamide / TBE-Urea gel. Lysates from either HUVECs or K562 cells were resolved on SDS-PAGE as described above and immunoblotted with specific antibody to IL-11 receptor a chain. The IL-11 receptor a chain was detected in HUVECs and K562 cells at about MW 83 kD.
[0061] Next, HUVECs were either untreated (control), treated with IL-11 (100 ng / ml), or oncostatin M (20 ng / ml) for 2 min and 10 min. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with specific antibody to gp130. Immune complexes were resolved on SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with a phosphotyrosine specific antibody as described above. The results indicate that IL-11 tyrosine phosphorylates gp130 in HUVECs.
[0062] To test wh...
example 2
The IL-11 Receptor Alpha Chain is Expressed on B and T Lymphocytes
[0066] Murine B Cells and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were purified from Balb / c spleens using positive selection with MACS (Magnetic Cell Sorting) Microbeads conjugated to anti-mouse B220, CD4 or CD8 antibodies, as per manufacturers protocol (Miltenyi Biotec, Sunnyvale, Calif.). RNA was extracted from purified cell populations as described above using RNA Stat-60 (Tel-test, Inc., TX) as per manufacturer's protocol. RNA was DNase treated (RQ1 DNase, Promega, Madison, Wis.) for 30 min at 37° C., then heat inactivated for 5 min at 75° C. RT-PCR was performed (GeneAmp RNA PCR Kit, Perkin Elmer) using 40 ng RNA (10 ng for GAPDH) and oligo pairs specific for murine GAPDH, IL-11 receptor a chain, IL-10 receptor, IL-6 receptor or gp130, and visualized on an ethidium-stained agarose gel. PCR reactions on RNA samples in the absence of reverse transcriptase were negative for each oligo pair, and served as a control for DNA contaminat...
example 3
IL-11 Increases Antigen Specific Cytolytic Activity in Bulk Spleen Cultures
[0067] Seven day splenic bulk cultures from cells treated with IL-2, or IL-2 and IL-11, were serially diluted and added to 1×104 51Cr-labelled P815.P1HTR cells, which were pulsed for one hour in the presence or absence of NP peptide. The cells were incubated for 4 hours. Supernatants were harvested, and 51Cr release was determined. Maximum lysis on the target cells was induced with 2% Triton-X 100. % lysis=[(CPM−spontaneous CPM of NP peptide pulsed targets) / (maximum CPM of NP peptide pulsed targets−spontaneous CPM of NP peptide pulsed targets)]×100. % specific lysis=(% lysis on NP peptide pulsed target cells)−(% lysis of control target cells). The example indicates that IL-11 can significantly enhance the % specific lytic activity of NP peptide-specific cytotoxic T cells. At a 50:1 effector to target cell ratio, a 250% enhancement in % specific lysis is observed in cells treated with IL-2 and IL-11 versus ce...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com