Magnetic molecularly imprinted nano-particle as well as preparation method and application thereof
A magnetic molecular imprinting and nanoparticle technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of poor biocompatibility and poor selectivity, and achieve uniform particle size, simple preparation method and few steps. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1. Preparation of Western Blot Magnetic Fluorescent Nanoparticles
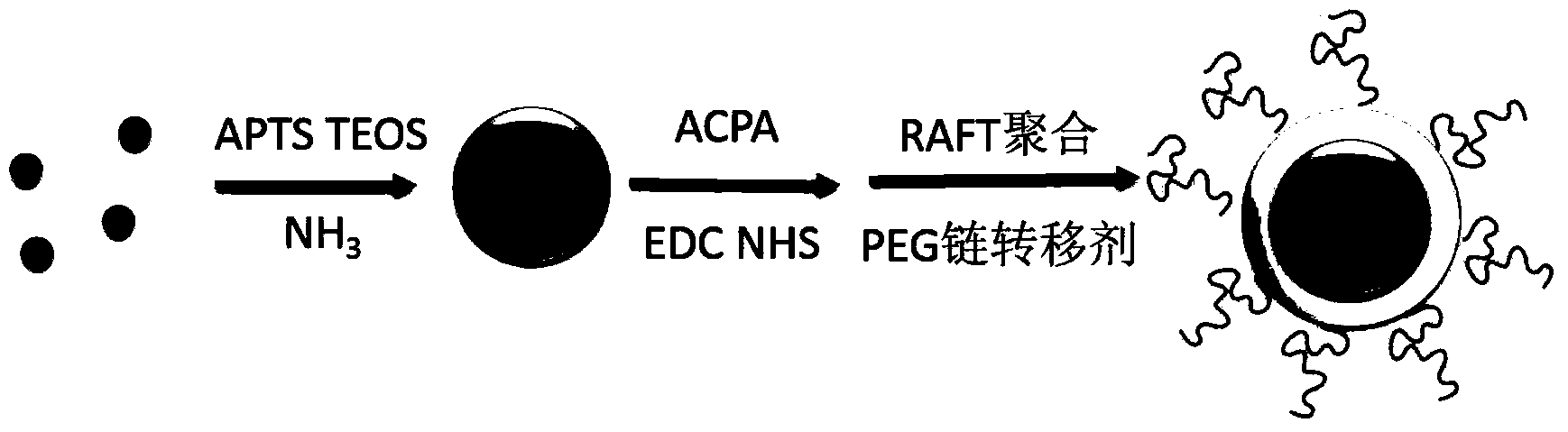
[0042] The process of preparing Western imprinted magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles in the present invention is as follows: figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
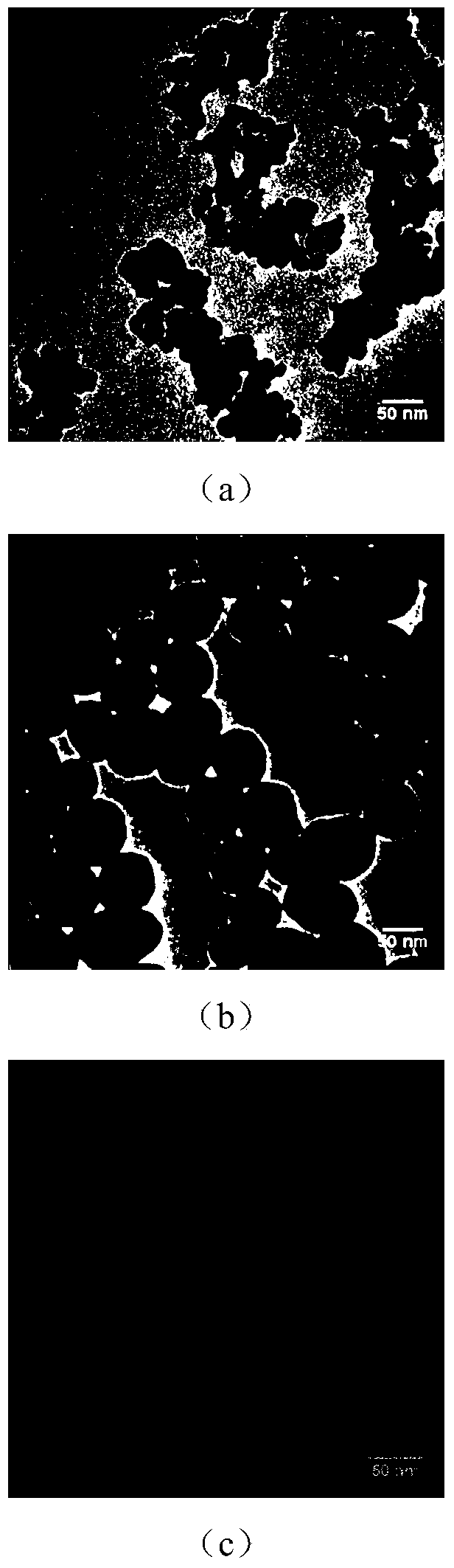
[0043] 1) Synthesis of Fe with suitable size 3 o 4 SiO 2 Nanoparticles (wherein, the diameter of the magnetic core is 5-10nm, and the thickness of the silicon dioxide layer is 10-20nm), and the surface of the silicon dioxide has amino groups, such as figure 2 (b) shown.
[0044] 90 mg of dry hydrophilic amino-modified Fe 3 o 4 Magnetic nanoparticles (such as figure 2 (a)) was fully ultrasonically dispersed in 20 mL of deionized water, and was added dropwise to a mixed solution containing 462 mL of cyclohexane, 120 g of Triton X-100 and 96 mL of n-hexanol under vigorous stirring.
[0045] Add 0.45mL tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) dropwise, react for 30min, then add 1.8mL concentrated ammonia water dropwi...
Embodiment 2
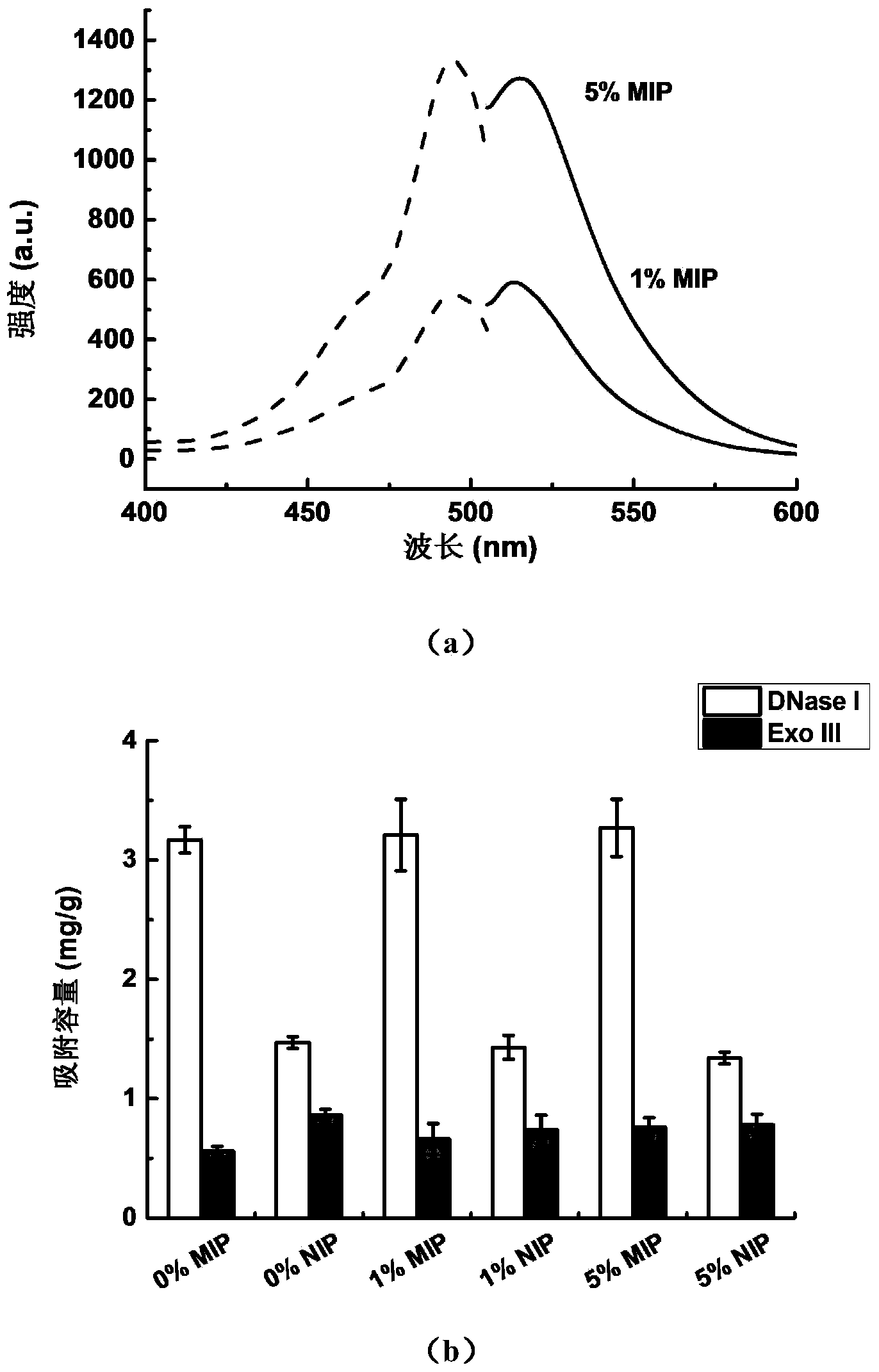
[0056] Example 2: Selective inhibition of deoxyribonuclease in solution and direct detection of its activity with DNA fluorescent probes
[0057] Without SiO 2 Due to the positive charge of the amino groups on the surface of the encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles, and the weak positive charge on the surface of the unmodified polyethylene glycol magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer, both of them have non-specific adsorption to DNA fluorescent probes, which will interfere with DNA fluorescence. In situ detection of probes. After silicon-coating and polyethylene glycol modification, the magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer has good dispersibility and stability in aqueous solution, and it can be added to the system to be tested to specifically inhibit the target enzyme. At this time, it can be directly added DNA fluorescent probe was used to measure its activity.
[0058] In addition, when there are other enzymes in the system (example III (Exo III) as an example), directly...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3. Western Blot Magnetic Fluorescent Nanoparticles Rapidly Introduced into Cells and Imaging under the Action of a Magnetic Field
[0074] The prepared magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer has good stability and biocompatibility, and can be quickly introduced into Hela cells through endocytosis under the action of a magnetic field and inhibit the activity of DNase I therein. Afterwards, streptolysin O (SLO) protein was used to form micropores on the cell membrane, and DNA fluorescent probes were introduced into the cells to perform fluorescence imaging of DNase I activity to prove the in situ inhibitory effect of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles on DNase I. The detection and comparison of the activity of Exo III shows that its activity is not affected by the DNase I molecularly imprinted polymer. The DNase I probe uses the same sequence as above, the Exo III probe is limited by the detection channel of the fluorescence microscope, the FAM fluorescent labeli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com