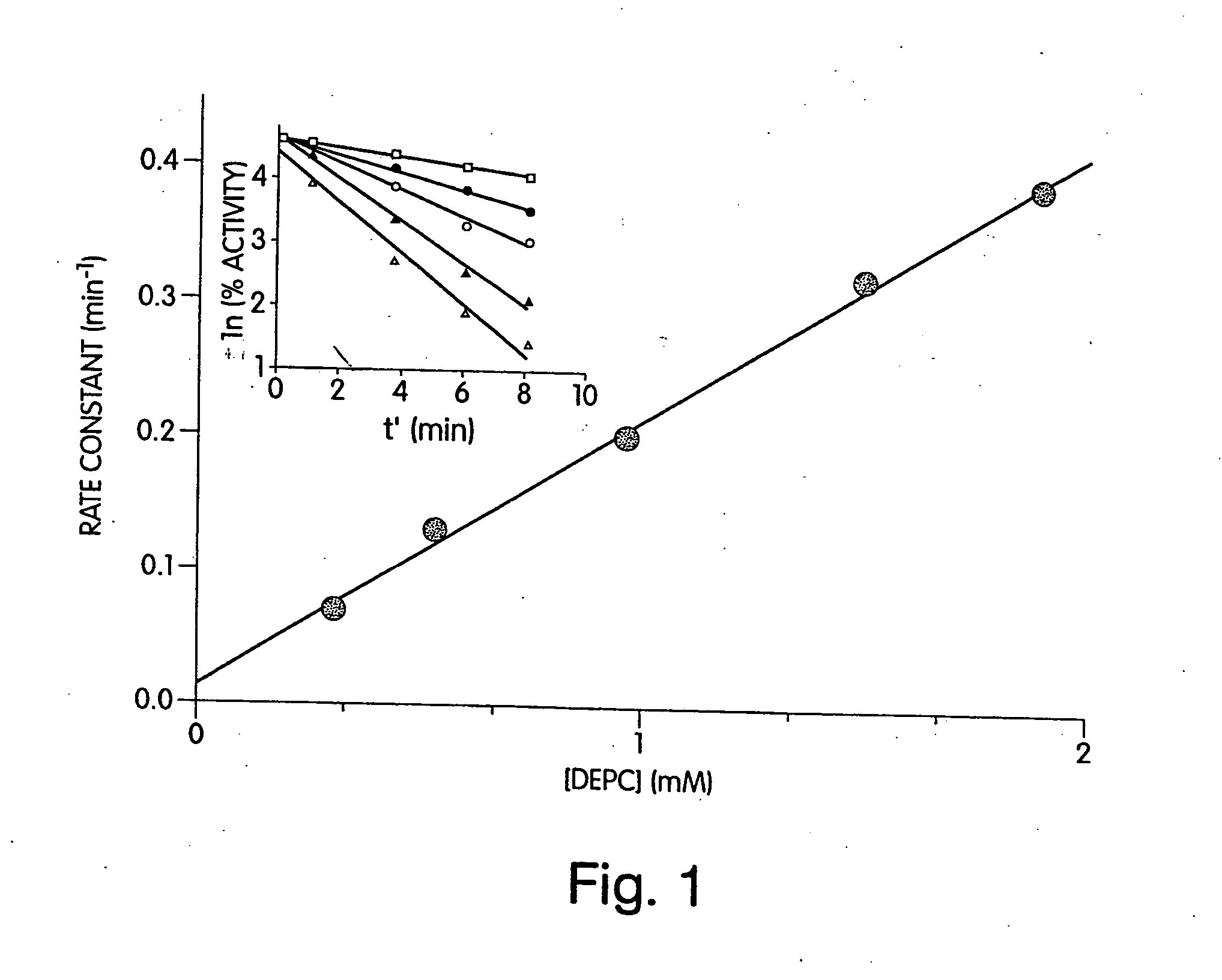
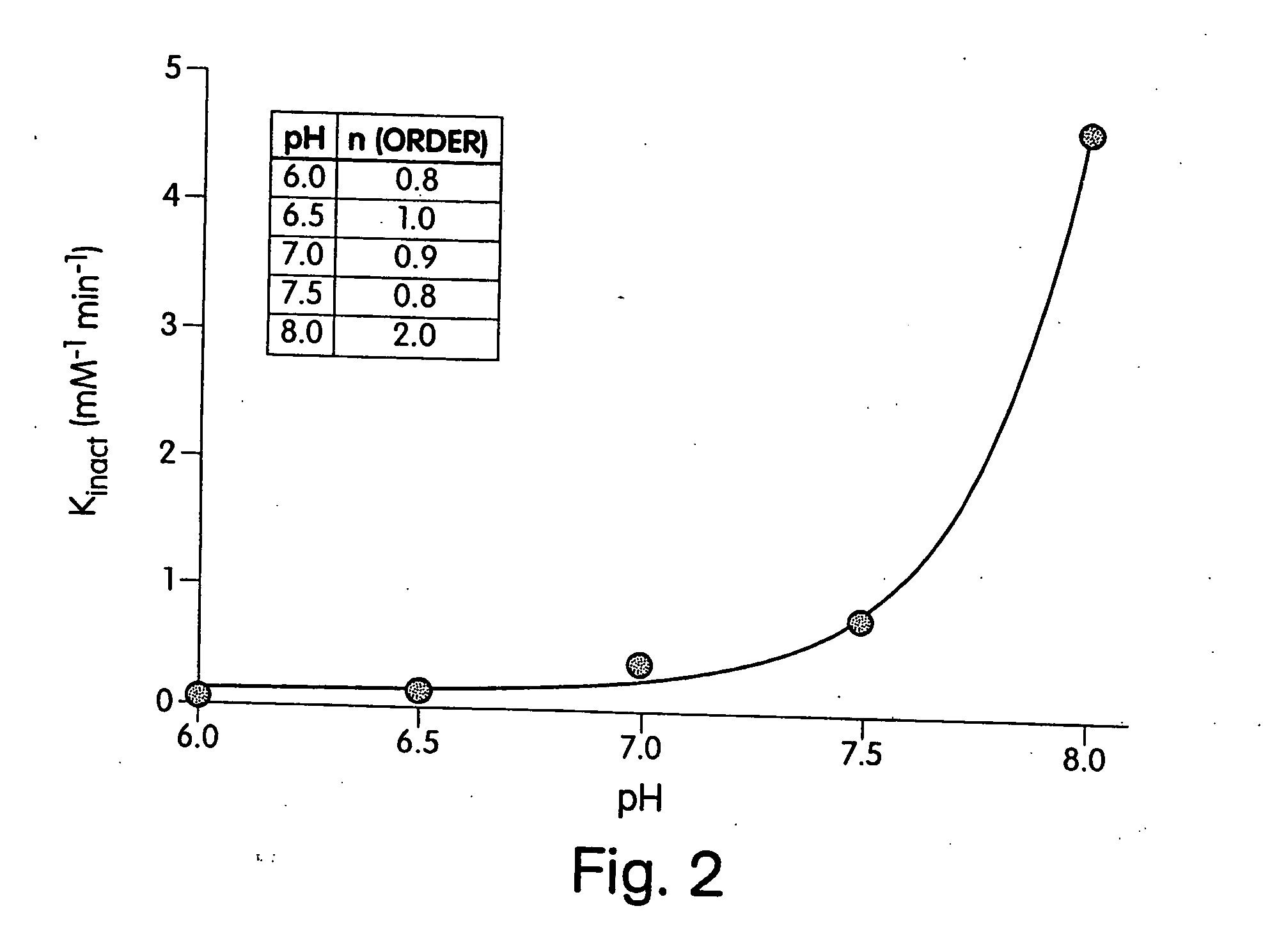
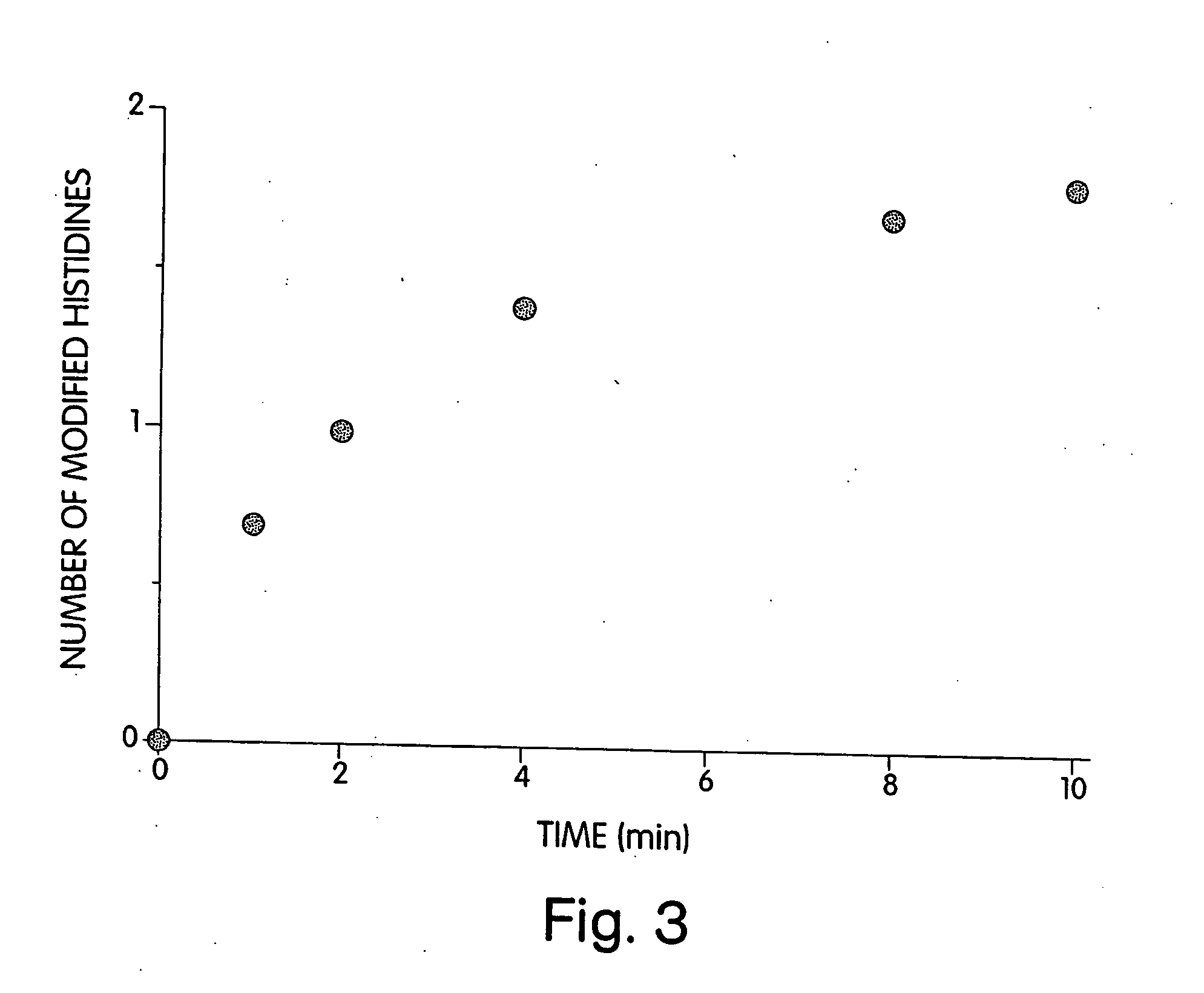
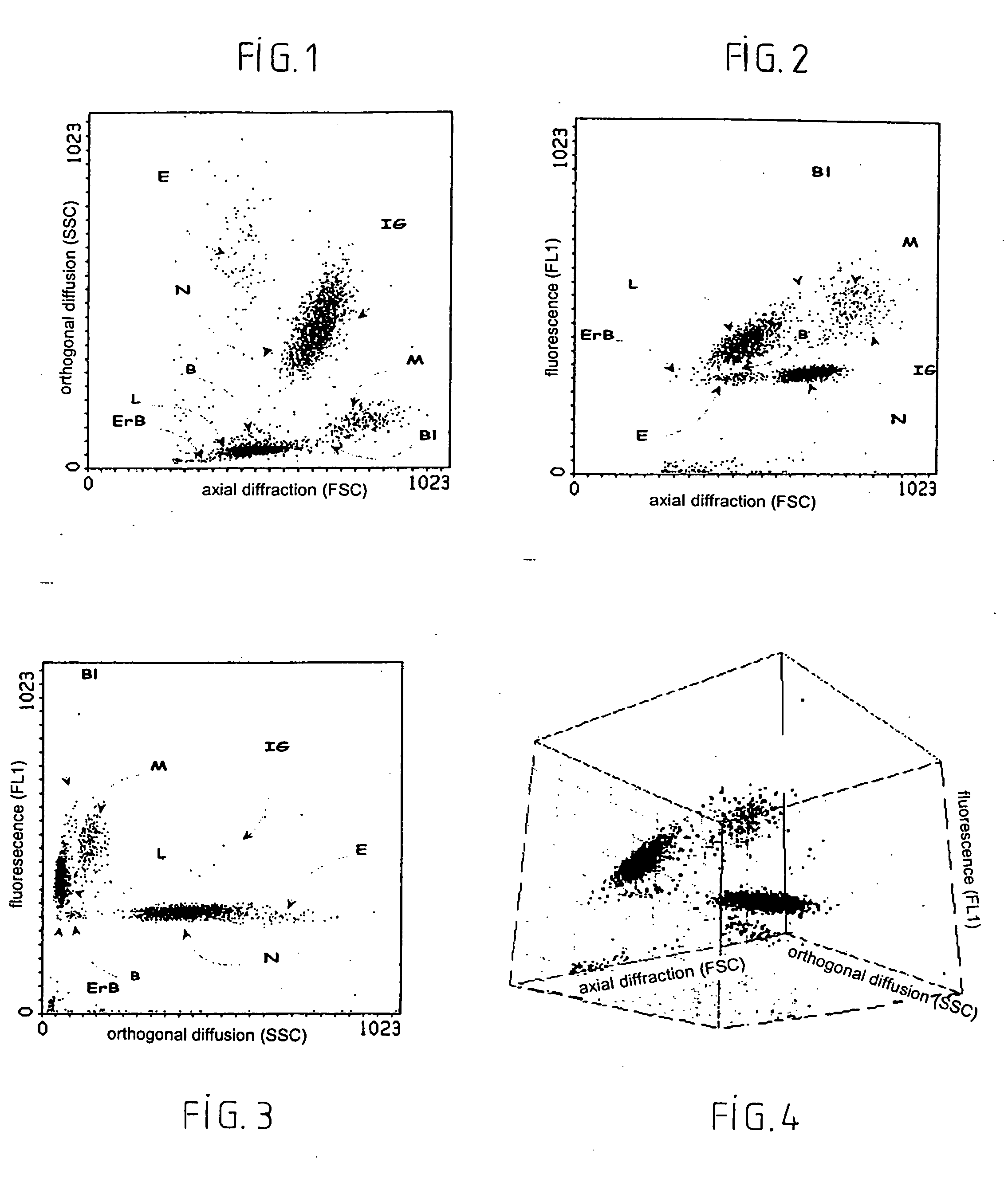
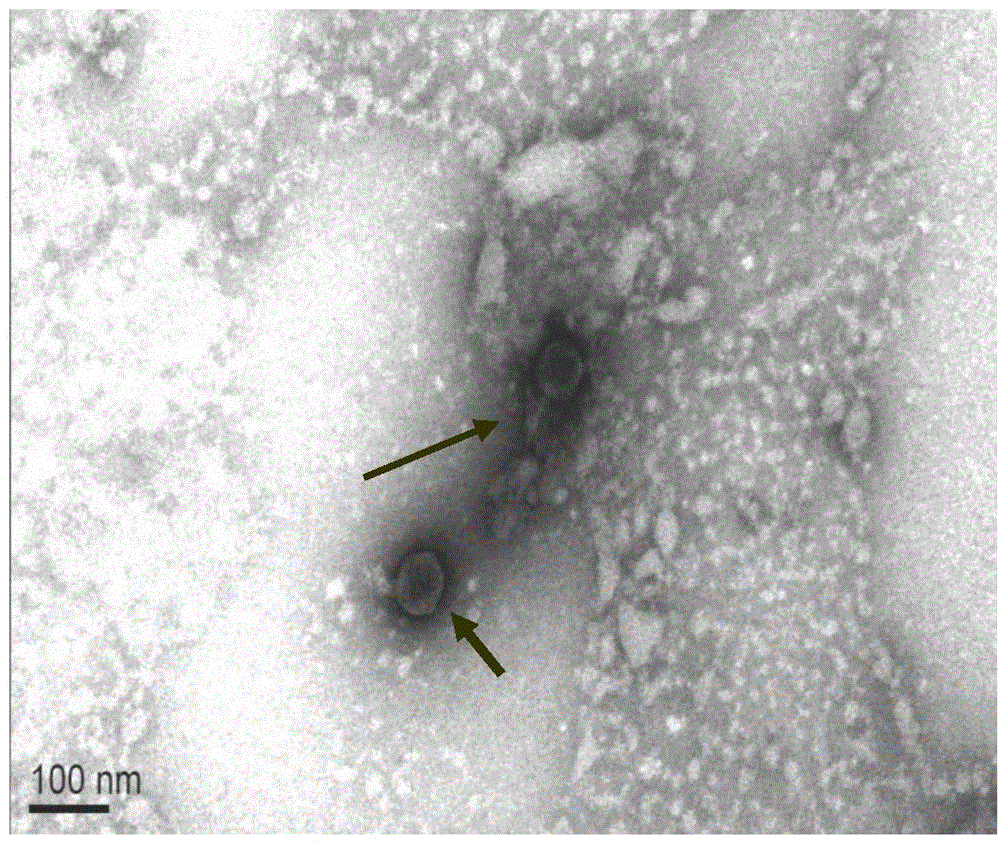
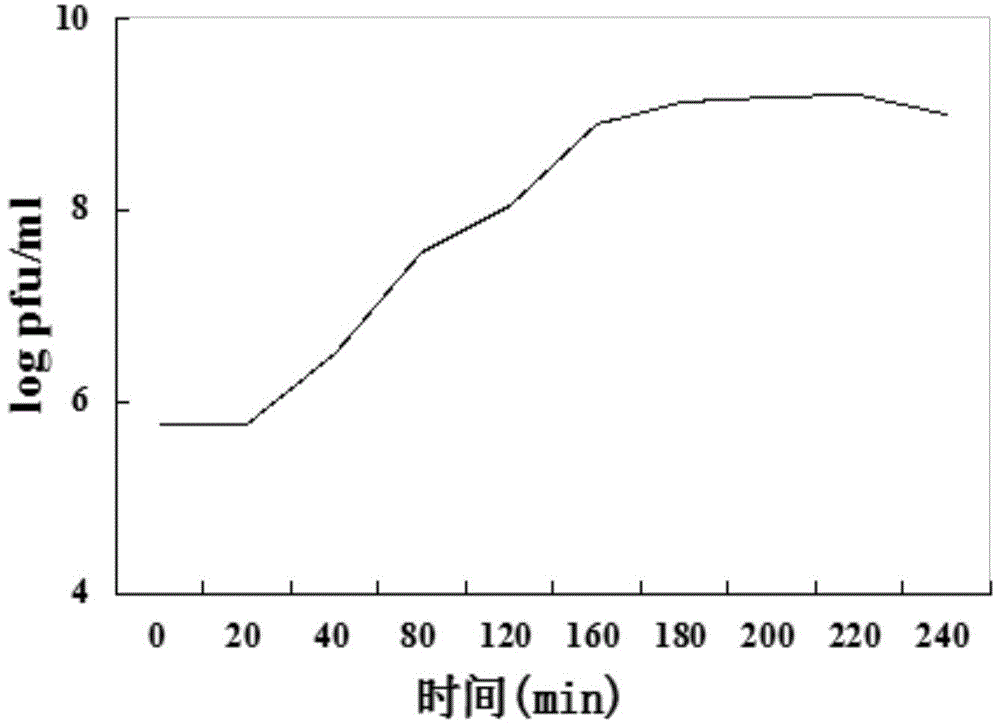
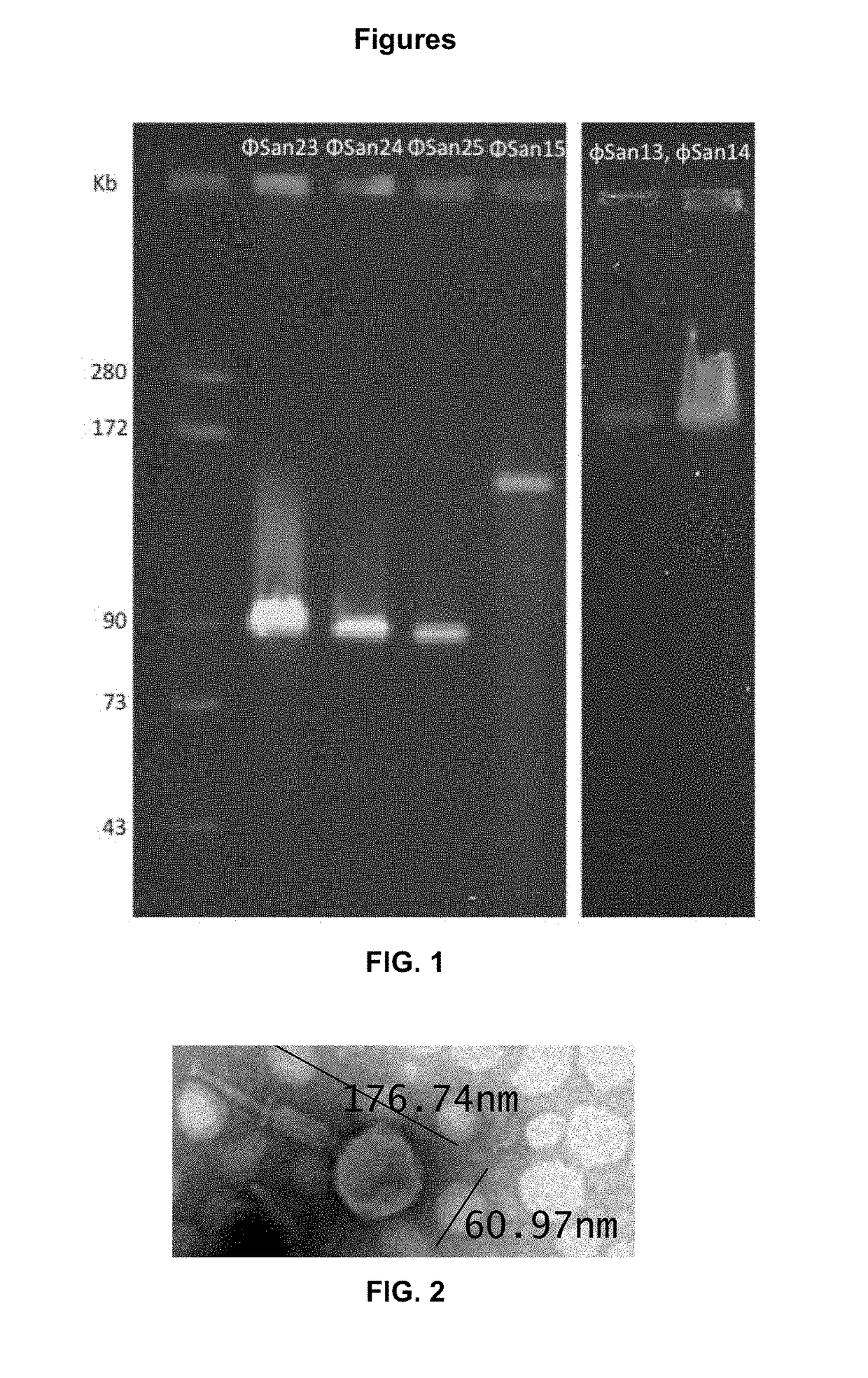
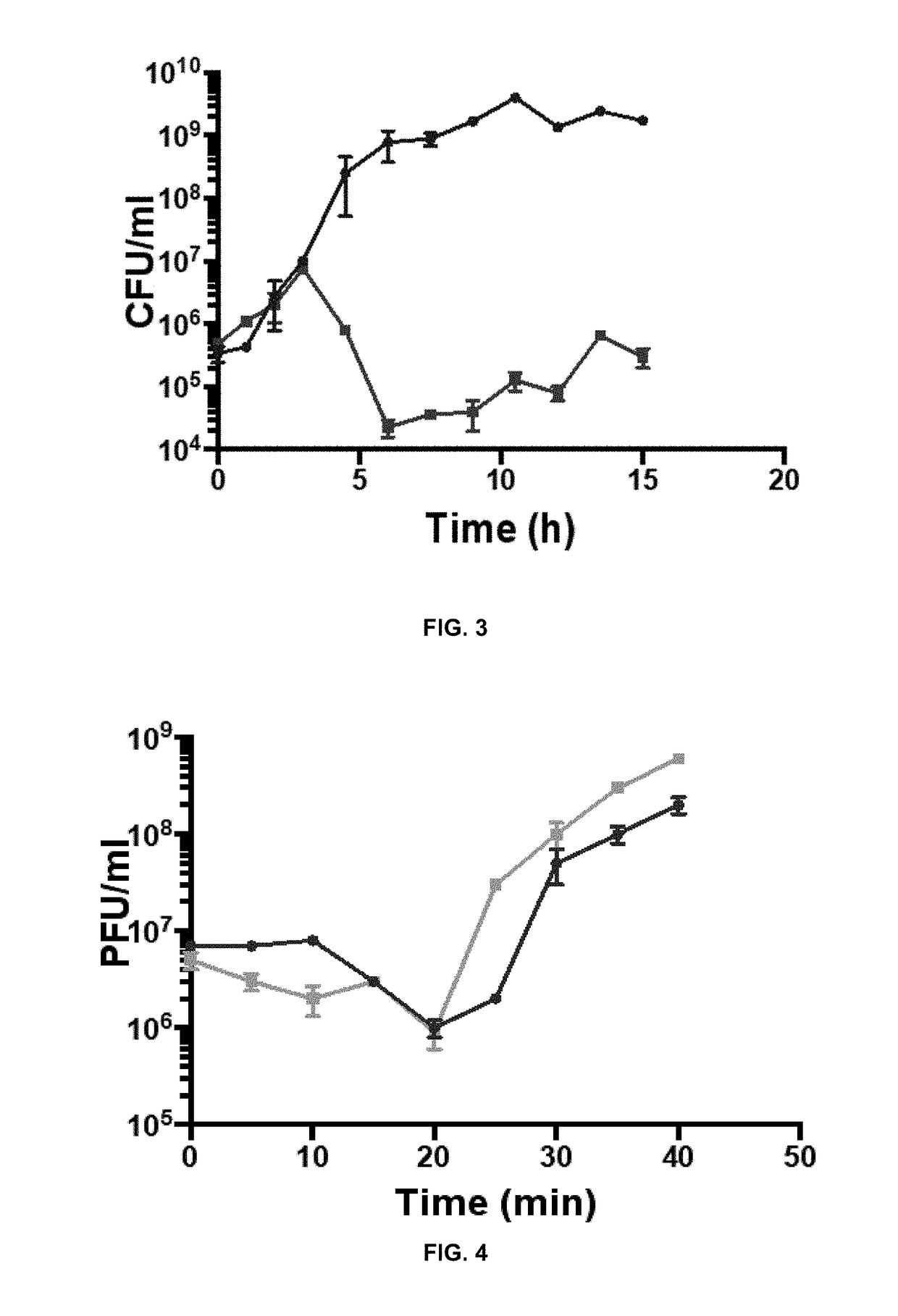
Patents
Literature
50 results about "Specific lysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tissue Specific Lysis Buffer. A convenient, ready-to-use tissue lysis buffer that is generally used for western blot, Co-IP, Chromatin IP (ChIP), enzyme activity assays, etc.
Heparinase III and methods of specifically cleaving therewith
InactiveUS20060067928A1Organic active ingredientsCompound screeningLymphatic SpreadAngiogenesis growth factor
The invention relates to heparinase III and mutants thereof. Modified forms of heparinase III having reduced enzymatic activity which are useful for a variety of purposes, including sequencing of heparin-like glycosaminoglycans (HLGAGs), removing active heparan sulfate from a solution, inhibition of angiogenesis , etc. have been discovered according to the invention. The invention in other aspects relates to methods of treating cancer and inhibiting tumor cell growth and / or metastasis using heparinase III, or products produced by enzymatic cleavage by heparinase III of HLGAGs.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Inhibitor which is deactivatable by a reagent produced by a target cell
ActiveUS8809504B2Undesirable effectModulating responseNGF/TNF-superfamilyAntibody ingredientsActive agentWhole body
The invention relates to molecules inhibiting biologically active compounds and further comprising moieties specifically cleavable by a reagent produced by a target cell. The invention relates to inhibitors that bind, inhibit, suppress, neutralize, or decrease activity of a biologically active agent. Inhibitors comprise at least one moiety that bind, inhibit, suppress, neutralize, or decrease activity of a biologically active agent and at least one moiety that can be cleaved specifically by a reagent produced by target cells. The cleavage deactivates the inhibitor. Following cleavage, the active agent is liberated into the local environment. Administration of the inhibitor alone or together with the active agent suppress the compound's activity until it reaches the proximity of a target cell. Targeted specific release enables the agent concentration in specific site to reach levels that have desired therapeutic effects without systemic toxicity.
Owner:VYTACERA BIO LLC
Reagent and process for the identification and counting of biological cells
InactiveUS20070111276A1Avoid disadvantagesShort timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological cellFlow cytometry
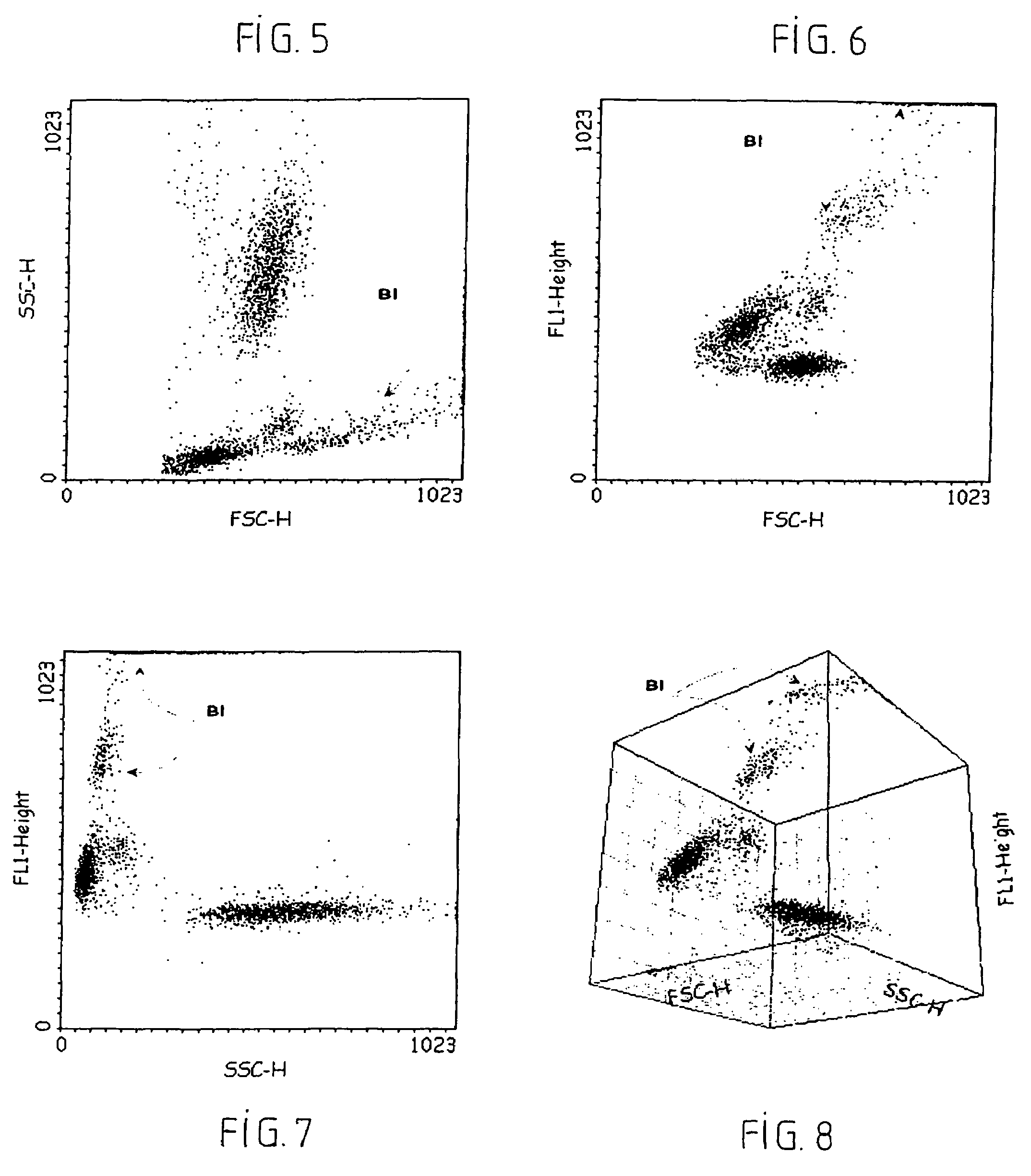
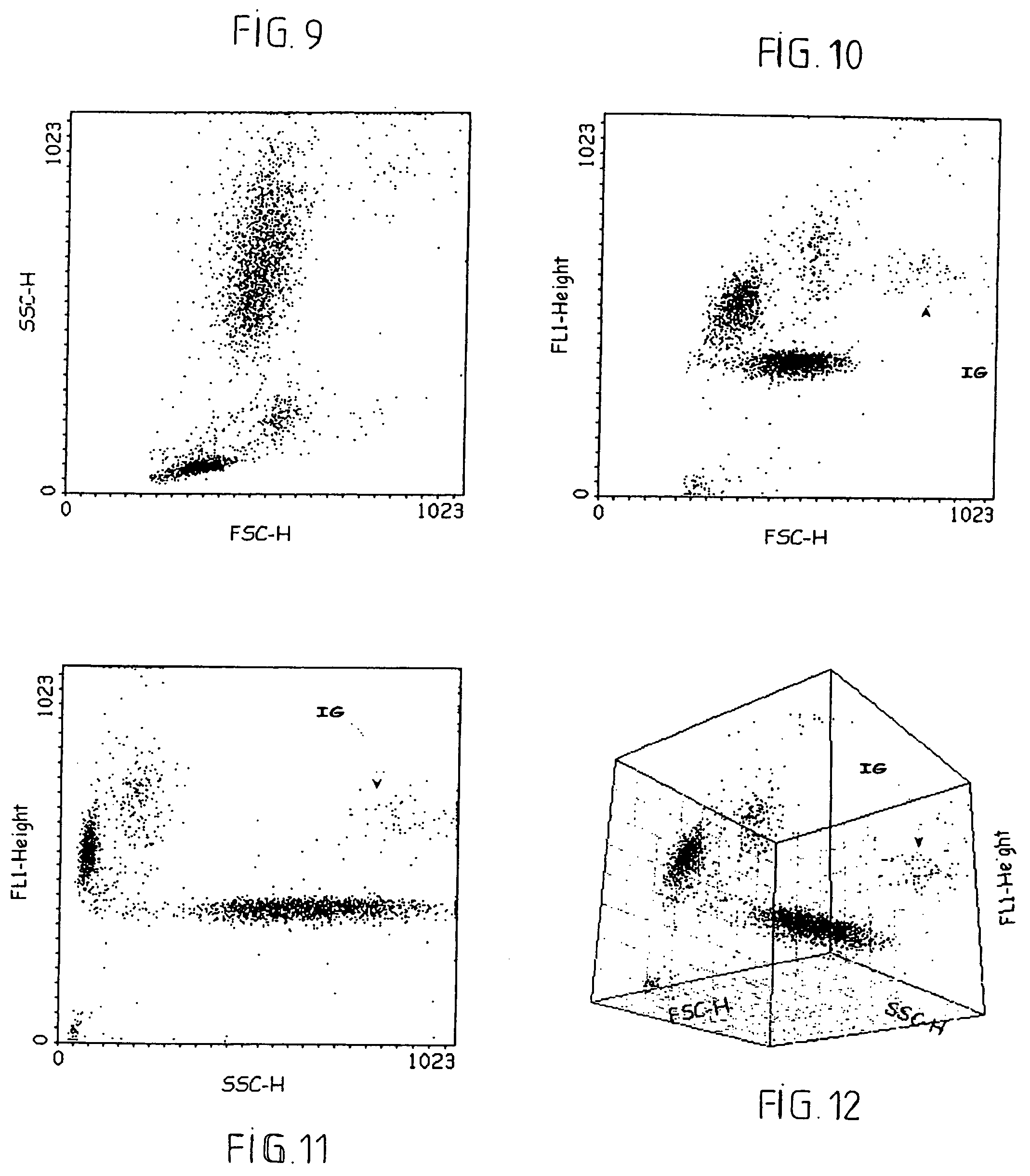
The invention relates to a reagent and a process for the identification and counting of biological cells in a sample. This reagent comprises a cell lysing agent selected from at least one detergent in a concentration capable of specifically lysing a given type of cells in the sample, and a stain capable of marking the intracellular nucleic acids of the remaining unlysed cells. Application in particular for the identification and counting of cells using an automated analysis system based on flow cytometry.
Owner:HORIBA ABX SAS
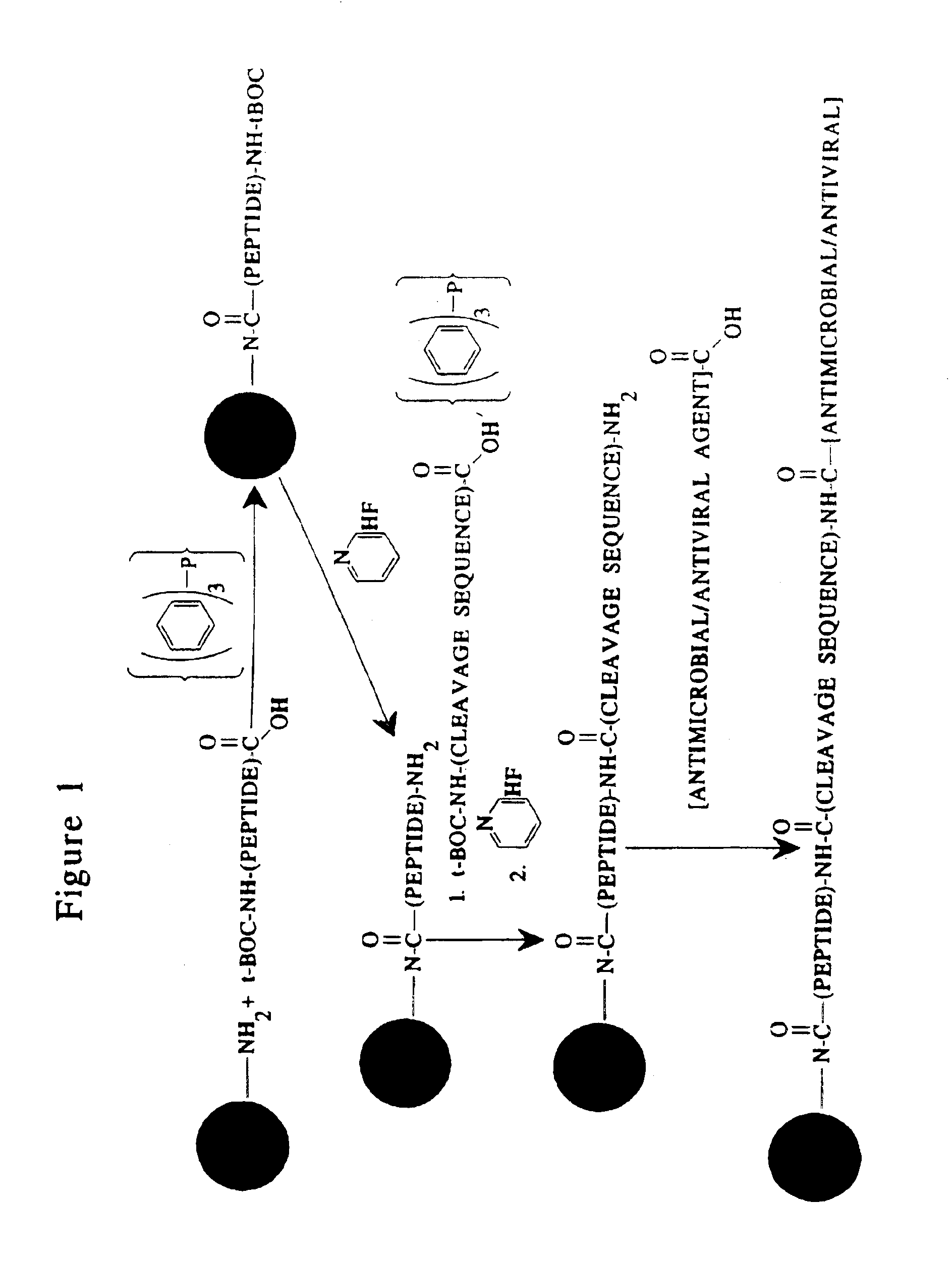
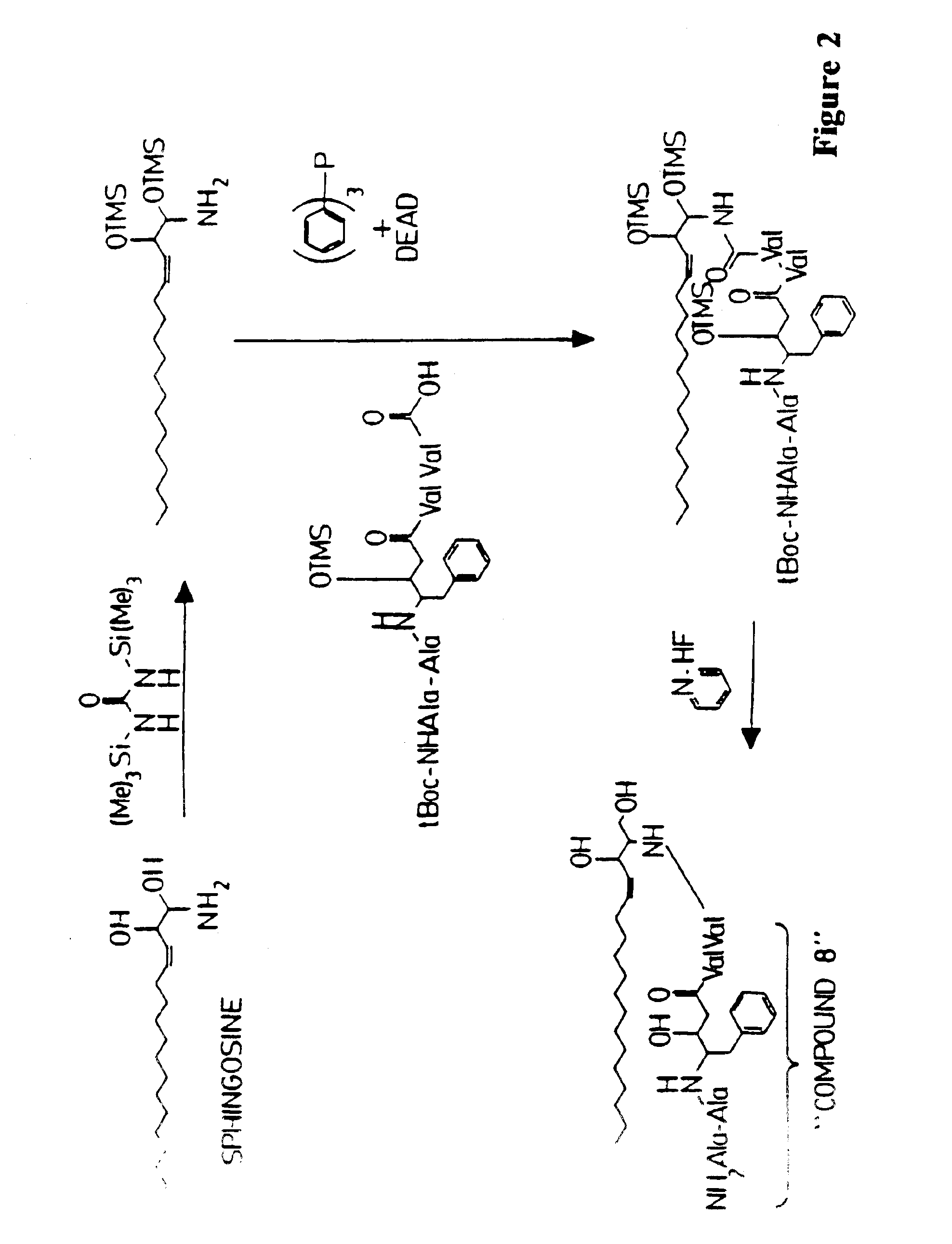
Composition containing porous microparticle impregnated with biologically-active compound for treatment of infection
Methods and reagents are provided for specifically targeting biologically active compounds such as antiviral and antimicrobial drugs, or prodrugs containing the biologically active compound to specific sites such as specific organelles in phagocytic mammalian cells. The biologically active compound or prodrug is linked to a microparticle with a linker that is non-specifically or specifically cleaved inside a phagocytic mammalian cell. Alternatively, the biologically active compound or prodrug is impregnated into a porous microparticle or coated on a nonporous microparticle, and then coated with a coating material that is non-specifically or specifically degraded inside a phagocytic mammalian cell. The prodrug contains the biologically active compound linked to a polar lipid such as ceramide with a specific linker such as a peptide that is specifically cleaved to activate the prodrug in a phagocytic mammalian cell infected with a microorganism. A microparticle linked antimicrobial drug or prodrug may be used for killing a microorganism infecting a phagocytic mammalian cell in vivo or in vitro.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
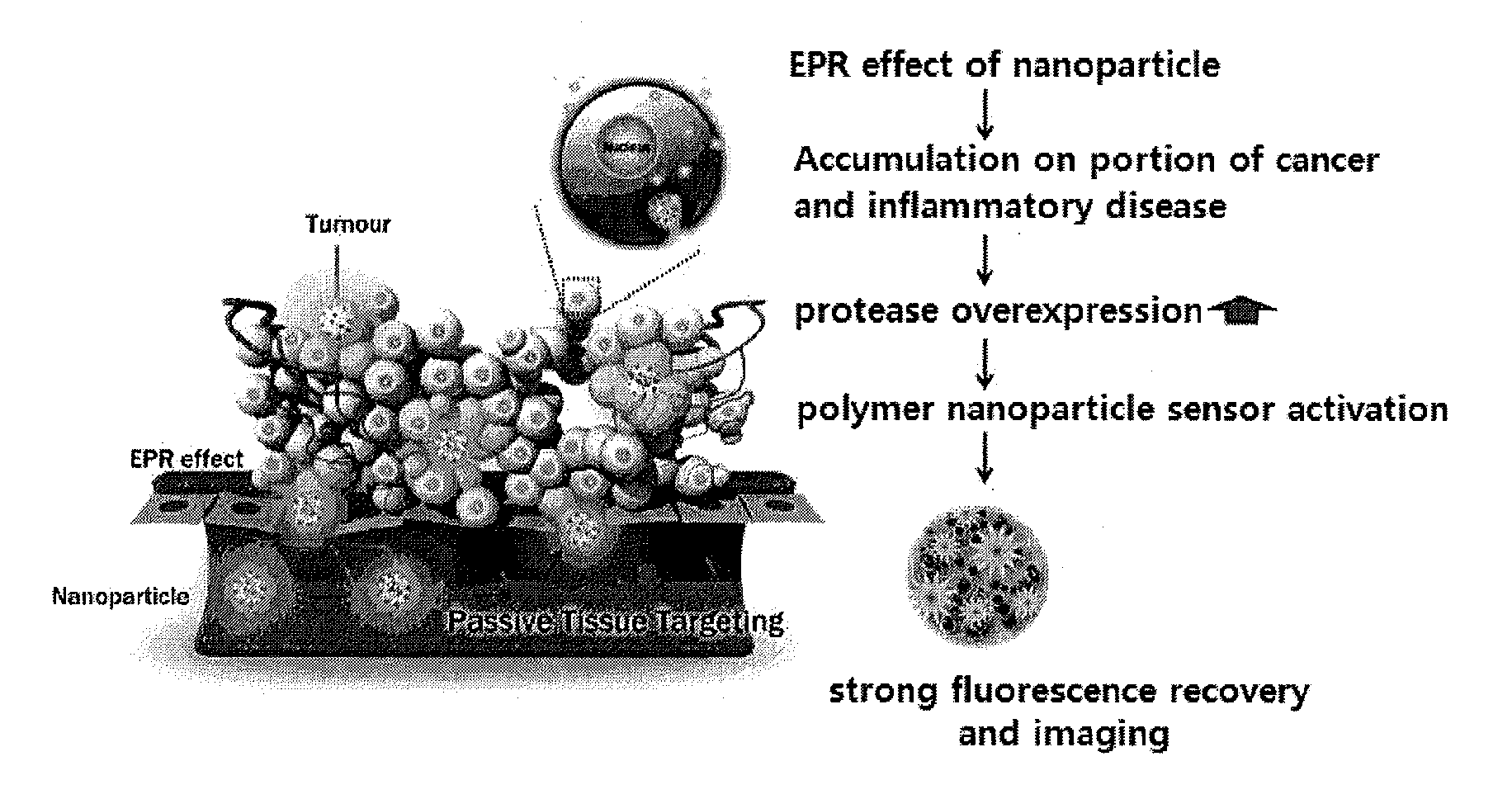
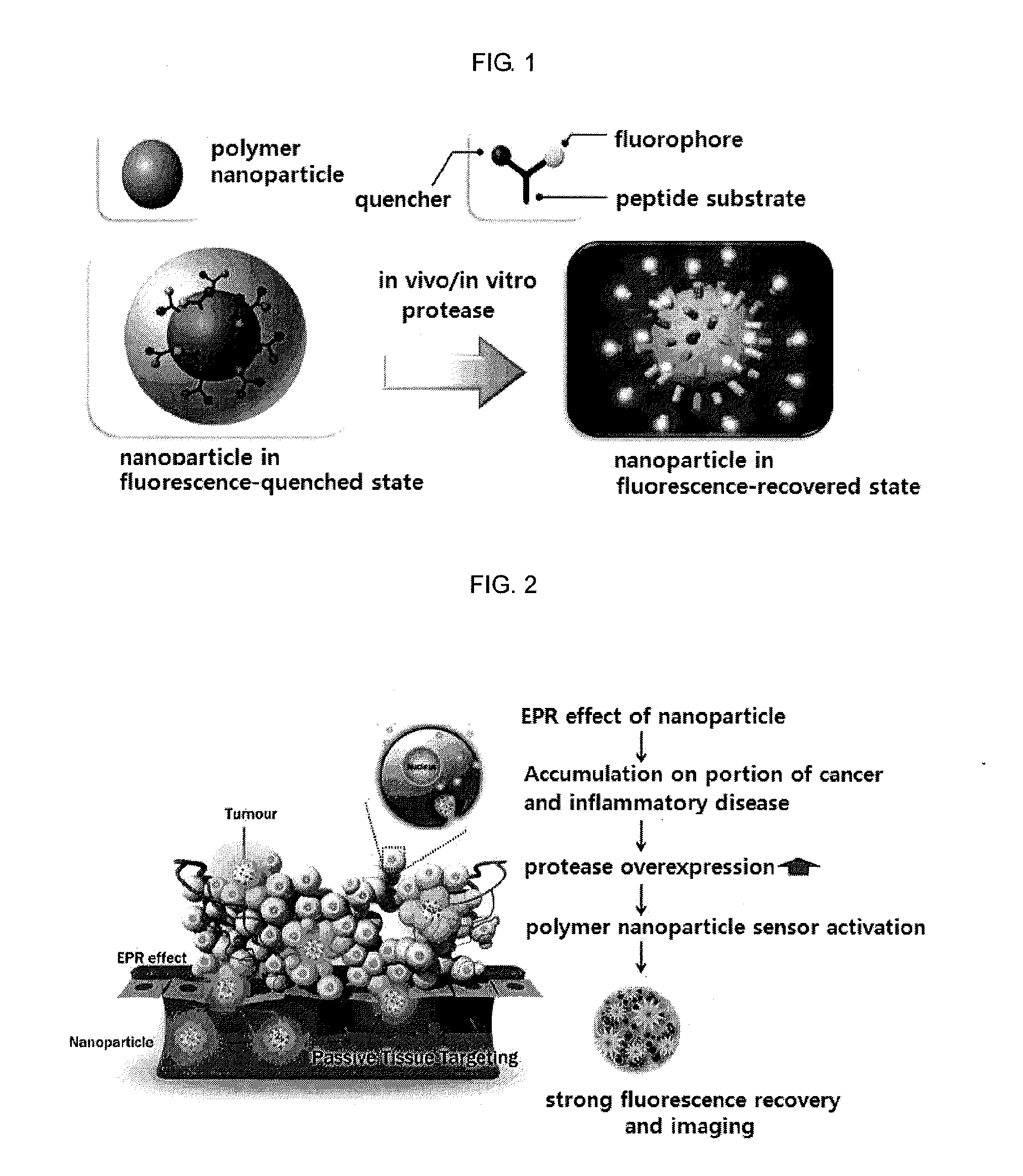
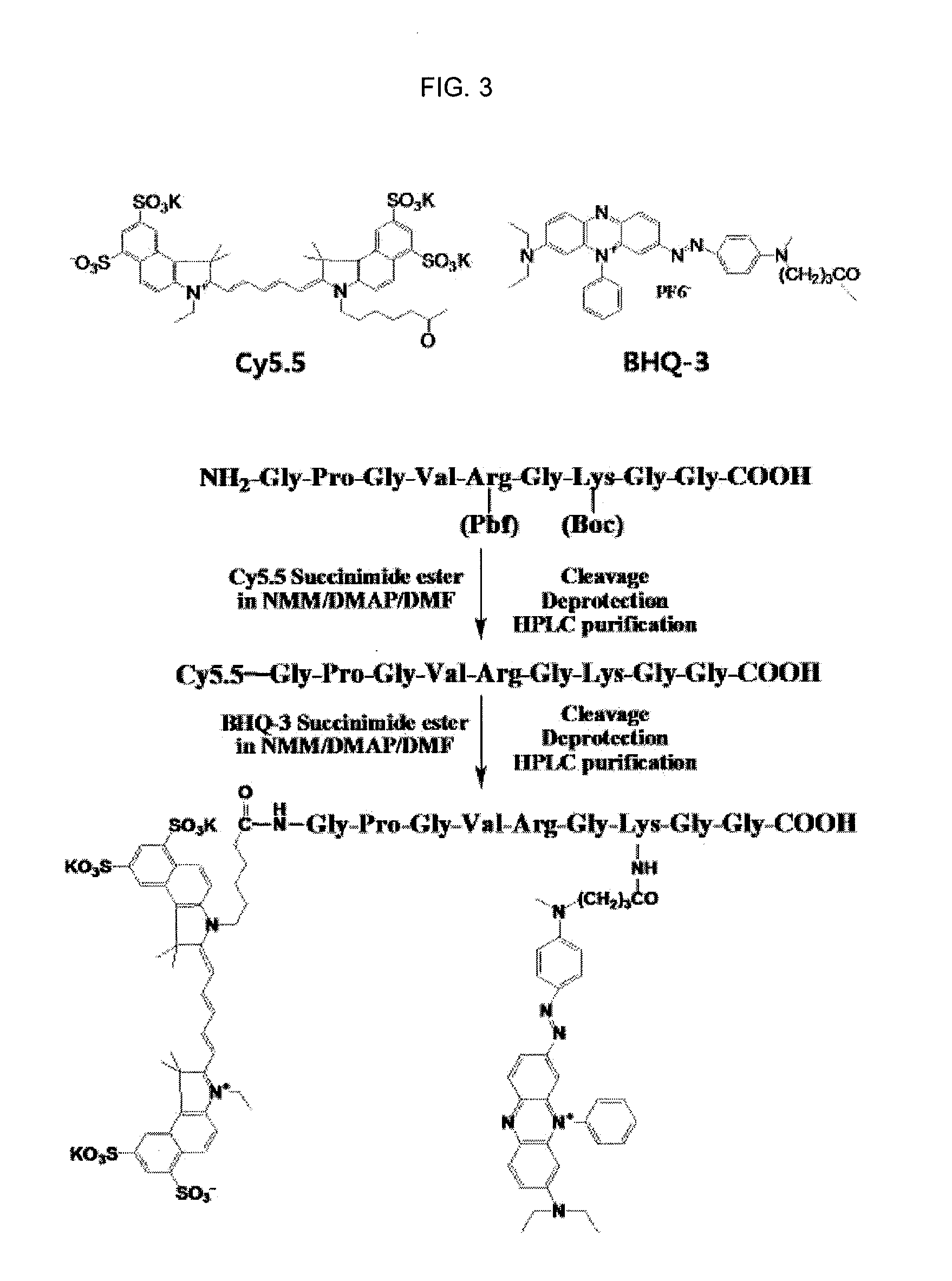
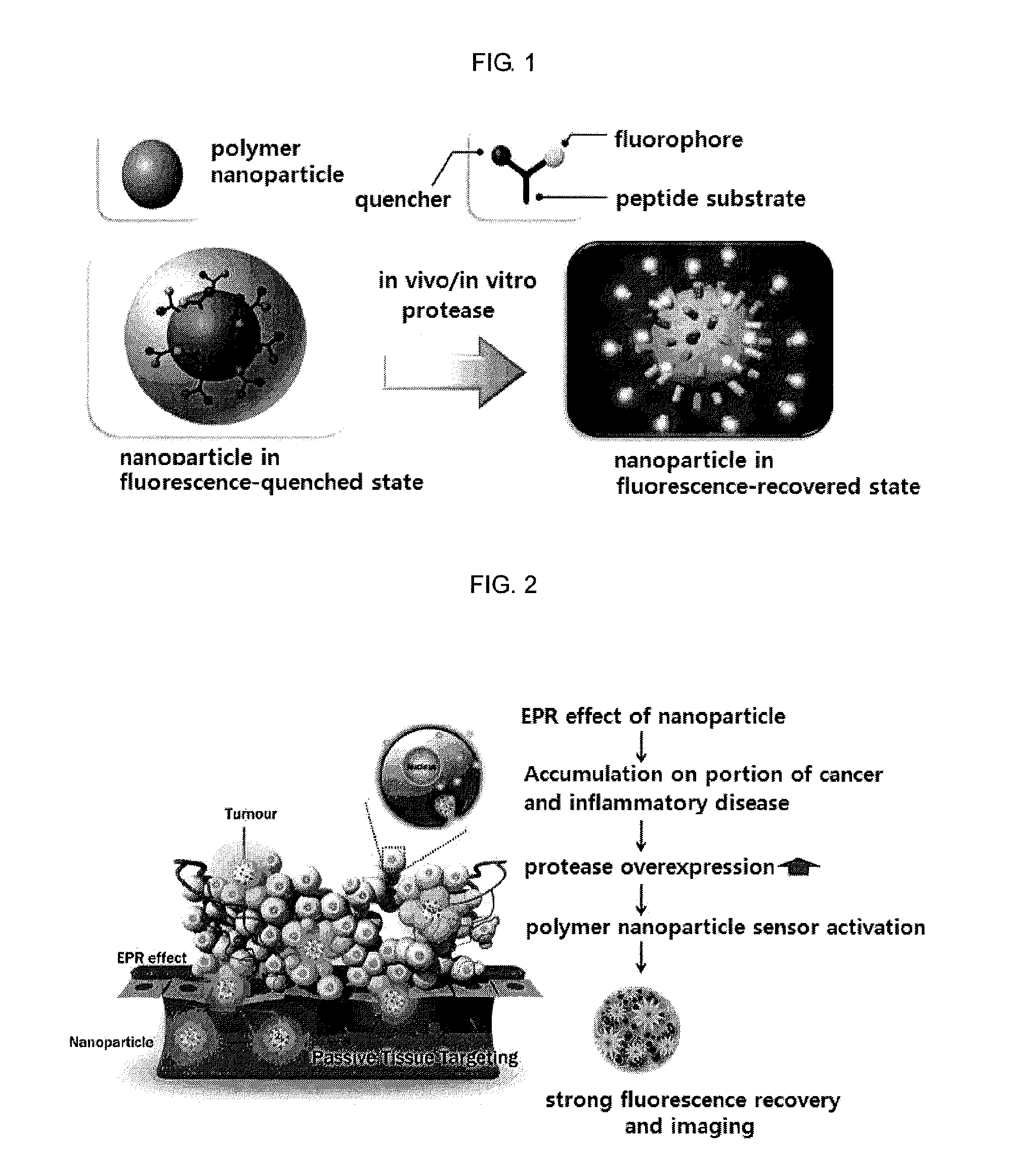
Nanoparticle sensor for measuring protease activity and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110213121A1Microbiological testing/measurementNanomedicineIncurable diseasesAutoimmune disease
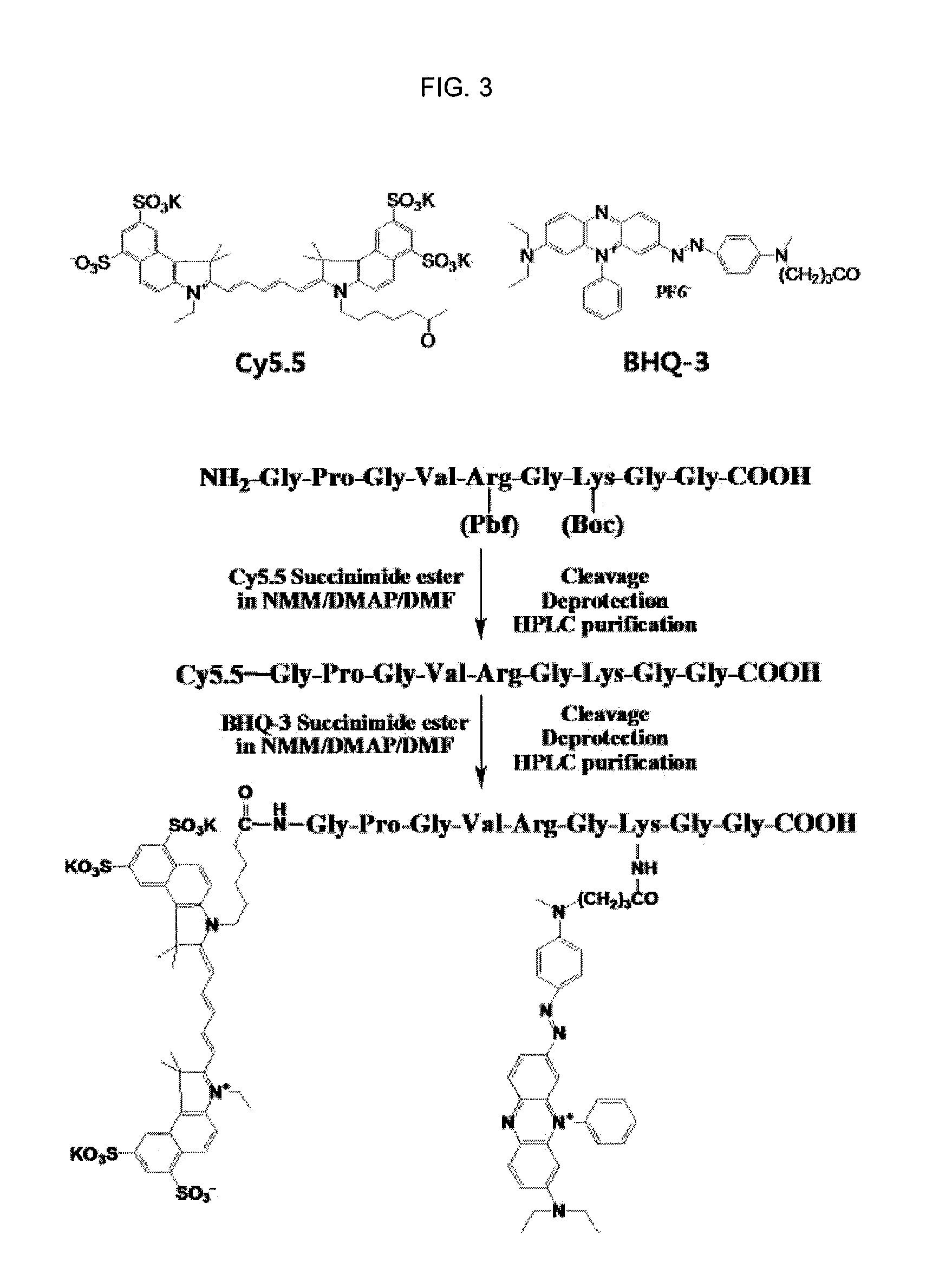
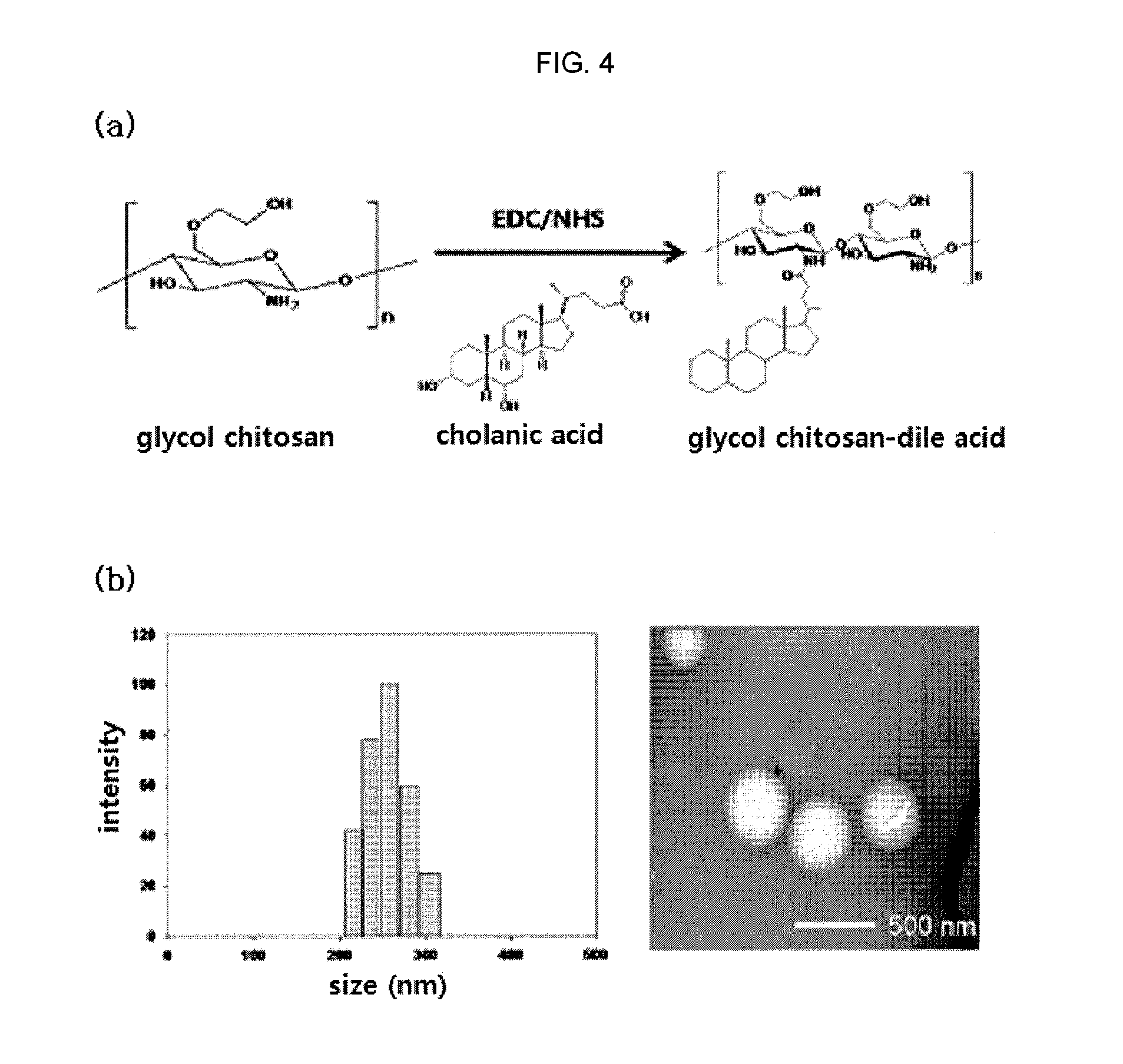
Disclosed are a nanoparticle sensor for measuring protease activity, for protease imaging, and a method for preparing the same. More specifically, the present invention relates to a nanoparticle sensor for measuring protease activity in which a fluorophore- and a quencher-conjugated peptide substrate is conjugated to a biocompatible polymer nanoparticle. The peptide substrate is specifically lysed by a protease. The sensor according to the present invention is capable of inhibiting emission of fluorescence with high extinctive activity of the quencher on a fluorescent material. But strong fluorescence is specifically emitted only if the peptide substrate is lysed by a specific protease. Therefore, the sensor is especially useful as a method for screening a novel drug such as a protease overexpression inhibitor, and early diagnosis of incurable diseases and various diseases such as autoimmune diseases including cancer, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and dementia.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH +2
Reagent and process for the identification and counting of biological cells
InactiveUS7638290B2Avoid disadvantagesShort timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological cellBiochemistry
The invention relates to a reagent and a process for the identification and counting of biological cells in a sample. This reagent comprises a cell lysing agent selected from at least one detergent in a concentration capable of specifically lysing a given type of cells in the sample, and a stain capable of marking the intracellular nucleic acids of the remaining unlysed cells. Application in particular for the identification and counting of cells using an automated analysis system based on flow cytometry.
Owner:HORIBA ABX SAS
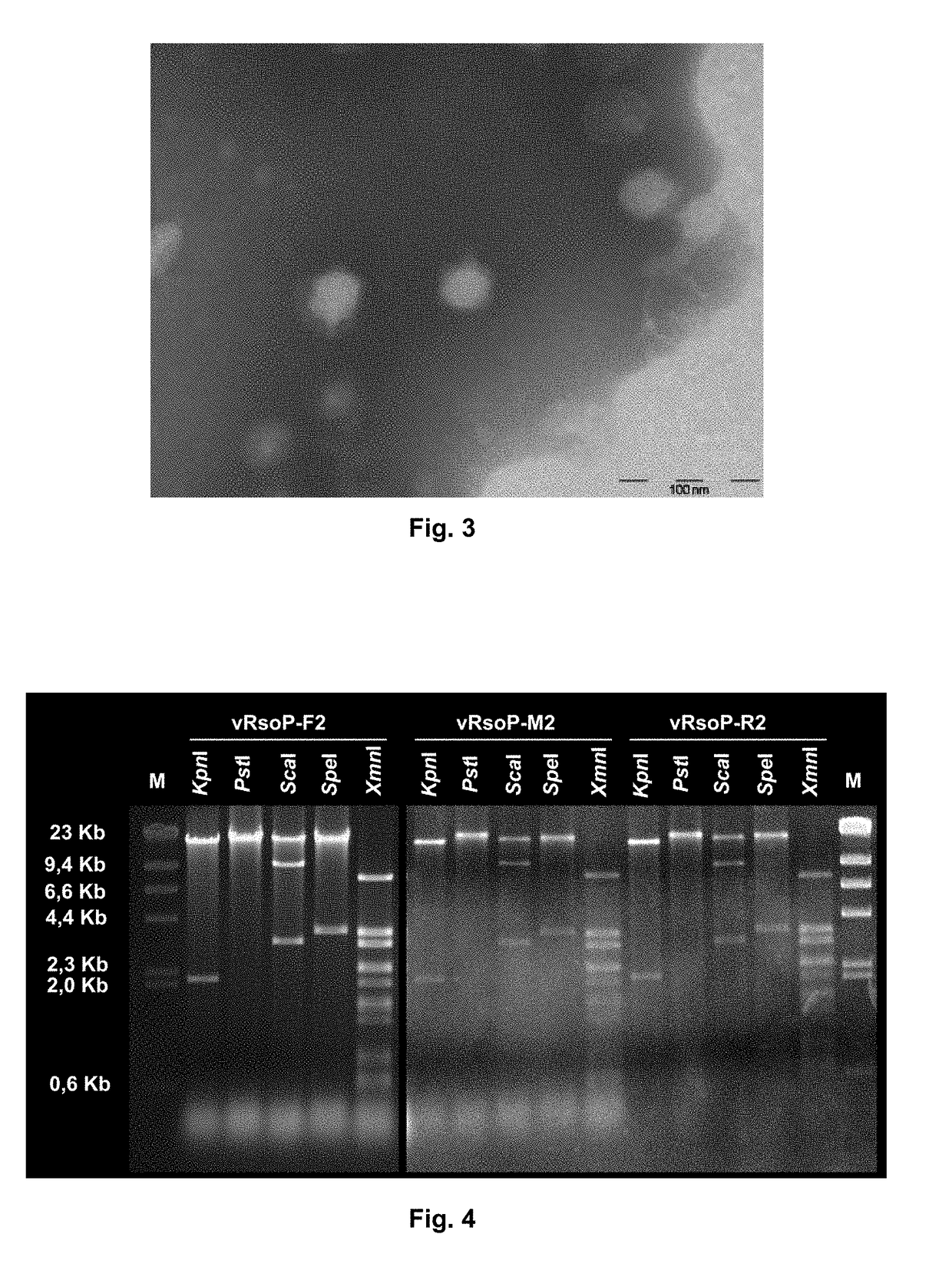
Phage for preventing and controlling soil-borne bacterial wilt, and application thereof
The invention discloses a phage for preventing and controlling soil-borne bacterial wilt, and an application thereof. The phage is a special Ralstonia solanacearum phage NN-742, and the special Ralstonia solanacearum phage NN-742 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on March 6, 2018 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2018102, and is named Podoviridae phage. The pathogen-specific phage can efficiently lyse bacteria to make the bacteria dead when used in biological control, and is nontoxic to the environment; and the phage has a strong specificity, does not destroy other normal florae, and can keep soil microbes balanced. The phage can specifically lyse bacterial wilt pathogens, and can be used to prevent and control tomato soil-borne bacterial wilt .
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
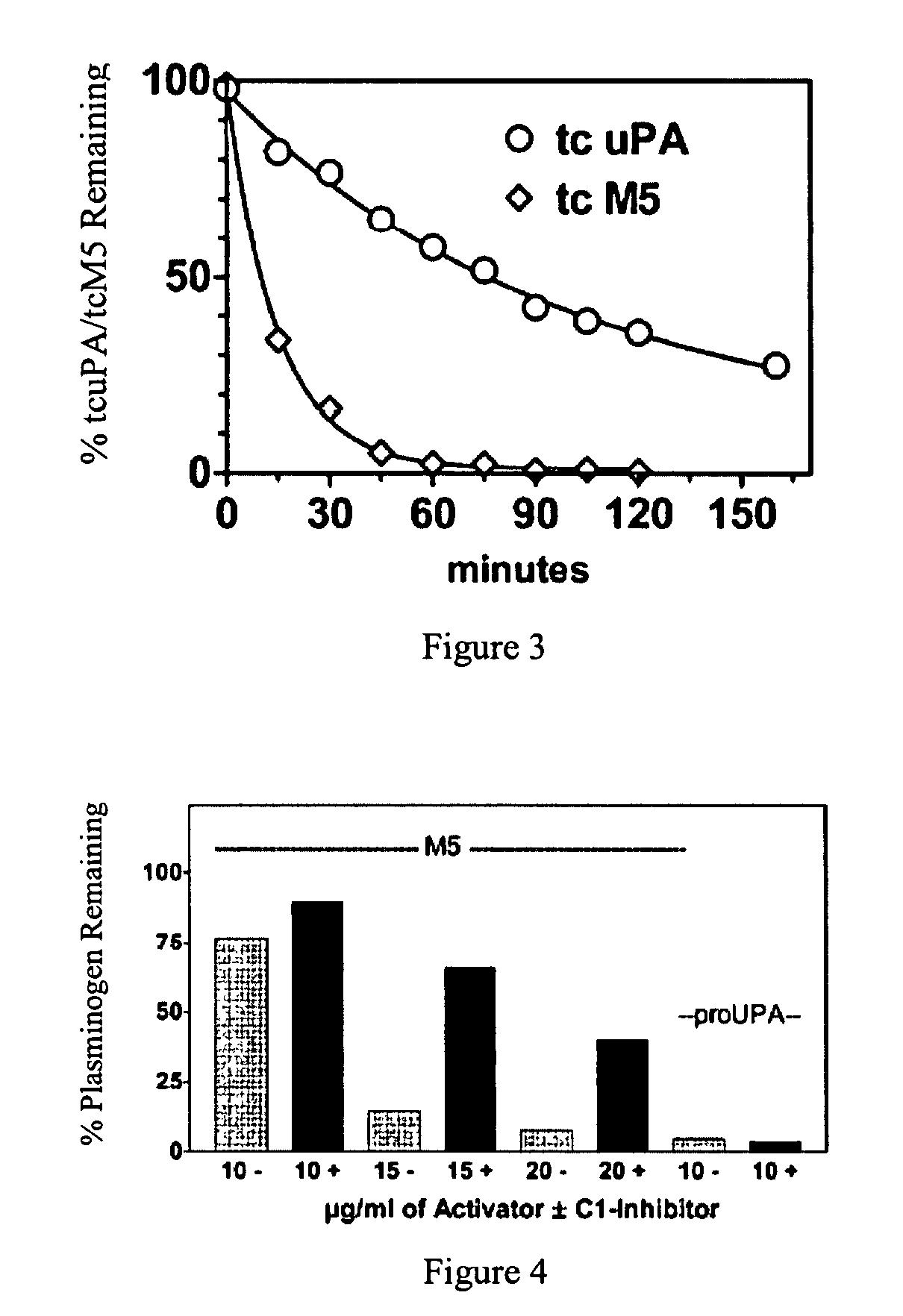
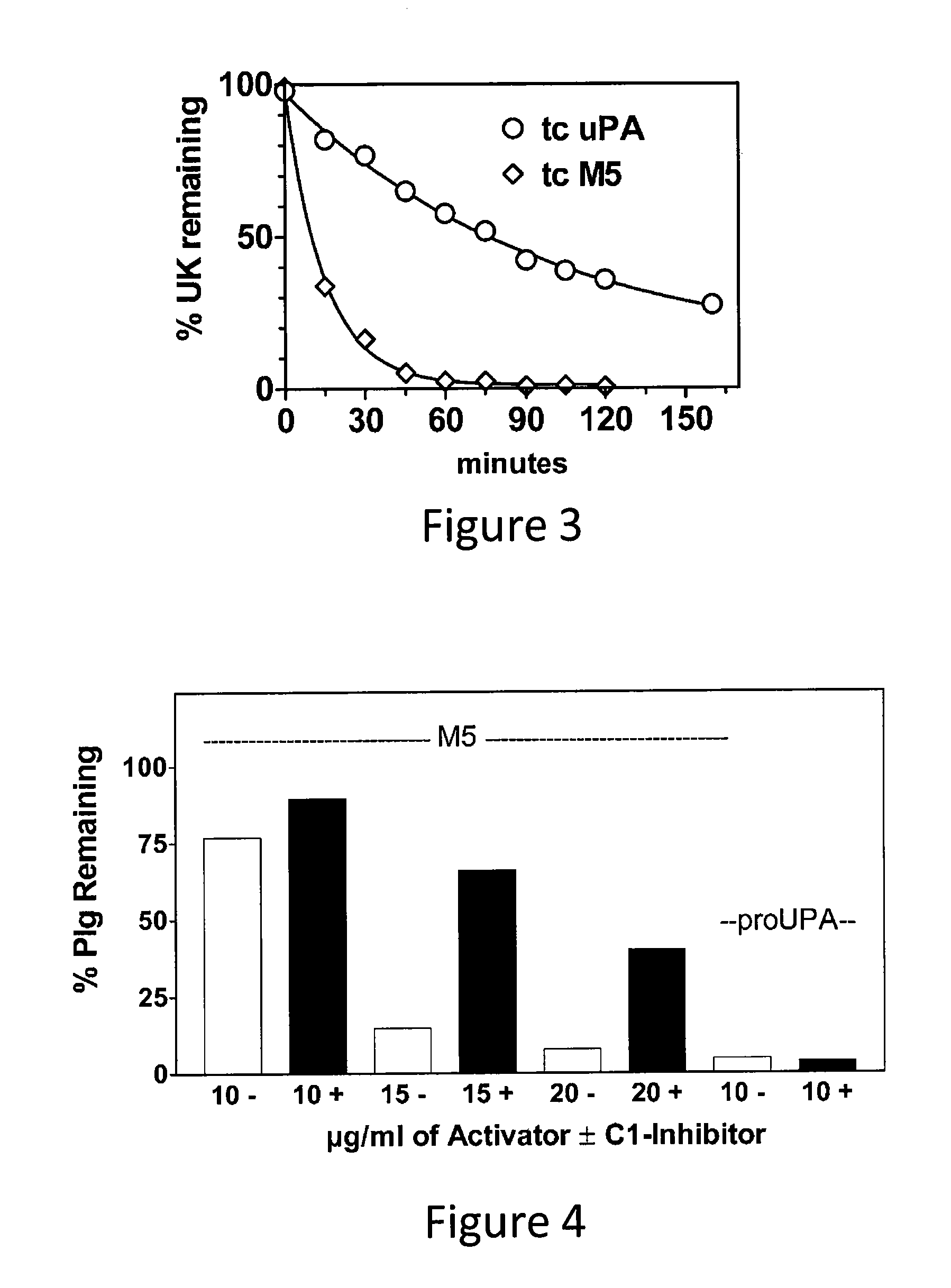
C-1 inhibitor prevents non-specific plasminogen activation by a prourokinase mutant without impeding fibrin-specific fibrinolysis
ActiveUS7837992B2Attenuation of rateHigh dose tolerancePeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderC1-inhibitorHigh doses
Owner:THROMBOLYTIC SCI +1
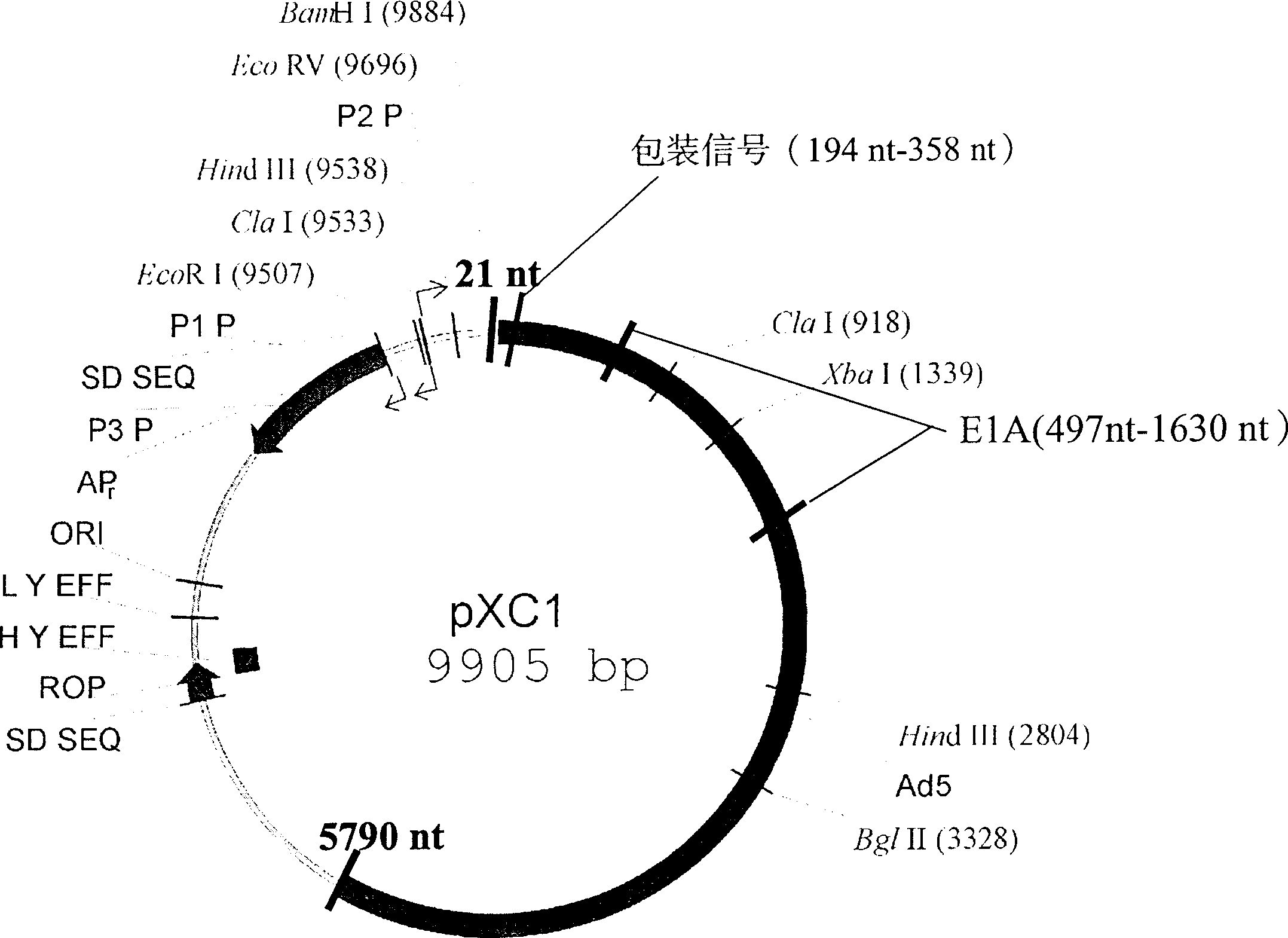
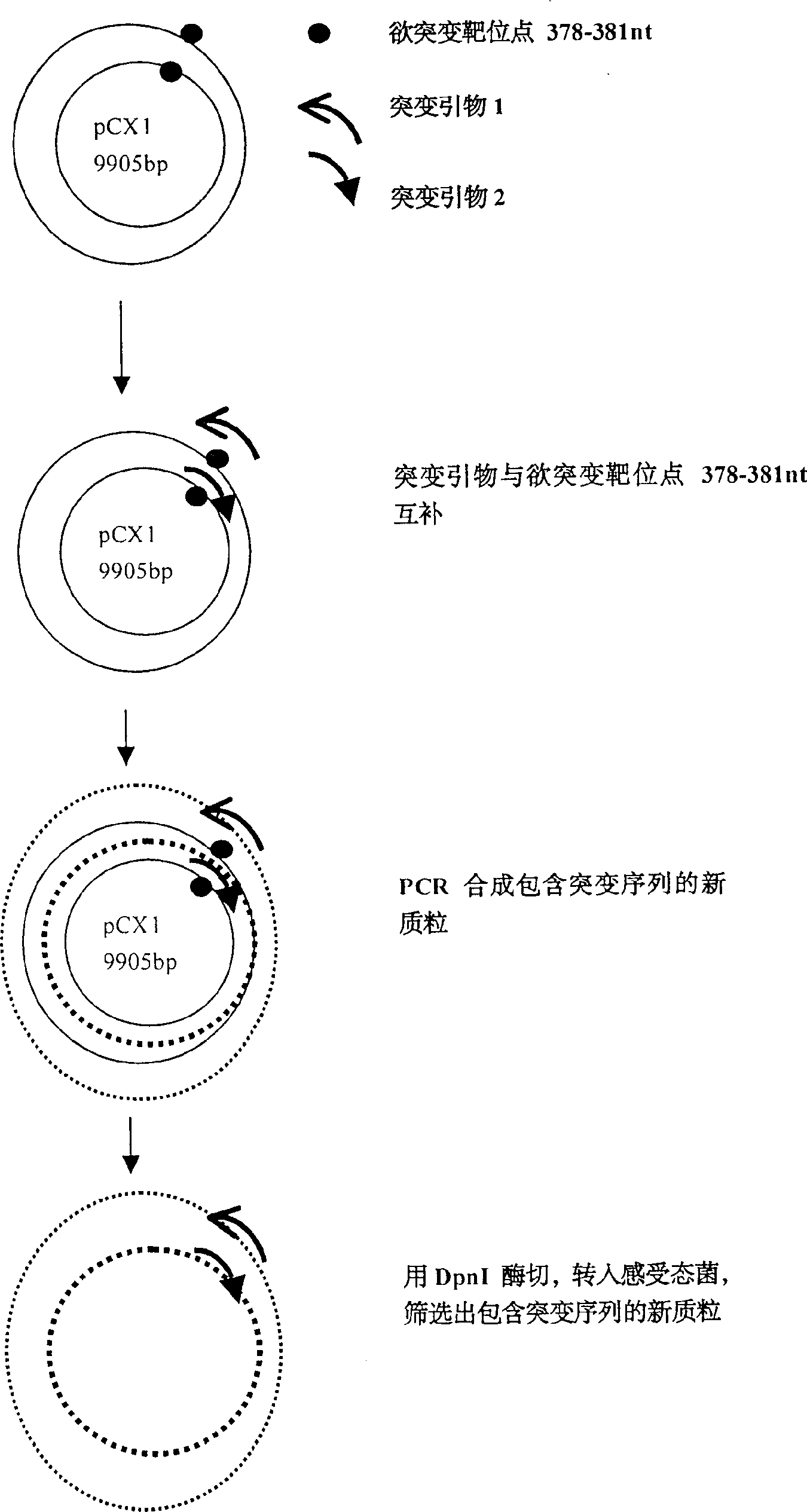
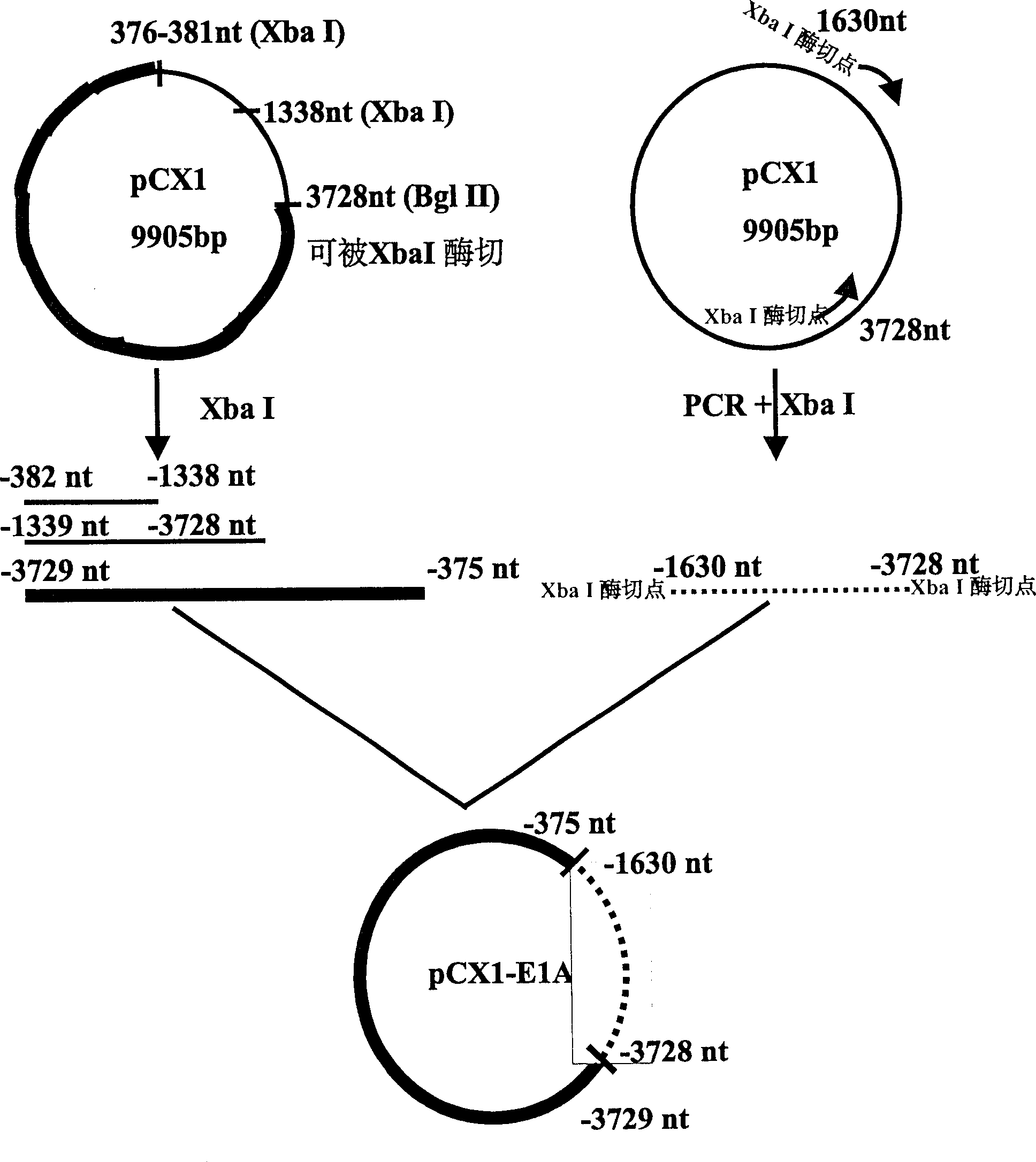
Recombination adenovirus construction body with deletion E1A code sequence and its use
InactiveCN1427075AReliable diagnosisNo significant effect on activityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsTumor cellsMutation
A recombinant adenovirus configurator deleted EIA coding sequence in human adenovirus type 5 genom and its application to diagnosing and treating tumor are disclosed. The site-directed mutation, PCR augmentation, enzyme severing, linking, subcloning, transfection, and single-cloning purification of recombinant adenovirus technologies, and the deleted EIA (382-1630 nt) sequence are used to screen the recombinant adenovirus configurator of being unable to express the EIA function protein. It can specifically kill tumor cells, but not normal cells, and has synergestic action to chemicotherapeutic medicines.
Owner:深圳市天达康基因工程有限公司
Lytic phage strain capable of preventing and controlling tomato bacterial wilt and applications of lytic phage strain
ActiveCN108642018AHigh activityStrong cracking abilityBiocideDisinfectantsBacteriophagePathogenic bacteria
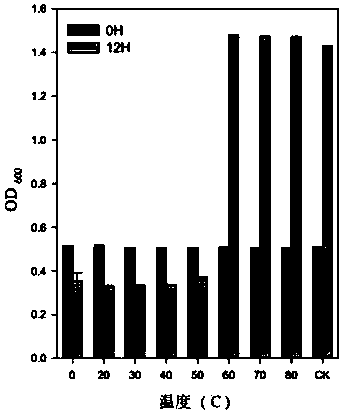
The invention discloses a lytic phage strain NJ-P3 capable of preventing and controlling tomato bacterial wilt, the classification name of the lytic phage strain NJ-P3 is Podoviridae phage, and the lytic phage strain NJ-P3 is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on March 6, 2018, and is assigned with the accession number of CCTCC NO:M 2018099. The invention further discloses applications of the phage NJ-P3 in preventing and treating soil-borne bacterial wilt of tomato and applications of the phage NJ-P3 in preparing phage preparations for preventing and treating soil-borne bacterial wilt of tomato. The phage can realize specific splitting of pathogenic bacteria of bacterial wilt, when the temperature is 20-40 DEG C and the pH is 5-9, the phage has the highest activity and the strongest splitting capacity, the bactericidal ability is shown, the indoor antibacterial test shows that the antibacterial rate achieves 72.4%, and thus the phage can be used for preventing and treating soil-borne bacterial wilt of tomato. When the phage provided by the invention is used for preventing and treating soil-borne bacterial wilt of tomato, the disease prevention rate for the potted plant achieves 60%, and the biocontrol rate for the field achieves 85.19%.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for extracting DNA from plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and particularly relates to a method for extracting DNA from a plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol. The provided method for extracting DNA from the plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol comprises the following steps: using a specific lysis solution to lyse a cell, extracting the DNA with Tris phenol-chloroform mixed solution, chloroform and a sodium perchlorate combination solution, and purifying the extracted DNA through a self-made adsorption column membrane, thereby obtaining the high-quality genomic DNA. The purity of the DNA extracted through the method for extracting DNA from the plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol is high, the impurity is low, the DNA is further prevented from being damaged by asuperoxide anion free radical or active oxygen, the completeness of the extracted genomic DNA is guaranteed, and the method is favorable for the scientific researches like construction of the gene library, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analysis, and Southern hybridization.
Owner:广州海思医疗科技有限公司
Nanoparticle sensor for measuring protease activity and method for manufacturing the same
Disclosed are a nanoparticle sensor for measuring protease activity, for protease imaging, and a method for preparing the same. More specifically, the present invention relates to a nanoparticle sensor for measuring protease activity in which a fluorophore- and a quencher-conjugated peptide substrate is conjugated to a biocompatible polymer nanoparticle. The peptide substrate is specifically lysed by a protease. The sensor according to the present invention is capable of inhibiting emission of fluorescence with high extinctive activity of the quencher on a fluorescent material. But strong fluorescence is specifically emitted only if the peptide substrate is lysed by a specific protease. Therefore, the sensor is especially useful as a method for screening a novel drug such as a protease overexpression inhibitor, and early diagnosis of incurable diseases and various diseases such as autoimmune diseases including cancer, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and dementia.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH +2
Toxic Microcystis cracking cyanophage and separation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105176933AStrong specificityNo harmRecovery/purificationBiological water/sewage treatmentCyanophagesMicroorganism
The invention discloses toxic Microcystis cracking cyanophage and a separation method and application thereof. The toxic Microcystis cracking cyanophage is characterized in that the cyanophage is a MaSSC-P strain, is classified and named as Microcystis aeruginosa single-stranded DNA cyanophage MaSSC-P, collected at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 25th May, 2015 and numbered as CGMCC No.10598. A purified cyanophage suspension is added into a Microcystis water sample, and the toxic Microcystis cracking cyanophage has specific cracking effect on Microcystis in the water sample and has cracking effect on Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis wesenbergii and Microcystis viridis. The toxic Microcystis cracking cyanophage has the advantage of being capable of safely, efficiently and quickly cracking toxic Microcystis in fresh water.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
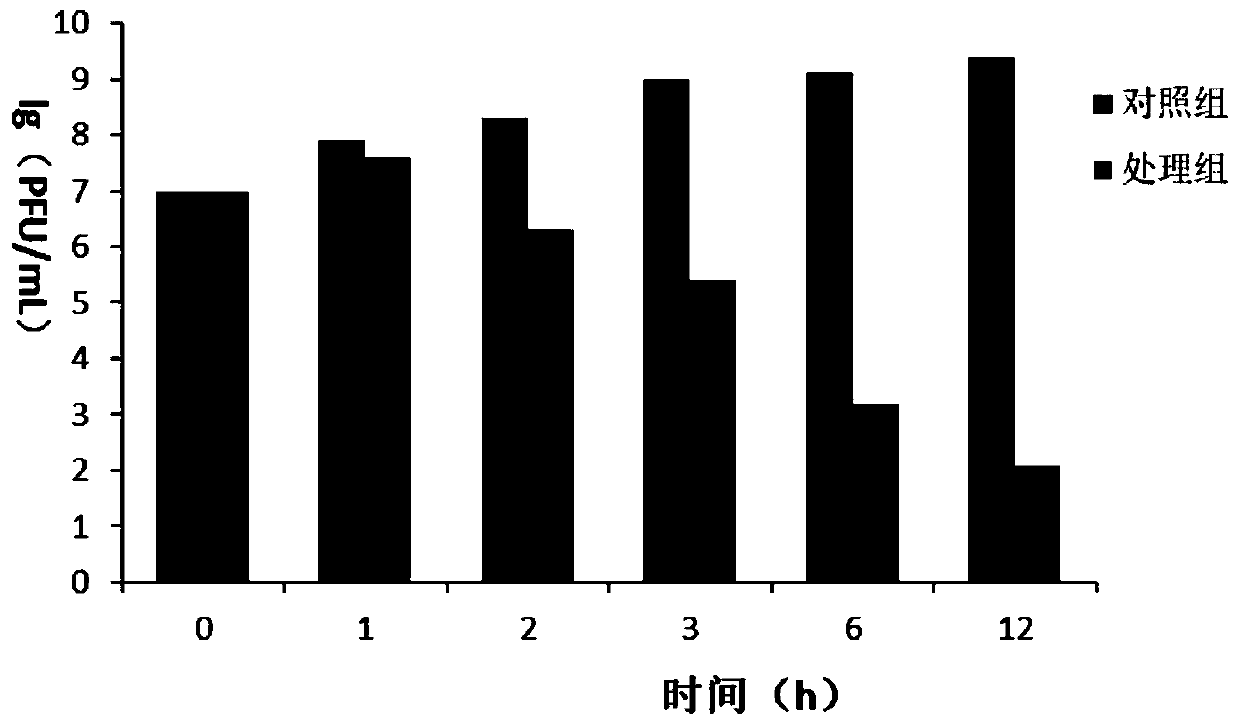
Staphylococcus aureus phage and bacteriostatic application thereof
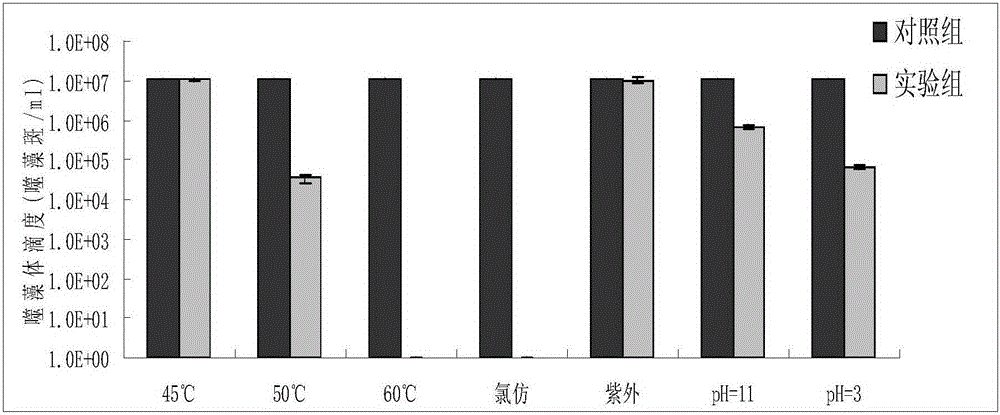
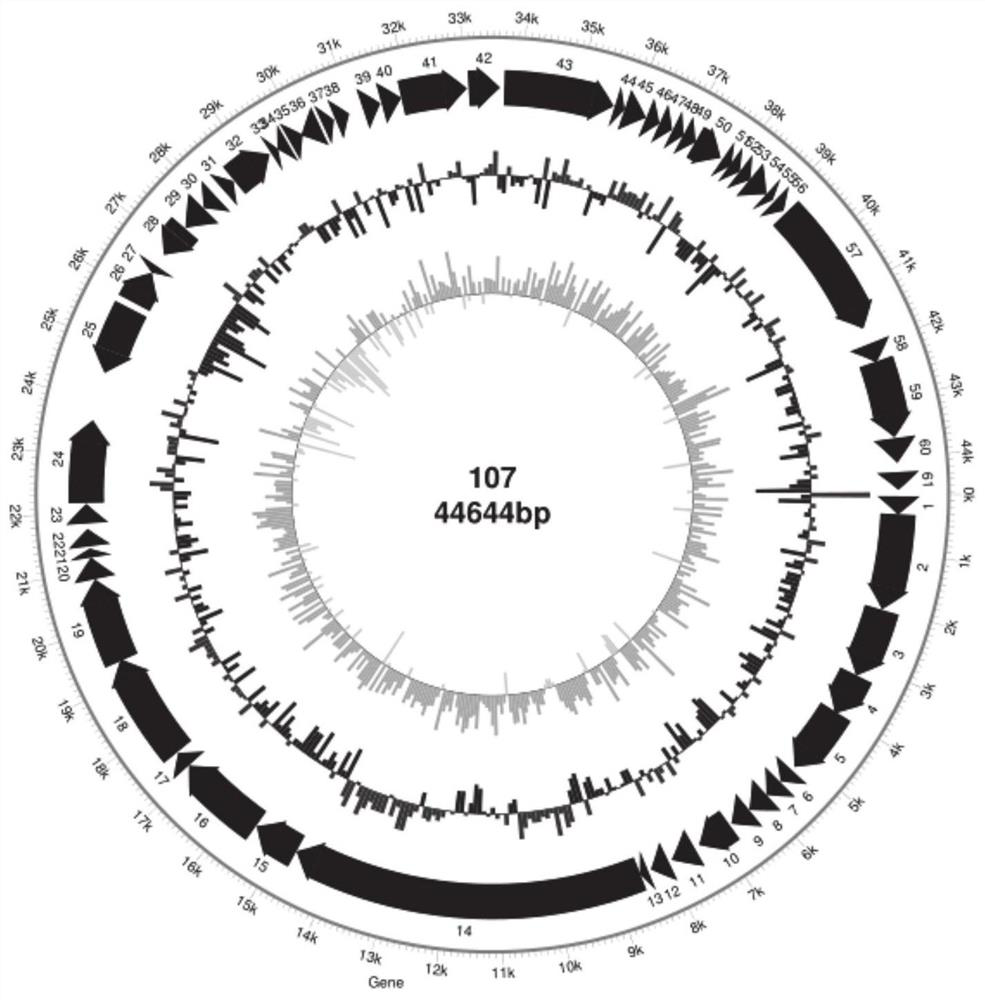
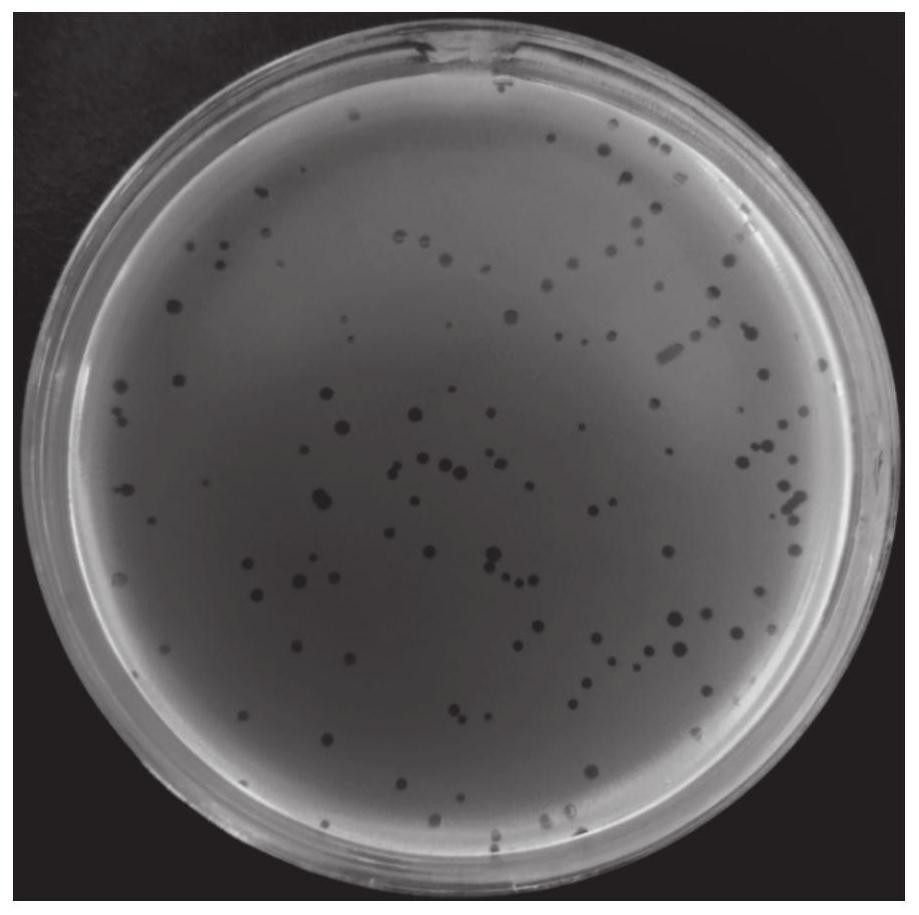
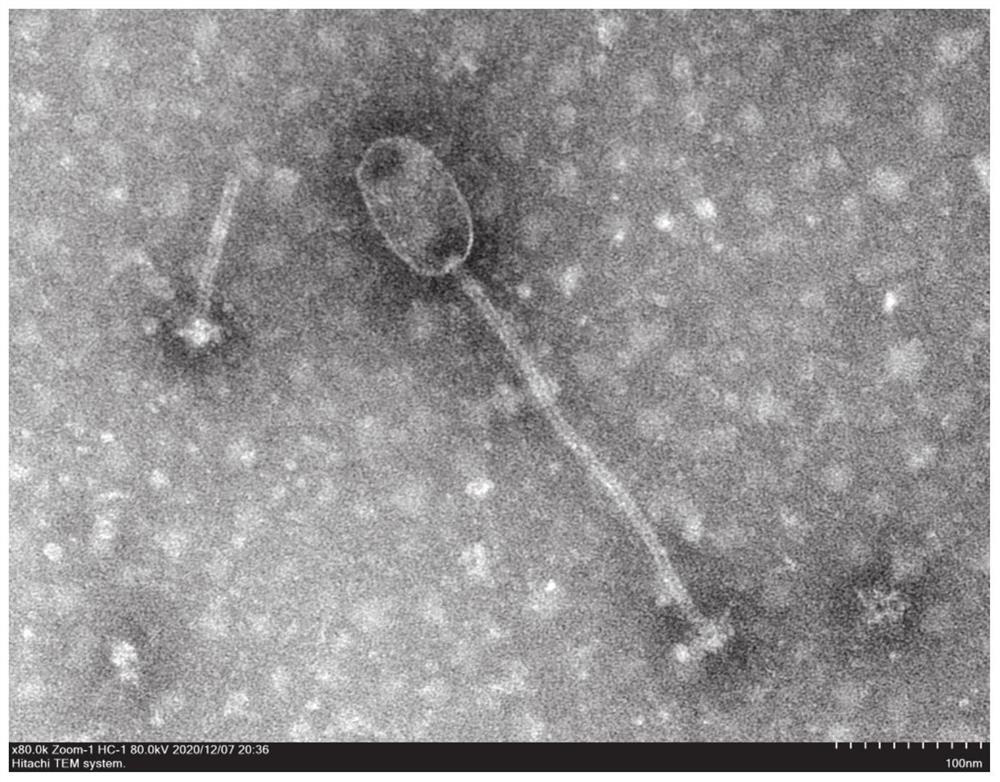
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a Staphylococcus aureus phage and bacteriostatic application thereof. The Staphylococcus aureus phages107 is sent to China Center for Type Culture Collection for Preservation, the classification name is Staphylococcus aureus phages107, the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2021125, the preservation date is January 21, 2021, and the address is Wuhan University, Wuhan City, China. The phages107 has high titer up to 2.31 * 10<10>PFU / mL, good pH stability, good temperature stability and wide lysis spectrum, and has lysis ability on 9 strains of Staphylococcus aureus, wherein the 9 strains of Staphylococcus aureus have certain drug resistance and no lysis ability on escherichia coli. The Staphylococcus aureus phage has specific lysis spectrum for Staphylococcus aureus, and has strong lysis ability. The Staphylococcus aureus phages107 can be used for preparation of drugs for treating Staphylococcus aureus induced dairy cow mastitis and other diseases.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
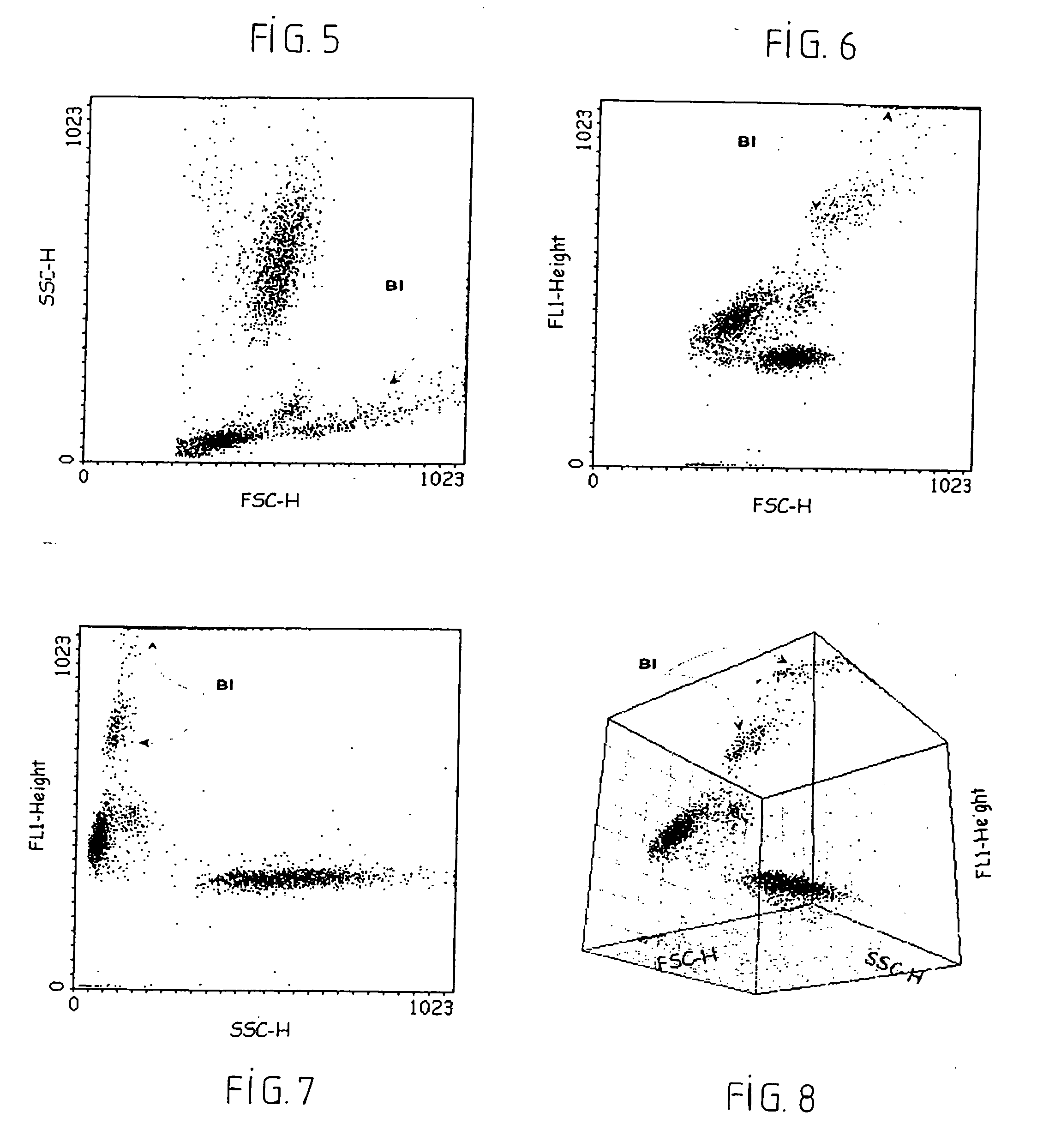
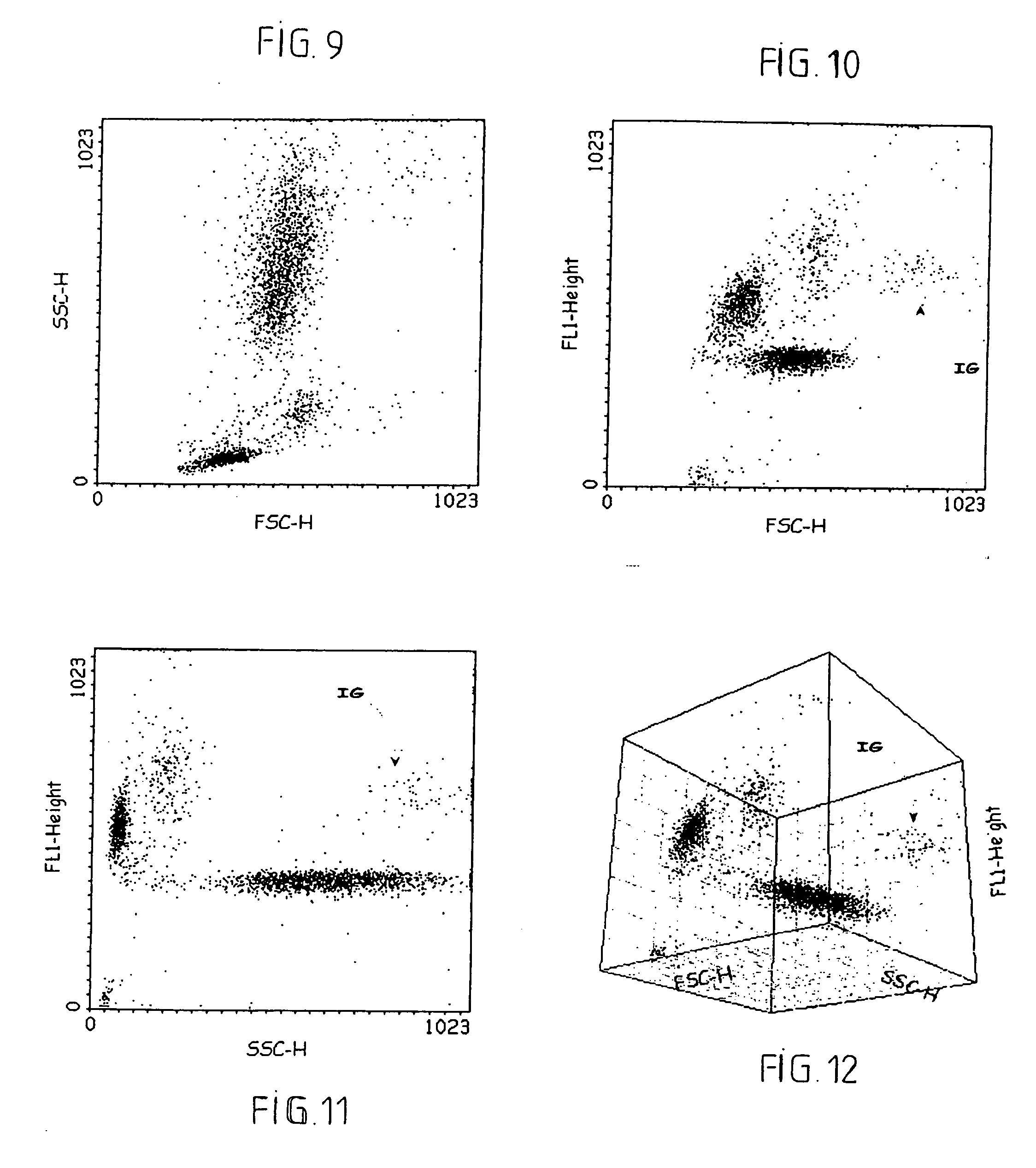
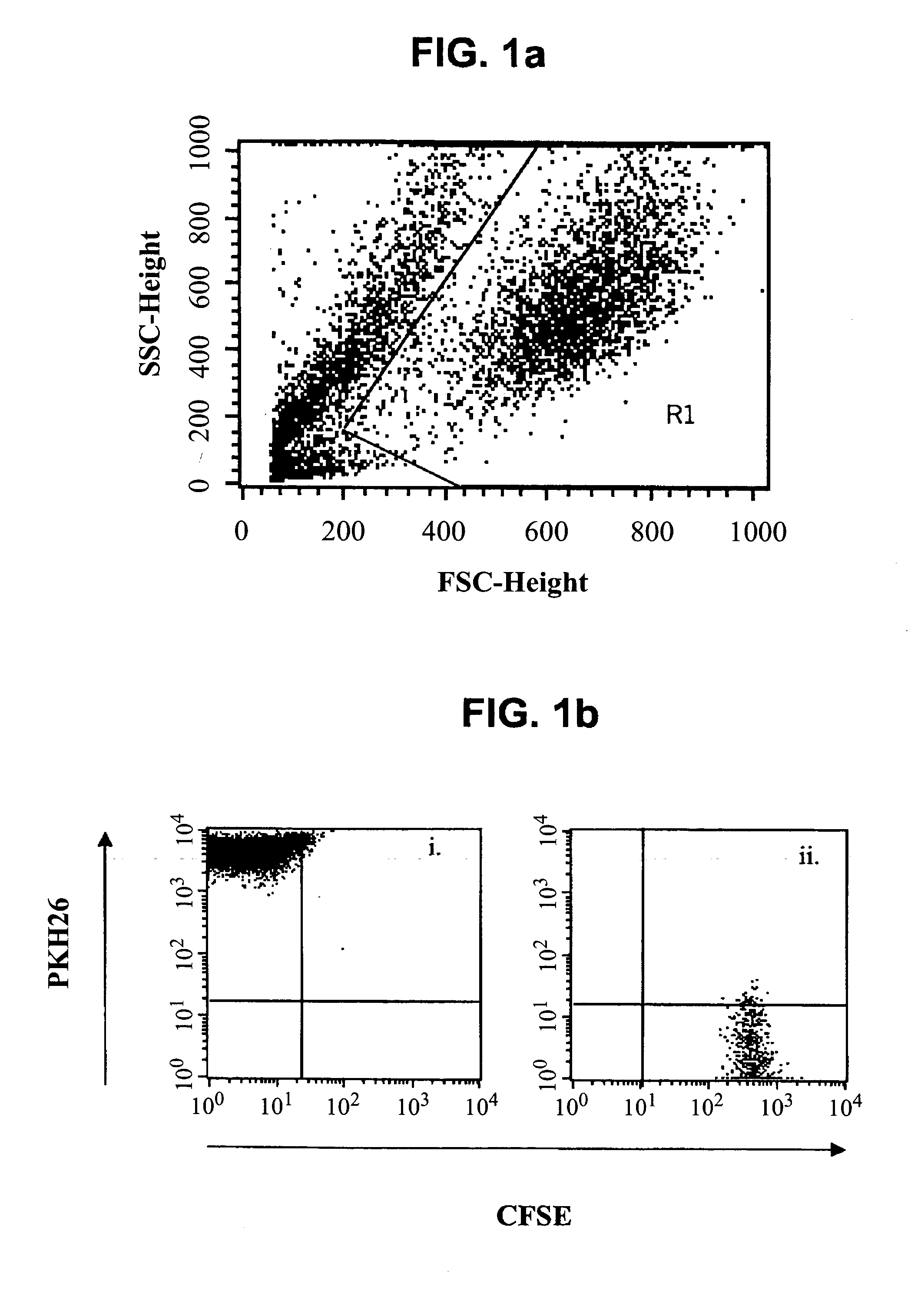
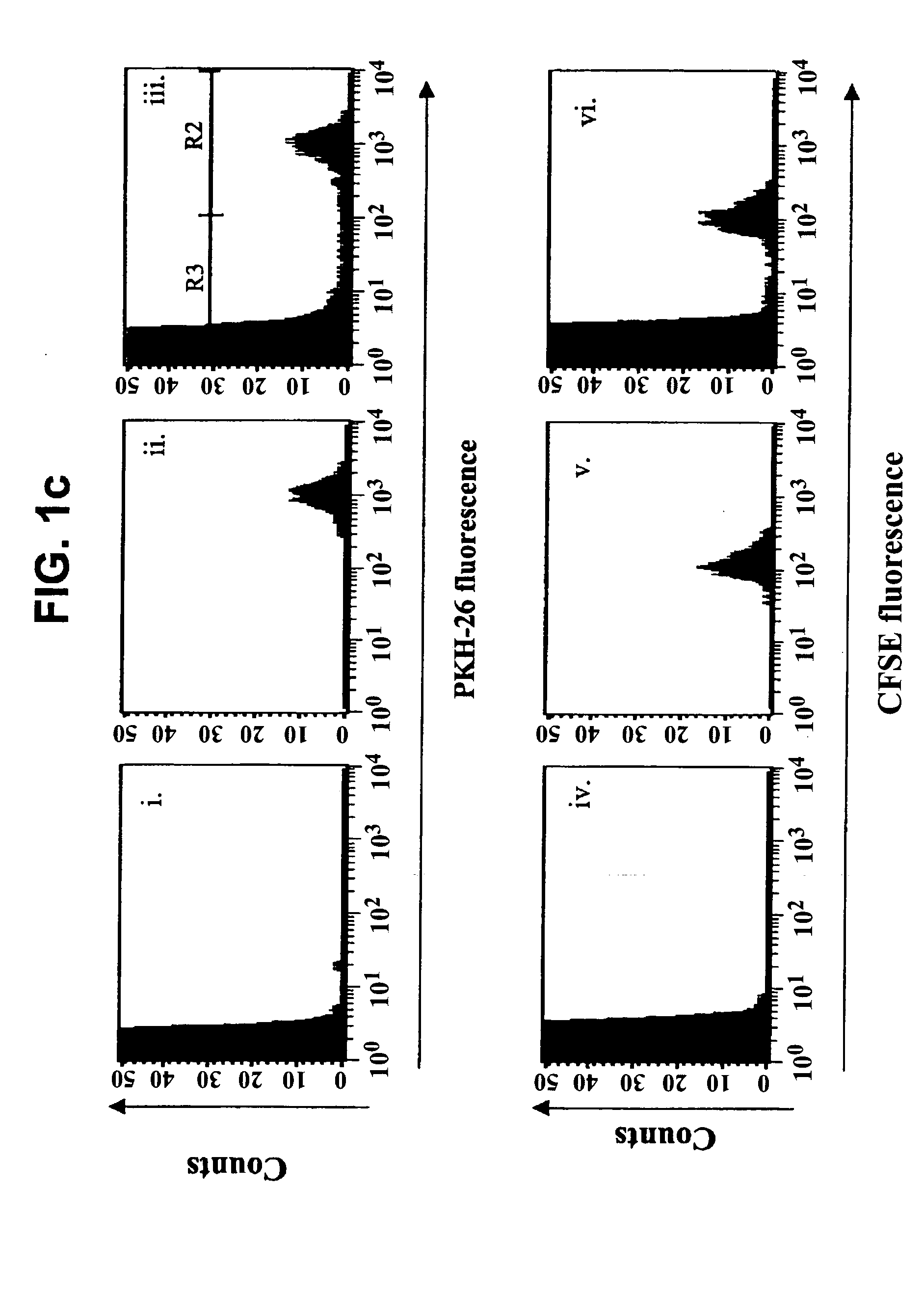
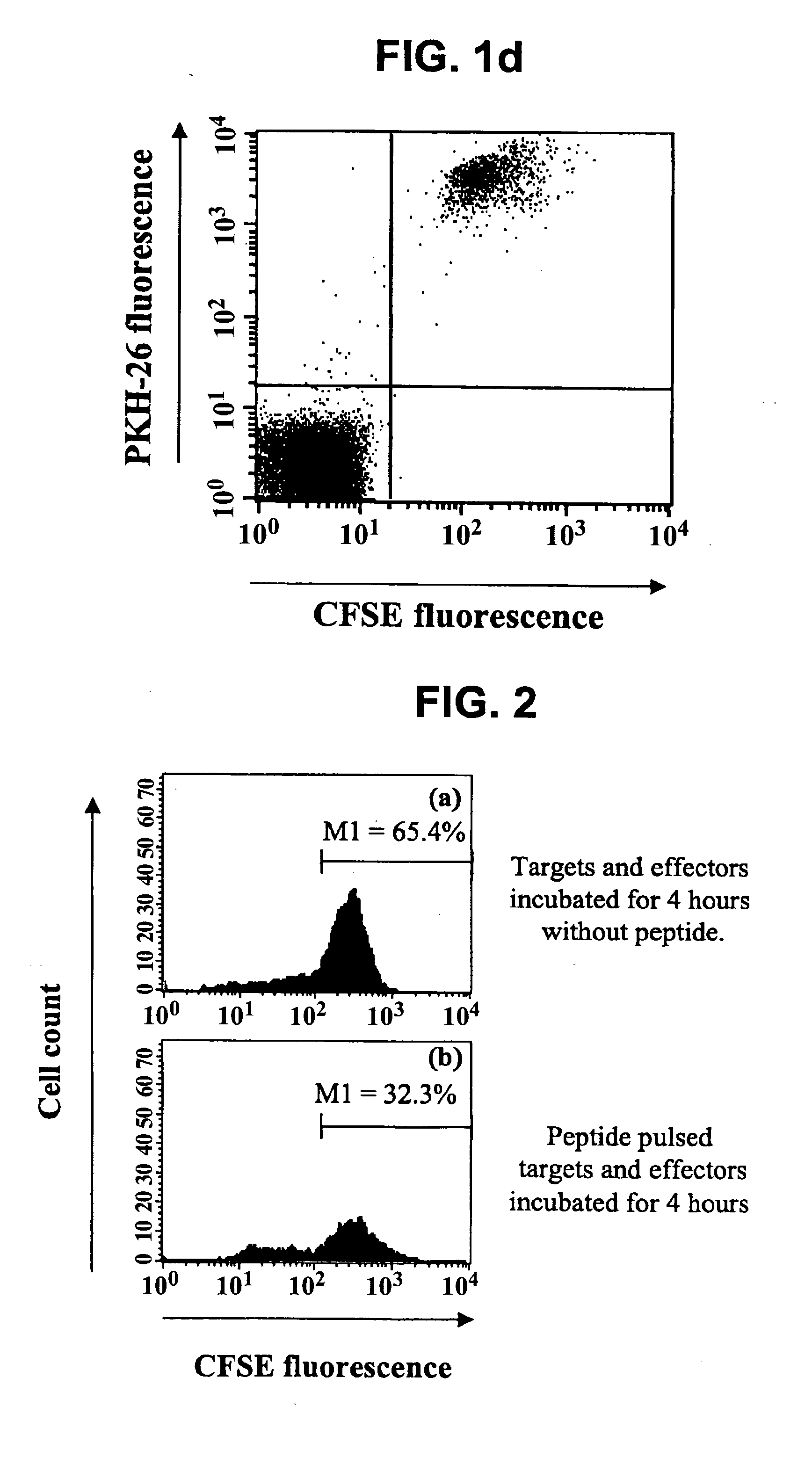
Methods of detecting specific cell lysis
The present invention provides methods of detecting specific lysis of a cell by a lytic agent. The methods generally involve contacting a labeled target cell with a lytic agent; and detecting fluorescence in the target cell. The target cells are labeled with two fluorescent labels: a first fluorescent label that labels the plasma membrane; and a second fluorescent label that labels the cytosol. Release of the cytosolic label from the target cell indicates that the target cell has been lysed. The invention further provides methods of detecting the presence in a sample of a cell that specifically lyses a target cell. The invention further provides methods of detecting the presence in a sample of an antibody that specifically lyses a target cell. The methods are useful in a variety of applications.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
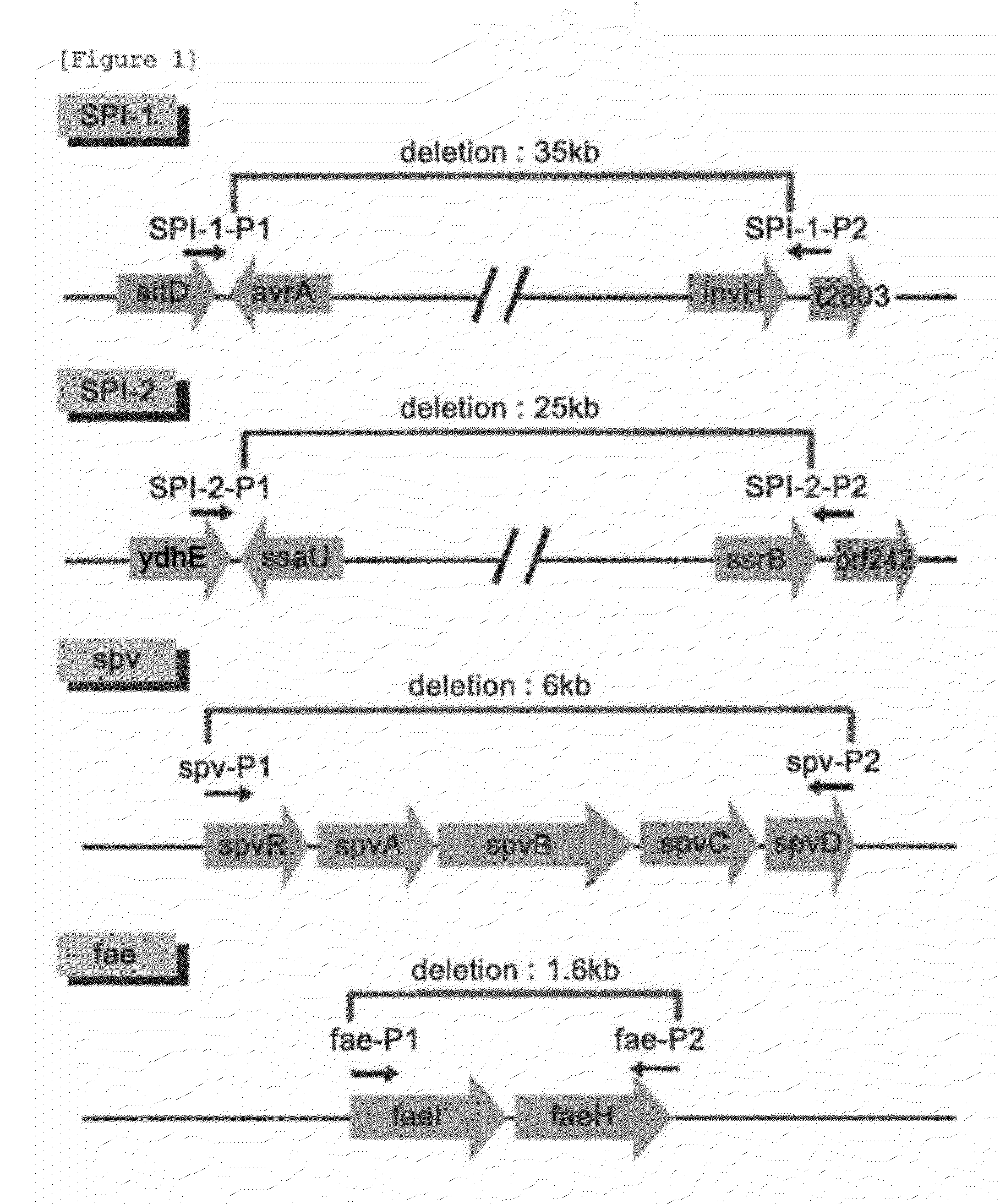
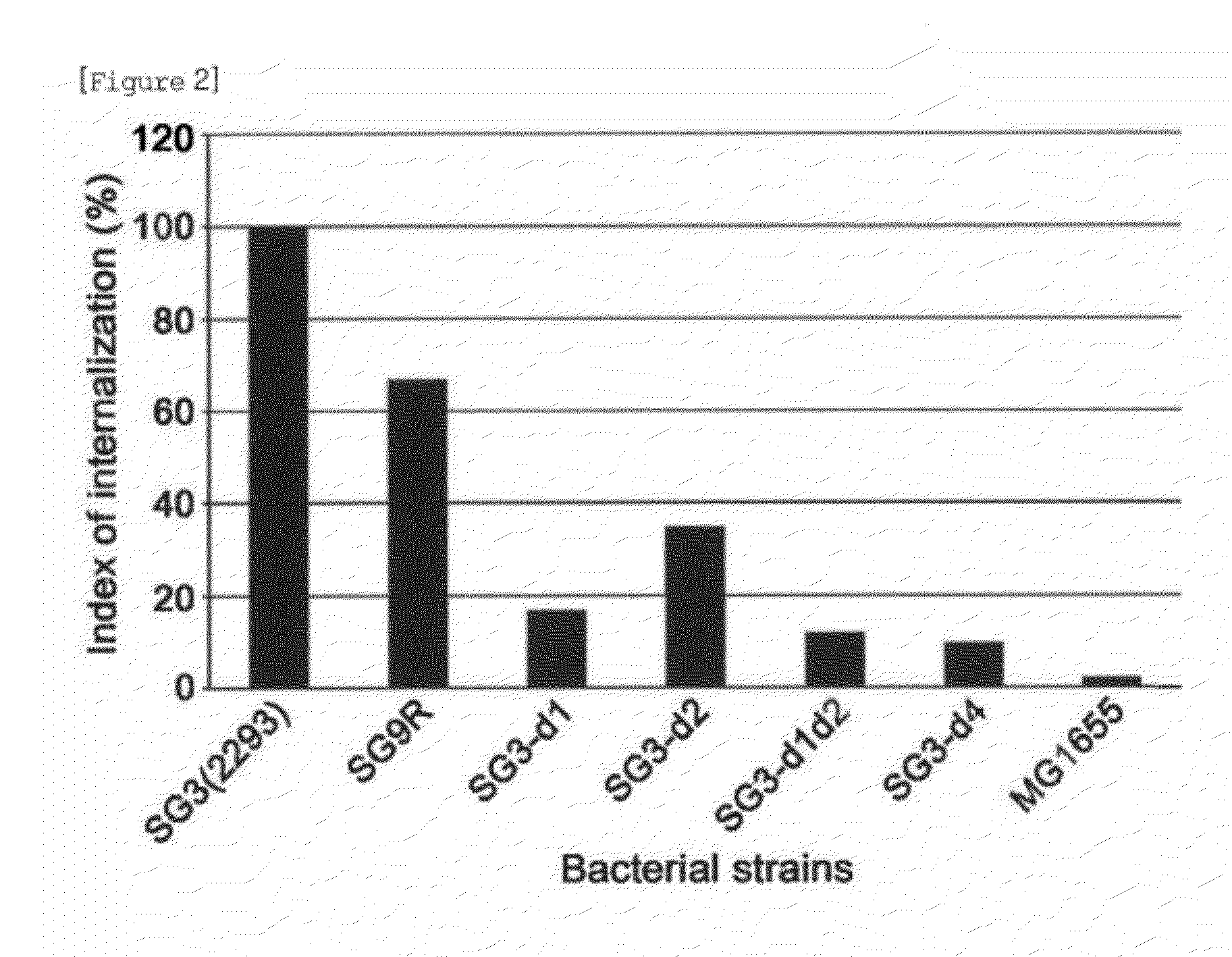
Avirulent Salmonella Gallinarum Variants and Pharmaceutical Composition Using the Same
ActiveUS20120294892A1Increase valueAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsSalmonella GallinarumVirulent characteristics
The present invention relates to avirulent Salmonella Gallinarum variants by inactivating virulence gene clusters of Salmonella Gallinarum (SG), a main pathogen of avian salmonellosis, and various uses thereof notably in the production of Salmonella-specific lytic bacteriophages, pharmaceutical compositions and feed additives.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
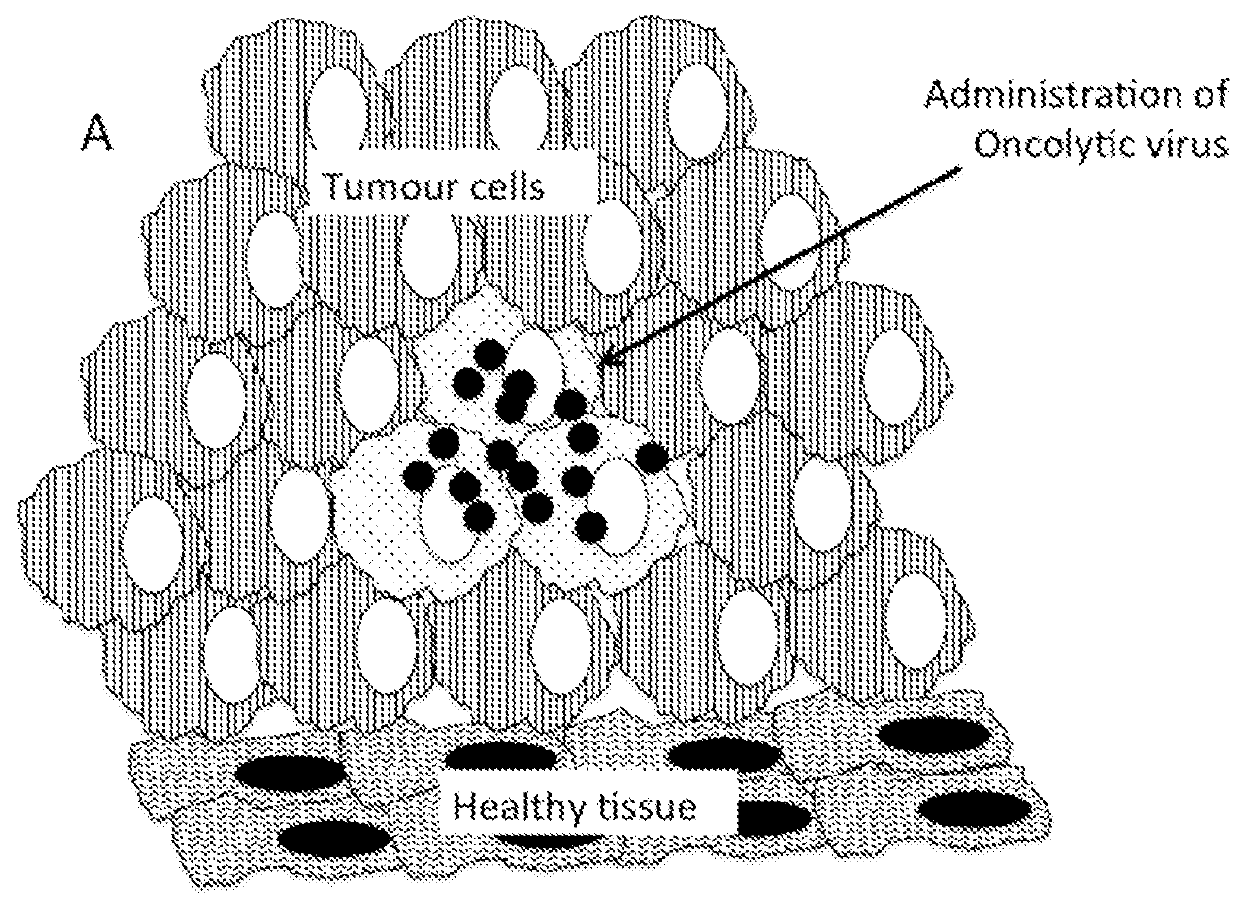
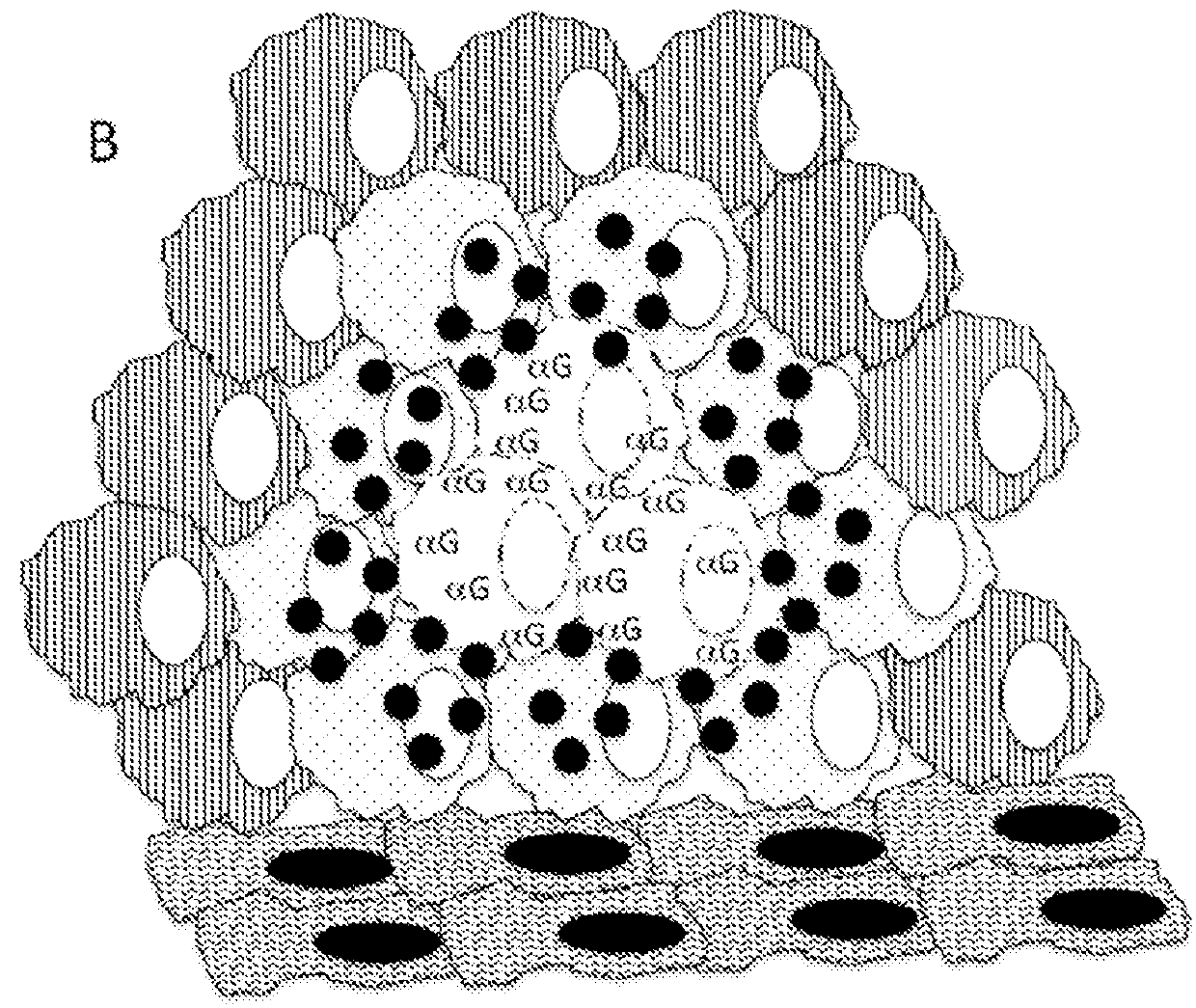
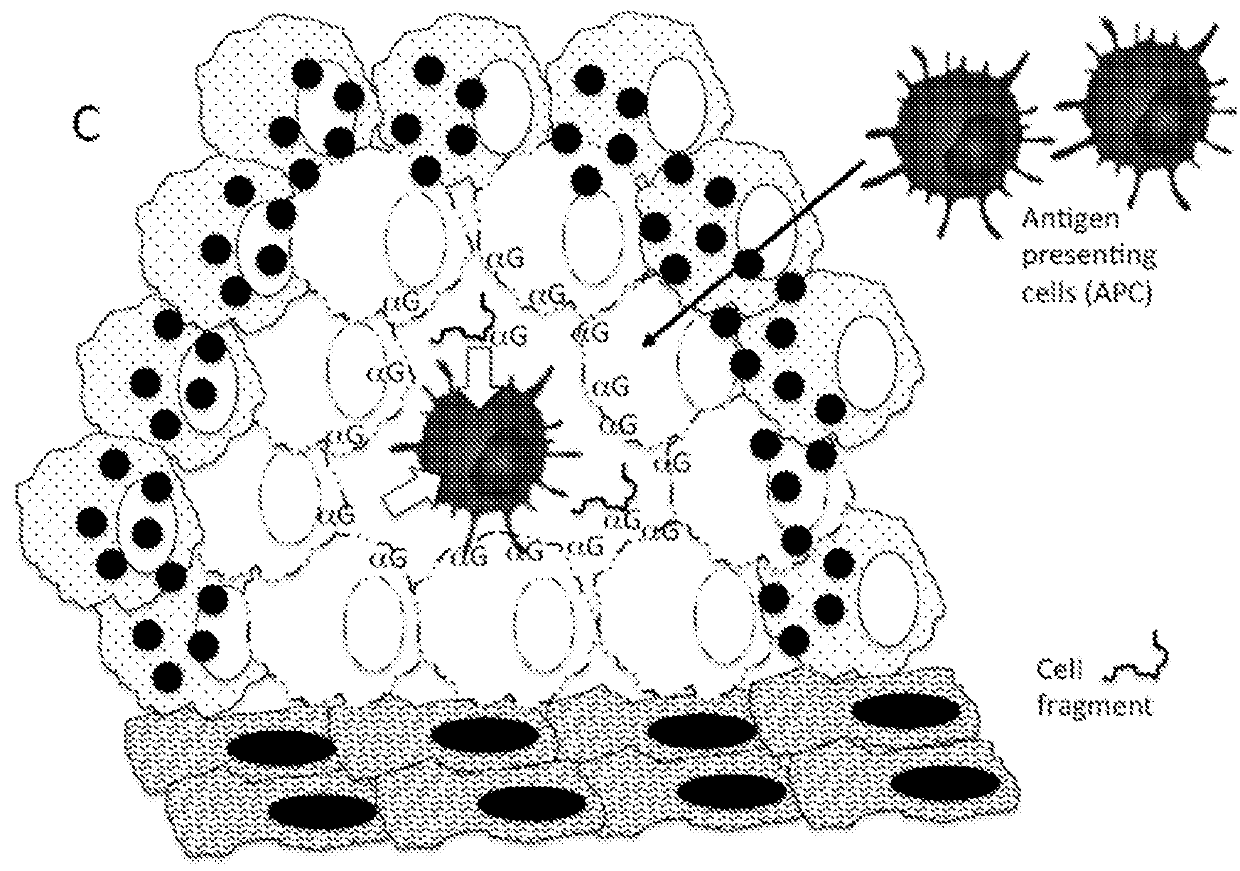
Therapeutic compositions and methods of use for treating cancer
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for treating cancer. More specifically, the present invention relates to compositions of engineered oncolytic viruses for administration to a subject with cancer that specifically lyse tumor cells and actively target tumor cells and cell debris to antigen presenting cells, in order to generate anti-tumor immunity.
Owner:AGALIMMUNE
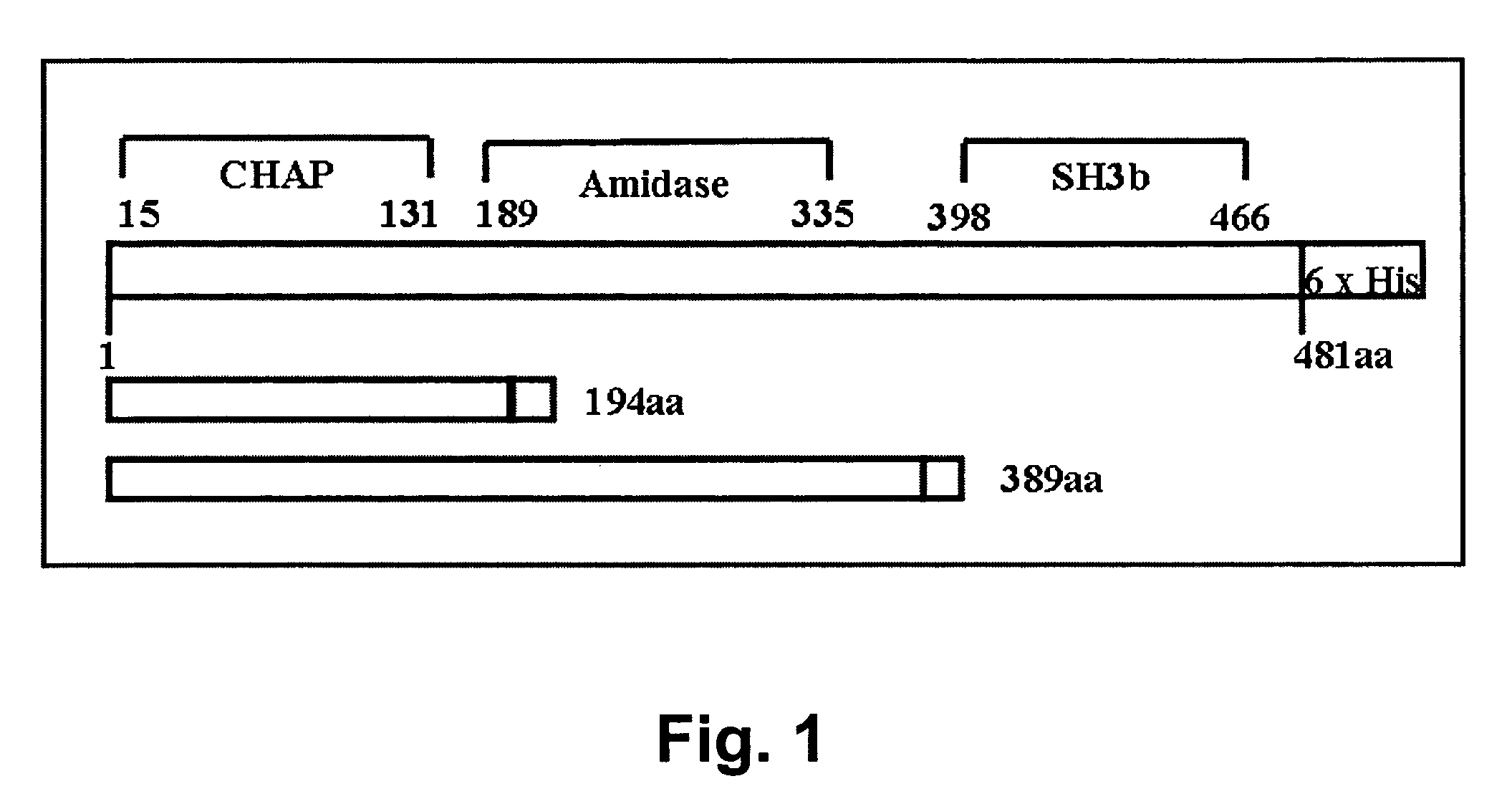
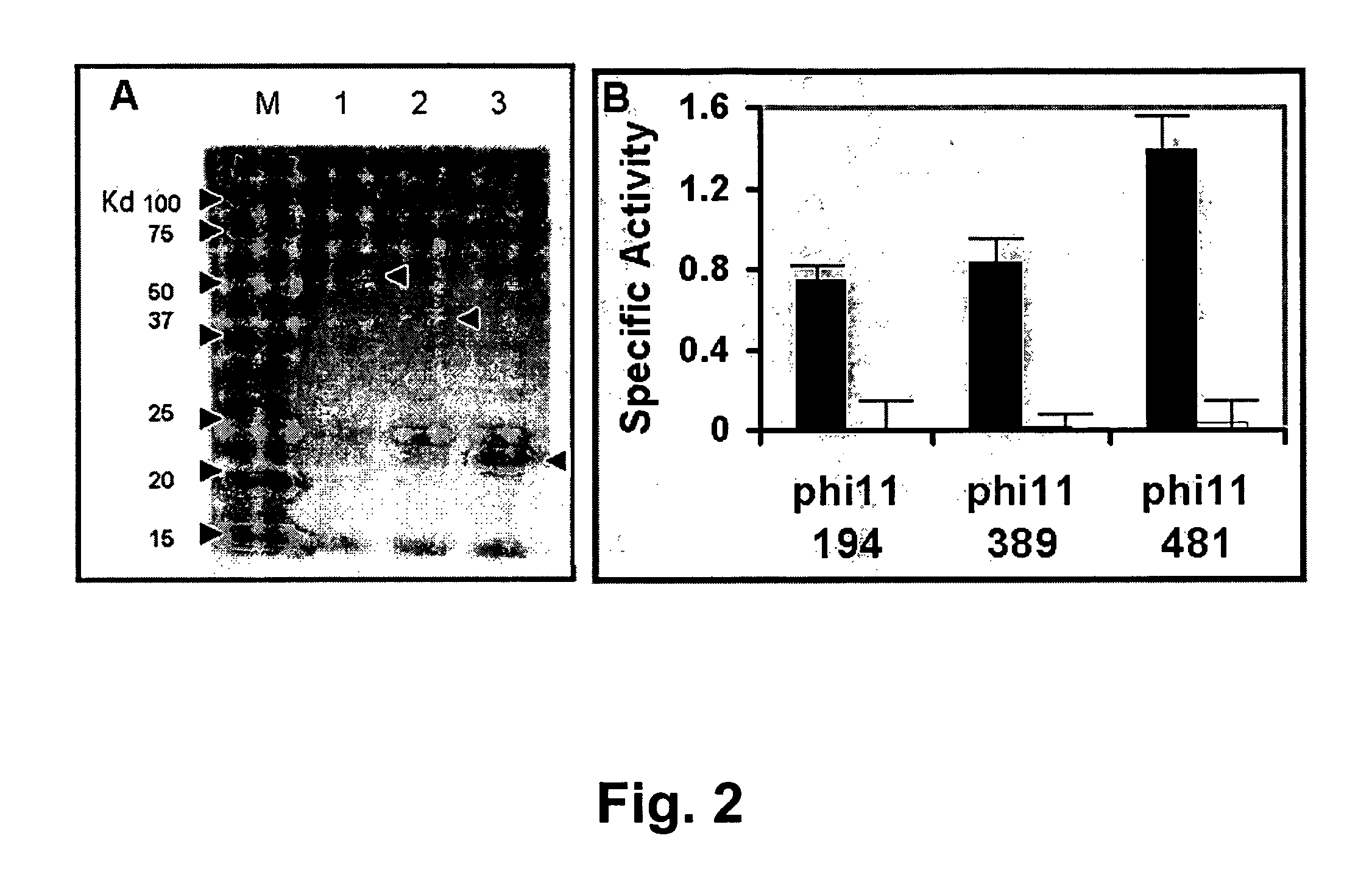
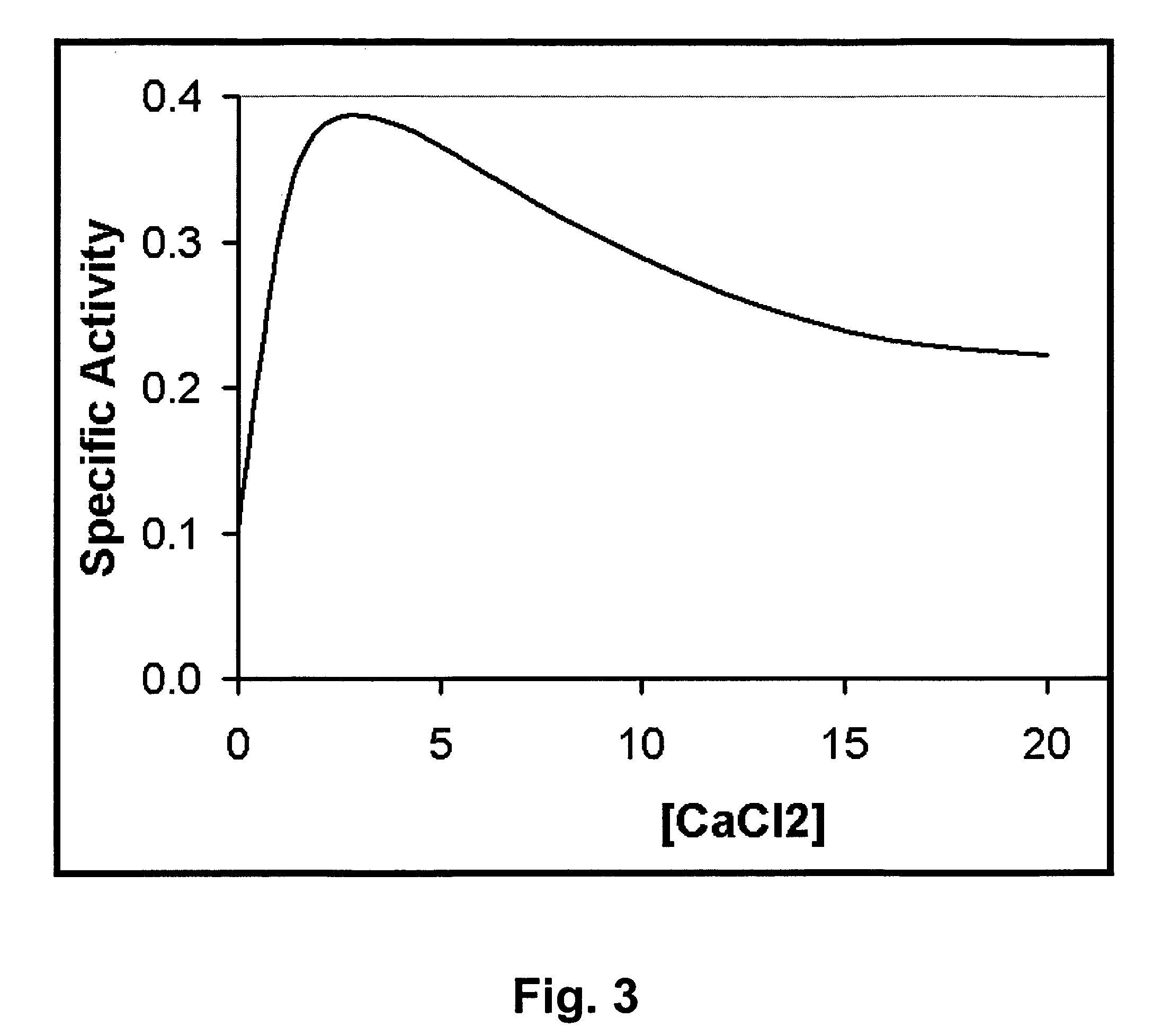
Specific lysis of staphylococcal pathogens by bacteriophage phi11 endolysin
InactiveUS8012730B1Readily apparentAntibacterial agentsBacteriaStaphylococcus cohniiPeptidoglycan Hydrolase
The Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage phi11 endolysin has two peptidoglycan hydrolase domains (endopeptidase and amidase) and a SH3b cell wall-binding domain. In turbidity reduction assays, the purified protein can lyse untreated staphylococcal mastitis-causing pathogens, S. aureus and coagulase negative staphylococci (S. chronogenes, S. epidermis, S. hyicus, S. simulans, S. warneri, and S. xylocus), making it a strong antimicrobial protein and an effective candidate for treating multidrug-resistant staphylococci. Lytic activity is maintained at the pH (6.7) and the ‘free’ calcium concentration (3 mM) of milk. Truncated endolysin-derived proteins, containing just the endopeptidase domain, also lyse staphylococci, in the absence of the SH3b-binding domain.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
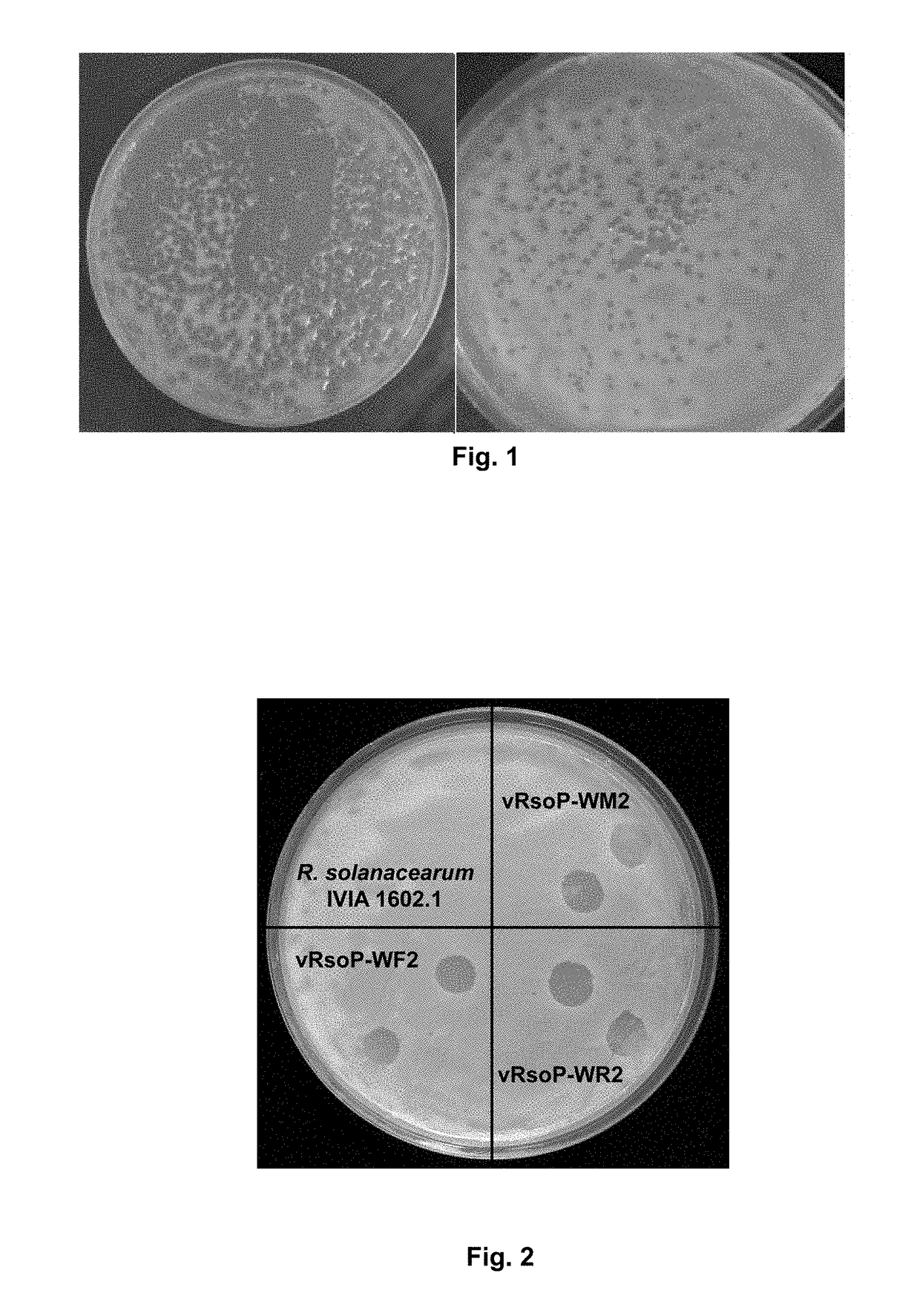
Method for the prevention and/or the biological control of bacterial wilt caused by ralstonia solanacearum, via the use of bacteriophages suitable for this purpose and compositions thereof
ActiveUS20180312814A1Improve survival rateReduce witheringBiocideSelf-acting watering devicesBacteroidesRalstonia solanacearum
A method is for prevention and / or biological control of wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum, by use of suitable bacteriophages. In addition a method uses the structural characterisation, genome sequence and activity of three specific lytic bacteriophages of R. solanacearum. Podovirus presents an elevated stability between 4° C. and 30° C. in an aqueous medium in the absence of a host. As a result of the high level of stability, lytic activity, elevated specificity towards R. solanacearum and the absence of activity against the microbiota associated with the plants to be protected, bacteriophages are used for the biological control of R. solanacearum in river courses and irrigation water, as well as in a method for preventing and / or controlling the wilt produced by the bacteria, in which at least one of the bacteriophages, or combinations thereof, are delivered to the plants and / or the soil in the irrigation water.
Owner:UNIV DE VALENCIA +1
C-1 Inhibitor prevents non-specific plasminogen activation by a prourokinase mutant without impeding fibrin-specific fibrinolysis
InactiveUS20090010916A1High dose toleranceInhibition of activationPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderTolerabilityC1-inhibitor
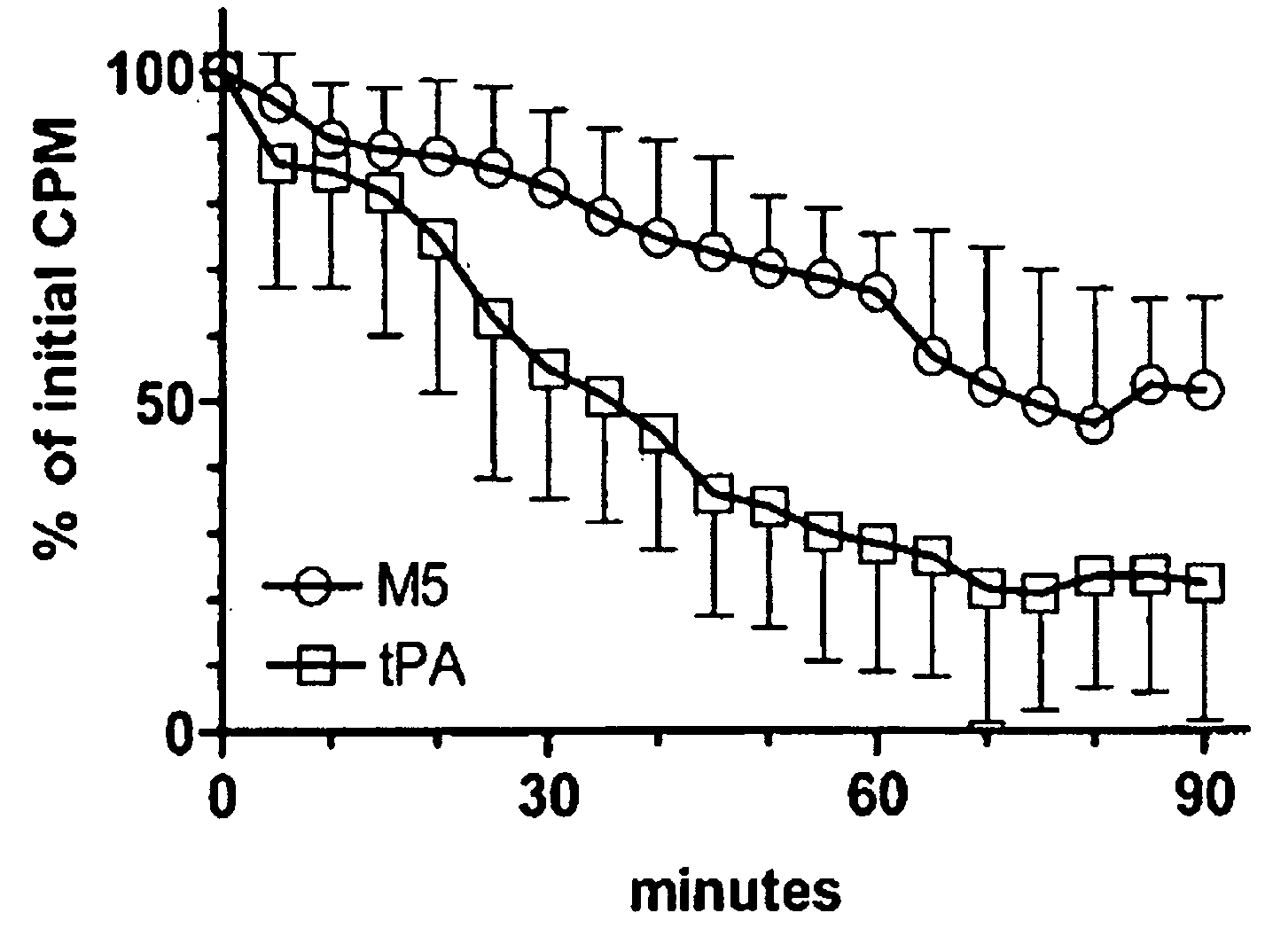
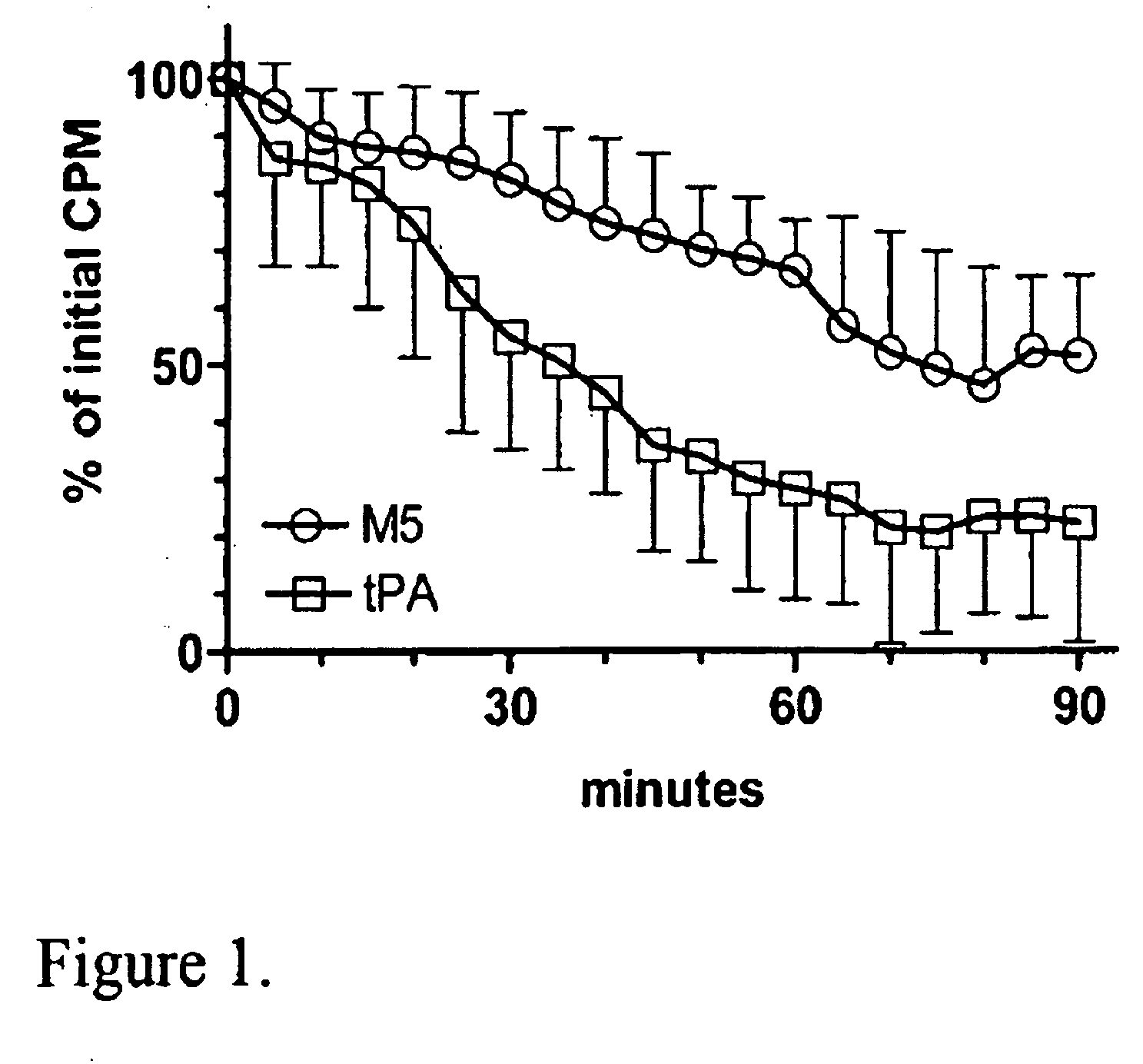
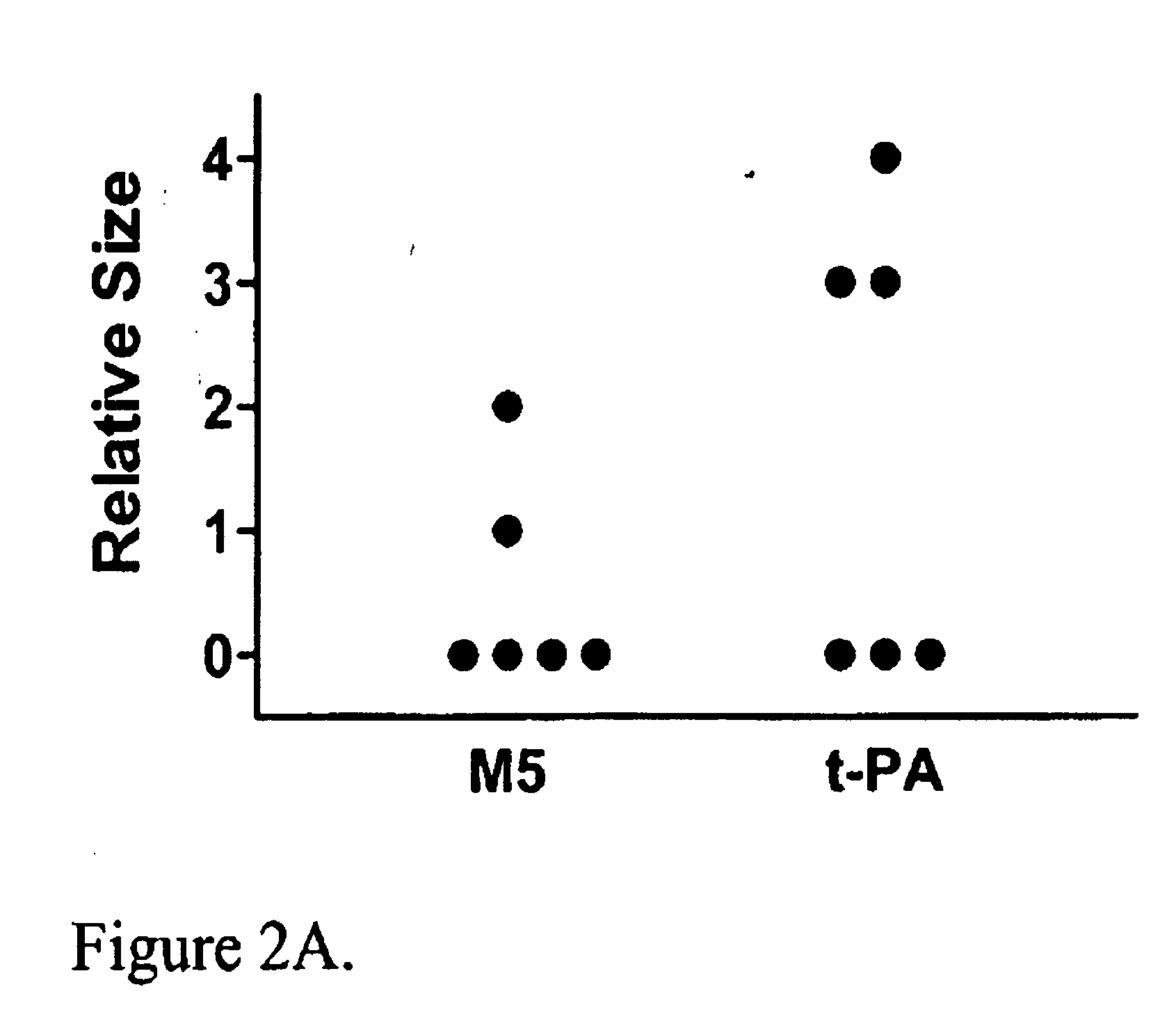
A mutant prourokinase plasminogen activator (M5) was developed to make prouPA less subject to spontaneous conversion to tcuPA in blood at therapeutic concentrations. Two-chain M5 was shown to form complexes with C1-inhibitor, which was the principal inhibitor of tcM5 in plasma. The effect of supplemental additions of C1-inhibitor on fibrinolysis and fibrinogenolysis by M5 was determined. Supplemental C1-inhibitor restored the stability of high-dose M5 and prevented fibrinogenolysis but not fibrinolysis, the rate of which was not compromised by the inhibitor. Due to higher dose tolerance of M5 in the presence of supplemental C1-inhibitor, the rate of fibrin-specific lysis reached that achievable by nonspecific fibrinolysis, which is the maximum possible for a plasminogen activator. Plasma C1-inhibitor stabilized M5 in plasma by inhibiting tcM5 which would otherwise greatly amplify non-specific plasminogen activation causing more tcM5 generation from M5. This unusual dissociation of inhibitory effects, whereby fibrinogenolysis and not fibrinolysis is inhibited, has significant implications for improving the safety and efficacy of fibrinolysis. Methods of reducing bleeding and non-specific plasminogen activation during fibrinolysis by administering M5 along with exogenous C1-inhibitor are disclosed.
Owner:THROMBOLYTIC SCI
C1-Inhibitor Prevents Non-Specific Plasminogen Activation by a Prourokinase Mutant without Impeding Fibrin-Specific Fibrinolysis
ActiveUS20110081334A1Attenuation of rateHigh dose tolerancePeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderC1-inhibitorHigh doses
A mutant prourokinase plasminogen activator (M5) was developed to make prouPA less subject to spontaneous activation during fibrinolysis. C1-inhibitor complexes with tcM5. The effect of C1-inhibitor on fibrinolysis and fibrinogenolysis by M5 was determined. Supplemental C1-inhibitor restores the stability of M5 but not that of prouPA. Clot lysis by M5 with supplemental C1-inhibitor showed no attenuation of the rate of fibrinolysis, whereas fibrinogenolysis was prevented by C1-inhibitor. Due to higher dose tolerance of M5 with C1-inhibitor, the rate of fibrin-specific lysis reached that achievable by nonspecific fibrinolysis without inhibitor. Plasma C1-inhibitor stabilized M5 in plasma by inhibiting tcM5 and thereby non-specific plasminogen activation. At the same time, fibrin-specific plasminogen activation remained unimpaired. This unusual dissociation of effects has significant implications for improving the safety and efficacy of fibrinolysis. Methods of reducing bleeding and non-specific plasminogen activation during fibrinolysis by administering M5 along with exogenous C1-inhibitor are disclosed.
Owner:THROMBOLYTIC SCI
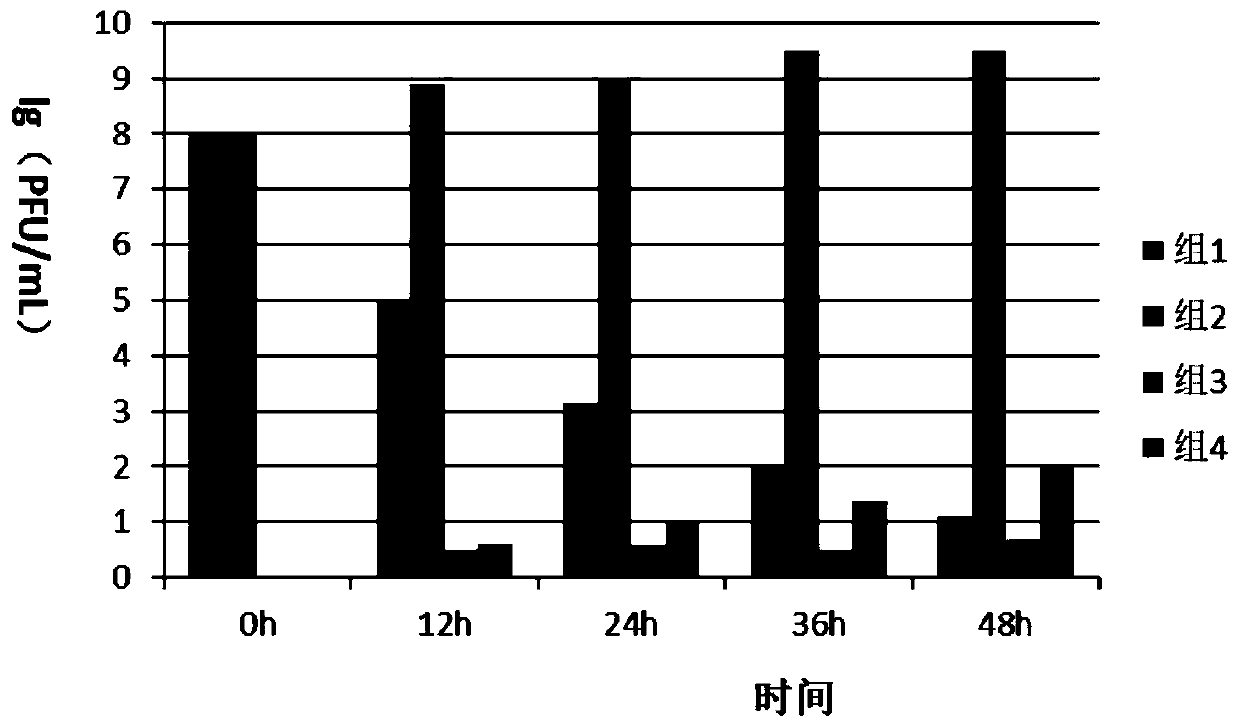
Vibrio campbellii phage and application thereof
ActiveCN111575243AHigh potencyEffective controlSpecific water treatment objectivesClimate change adaptationNucleotideMicrobiology
The invention provides a vibrio campbellii phage capable of effectively lysing vibrio campbellii and application of the vibrio campbellii phage. The vibrio campbellii phage has a specific nucleotide sequence. The vibrio campbellii phage provided by the embodiments can specifically lyse the vibrio campbellii, the titer is high, so that vibrio campbellii disease can be effectively controlled in aquaculture after the vibrio campbellii phage is used alone or in combination.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
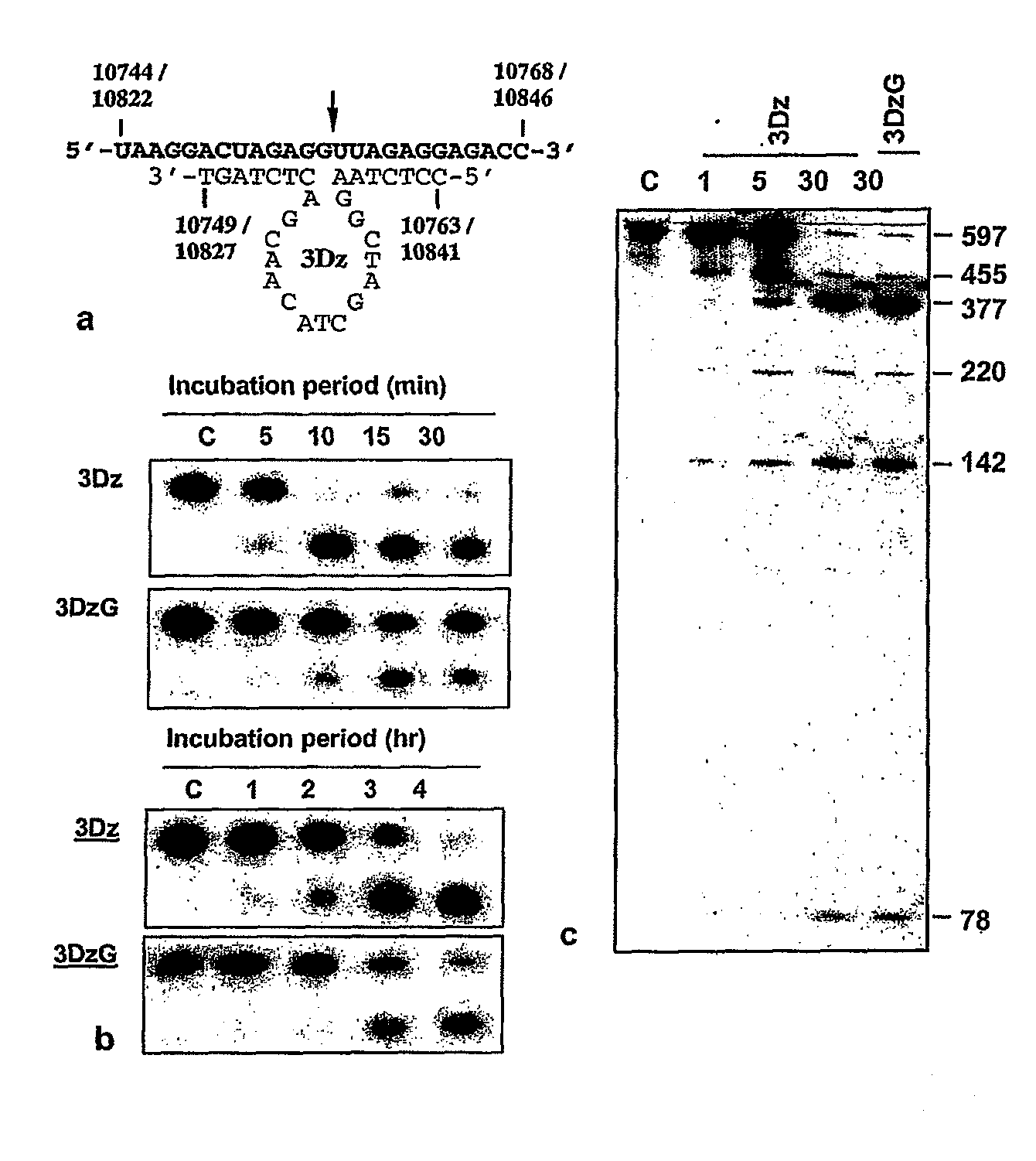
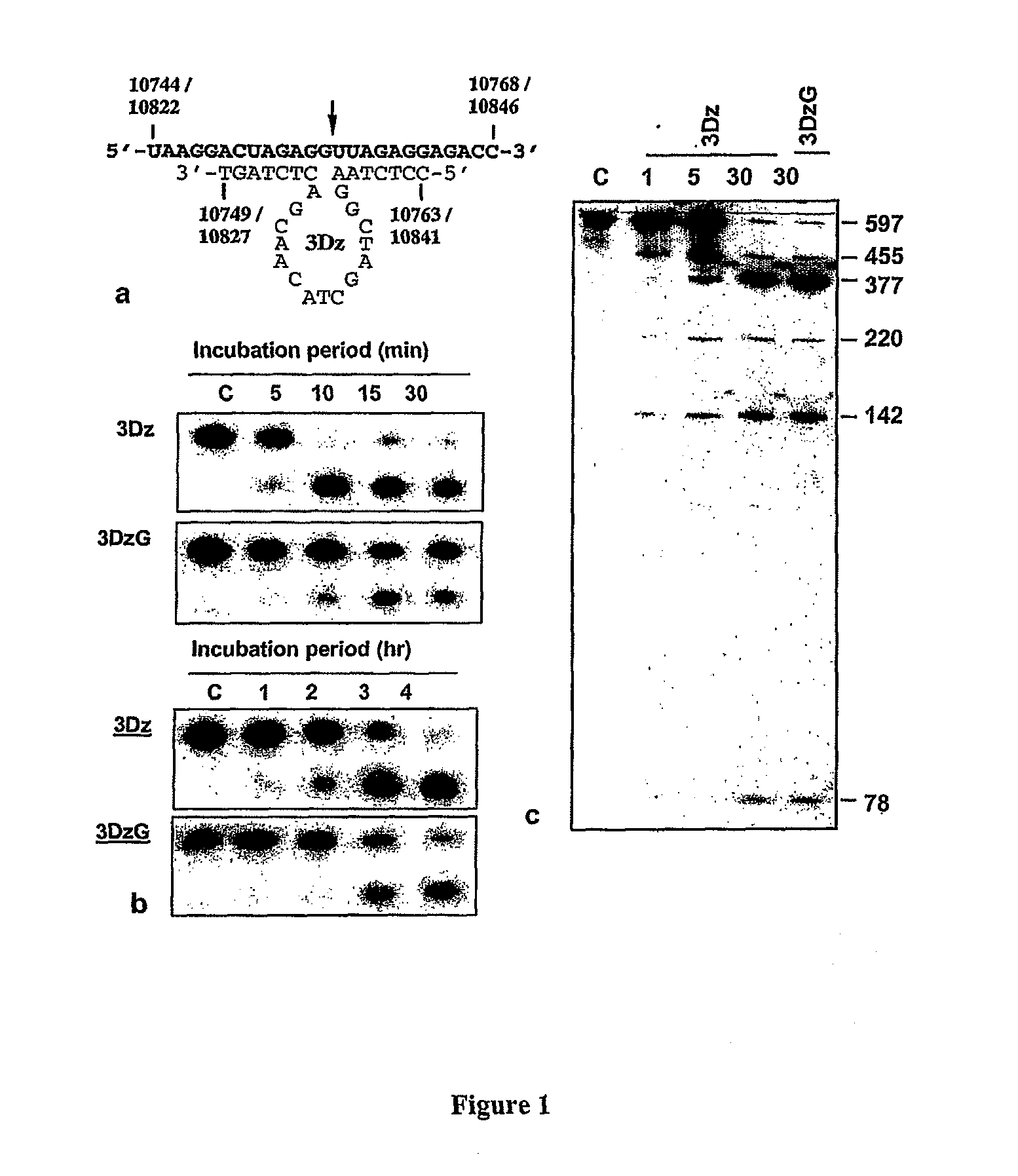
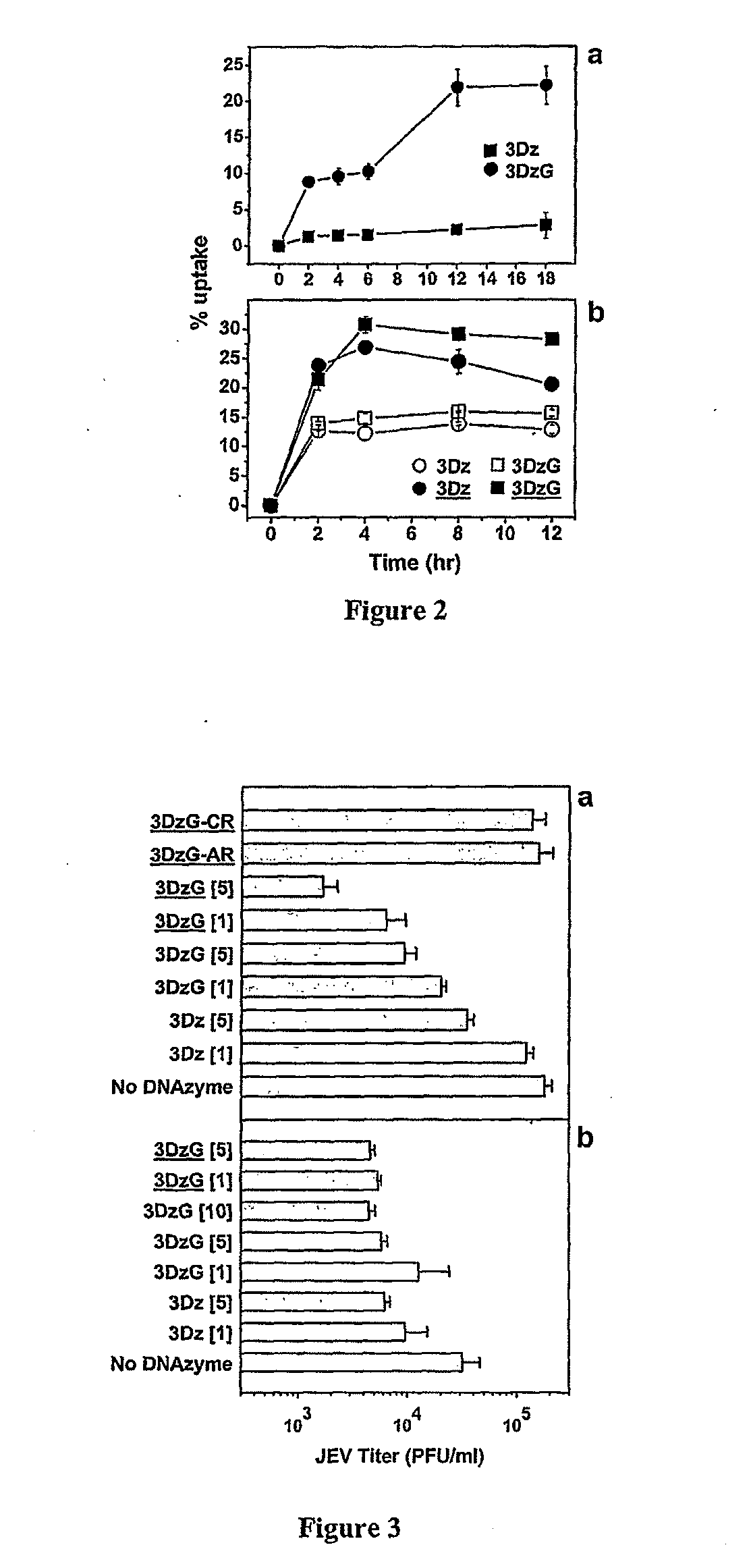
Dnazymes for Inhibition of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Replication
InactiveUS20090010907A1Efficient deliverySsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsInfected cellNucleotide
The present invention relates to synthetic catalytic DNA molecules or DNAzymes which specifically cleave the RNA sequences of the Japanese Encephalitis Viral genome and is useful in treating Japanese Encephalitis infection. The DNAzyme comprises of a chemical modification, a catalytic domain and two hybridizing arms. The DNAzymes are 29-45 nucleotides in length. The 3′ end of the DNAzyme is tethered to a poly-(G)10 tail (SEQ ID NO: 46) and the molecule comprises of at least one chemical modification. The chemical modifications are in the form of sugar modification, nucleic acid base modification, and / or phosphate backbone modification. The catalytic DNA molecule inhibits JEV replication in vitro in cultured cells and in vivo in the mouse brain. The present invention also relates to the method of treatment of Japanese encephalitis comprising the steps of introducing the catalytic DNA molecule or DNAzyme into the infected cells under conditions suitable for cleavage and reduction of viral titres.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTUTUTE OF IMMUNOLOGY
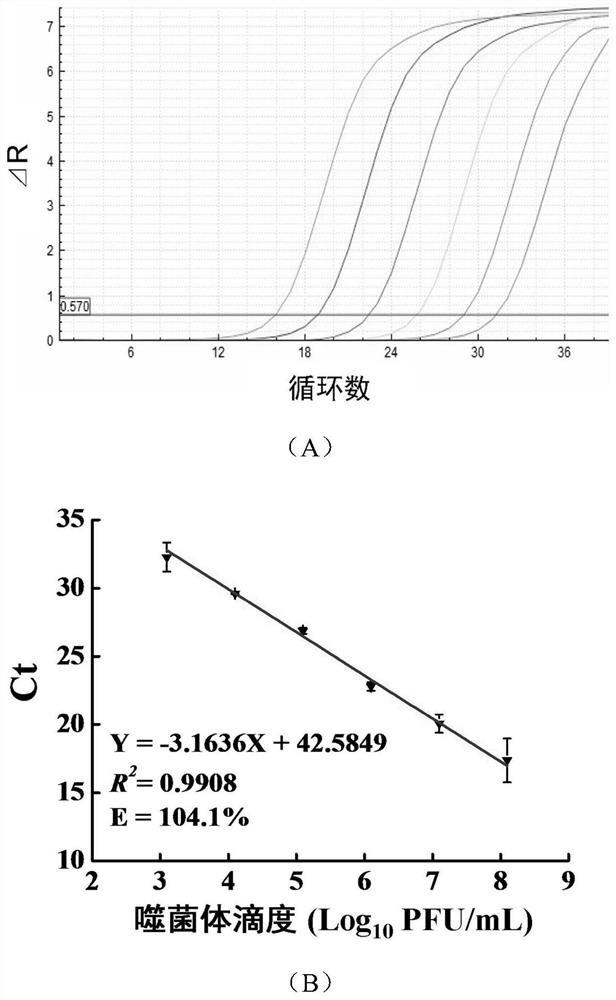
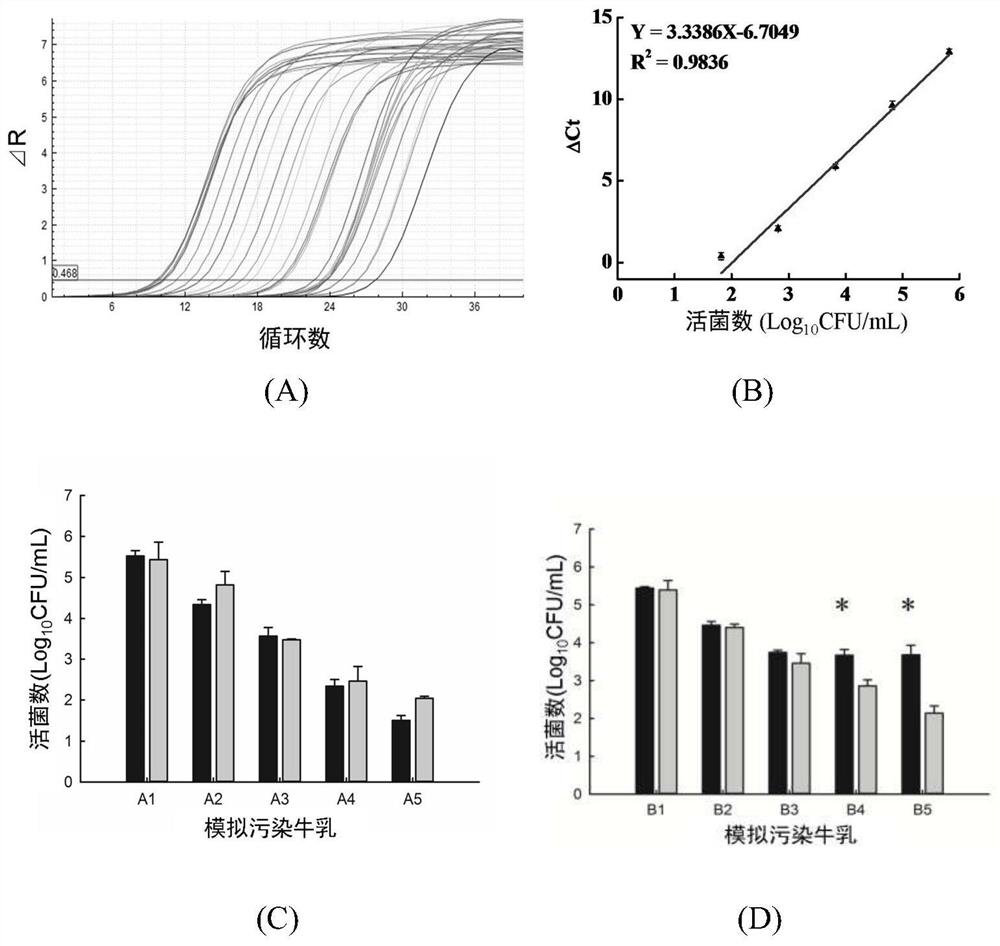
Rapid quantitative detection method capable of specifically identifying survival cells of enterobacter sakazakii and primer thereof
ActiveCN112063732ARapid Quantitative DetectionImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEnterobacterCronobacter sakazakii
The invention discloses a rapid quantitative detection method capable of specifically identifying survival cells of enterobacter sakazakii and a primer thereof. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a specific lysis culture solution containing enterobacter sakazakii bacteriophage; 2) co-culturing the lysis culture solution prepared in the step 1) with a standard strain gradient suspension and a sample diluent respectively; 3) determining the variation of a Ct value of a co-cultured substance in the step 2) through qPCR; and 4) calculating the number of the survival cells of the enterobacter sakazakii in a sample according to a linear relation between the delta Ct value in the step 3) and the viable count of the standard strain gradient suspension, so as to realize rapid quantitative determination of the number of the survival cells of the enterobacter sakazakii in the sample. The detection method disclosed by the invention has no cross reaction on dead cellsand other strains; the detection period is 5.5h and the detection flux is high; and the detection method is suitable for quantitative detection of the survival cells of the enterobacter sakazakii in food or environment samples and is used for rapidly evaluating the effectiveness of disinfection and sterilization conditions on the enterobacter sakazakii.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
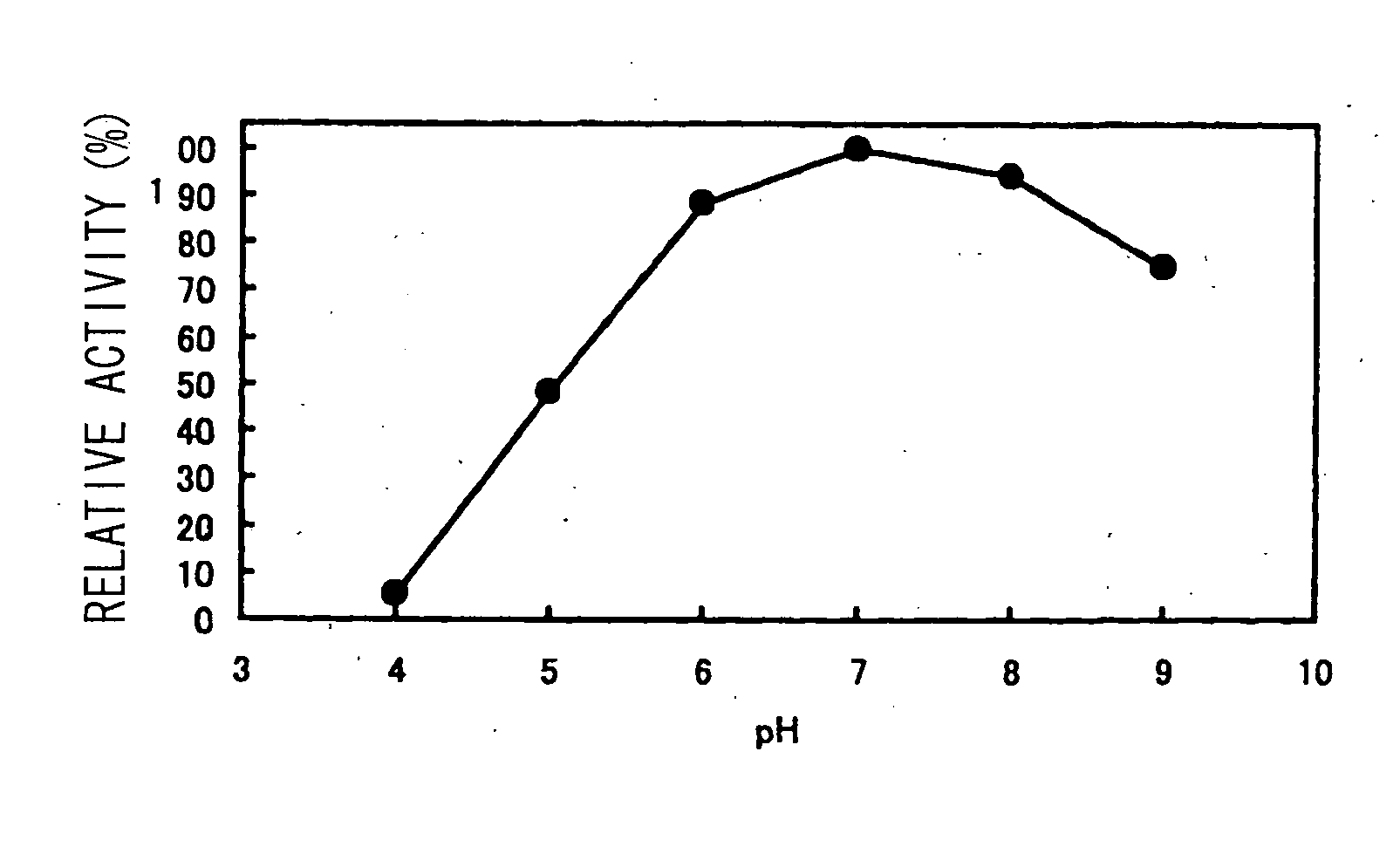
Milk-coagulating enzyme originating in bacterium and process for producing cheese using the same
The present invention relates to a milk-coagulating enzyme of bacterial origin and a process for producing cheese by using this enzyme, namely, an enzyme that is produced by a bacterium belonging to the genus Paenibacillus and exhibits milk-coagulating activity, characterized by having the following enzymological properties: 1) function: having an activity of coagulating milk to form a curd; 2) substrate specificity: acting on κ-casein as a substrate and specifically cleaving Thr94-Met95 in the presence of calcium; 3) optimum pH: 6.0-7.0, and 4) molecular weight: 35,000-37,000 Da when measured by SDS-PAGE; a process for producing the enzyme; a process for producing cheese; and a cheese-like food product.
Owner:MAHOROBA
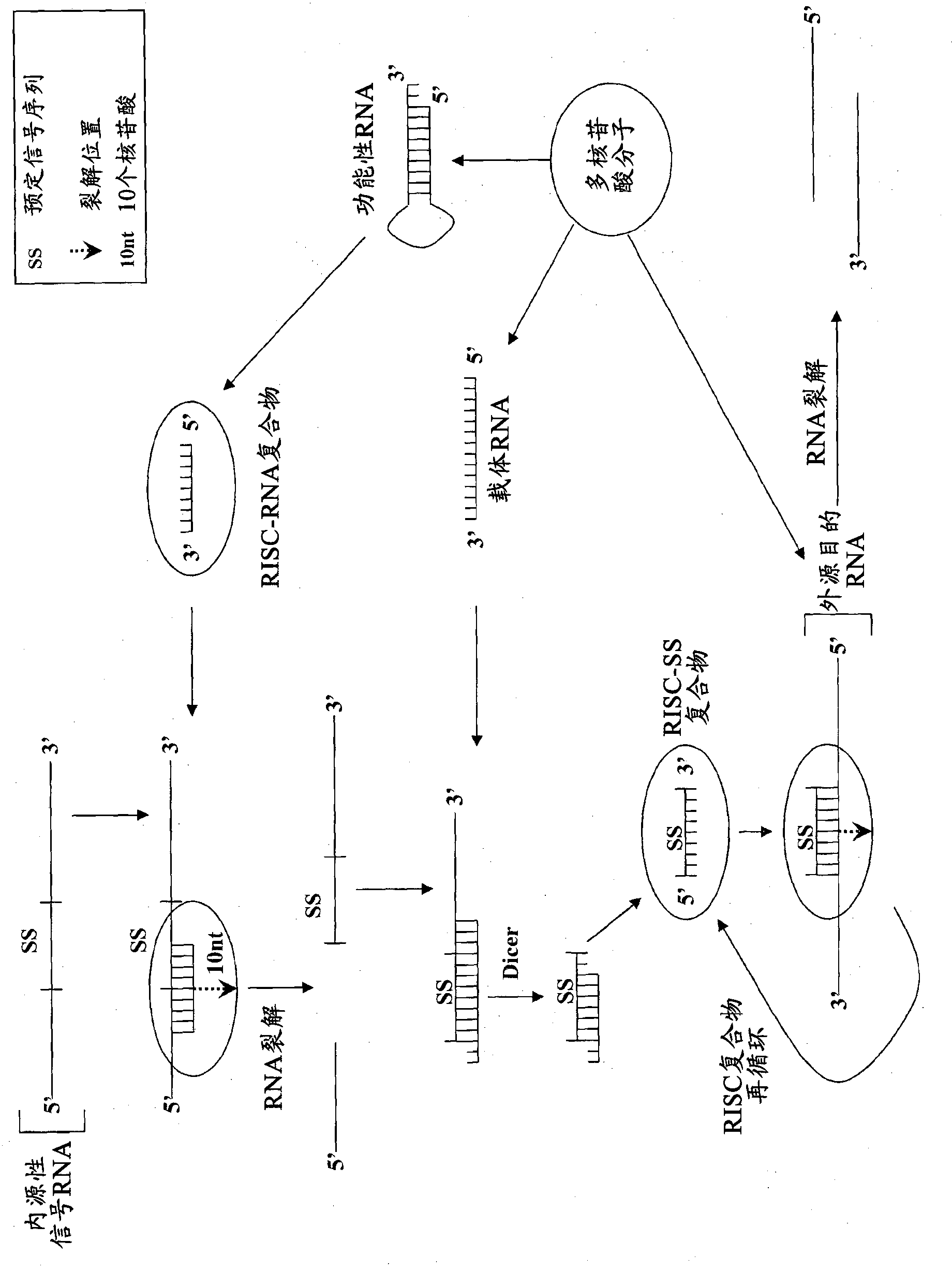
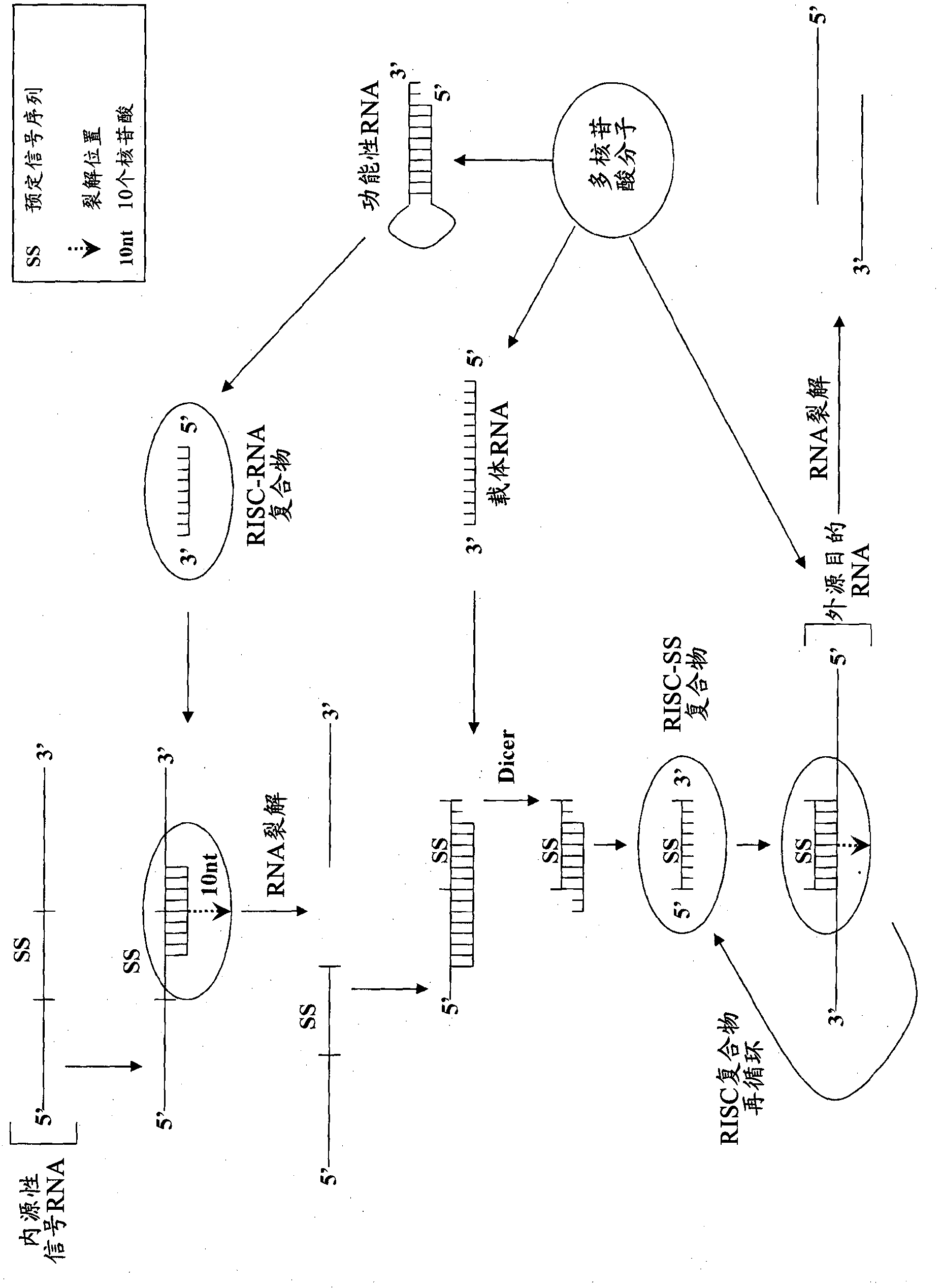
Compositions and methods for specific cleavage of exogenous rna in a cell
There are provided compositions for cleaving an exogenous RNA of interest only in the presence of an endogenous signal RNA sequence, thereby activating expression of a polynucleotide of interest only in the presence of the endogenous signal RNA sequence. There are provided methods for the preparation of the composition and uses thereof in treatment and diagnosis of various conditions and disorders, for example by selectively activating expression of a toxin only in specific target cell populations.
Owner:NANODOC
Vibrio parahaemolyticus phage and application thereof in prevention of stichopus japonicus disease
ActiveCN110468110AAvoid infectionReduce abundanceAntibacterial agentsMicroorganism based processesAnaplasma phagocytophilumVibrio parahemolyticus
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a phage isolate capable of specifically cracking Vibrio parahaemolyticus and application of the phage in the field of sea cucumber disease prevention, so that the economic benefit of sea cucumber breeding enterprises is improved, and food safety is guaranteed from the source. The vibrio parahaemolyticus phage vB_VpaP_VP-ABTNL-1 has a preservation number of CGMCC No.17991. The vibrio parahaemolyticus phage provided by the invention is applied to the prevention of the stichopus japonicus disease and can effectively prevent the infection of the vibrio parahaemolyticus in the breeding process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
C-1 inhibitor prevents non-specific plasminogen activation by a prourokinase mutant without impeding fibrin-specific fibrinolysis
ActiveUS20070298023A1High catalytic activityReduce ratePeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderC1-inhibitorHigh doses
A mutant prourokinase plasminogen activator (M5) was developed to make prouPA less subject to spontaneous activation during fibrinolysis. C1-inhibitor complexes with tcM5. The effect of C1-inhibitor on fibrinolysis and fibrinogenolysis by M5 was determined. Supplemental C1-inhibitor restores the stability of M5 but not that of prouPA. Clot lysis by M5 with supplemental C1-inhibitor showed no attenuation of the rate of fibrinolysis, whereas fibrinogenolysis was prevented by C1-inhibitor. Due to higher dose tolerance of M5 with C1-inhibitor, the rate of fibrin-specific lysis reached that achievable by nonspecific fibrinolysis without inhibitor. Plasma C1-inhibitor stabilized M5 in plasma by inhibiting tcM5 and thereby non-specific plasminogen activation. At the same time, fibrin-specific plasminogen activation remained unimpaired. This unusual dissociation of effects has significant implications for improving the safety and efficacy of fibrinolysis. Methods of reducing bleeding and non-specific plasminogen activation during fibrinolysis by administering M5 along with exogenous C1-inhibitor are disclosed.
Owner:THROMBOLYTIC SCI +1
Rice bacterial brown streak germ phage and application thereof
ActiveCN104630154AStrong cracking abilityBiocideMicroorganism based processesInfected cellAnaplasma phagocytophilum
The invention discloses a rice bacterial brown streak germ phage and an application thereof. The classification term of the phage is rice bacterial brown streak germ phage AP1 (Acidovorax avenae subsp.Avenae phage AP1), and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2014599. The application comprises an application of the rice bacterial brown streak germ phage in preparation of a phage preparation used for inhibiting rice bacterial brown streak germs, an application for inhibiting the rice bacterial brown streak germs and an application of preventing and treating the rice bacterial brown streak germs. The rice bacterial brown streak germ phage disclosed by the invention can specifically crack the rice bacterial brown streak germ, the burst size is about 160PFU / infected cells, and the cracking performance is stronger, so that the rice bacterial brown streak germ phage can be used for preventing and treating rice bacterial brown streak caused by the rice bacterial brown streak germs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Composition comprising bacteriophages for reducing, eliminating and/or preventing salmonella enteritidis, salmonella typhimurium and salmonella paratyphi b
ActiveUS20190070231A1Inhibition of colonizationBlock cycle of colonizationAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsSlaughter houseDisinfectant
The present invention relates to a new cocktail of bacteriophages with specific lytic activity against Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella paratyphi B., for reducing, eliminating and / or preventing them in farm animals and animals from the poultry sector, such as poultry, hens and breeding hens, in addition to eggs. It may be administered as an additive in the feed, in water or by spray. Moreover, the cocktail may be used as a disinfectant in work areas of farms and abattoirs, and in processed foods, without affecting the organoleptic properties of the product.
Owner:UNIV DE LOS ANDES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com