Methods for fabricating solid state image sensor devices having non-planar transistors
a solid-state image sensor and transistor technology, applied in the direction of transistors, solid-state devices, radiation control devices, etc., can solve the problems of not allowing random access to unit pixels, high cost of ccd image sensor devices, and high power consumption, so as to reduce the effects of image lag and dark curren
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] Exemplary CMOS image sensor devices and methods for fabricating such devices according to exemplary embodiments of the invention will now be described more fully with reference to the accompanying drawings. It is to be understood that the drawings are merely schematic depictions where the thickness and dimensions of various components, layers and regions are not to scale, but rather exaggerated for purposes of clarity. It is to be further understood that when a layer is described herein as being “on” or “over” another layer or substrate, such layer may be directly on the other layer or substrate, or intervening layers may also be present. It is to be further understood that the same reference numerals used throughout the drawings denote elements that are the same or similar or have the same or similar functions.
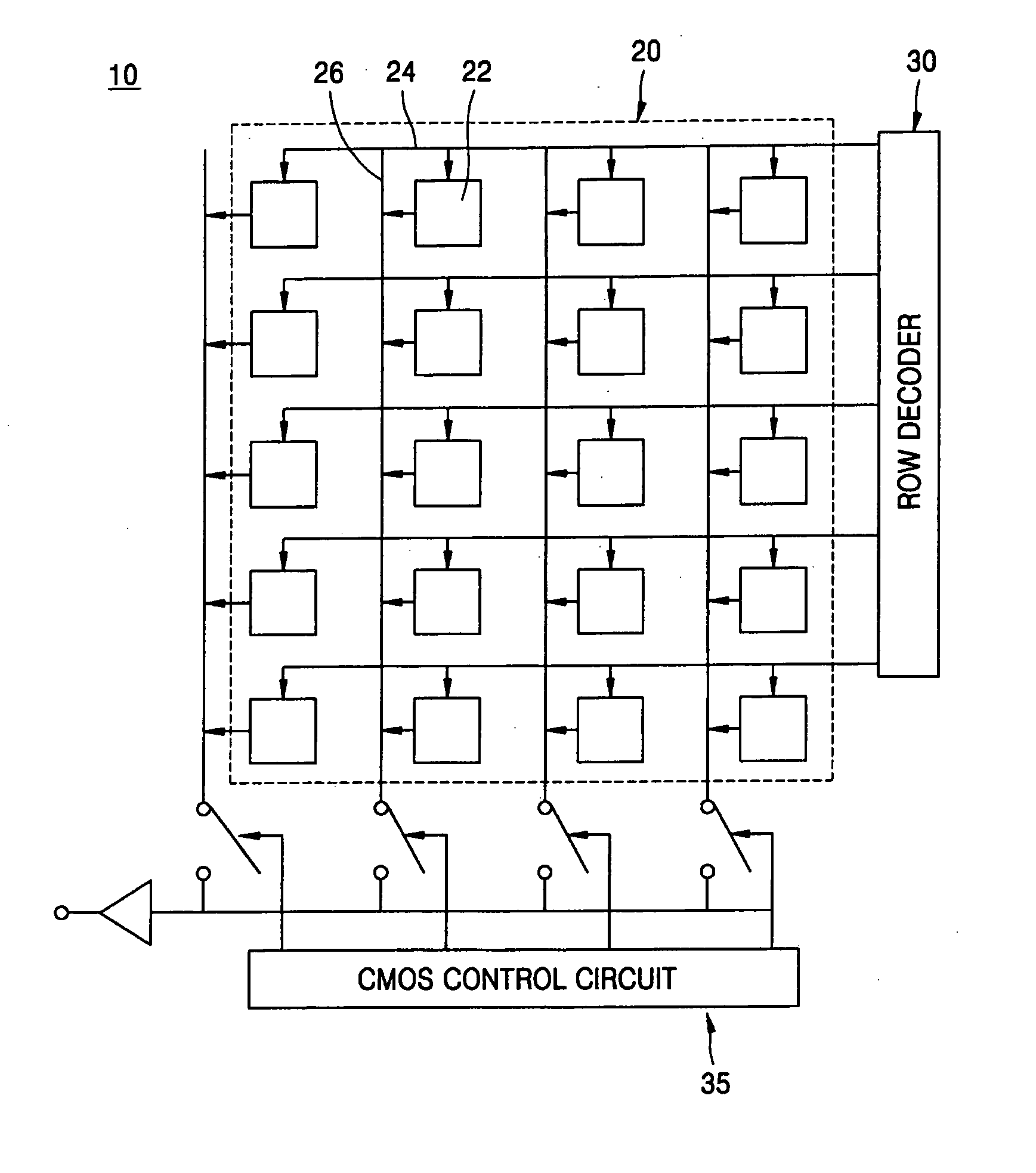
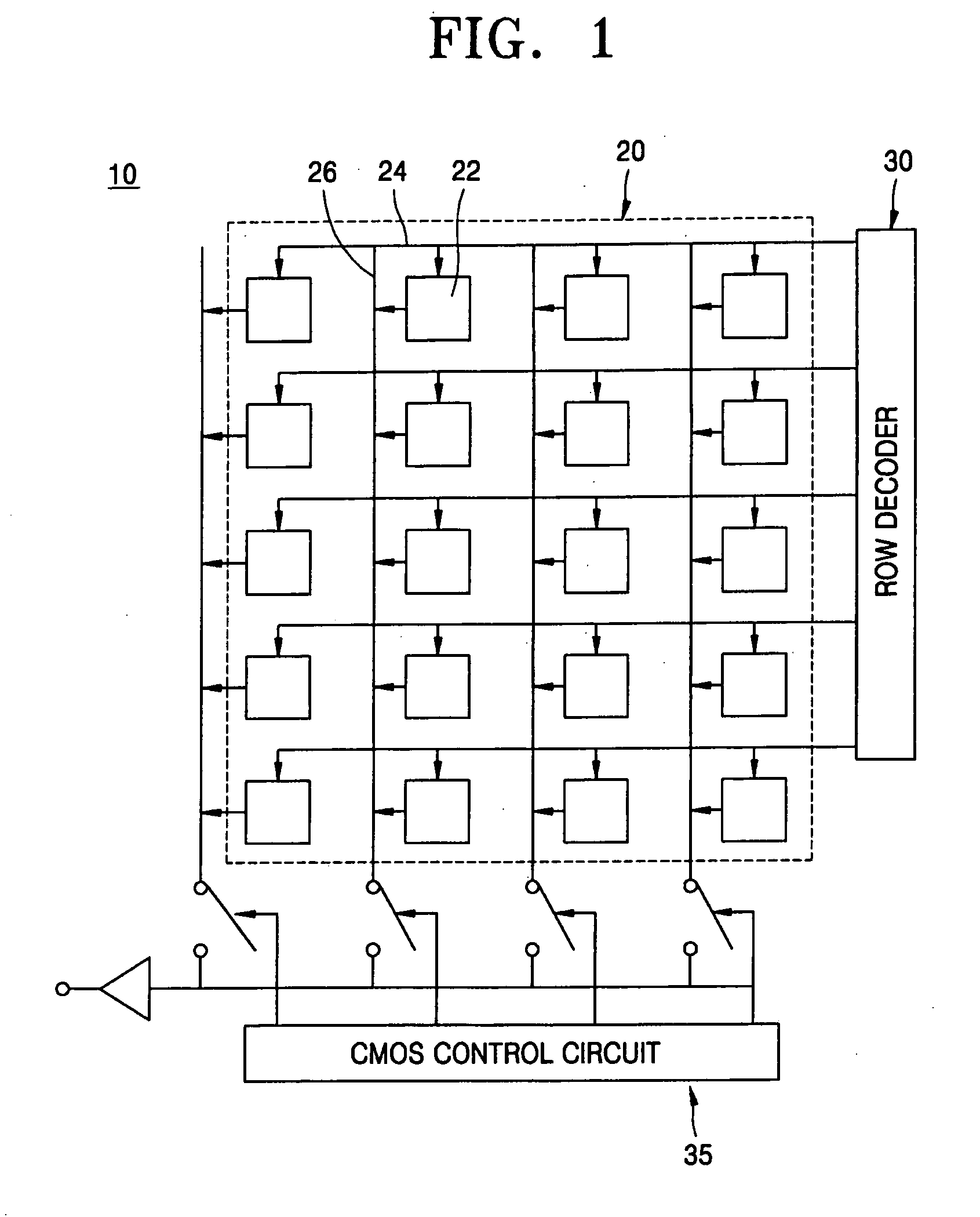
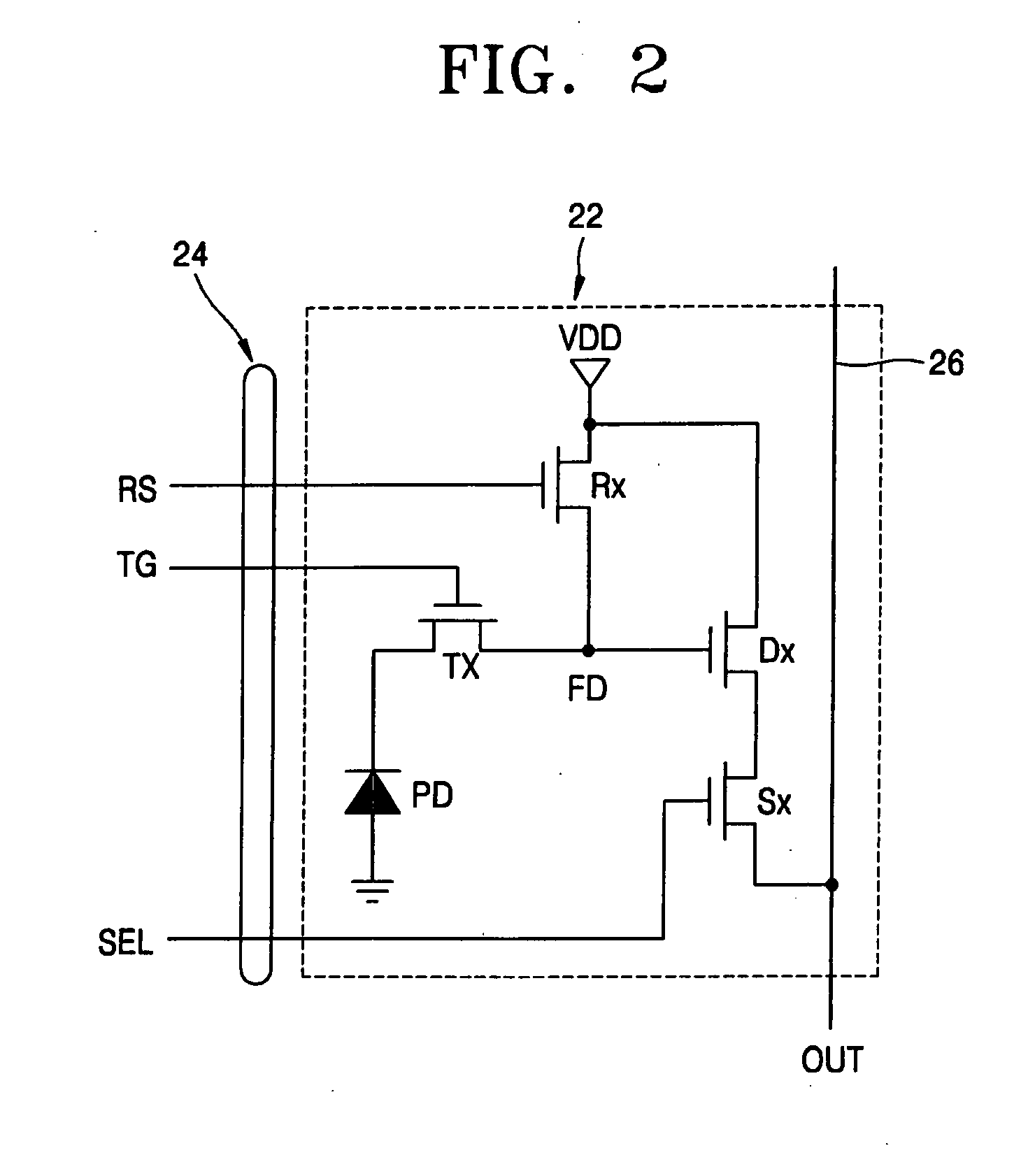
[0036]FIG. 1 is a high-level block diagram of a solid state CMOS image sensor device according to an exemplary embodiment of the invention. In particular, FIG. 1 illu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com