Position sensor, designed in particular for detecting a steering column torsion
a technology of position sensor and steering column, applied in the direction of engine lubrication, liquid/fluent solid measurement, electrical/magnetic means, etc., can solve the problems of loss of magnetic signal, loss of sensor structure, and poor prior art solution, and achieve the effect of better signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
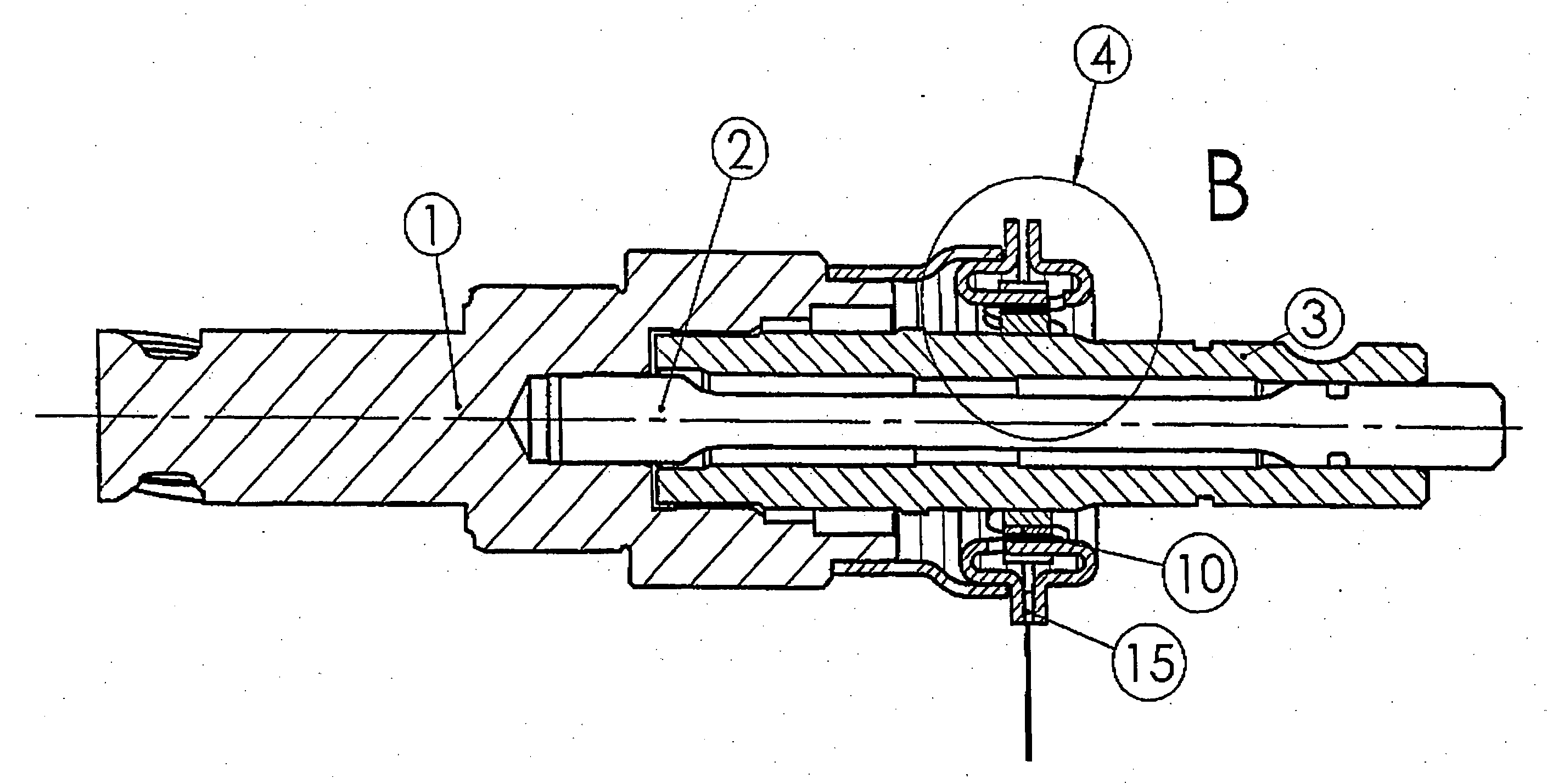
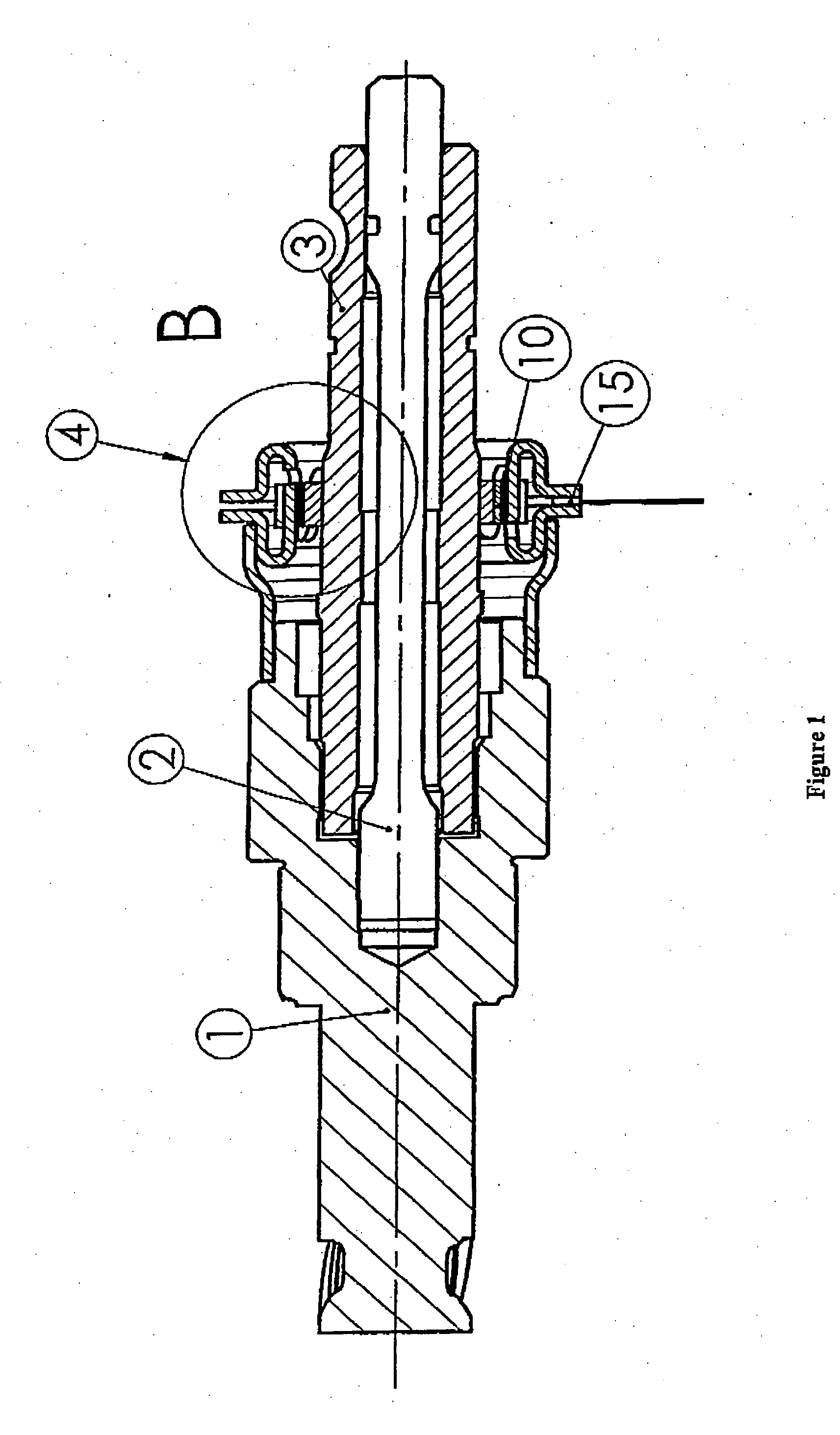
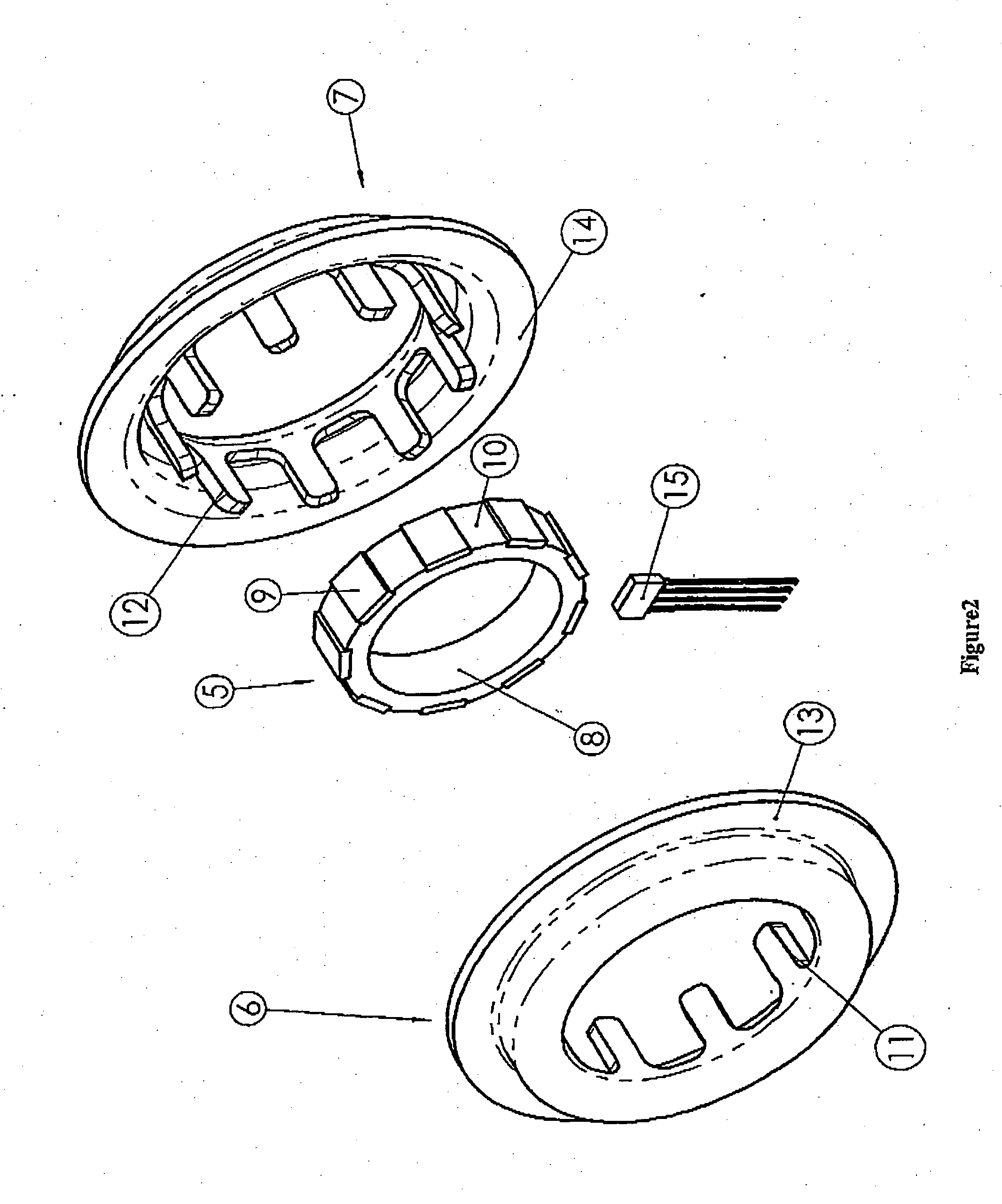
[0031] The object of the invention is to overcome these problems of low sensitivities and it relates to contactless position sensors intended for the measurement of angles similar to or smaller than 10° C., in applications such as steering-column torque sensors, for example (the signal then will be processed to provide steering assistance). The angular position sensor described hereinafter is intended for the measurement of a very small angular difference (a few degrees) between two shafts connected by a torsion bar. Such an application for torque measurement is described in FIG. 1. In the range of linear deformation of this torsion bar, this angular difference (α1-α2) will be proportional to the torque applied between the two shafts (1, 3) connected by an elastically deformable test member (2). The measurement of this angular difference by the sensor will allow an electrical signal proportional to the applied torque to be delivered at the output of the magnetosensitive element. In ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angles | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| torsional working angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| torsional working angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com