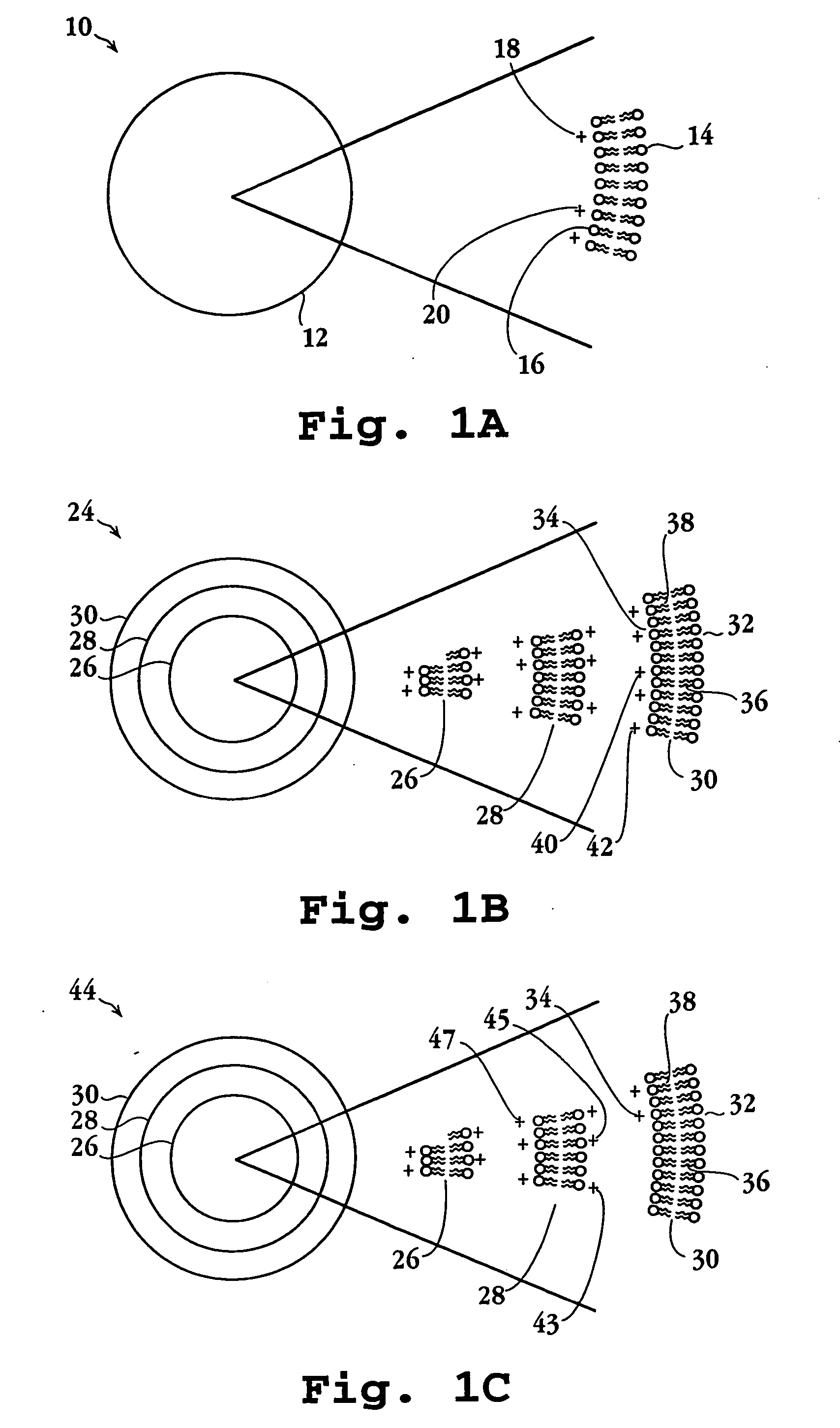
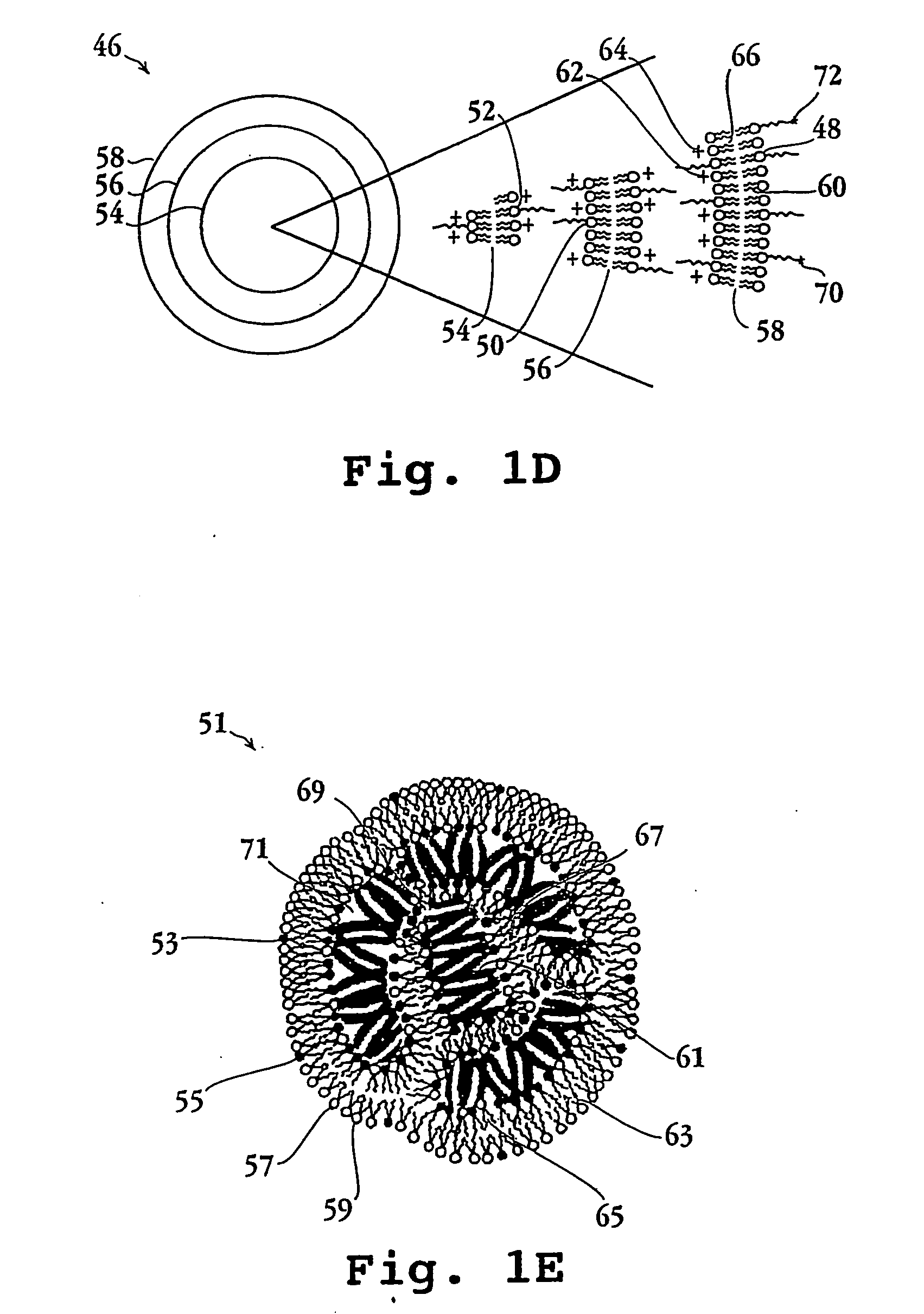
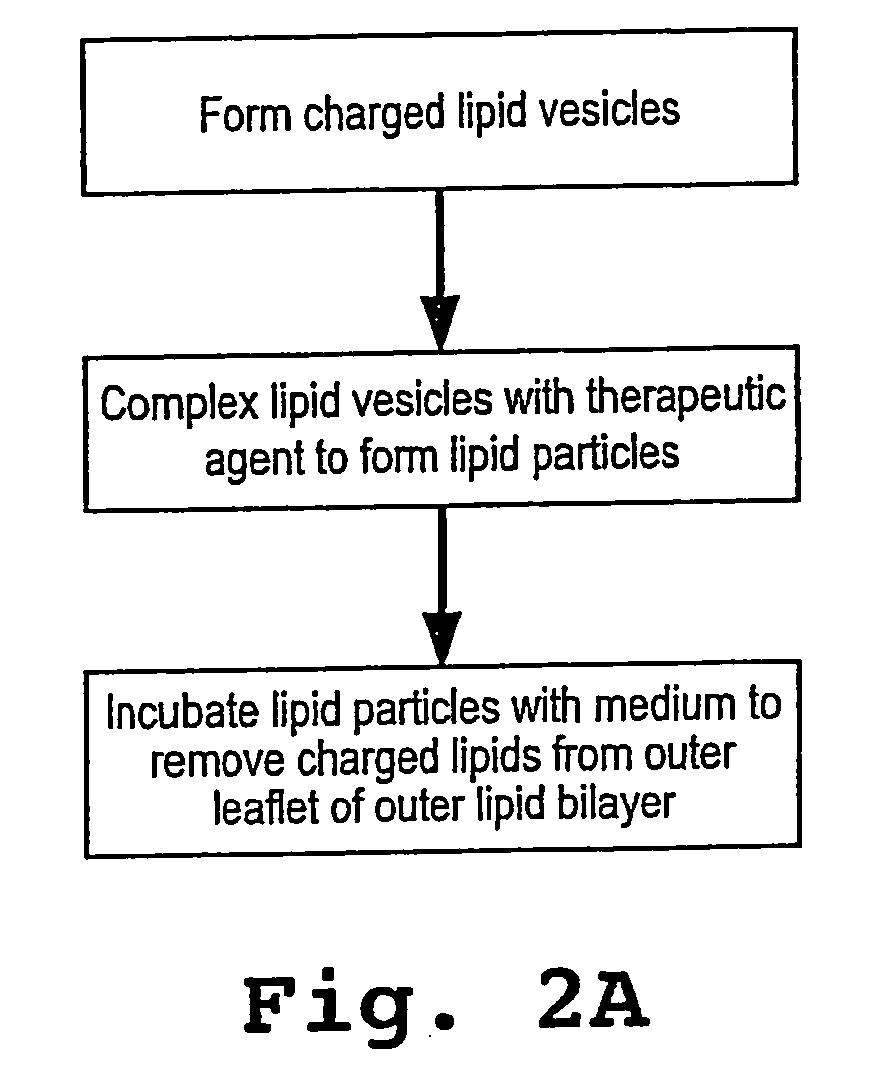
Lipid particles having asymmetric lipid coating and method of preparing same
a technology of lipid coating and lipid particles, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical delivery mechanism, biochemistry apparatus and processes, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of limited success in intracellular delivery of liposome-entrapped agents, inherent difficulty in delivering a molecule, in particular a large and/or charged molecule, and the difficulty of delivering charged molecules intracellularly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Asymmetric Lipid Particles
[0094] Cationic liposomes (small unilamellar vesicles) were prepared from a lipid composition of DMTAP / DOPE / CHOL / PEG-DS (50 / 24 / 24 / 2 mol / mol). Individual lipid stocks were made in chloroform / methanol (90:10 v / v) at 10 mg / mL for DMTAP (Avanti Polar Lipids, 890860, 20 mg / mL for DOPE (Avanti Polar Lipids, 850725), 20 mg / mL for cholesterol, and 10 mg / mL for mPEG-DS (methoxy-polyethyleneglycol-distearoyl, mPEG molecular weight 2000 Daltons, Shearwater Polymers Inc). Aliquots of solvent solutions containing appropriate amount of lipids for a final lipid suspension of 2 mL at 20 mM lipid concentration were taken using positive displacement pipettes and mixed in 10 mL round bottom flasks. The solvent was slowly removed by rotary evaporation at about 45° C. to form a thin film around the flask. The residual solvent was removed by vacuum overnight. The lipid was then hydrated by adding 2 mL of deionized water at 50° C. for 0.5-1 hour with stirring. The...
example 2
[0103] Asymmetric lipid-DNA particles and various controls prepared as described in Example 1 were compared in vitro. BHK cells were seeded in 6-well plates at 1.13×104 cells / well and incubated at 37° C., 5% CO2, for 48 hours with complete MEM media. Before the transfection, the cells were rinsed twice with 1.0 mL serum-free MEM media. An aliquot of the transfection sample was mixed with serum-free MEM media to achieve a desired concentration of plasmid DNA (typically 60-200 μg / mL pCC-Luc). For transfection, 1 mL was than overlayed onto the rinsed cells followed by incubation at 37° C. for 5 hours. After incubation, the sample-containing media was aspirated and replaced with 1.0 mL of complete MEM media and the incubation was continued under the same condition for an additional 16.5 hours.
[0104] The luciferease activity was assayed using Promega Luciferase Assay System (cat# E1500). The cells were rinsed twice with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and then 250 ...
example 3
Preparation of Asymmetric Lipid Particles
[0106] Lipid particles were formed as described in Example 1, except that the temperature of the incubation solution comprised of neutral SUVs (see step 4 C in Example 1) was maintained between 0-4° C. with an ice bath.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com