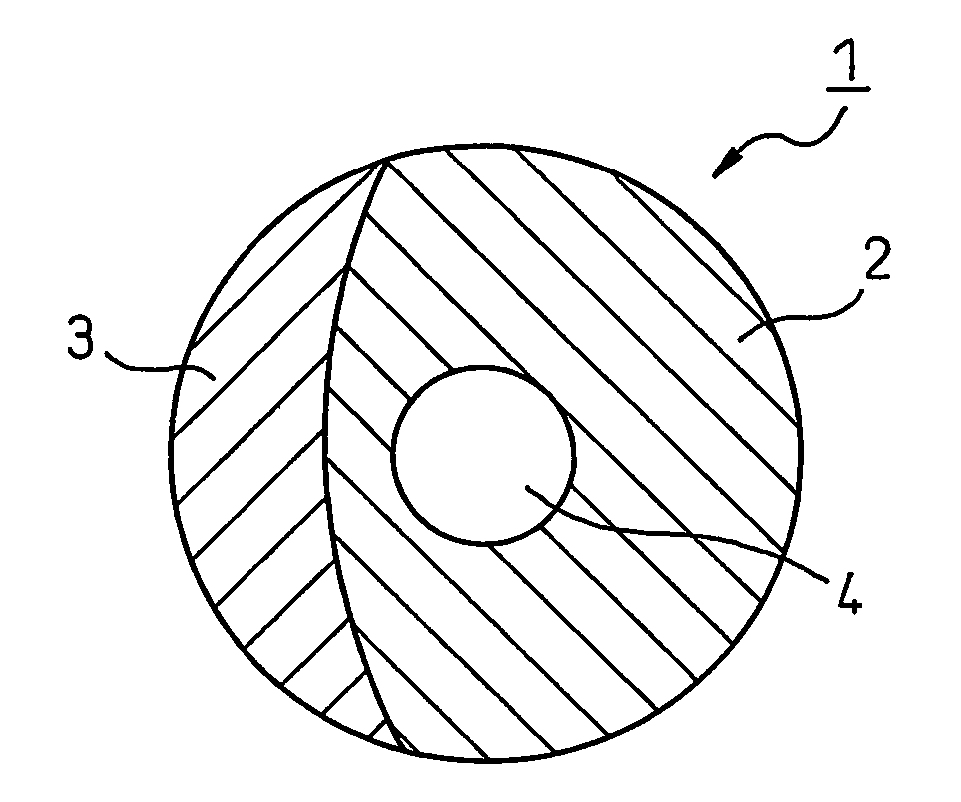
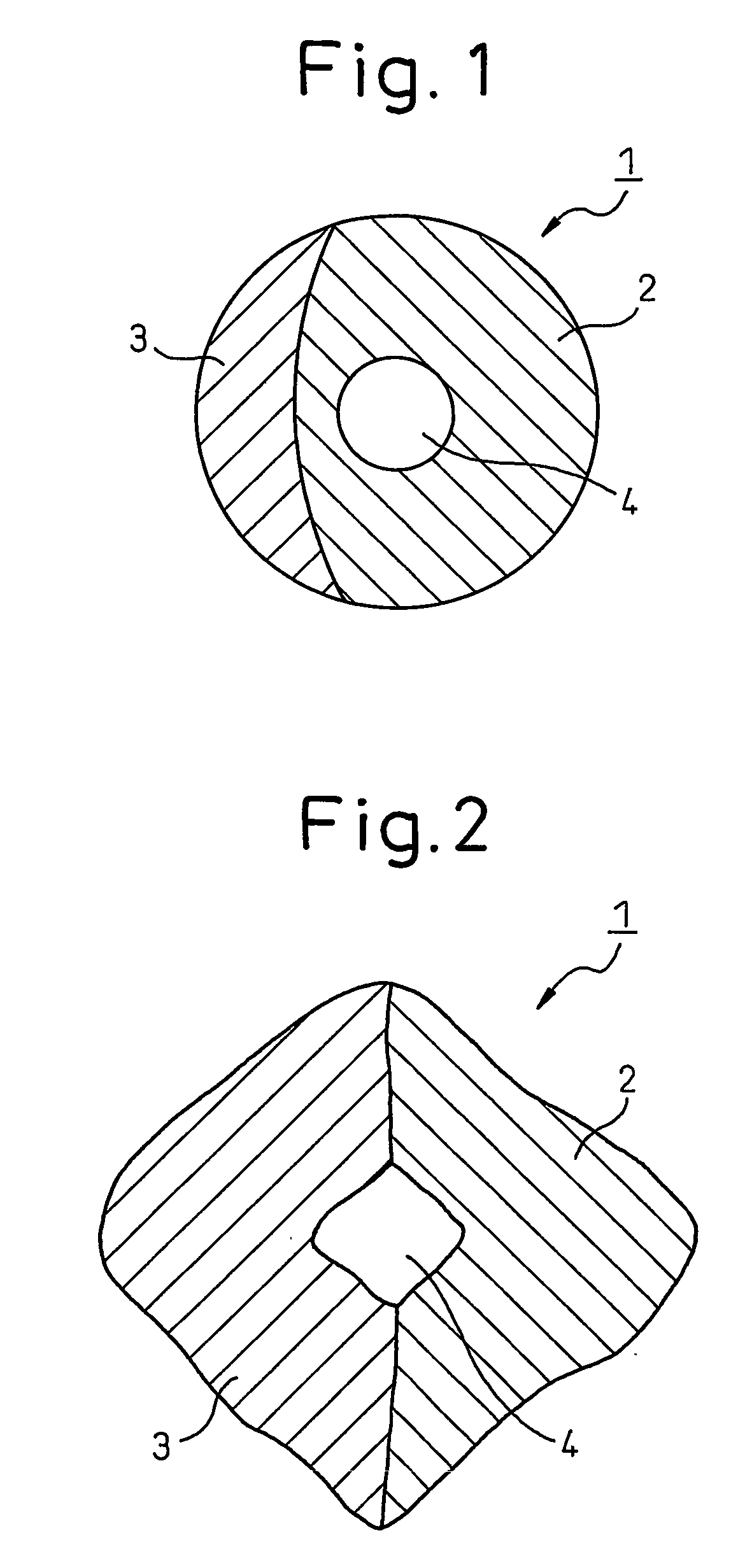
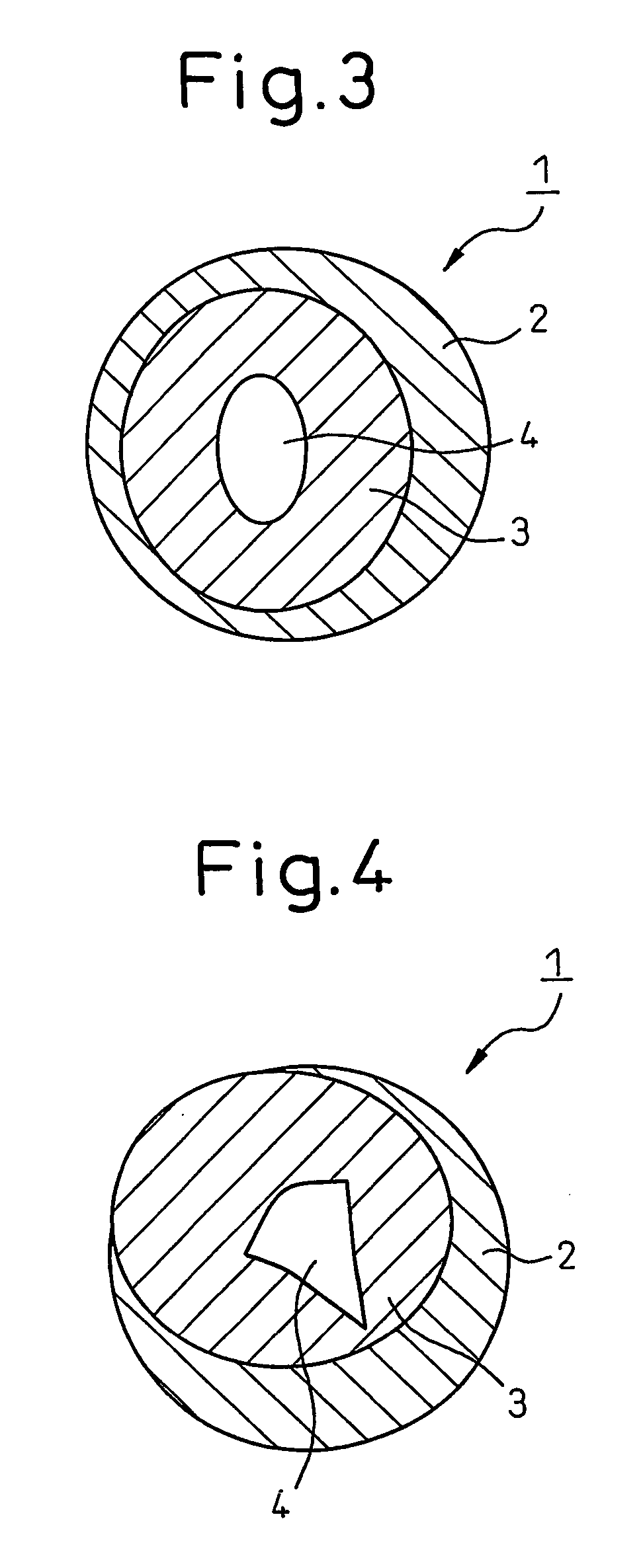
Polytrimethylene terephthalate hollow composite staple fibers and process for producing same
a technology of polytrimethylene terephthalate which is applied in the direction of filament/thread forming, transportation and packaging, yarn, etc., can solve the problems of composite filamentary streams that adhere to adjacent streams or to spinnerets, the melt-spinning procedure cannot be stably carried out, and the degree of bending of composite filamentary streams significantly increases with increasing the difference in intrinsic viscosity between the two polyester components. , to achieve the a polytrimethylene terephthalate and polytrimethylene terephthalate terephthalate terephthalate terephthalate terephthalate terephthalate terephthalate terephthalate terephthalate a polytrimethylene terephthalate and polytrimethylene terephthalate and composite staple fibers and a technology of polytrimethylene terephthalate and a process of production process, which is applied in filament/thrase three thr
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0062] The present invention will be further explained by the following examples.
[0063] In the examples and comparative examples, the following measurements were carried out.
(1) Intrinsic Viscosity [η]
[0064] The intrinsic viscosity of polyester resin was determined in a solution of the polyester resin in a solvent consisting of orthochlorophenol at a temperature of 35° C. by using an Ubbelohde viscometer.
(2) Velocity of Cooling Air Blast
[0065] A velocity of cooling air blast having a temperature of 25° C. and a humidity of 65% applied to filamentary streams of extruded polyester resin melt in the melt-spinning apparatus at right angles to the travelling direction of the filamentary streams, to cool and solidify the filamentary streams, was measured by a wind velocity meter.
(3) Cross-Sectional Proportion of Hollow Part in Hollow Composite Fiber
[0066] In a cross-sectional profile of a hollow composite fiber, a proportion of the area of a hollow part of the hollow composite fi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com