Earth boring tool
a drilling tool and earth technology, applied in the direction of drilling machines, borehole drives, cutting machines, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the wear resistance of pdc cutters, increasing the risk of abrasion, and affecting the use of earth boring tools, so as to reduce wear and other adverse effects, increase the tangential velocity of cutters, and reduce the effect of wear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
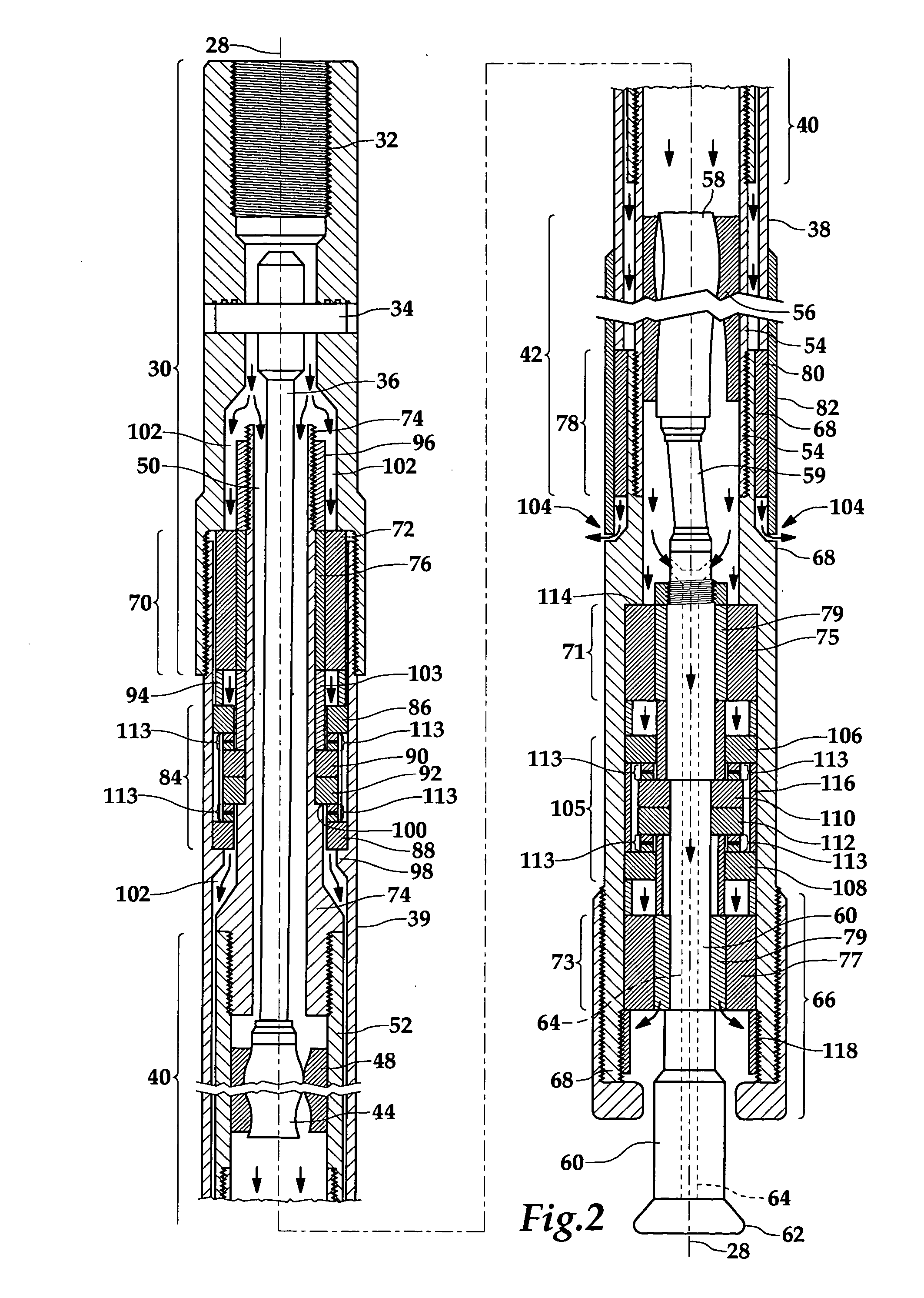
[0017] In the following description, like numbers throughout the figures refer to like elements.
[0018] Briefly, in the following example of an earth boring tool, the pilot bit and reamer are each driven by a separate motor, thereby avoiding the complexities of gears and problems occasioned by them. Examples of such problems include structural complexities necessary to have seals, with the attendant potential for failure. If seals are not used, there is a substantial risk of gear failure or jamming that is not easily addressed by merely hardening the gears.
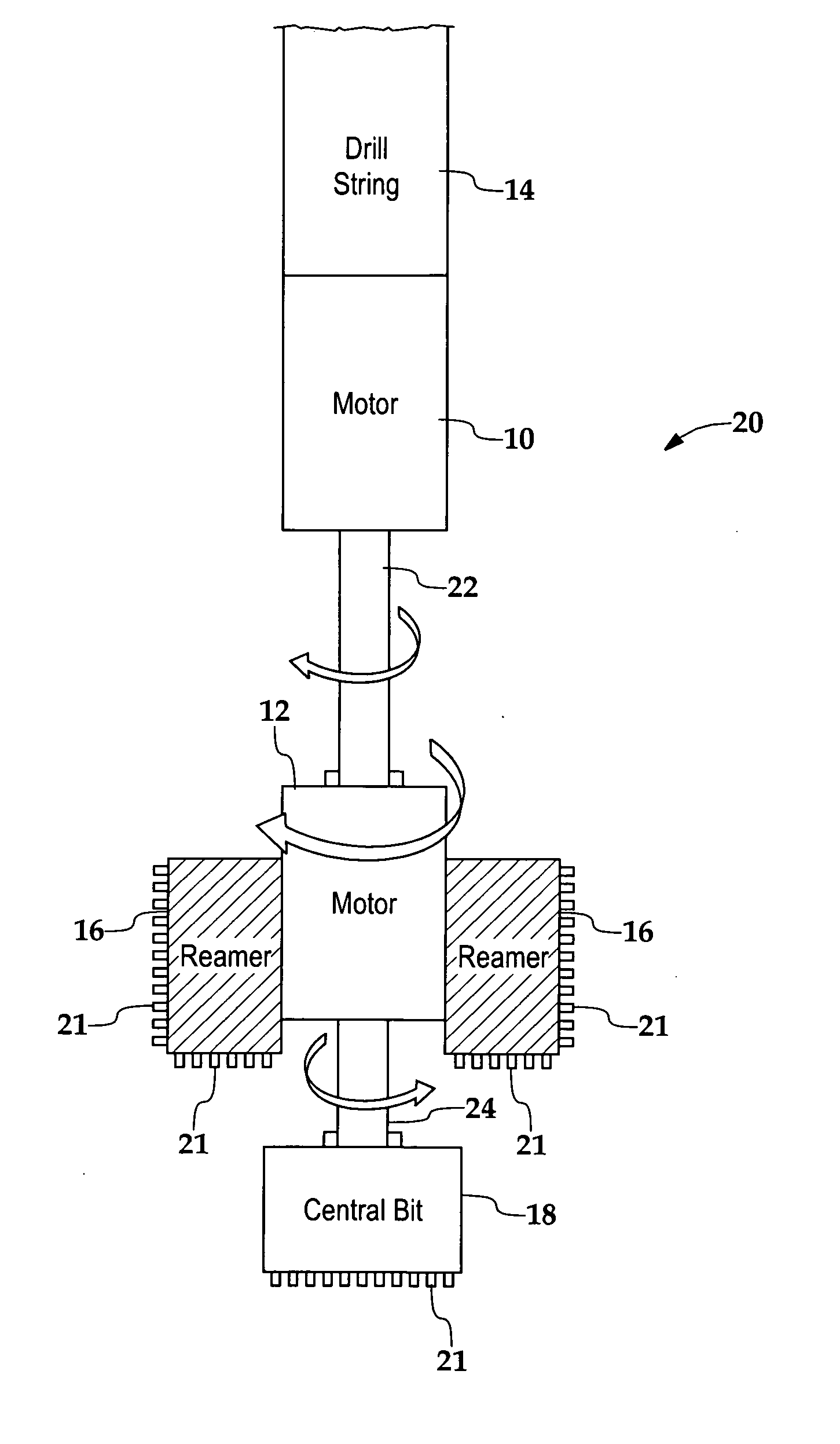
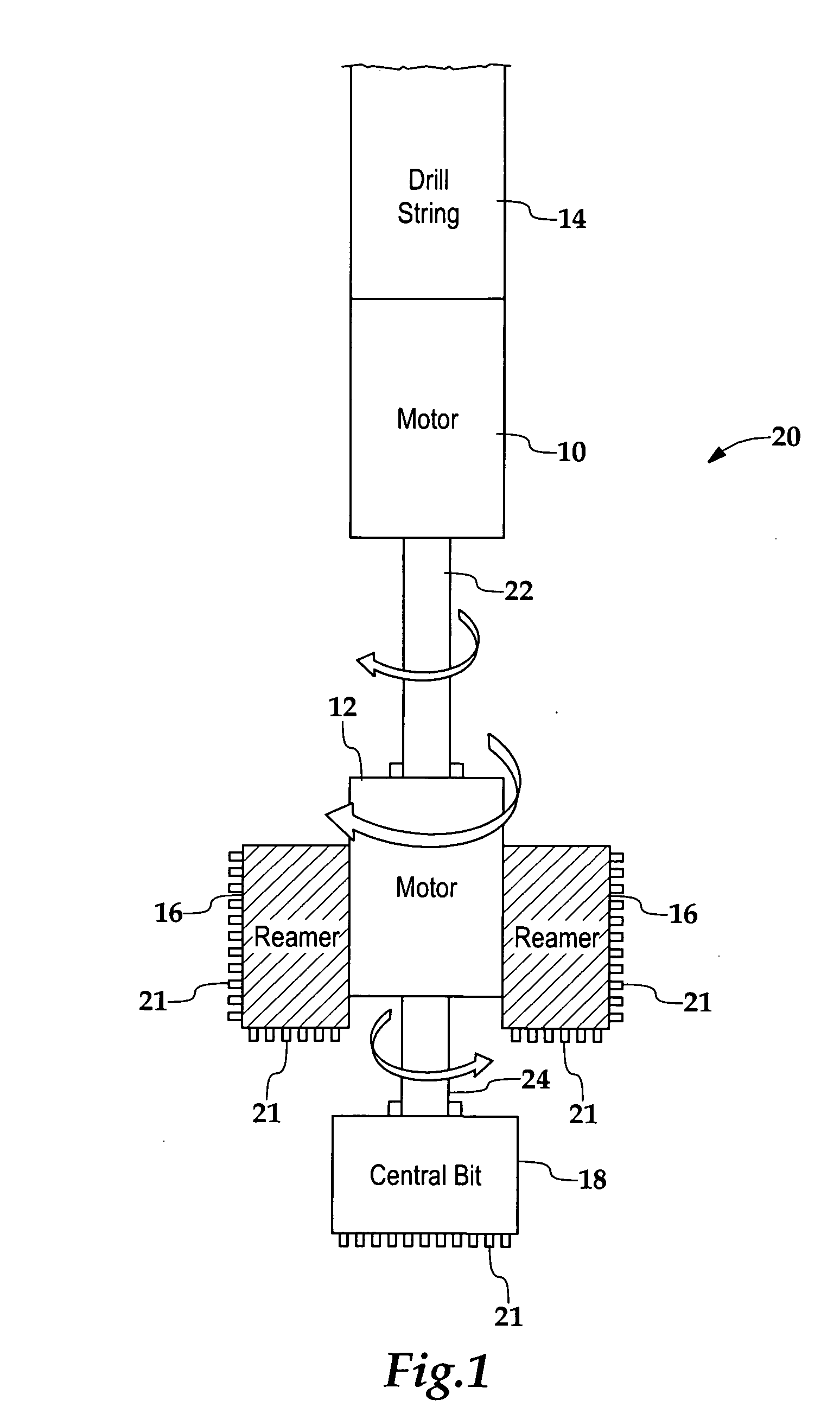
[0019]FIG. 1 schematically illustrates the functional and spatial relationships between two motors 10 and 12, a drill string 14, reamer 16 and a central bit 18 within an earth boring tool 20. The reamer and central bit each possess a plurality of cutters 21 along exterior cutting surfaces. The central bit drills a pilot hole; the sleeve-shaped or donut-shaped reamer, since it has an wider diameter, widens the hole. These cutters ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com