Process for the production of acetic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
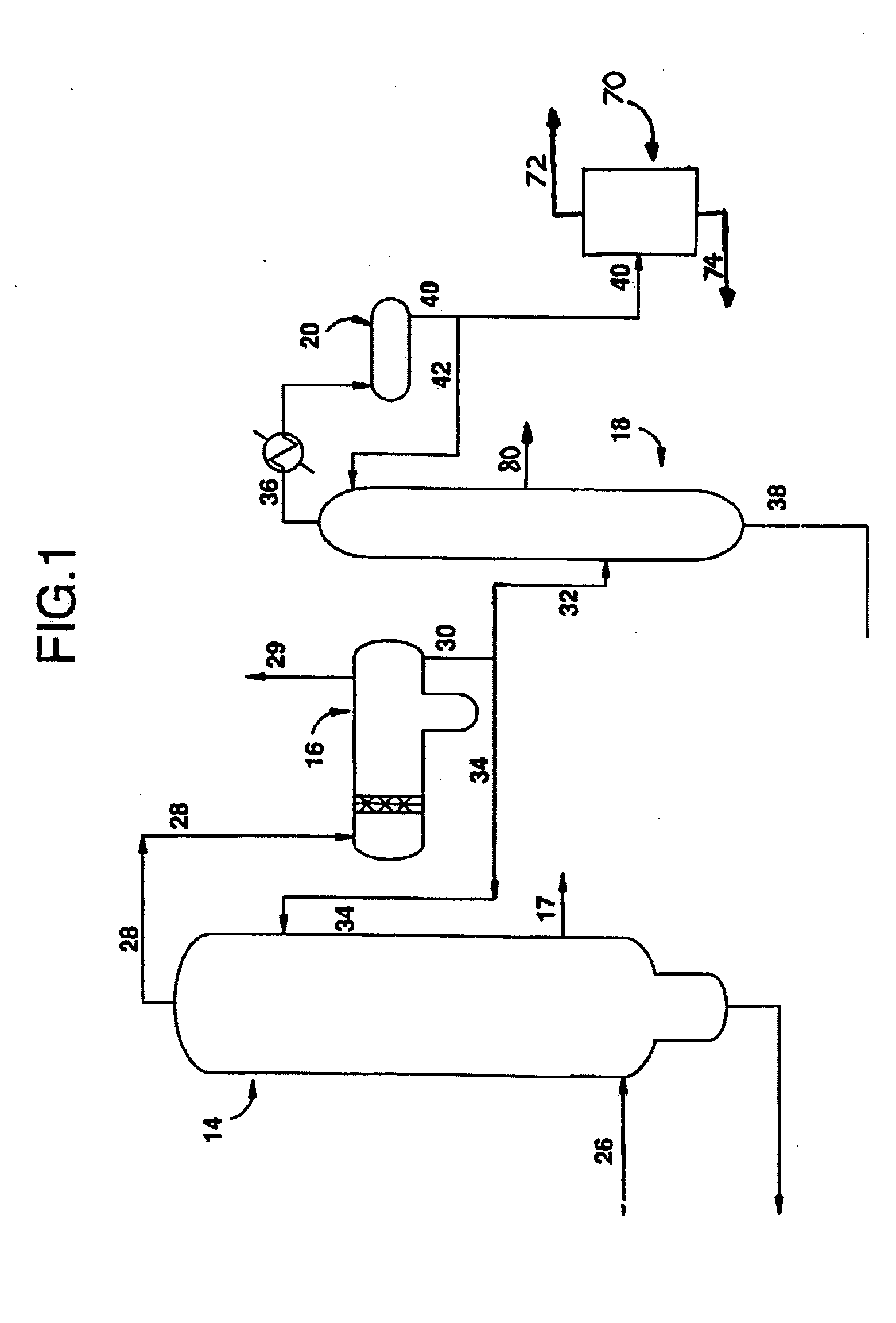
[0054] Further in accordance with this first embodiment of the present invention, second vapor phase stream 36 is extracted with water (generally indicated by 70) to remove and / or reduce PRC's, notably acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde is extracted by the water to obtain aqueous acetaldehyde stream 72, which is PRC-rich, and in particular acetaldehyde-rich. Aqueous acetaldehyde stream 72 will generally be treated as a waste, although in some embodiments acetaldehyde may be stripped, with the water being recirculated to the process. The raffinate, notably containing methyl iodide is desirably returned to the carbonylation process by stream 74. The efficiency of the extraction will depend on such things as the number of extraction stages and the water to feed ratio.
[0055] Extraction with water 70, in accordance with this first or other embodiments of the present invention, can be either a singlestage or multistage extraction and any equipment used to conduct such extractions can be used in t...
second embodiment
[0057] In accordance with the present invention, also illustrated in FIG. 1, low-boiling overhead vapor stream 28 is condensed in decanter 16 where it is biphasically separated to form a condensed heavy liquid phase and a condensed light liquid phase 30. The condensed light liquid phase 30 is provided to distillation column 18 via stream 30 / 32. Again, in this and other embodiments of the present invention, a portion of stream 30 can be directed back to the light ends column 14 as reflux stream 34. In distillation column 18, a second vapor phase stream 36 overhead and a higher boiling liquid phase residuum stream 38 are formed. A sidestream 80, comprising methyl acetate, is also taken.
[0058] The sidestream 80 allows the distillation column 18 to be operated under conditions desirable for obtaining a higher concentration of acetaldehyde in second vapor phase stream 36 while providing a mechanism for removing methyl acetate that might otherwise build up in the center of distillation co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Phase | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com