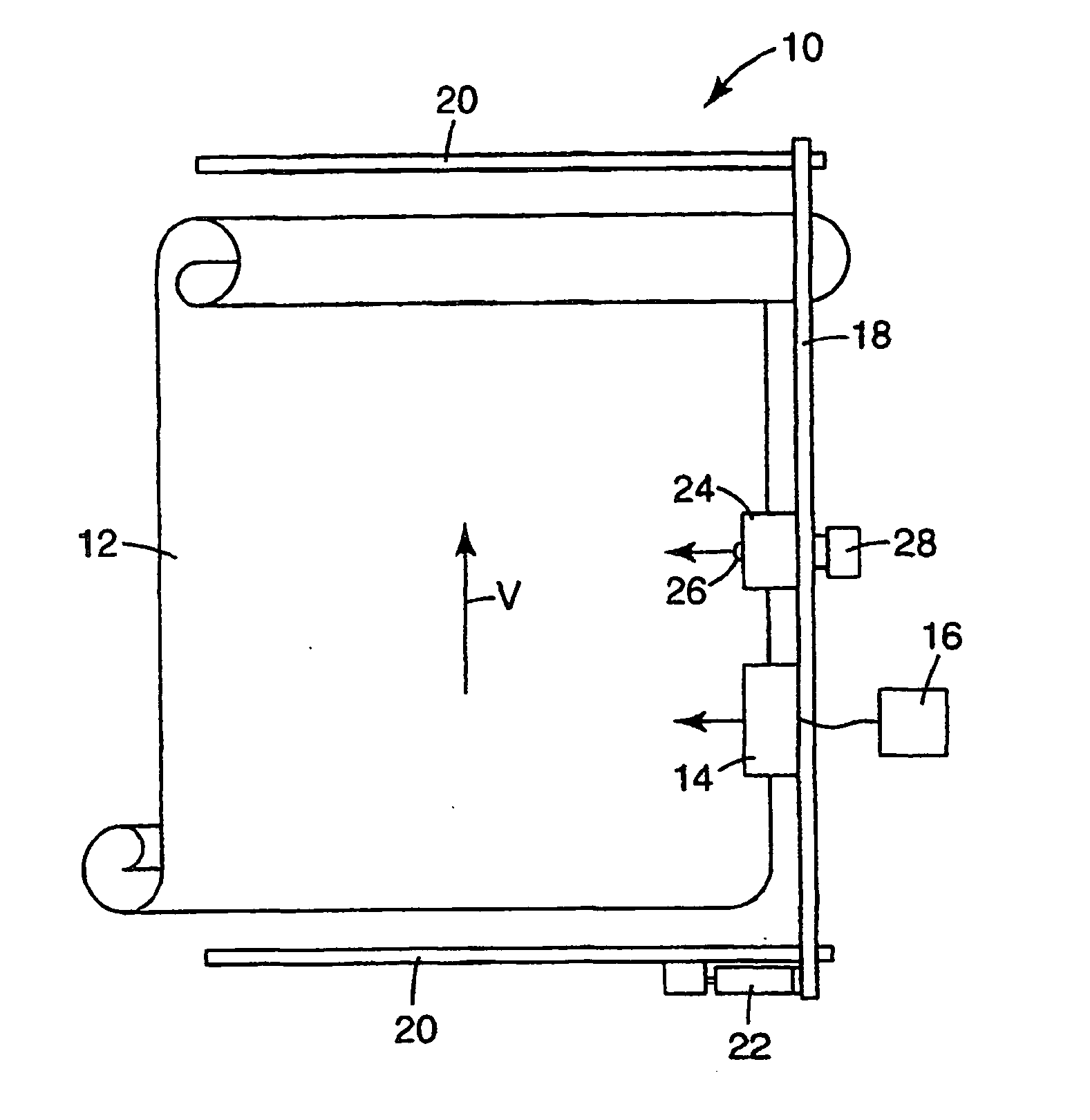
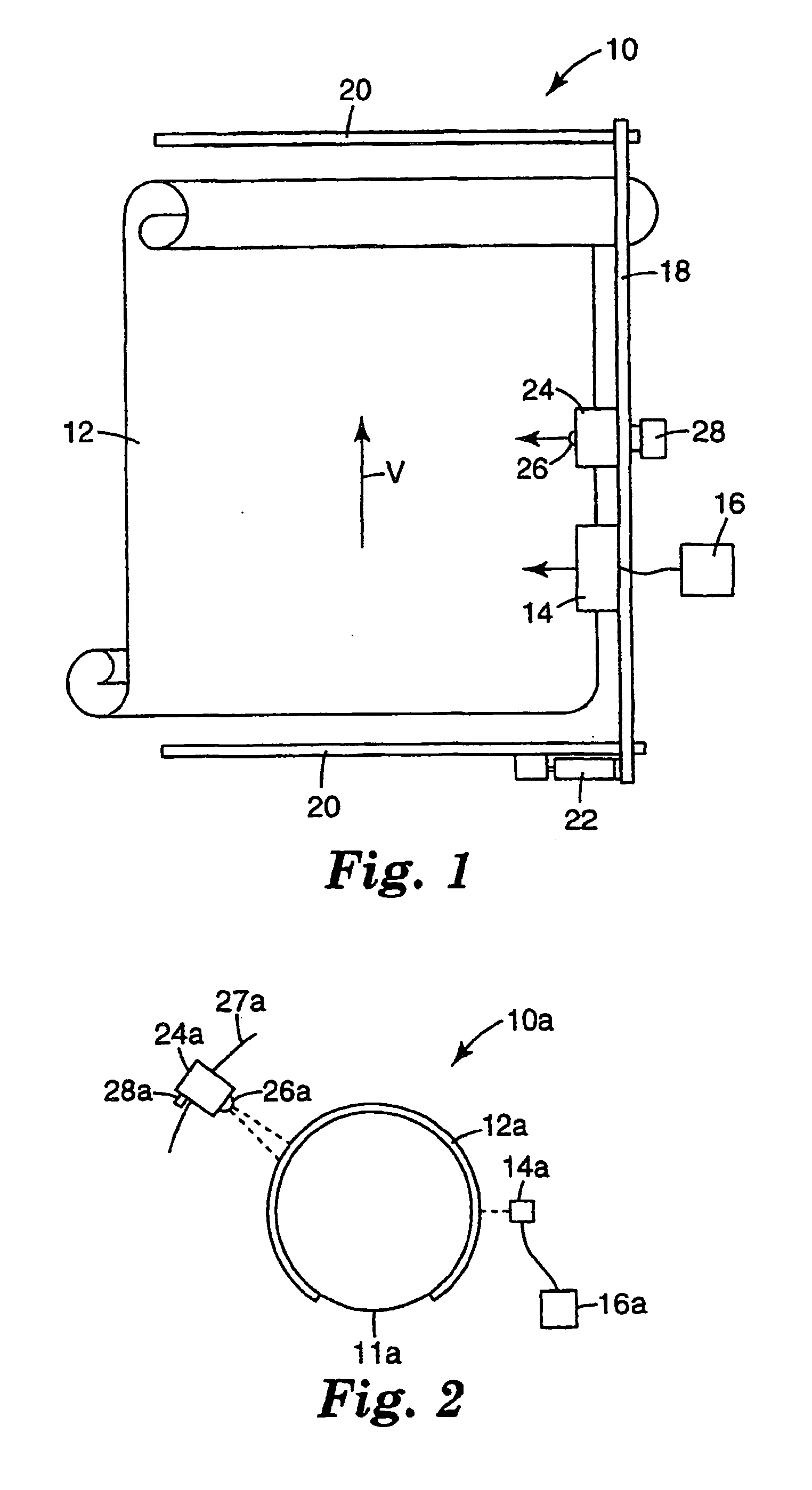
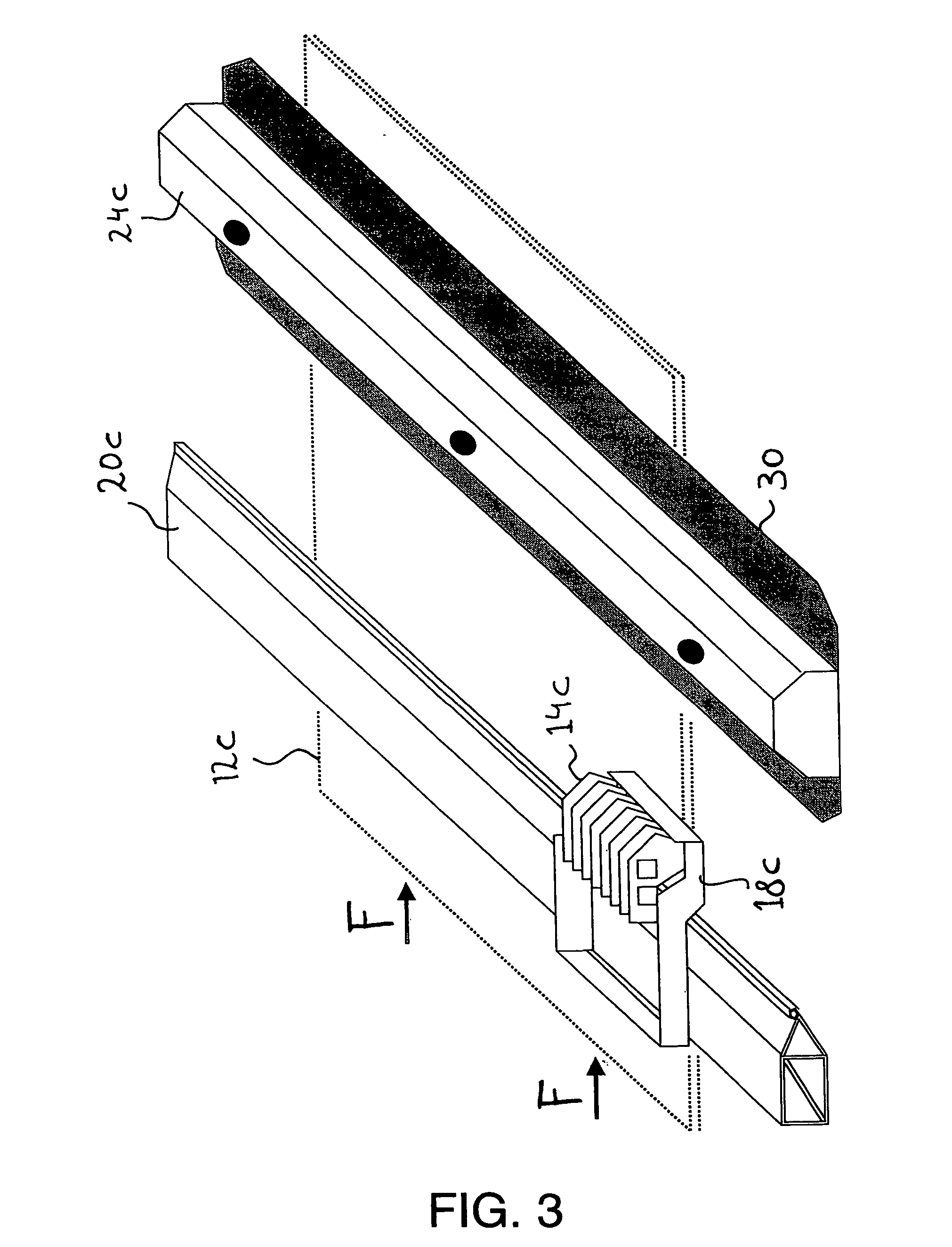
Method for printing a substrate with radiation curable ink, and an ink suitable for application in the said method
a technology of curable ink and substrate, which is applied in the field of printing a substrate with radiation curable ink, can solve the problems of inability to print inkjet printing, inability to meet the requirements of printing, and inability to achieve the effect of ensuring the quality of printing, avoiding the spread of ink, and enabling the fine-tuning of the dot gain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0036] A UV-curable ink has been made that is based on a carrier composition comprising 36,5 weight % 1,6-hexanediol-ethoxylate-diacrylate (see Formula 1 here-beneath), 36,5 weight % di-trimethylolpropane tetraacrylate (see Formula 2), 18 weight % N-vinylcaprolactam (see Formula 3) and 9 weight % of the photoinitiator 2 para tolyl-2-(dimethylamino)-4′-morfolinobutyrofenon available (at Ciba Specialty Chemicals, Basel, Switzerland) under the tradename Irgacure 379. To this carrier composition 1.5 parts per hundred parts carrier composition (1.5 phr) carbon black is added as a marking material. This carbon black is available as Nipex 150 at Degussa AG Germany, and is dispersed using Solsperse 39000 (1 part per part carbon black) and Solsperse 5000 (1 part per 4 parts Carbon black) both available from Noveon Inc., USA with 2-butanone as the dispersing medium. Next to this 1.5 phr stearon (i.e., (C17H35)2C═O) is added as a gelling agent. Note that stearone as a compound for inkjet inks ...
example 2
[0038] A second UV-curable ink has been made that is based on a carrier composition comprising 4.9 weight % Limoneen dioxide (LDO) (available from Arkema Inc, Philadelphia, USA), 24.9 weight % Bis{[1-ethyl(3-oxetanil)]methyl}ether (available as OXT-221 from DKSH-Market Intelligence, Zurich, Switzerland), 20.0 weight % Bis-(3-4-epoxycyclohexylmethyl)adipate (available as UVR-6128 from Dow Chemicals, Horgen, Switzerland), 32.35 weight % (m / m) 3-ethyl-3-phenoxymethyl-oxetane (available as OXT-211 from DKSH-market intelligence, Zurich, Switzerland). The carrier composition further comprises 1.25 weight % Carbon black, 1.5 % 2-ethyl-9,10-dimethoxy anthracene (available from Sigma-Aldrich, St.-Louis, USA), 15% Photo initiator Chivacure 1172 (available from Double Bond Chemical, Tapei Taiwan) and 0.1 % Byk UV3510 (available from Byk Chemie GmbH, Wesel, Germany). As a gelling agent 2 phr stearon is added. This ink can be used in the same way as the ink described under example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com