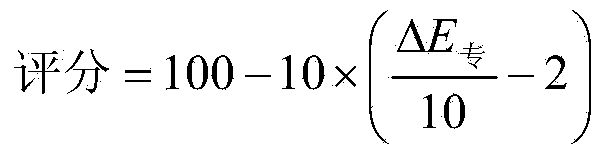Patents
Literature
64 results about "Dot gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dot gain, or tonal value increase, is a phenomenon in offset lithography and some other forms of printing which causes printed material to look darker than intended. It is caused by halftone dots growing in area between the original printing film and the final printed result. In practice, this means that an image that has not been adjusted to account for dot gain will appear too dark when it is printed. Dot gain calculations are often an important part of a CMYK color model.
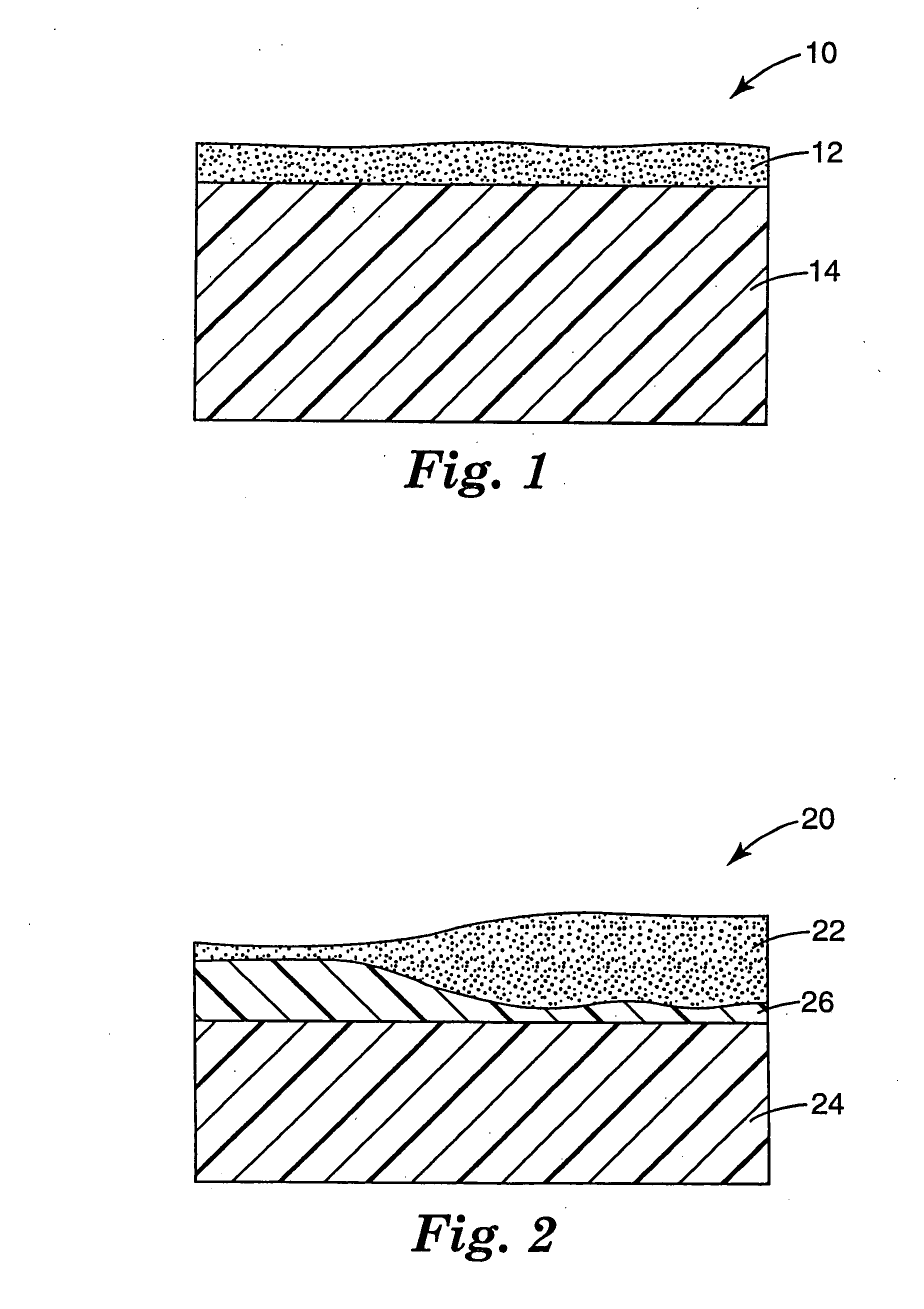
Reproduction color prediction apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050083346A1Improve accuracyAvoid difficult choicesDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionDot gain
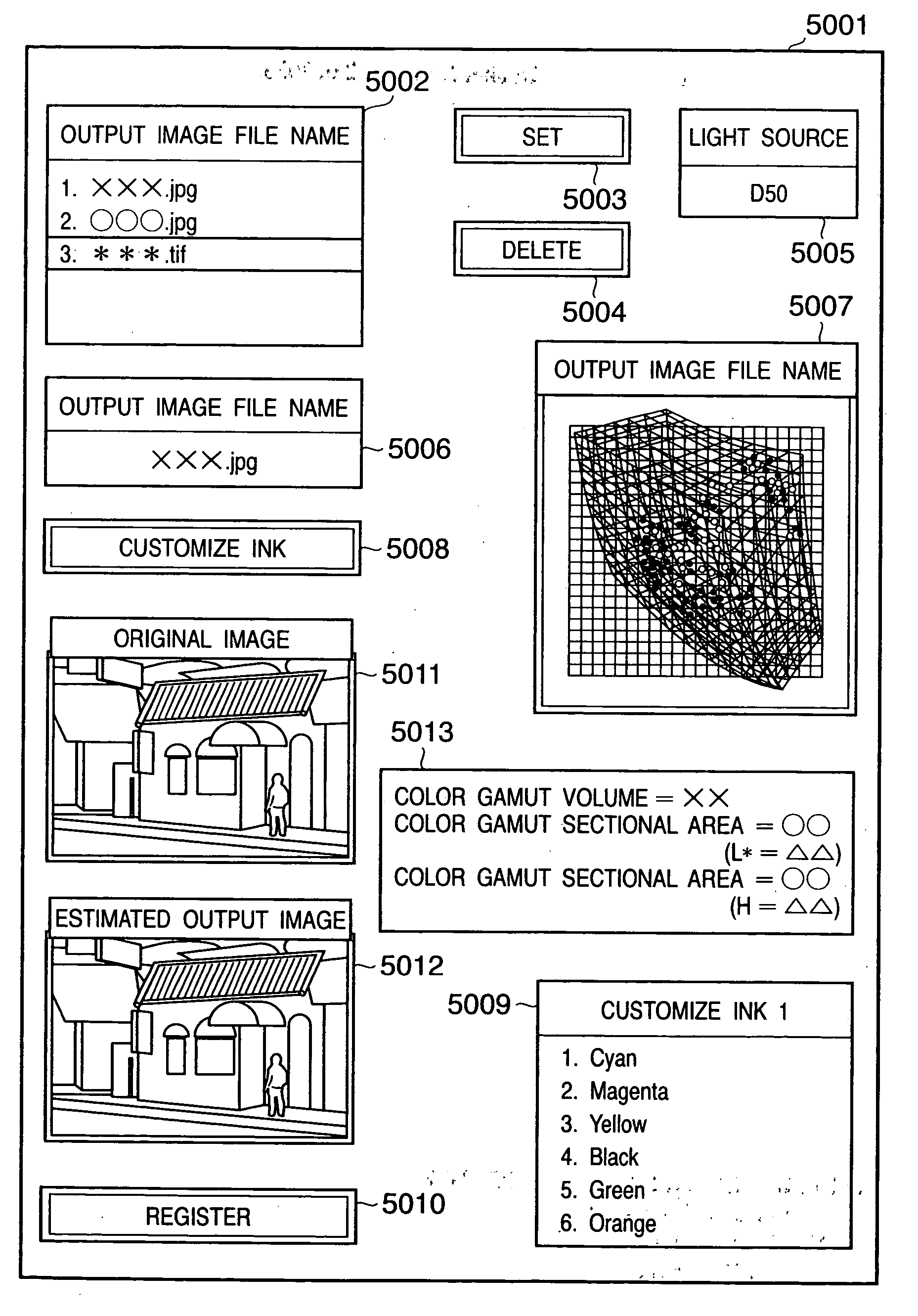
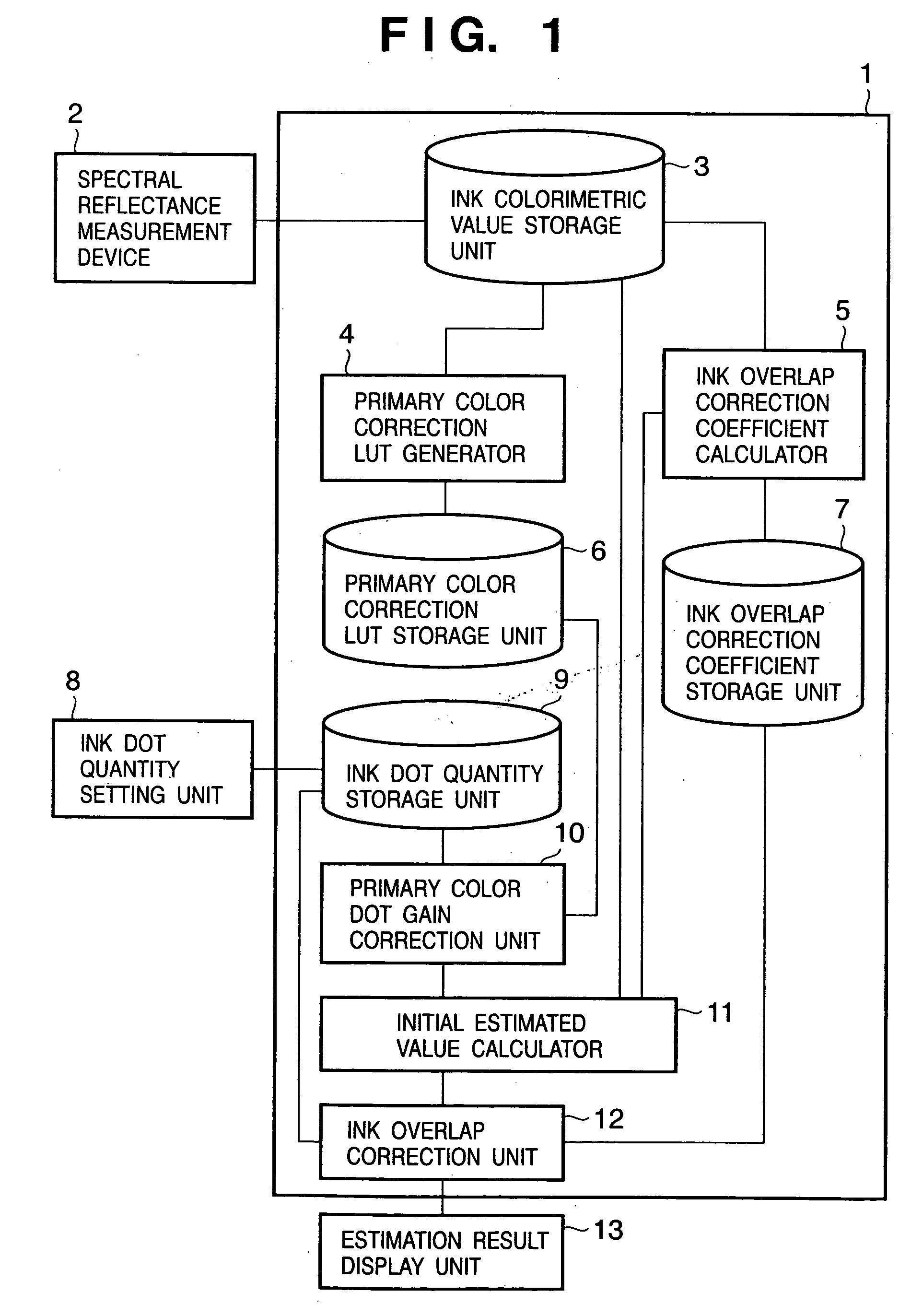
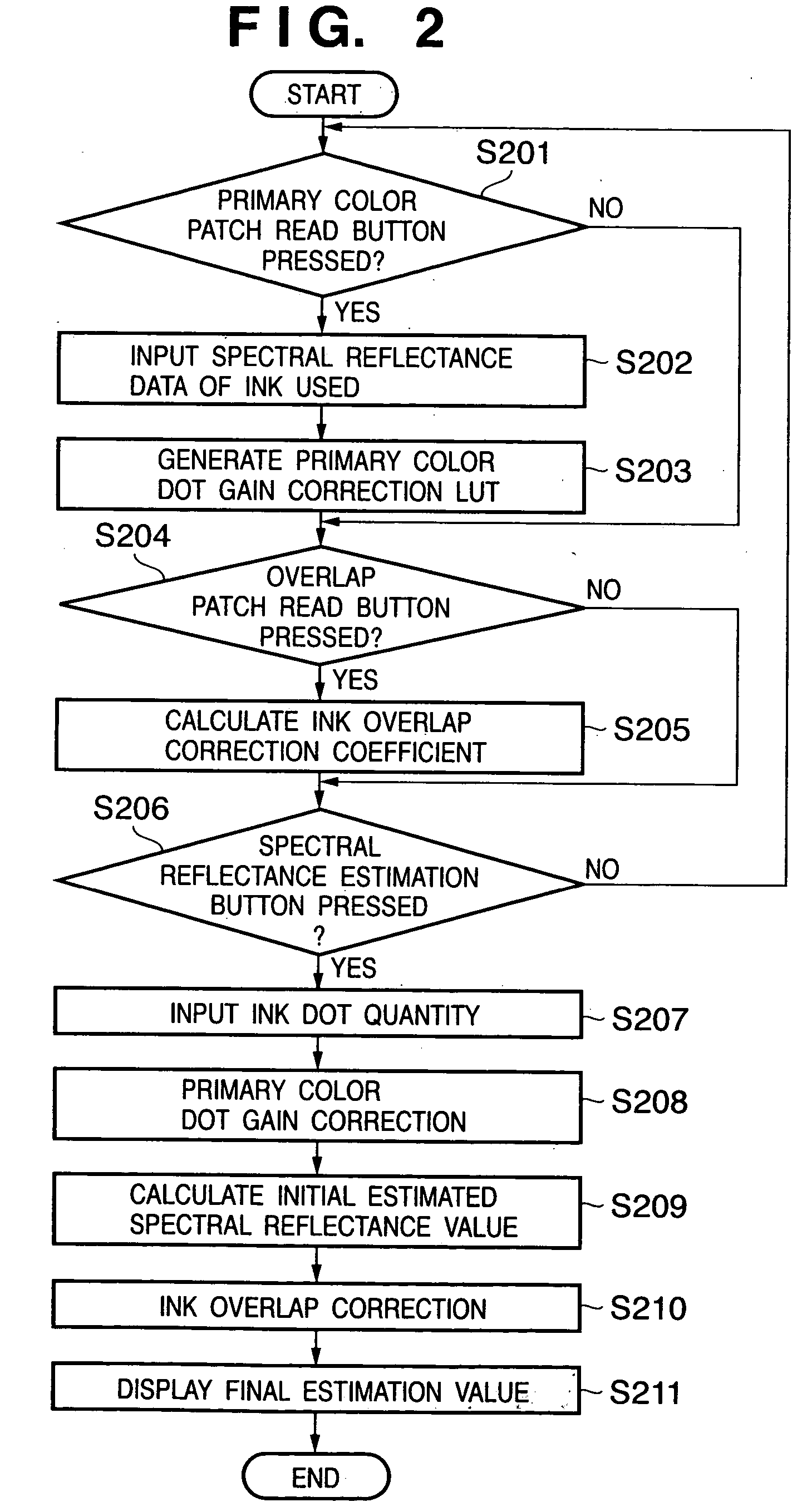
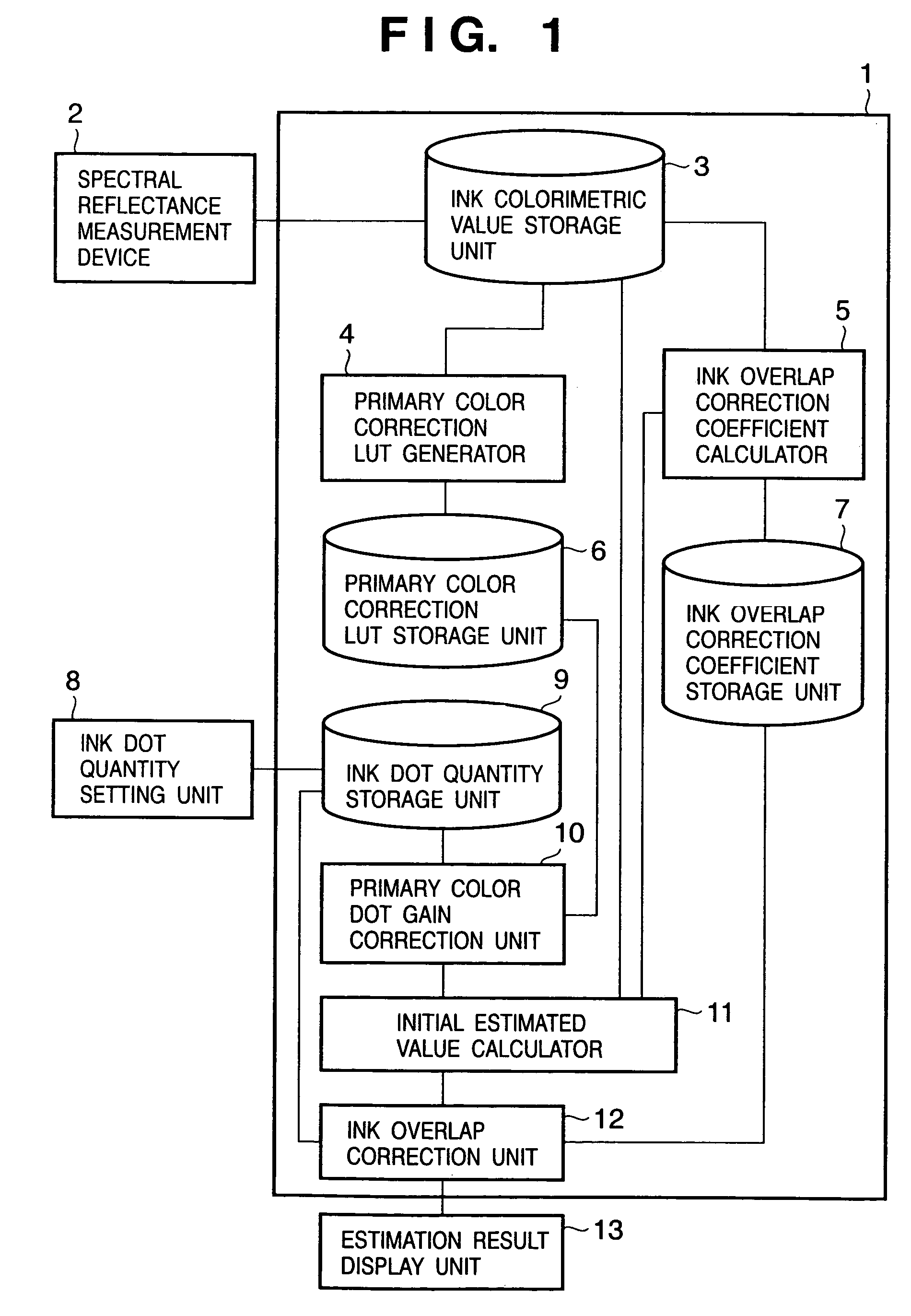
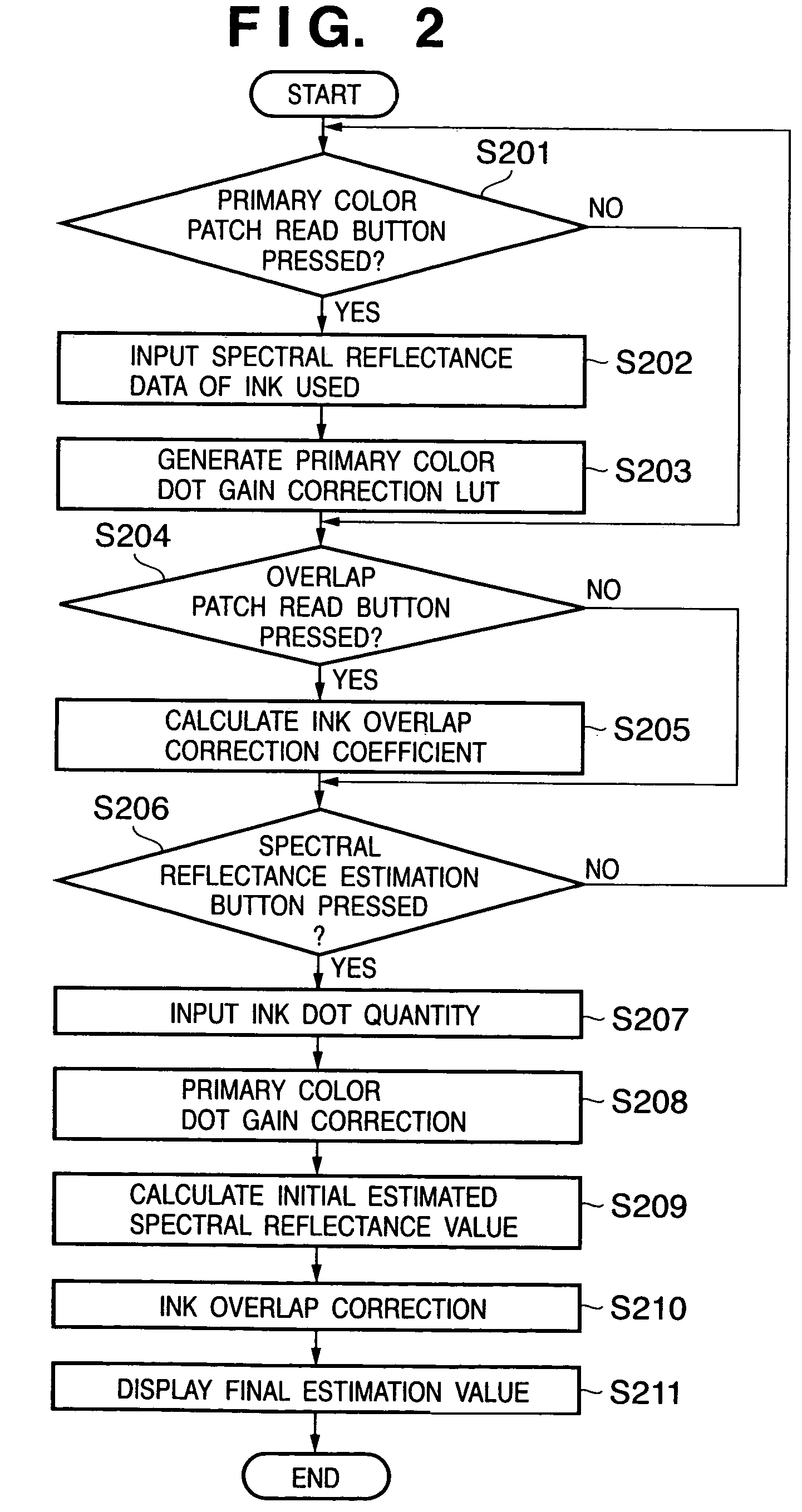
A primary color dot gain correction unit corrects the spectral reflectance of each of a plurality of color agents on the basis of the dot quantity set for each color agent. An initial estimated value calculator estimates a mixed color by the KM theory using spectral reflectance data corrected by the primary color dot gain correction unit. An ink overlap correction coefficient storage unit stores correction coefficients, which are determined on the basis of errors between the actually measured values of spectral reflectance data of color patches obtained using the plurality of color agents, and estimated values estimated by the initial estimated value calculator based on the dot quantities of the respective color agents on the color patches. An ink overlap correction unit obtains the prediction result of a reproduction color by correcting the spectral reflectance data of the mixed color calculated by the initial estimated value calculator on the basis of the correction coefficients stored in the ink overlap correction coefficient storage unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods and compositions for ink jet printing of pressure sensitive adhesive patterns or films on a wide range of substrates
InactiveUS20020128340A1Minimize dot gainLow viscosityAdhesive processesImpression capsDot gainFluid composition
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Imaged articles comprising a substrate having a primed surface
InactiveUS20030054139A1Decorative surface effectsSynthetic resin layered productsSolubilityImaging quality
The present invention relates to an imaged article comprising a substrate having a primed surface layer. The primed surface layer is comprised of a base polymer having a solubility parameter, molecular weight (Mw) and glass transition temperature within a specified range. The presence of the primer improves the overall image quality by improving at least one property including ink uptake, dot gain, color density and / or ink adhesion. Preferred primer compositions are soluble at least in part in the ink composition resulting in an increase in ink layer thickness that further improves the durability and / or day / night color balance. A variety of substrates may be primed including various sheeting for traffic control signage and commercial graphic films for advertising and promotional displays.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
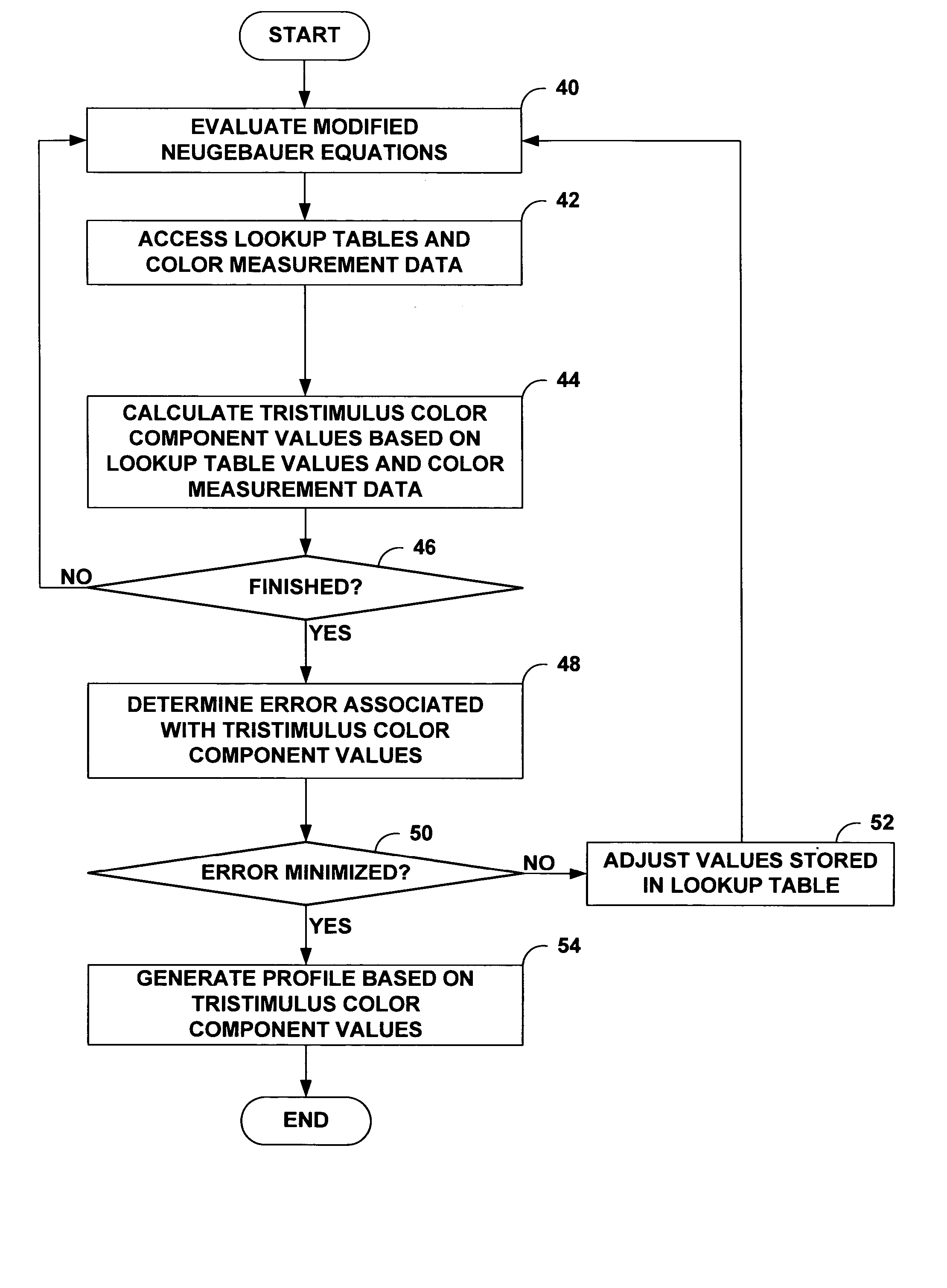
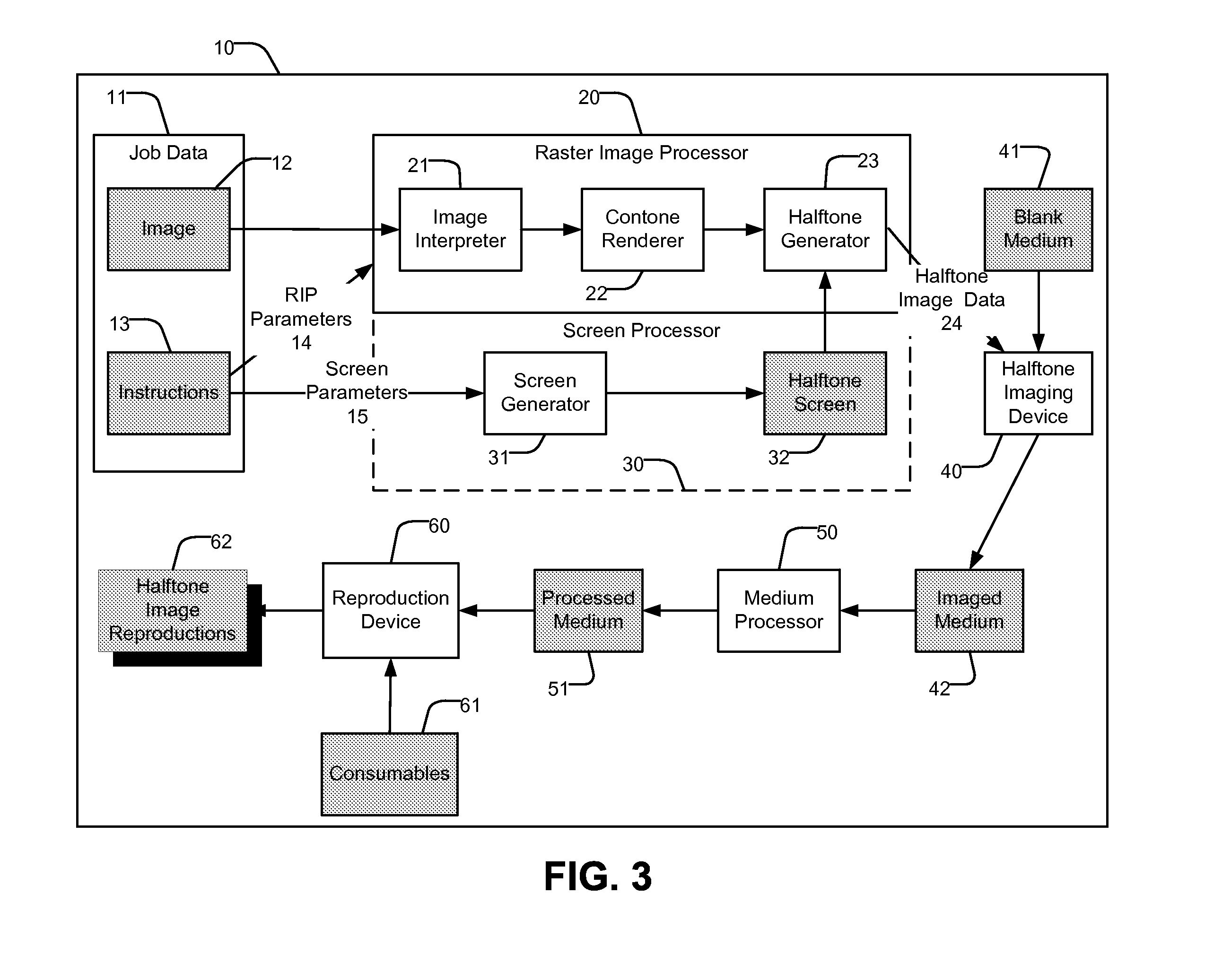
Modified neugebauer model for halftone imaging systems
ActiveUS20050036163A1Accurate and smooth characterizationAccuracyImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersColor printingDot gain
A technique for profiling a color printing device employs a modified Neugebauer color mixing model. The modeling technique makes use of a variable dot gain value and “n factor.” The variable dot gain adjustment value may vary according to the particular tristimulus channel under evaluation. In addition, the variable dot gain value may vary according to the particular Neugebauer primary over which a halftone dot is printed. Accordingly, the technique may rely on an array of different dot gain values and n factors that correspond to different combinations of color channels and overprint conditions. As a further feature, the techniques may rely on a dot gain formula that relates halftone dot variation, i.e., fringe thickness, to the size of the halftone dot. This relationship tends to produce a dot gain model that more closely resembles the actual dot gain behavior on a printing press.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
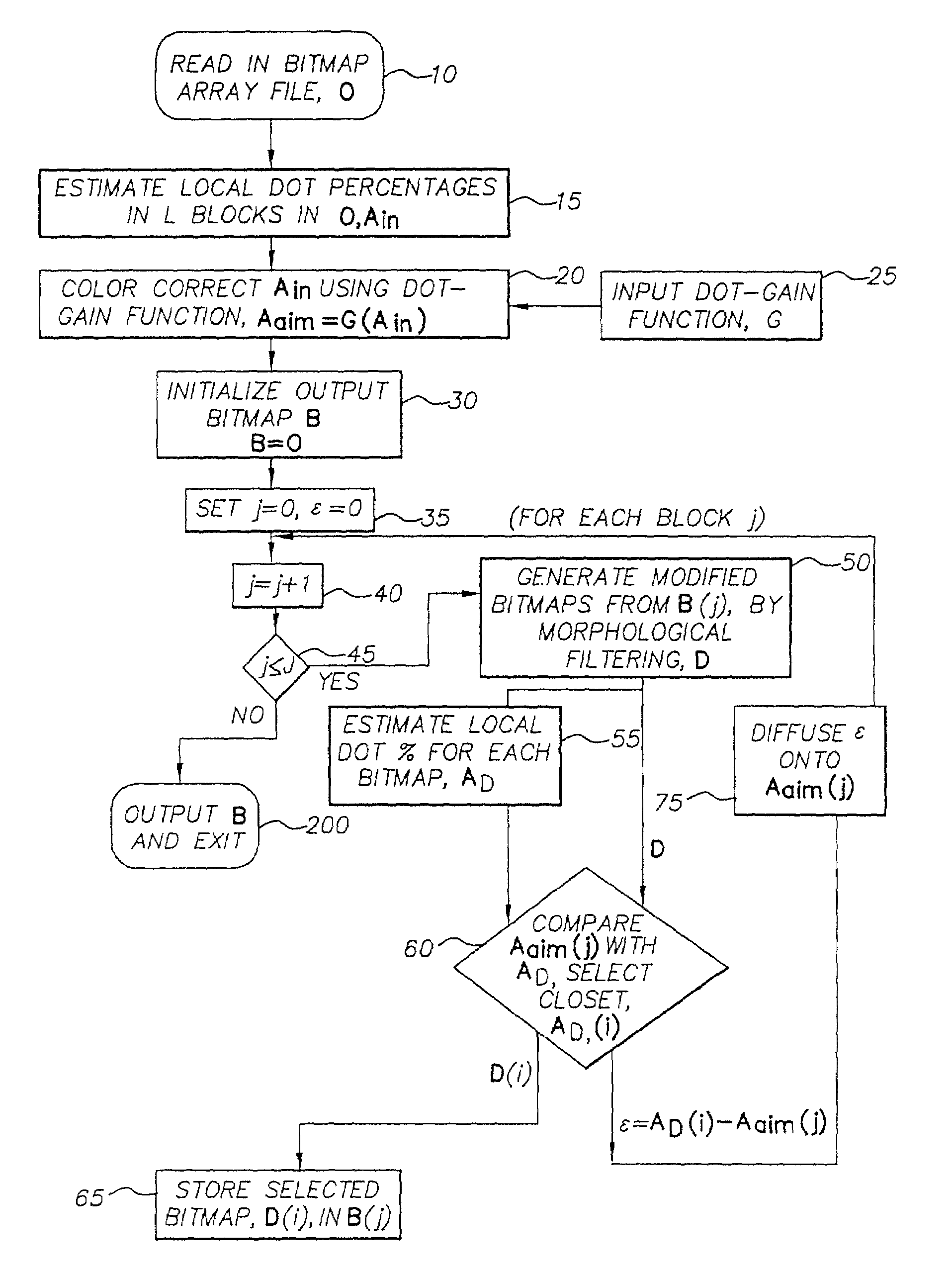
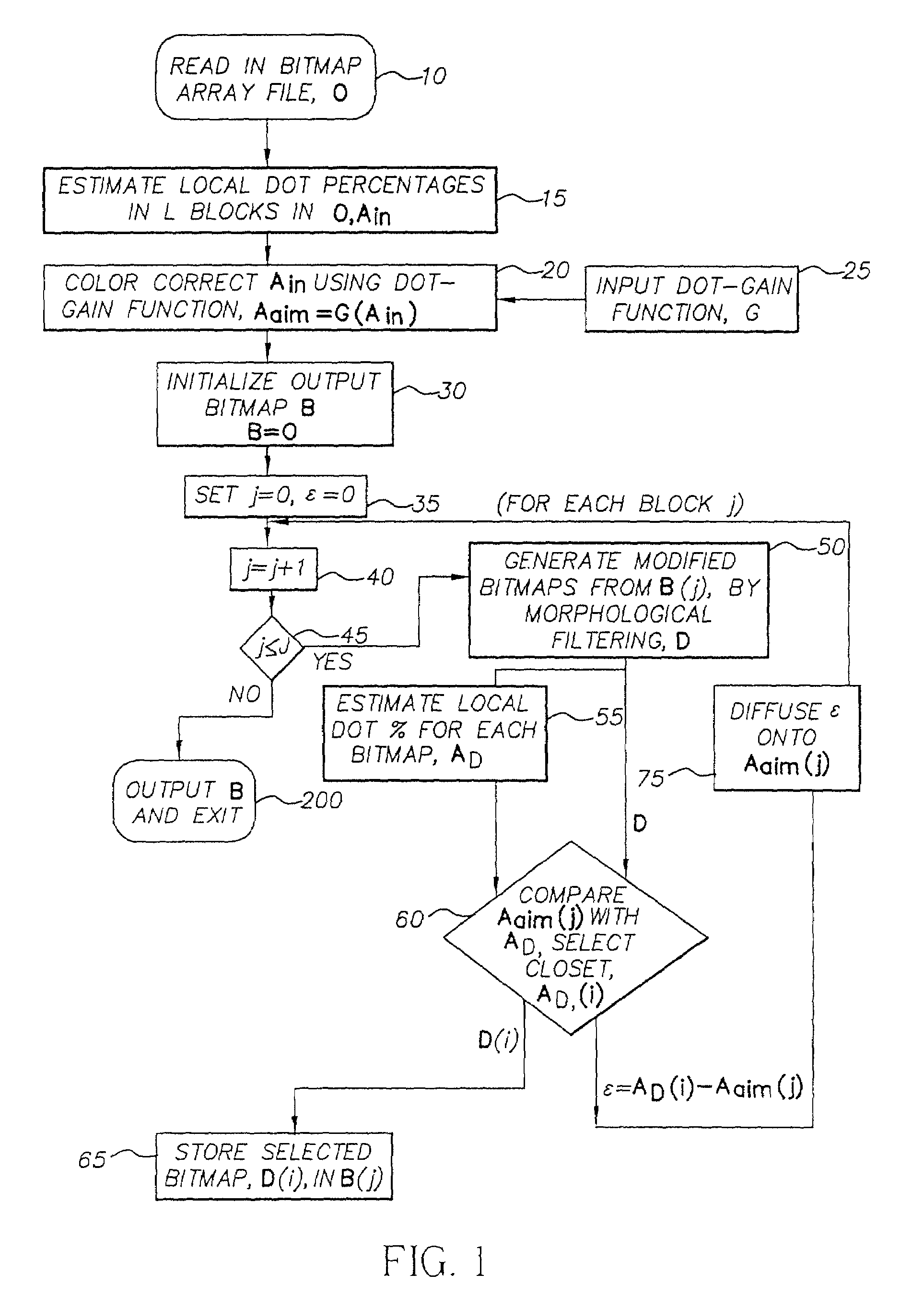
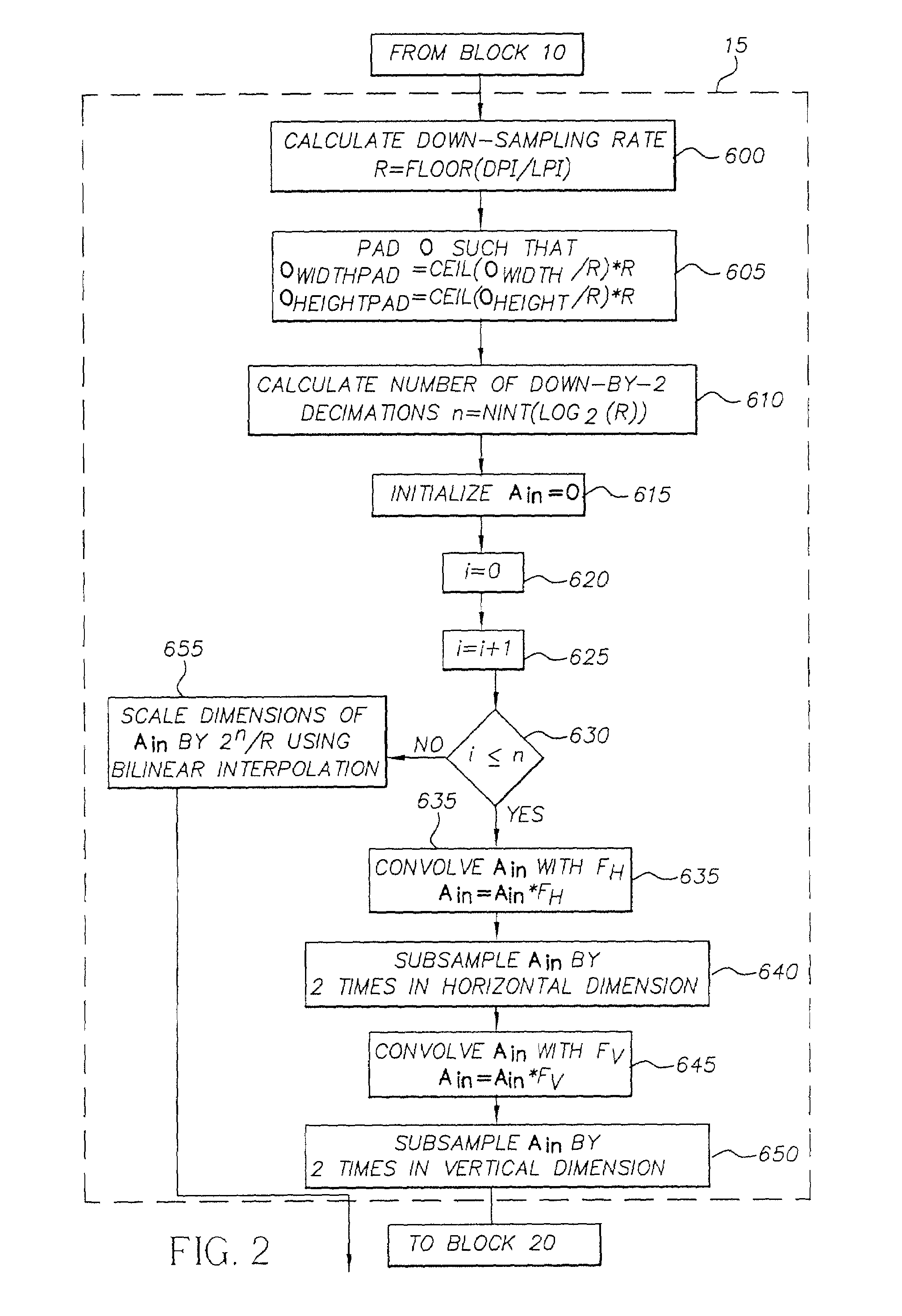
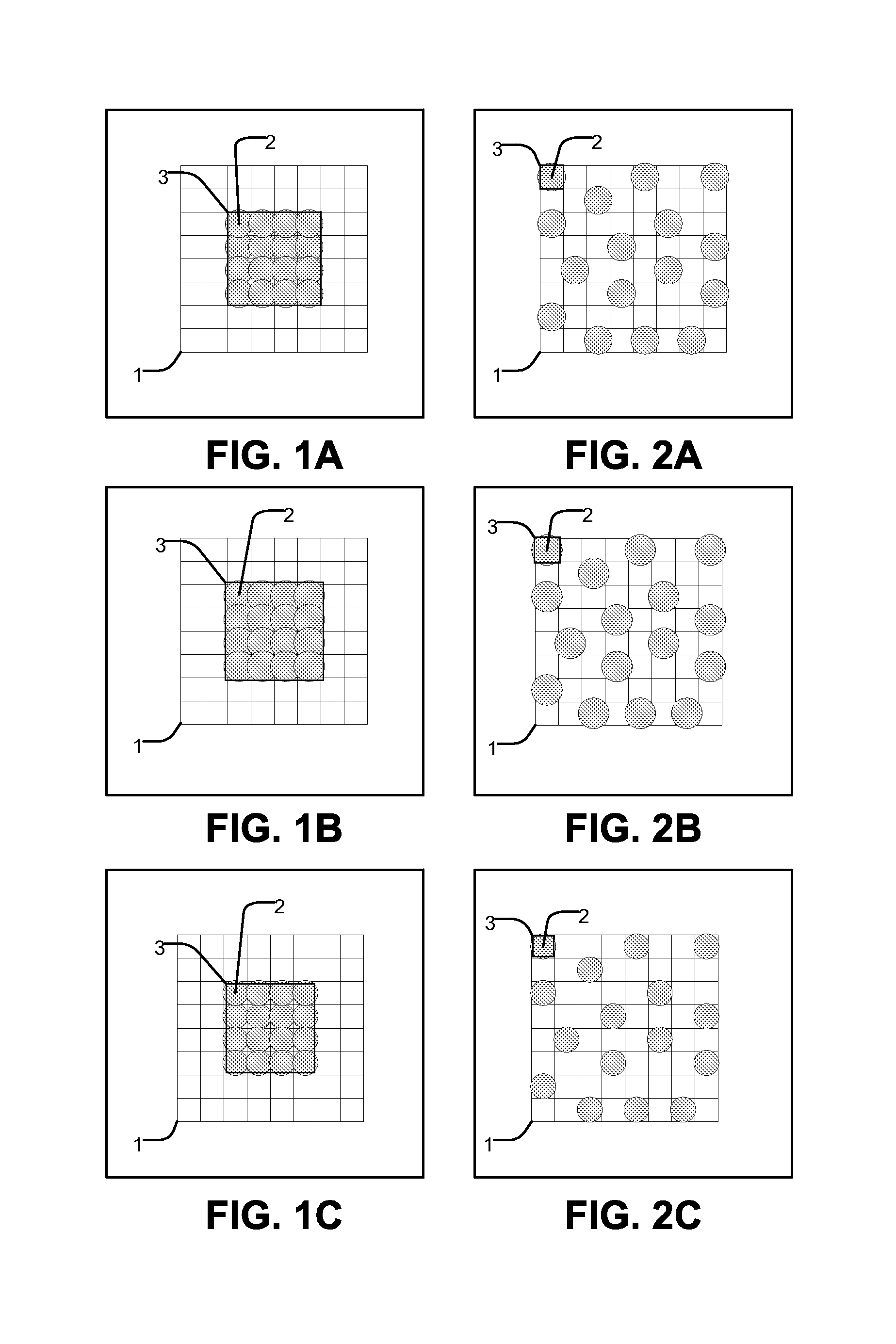
Halftone dot-growth technique based on morphological filtering
InactiveUS7365881B2Reduce errorsImprove visibilityImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersMorphological filteringDot gain
A method for converting an original halftone bitmap image to a color converted halftone bitmap image. A set of asymmetrical morphological filters is provided. The original halftone bitmap image is segmented into blocks and for each block: apply the set of morphological filters to the original halftone bitmap image to produce a set of modified halftone bitmap images; estimate the percent dot area of the original halftone bitmap image and the set of modified halftone bitmap images; a predetermined dot-gain to the percent dot area of the original halftone bitmap image to produce a modified percent dot area; select the modified halftone bitmap image whose percent dot area is closest to the modified percent dot area to produce a block of the color corrected halftone bitmap image; and replace the original halftone bitmap image with the combined blocks of selected modified halftone bitmap image.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Reproduction color prediction apparatus and method
InactiveUS7433102B2Avoid difficult choicesExact reproductionDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsDot gainErrors and residuals
A primary color dot gain correction unit corrects the spectral reflectance of each of a plurality of color agents on the basis of the dot quantity set for each color agent. An initial estimated value calculator estimates a mixed color by the KM theory using spectral reflectance data corrected by the primary color dot gain correction unit. An ink overlap correction coefficient storage unit stores correction coefficients, which are determined on the basis of errors between the actually measured values of spectral reflectance data of color patches obtained using the plurality of color agents, and estimated values estimated by the initial estimated value calculator based on the dot quantities of the respective color agents on the color patches. An ink overlap correction unit obtains the prediction result of a reproduction color by correcting the spectral reflectance data of the mixed color calculated by the initial estimated value calculator on the basis of the correction coefficients stored in the ink overlap correction coefficient storage unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Imaged articles comprising a substrate having a primed surface
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Methods and compositions for ink jet printing of pressure sensitive adhesive patterns or films on a wide range of substrates
InactiveUS6883908B2Low viscosityMinimize dot gainAdhesive processesImpression capsDot gainFluid composition
Methods, systems, and compositions that make it possible to form high resolution, pressure sensitive adhesive patterns or films on a wide range of substrates. The compositions generally incorporate a curable, fluid composition (i.e., pressure sensitive adhesive precursor). When cured, a pressure sensitive adhesive is formed. Ink jet printing and subsequent curing allows pressure sensitive adhesive features to be formed with high resolution and tremendous flexibility in the patterns by which adhesive features may be formed. Preferred embodiments of the invention incorporate rheology modifying agents that can be used to promote favorable dot gain and other printing characteristics, the ability to build print thickness, and mechanical properties of resultant cured adhesives.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method for detecting and analyzing printing quality of decorative paper
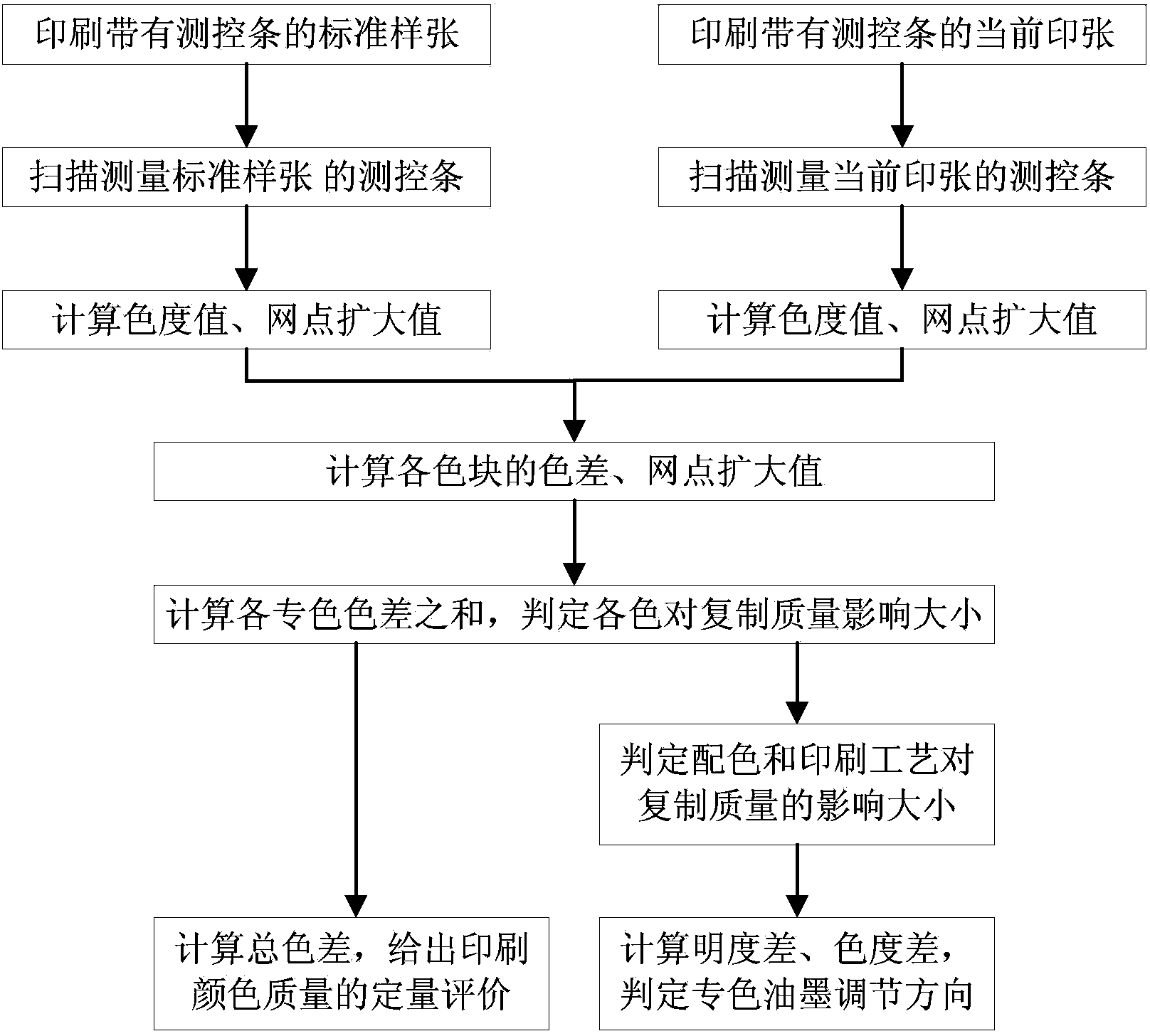
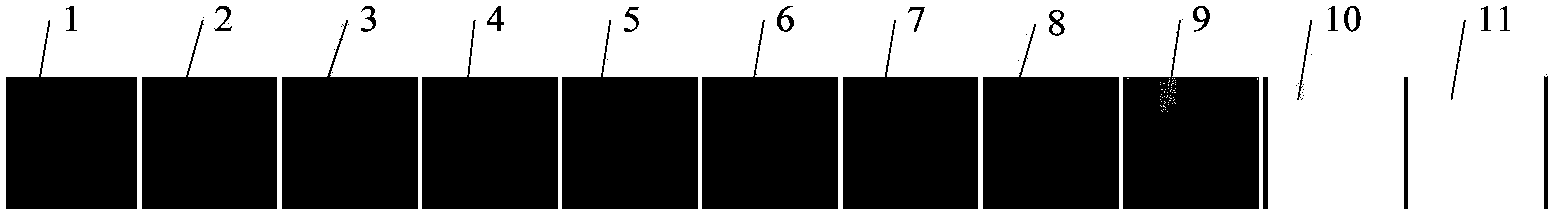
InactiveCN104034424ABeneficial quantitative evaluationGood for quantitative evaluationColor measuring devicesPrinting press partsDot gainAnalysis method
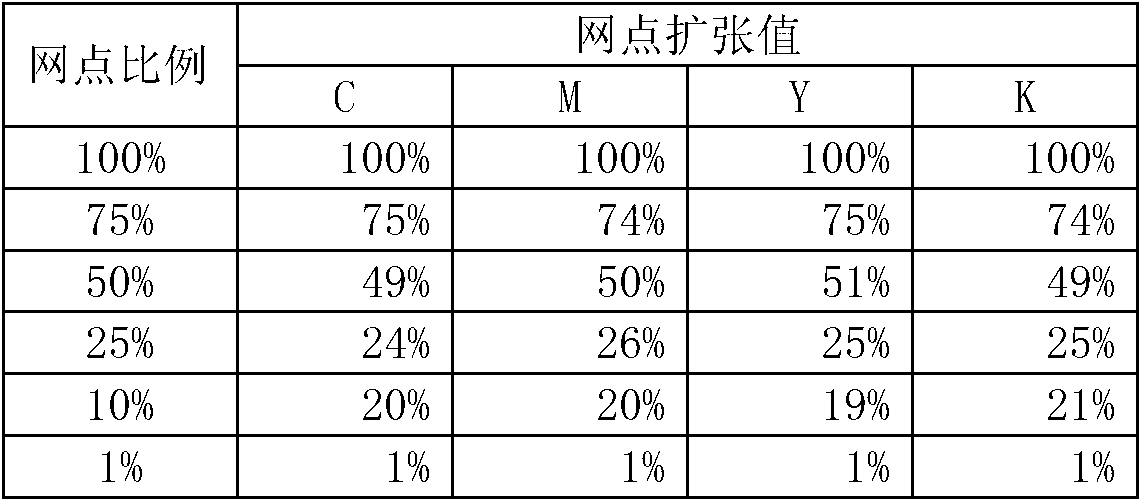
The invention discloses a method for detecting and analyzing the printing quality of decorative paper. The method comprises the steps of: scanning a control strip on standard sample paper by a spectrophotometer, obtaining spectroscopic data of each color lump in the control strip, and obtaining chromatic value and dot gain value of each color lump through further computation; re-scanning the control strip on current printed paper, obtaining spectroscopic data of each color lump in the control strip, and obtaining chromatic value and dot gain value of each color lump through further computation; comparing the chromatic value and dot gain value of the standard sample paper with these of the current printed paper, evaluating printing quality, and indicating printing technology adjustment information needed to be adopted. According to the method, the problem that detection and control of the printing quality of current decorative paper completely depends on experience of workers and are short of quantitative detection and control technologies is solved.
Owner:佛山市顺德区康强装饰材料有限公司
Electrophotographic device, electrophotography, and process for preparing sheet bearing toner images
InactiveUS6256051B1Electrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternLatent imageDot gain
The present invention can provide an electrophotographic apparatus and electrophotographic method which are less affected by dot gain, can realize smooth gray scale expression, are high in gray scale reproducibility, and are hard to generate moire.In an embodiment of the present invention, a continuous tone image is binarized by using the frequency modulation screening, to form a latent image free from the generation of moire and high in relative resolution. The latent image thus formed is developed using a liquid developer, to form a thin toner layer, for forming a toner image less in the generation of mechanical and optical dot gain.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Imaged articles comprising a substrate having a primed surface
InactiveUS20040258856A1Duplicating/marking methodsSynthetic resin layered productsSolubilityVitrification
The present invention relates to an imaged article comprising a substrate having a primed surface layer. The primed surface layer is comprised of a base polymer having a solubility parameter, molecular weight (Mw) and glass transition temperature within a specified range. The presence of the primer improves the overall image quality by improving at least one property including ink uptake, dot gain, color density and / or ink adhesion. Preferred primer compositions are soluble at least in part in the ink composition resulting in an increase in ink layer thickness that further improves the durability and / or day / night color balance. A variety of substrates may be primed including various sheeting for traffic control signage and commercial graphic films for advertising and promotional displays.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
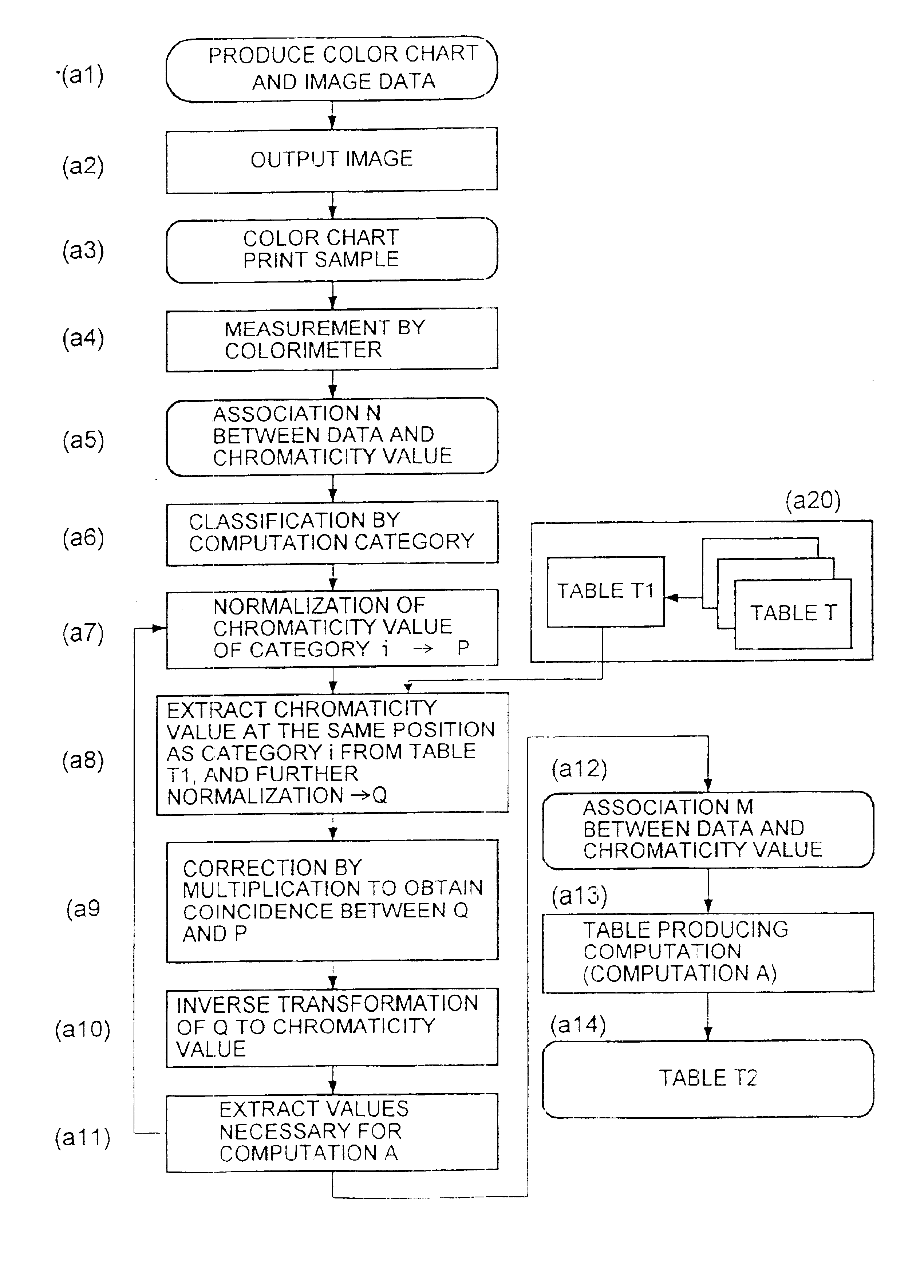
Profile producing method and profile producing apparatus
InactiveUS6888961B1Improve accuracyReduce the numberCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsColor imageDot gain
There are disclosed a profile producing method and a profile producing apparatus for producing a profile representative of the association between the colors on a color image and the color data in accordance with which the color image is outputted, in an output device such as a color printer and a printing machine for outputting color images in accordance with image data including color data. From among a plurality of existing profiles (tables), a suitable table is selected in accordance with an evaluation based on dot gains. A new profile is produced in accordance with the selected table and colorimetry data of a color chart involved in small number of patches.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
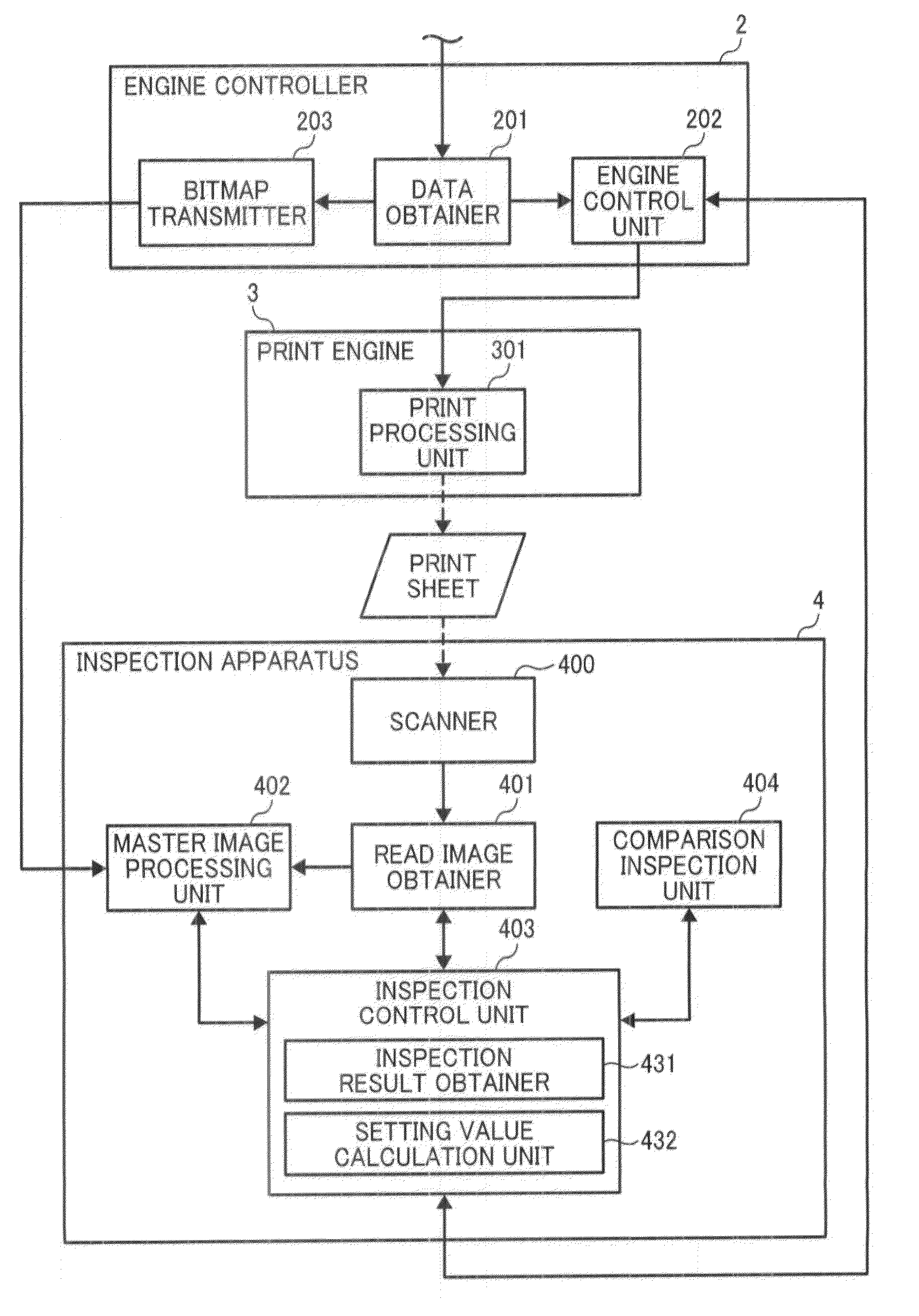
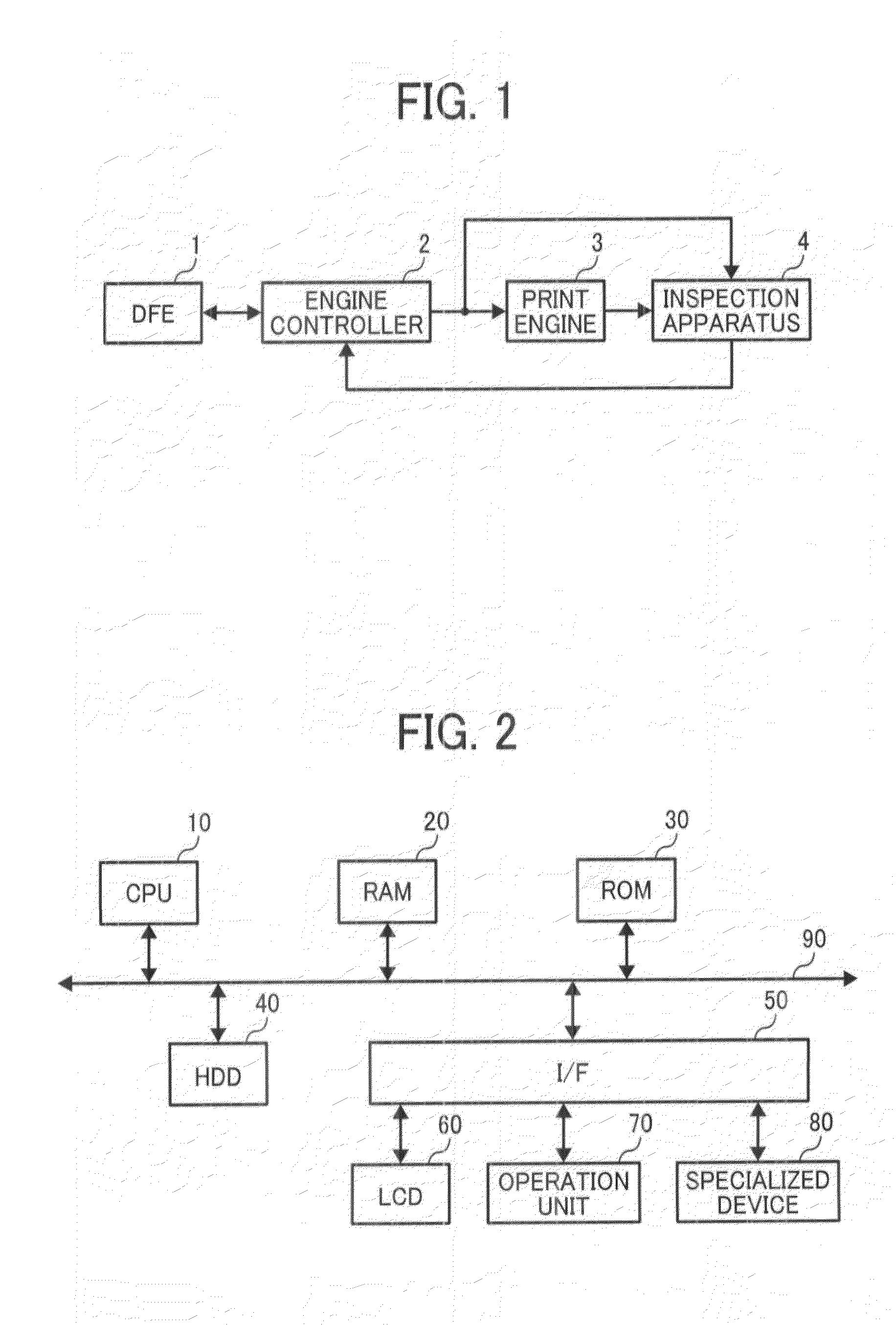
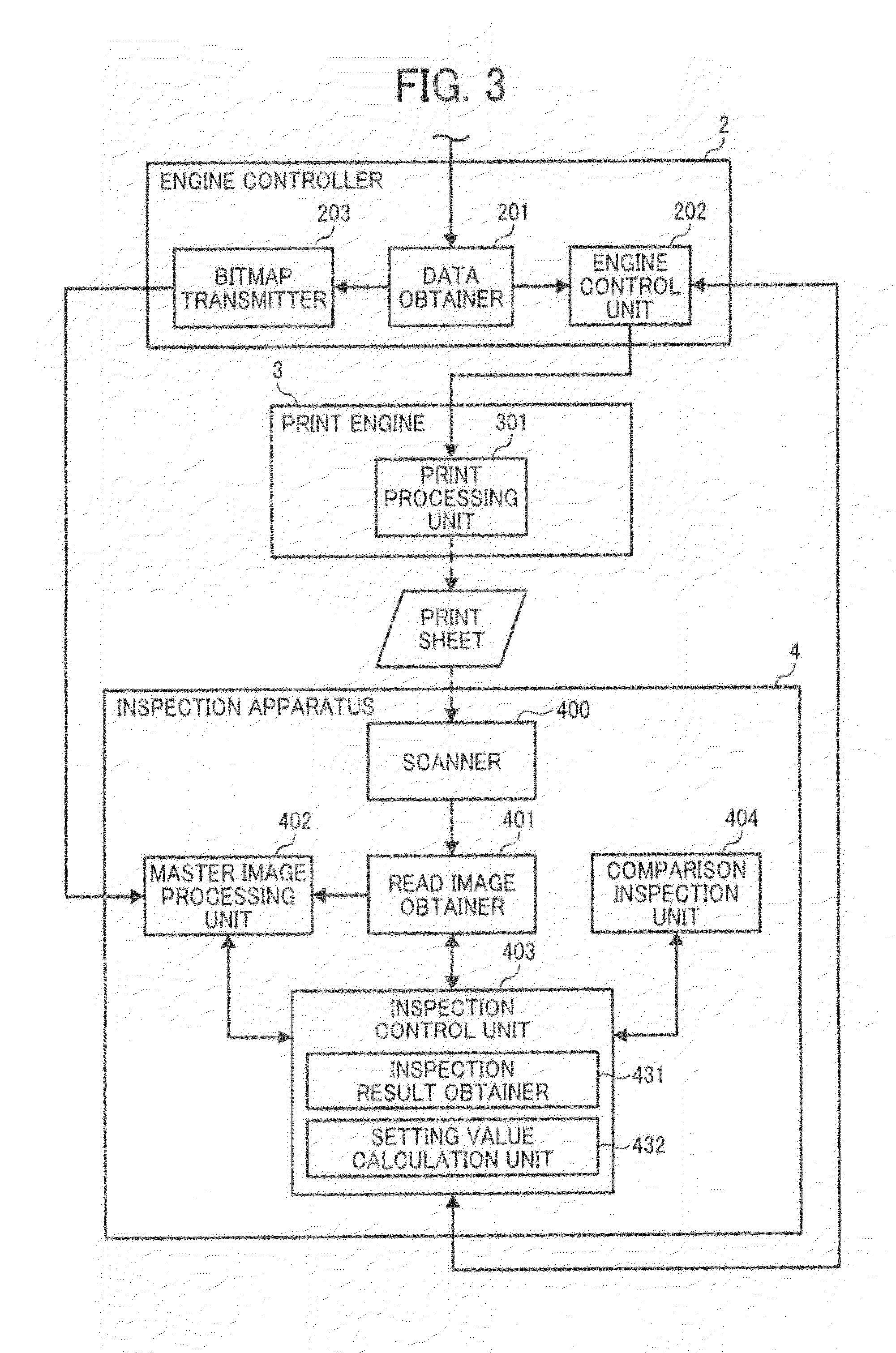
Apparatus, system, and method of inspecting image, and computer-readable medium storing image inspection control program
InactiveUS20140268260A1Colour-separation/tonal-correctionPictoral communicationImage InspectionInformation processing
An information processing apparatus including a read image obtainer and a setting value calculator implemented by circuitry. The read image obtainer obtains a scanned determination image, including a plurality of different dot patterns output by an image forming apparatus on a recording medium. The setting value calculator, for each of the different dot patterns of the obtained scanned determination image, determines densities of different colors of the respective dot pattern and a total number of pixels influencing the density of each coefficient of a dot gain correction filter, with respect to each target pixel. The setting value calculator further configured calculates the coefficients of the dot gain correction filter based on the determined densities of the different colors of the different dot patterns and the total number of pixels, determined for each coefficient of the dot gain correction filter and for each of the different dot patterns.
Owner:RICOH KK
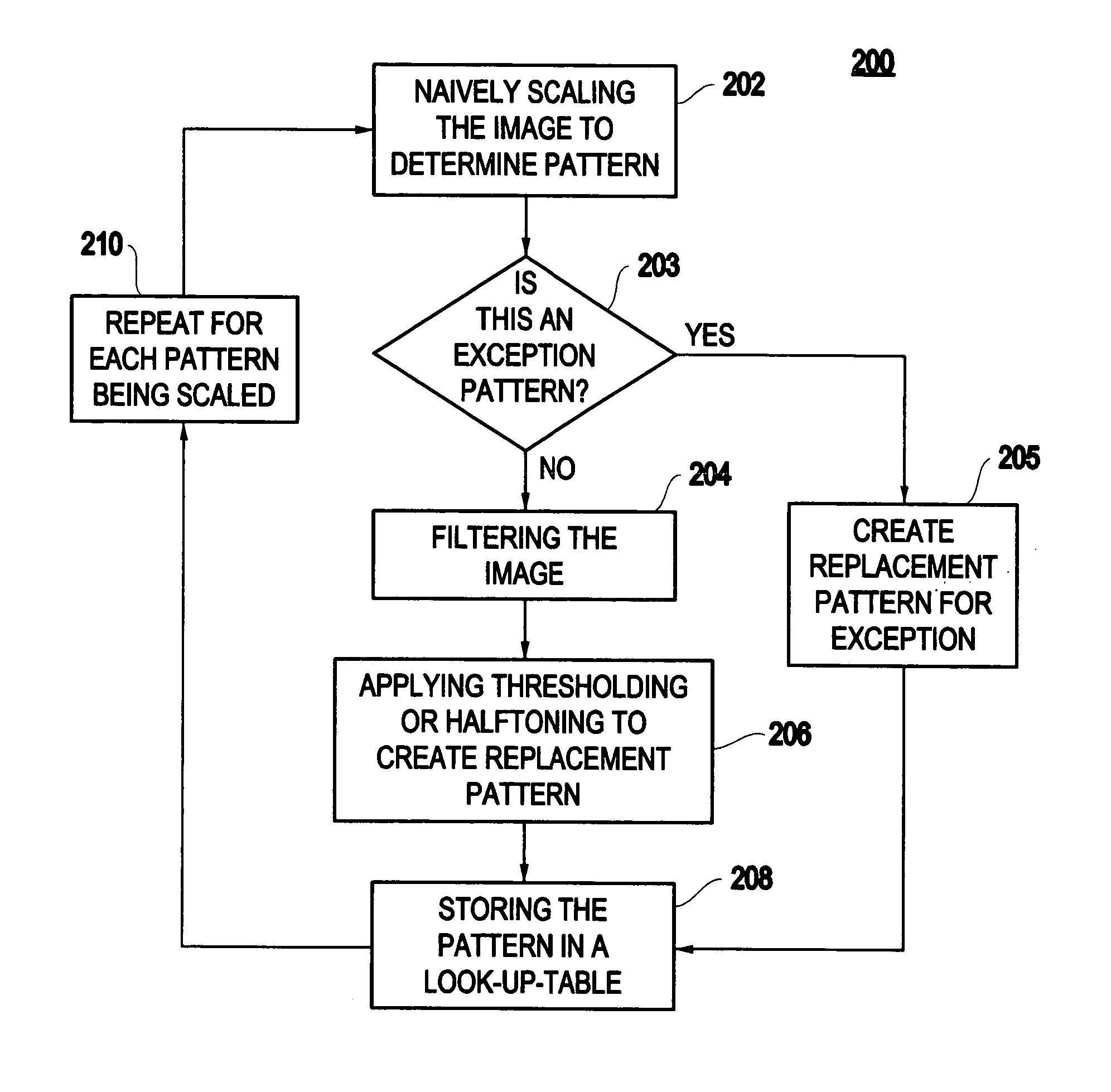
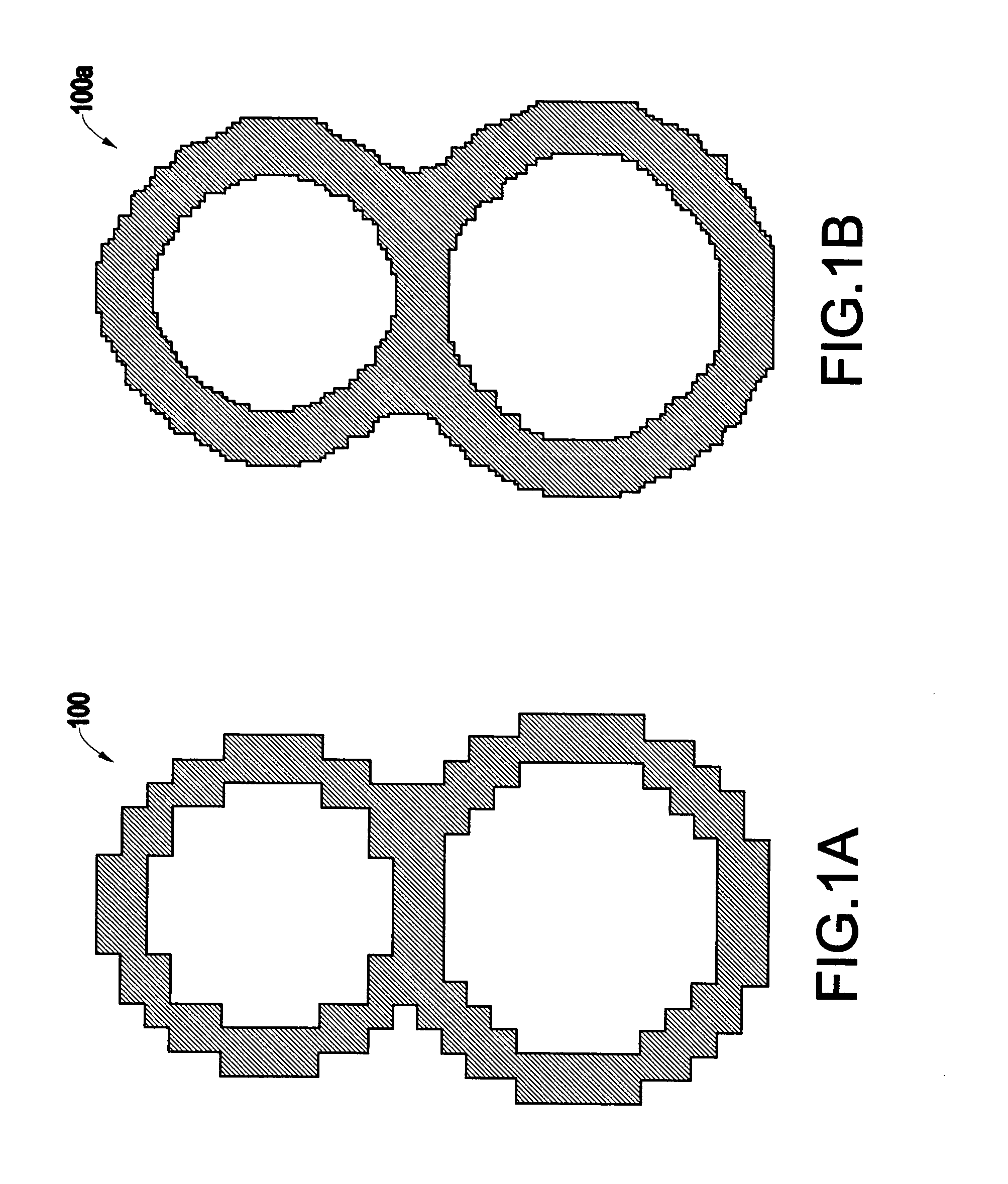
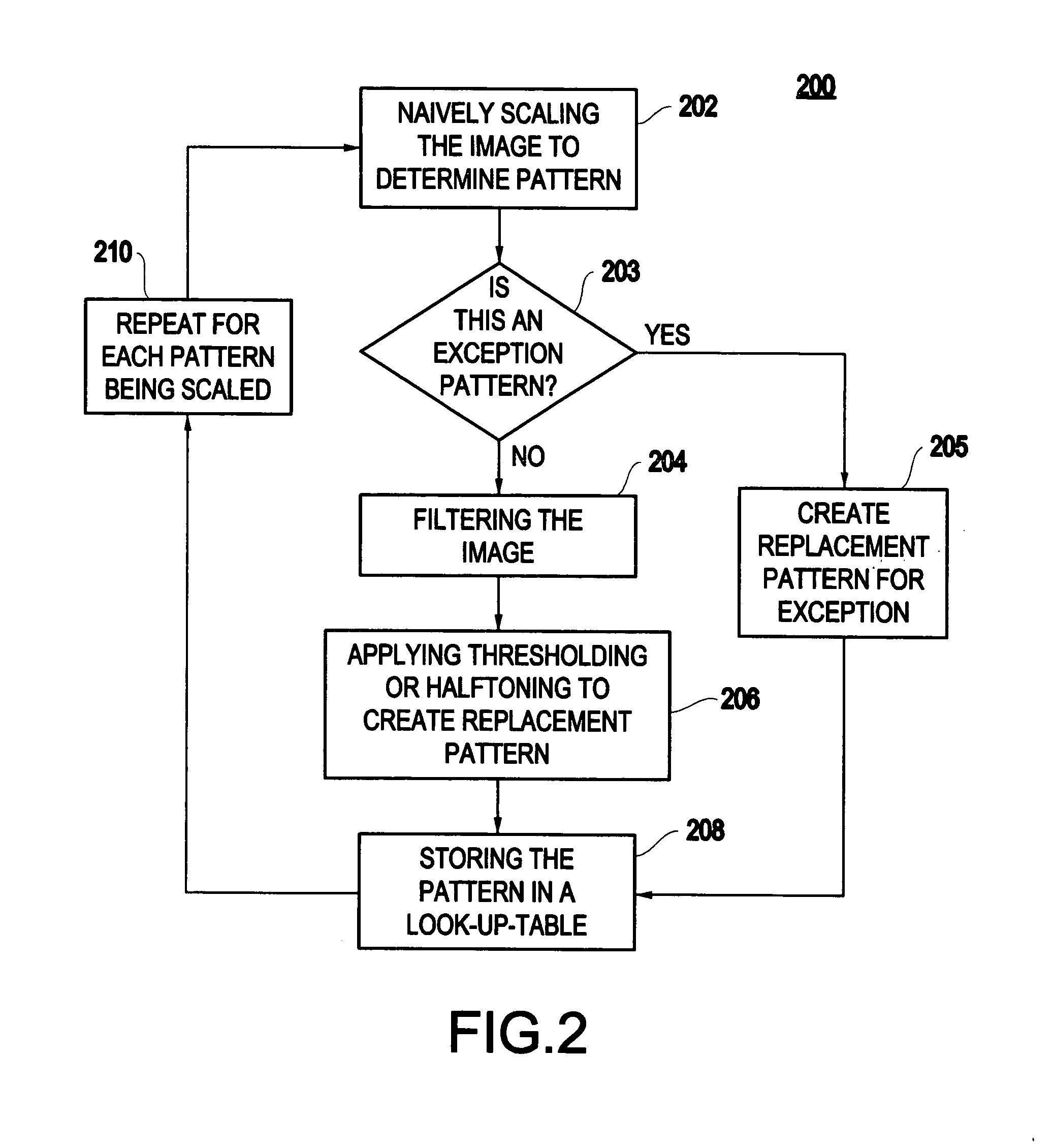
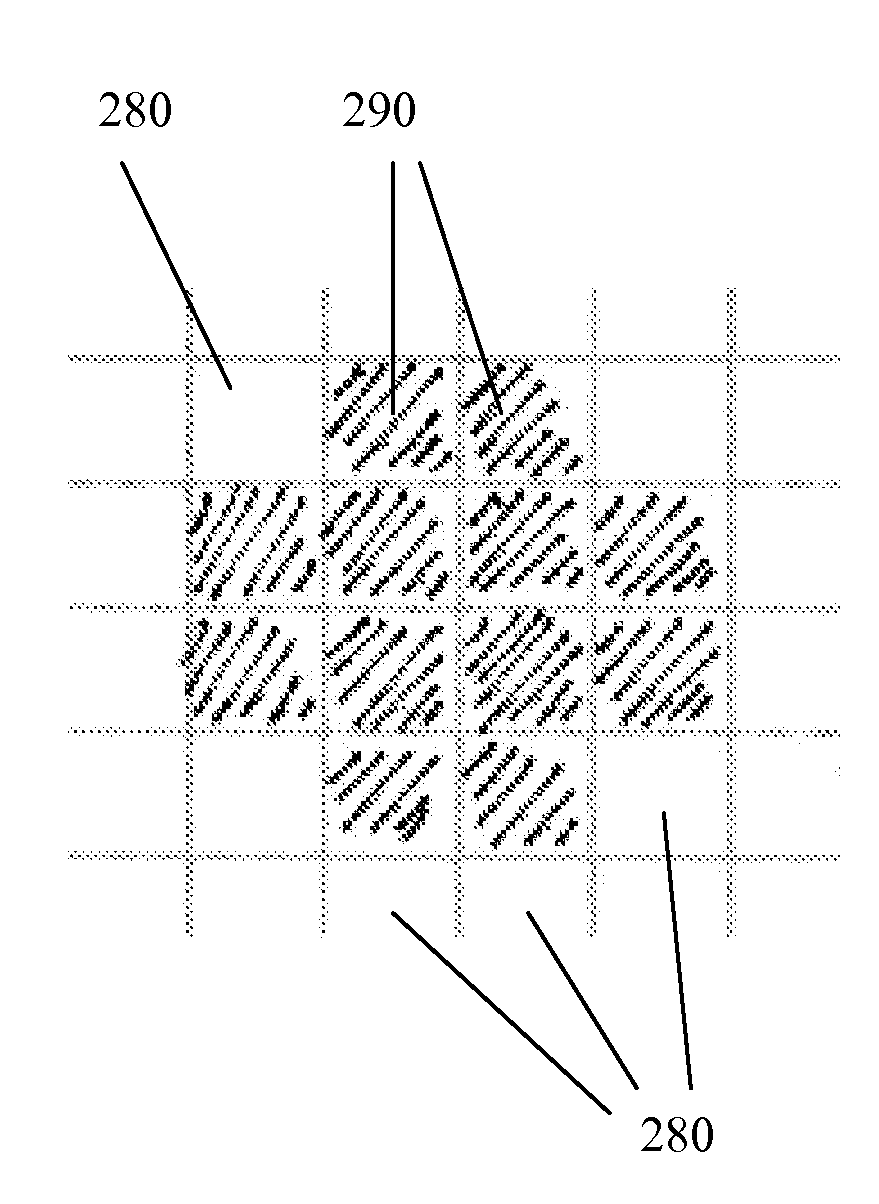
Method and system for scaling with dot gain control
InactiveUS20060215186A1Easy to controlEasily and systematically scalingDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImage resolutionComputer printing
A method (and system) for changing spatial resolution of an image includes systematically creating an image scaling look-up table including at least one pixel replacement pattern and applying a scaling algorithm to modify the image using the image scaling look-up table, thereby allowing a user to scale binary images with easy control of dot gain, output bit depth and other printer parameters.
Owner:INFOPRINT SOLUTIONS COMPANY LLC +1
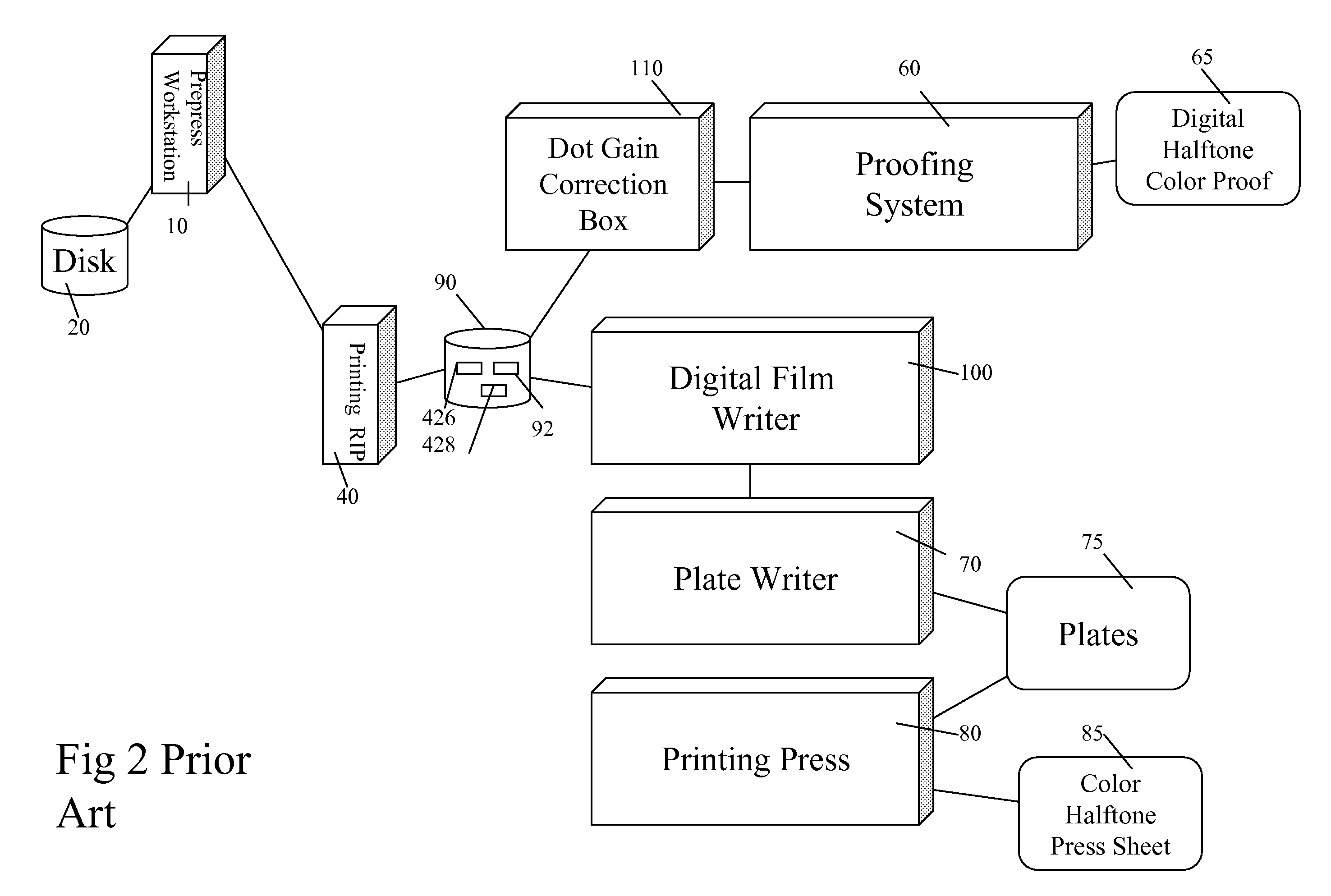
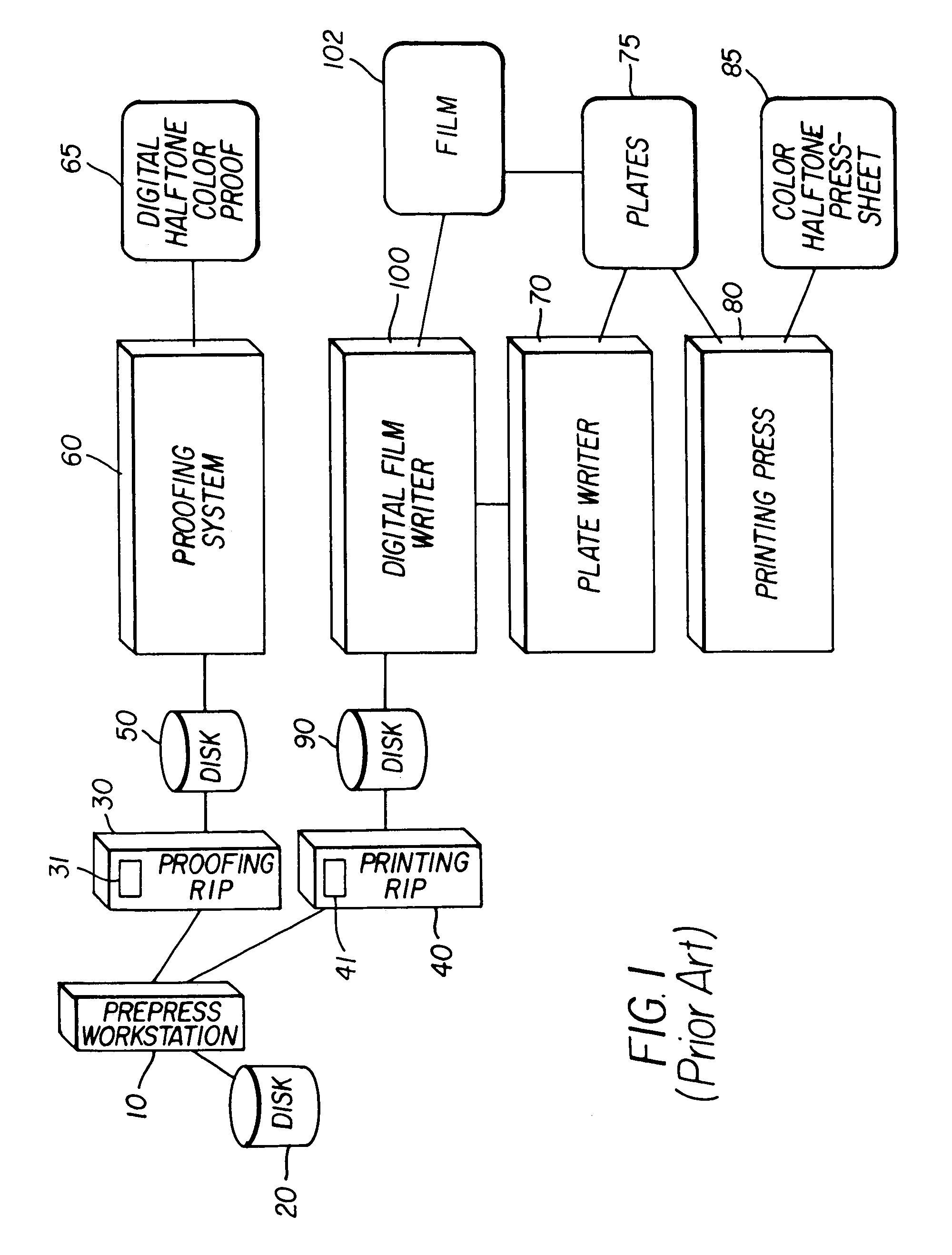
Asymmetrical digital filters for dot gain adjustments
ActiveUS20080297813A1Increase in sizeMaximizing numberDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsDot gainDigital filter
A method for adjusting dot-gain for a halftone binary bitmap file comprises inputting a halftone binary bitmap file consisting of binary pixels (400) to an asymmetric digital filter (500). The binary pixels are filtered with the asymmetric digital filter and generates multi-level pixels (506). The multi-level pixel are compared to a preset level (408) and generates a binary pixel output (410). The binary pixel output is collected and forms an adjusted halftone binary bitmap file (270).
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
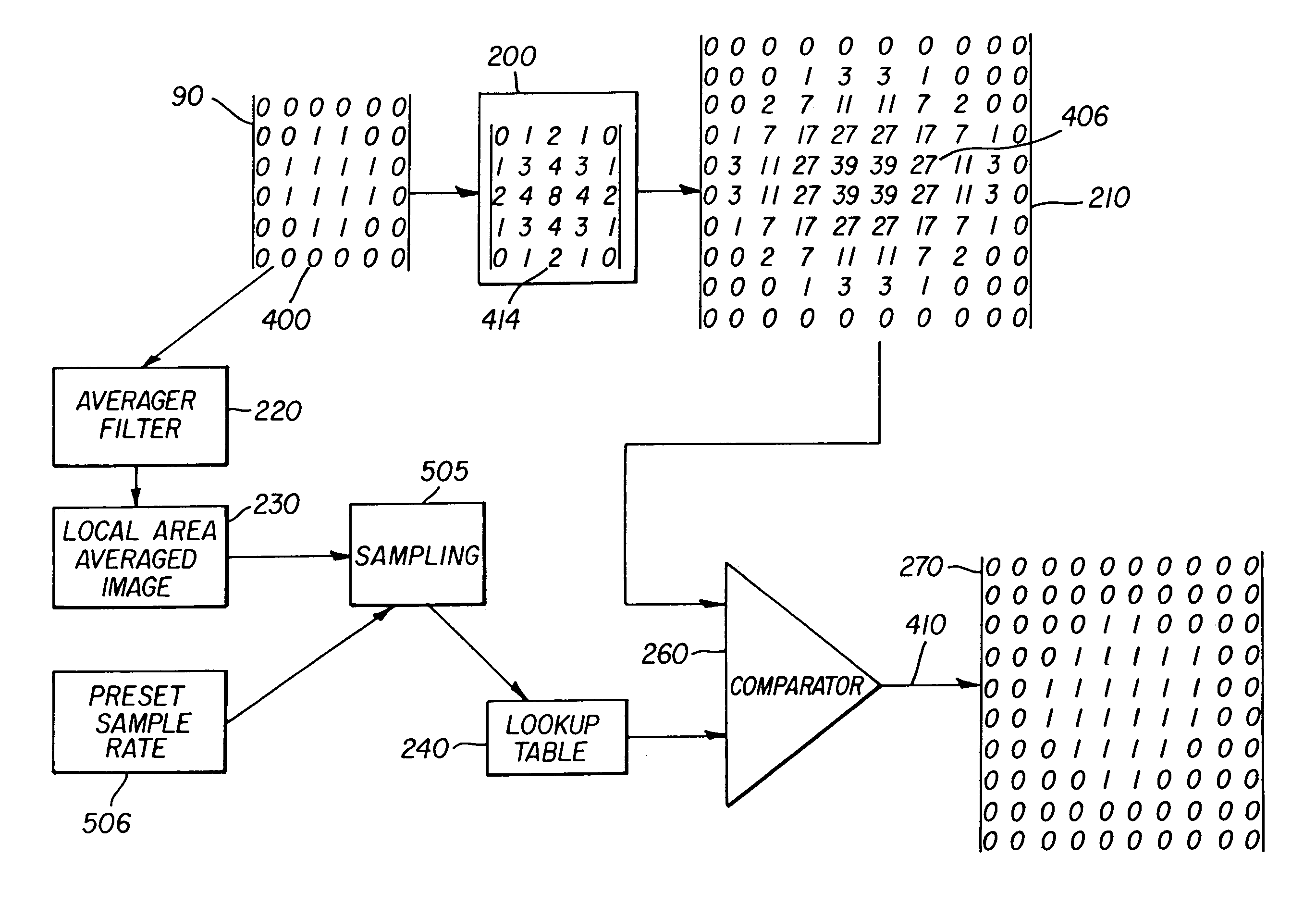
Lookup table for adjusting dot-gain on bitmap files based on average number of dots
InactiveUS7050200B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsElectrographic process apparatusDot gainDigital filter
A method for adjusting dot-gain for a halftone binary bitmap file by inputting a halftone binary bitmap file comprising binary pixels to a digital filter, filtering the binary pixels with the digital filter generating a weighted sum of the binary pixels producing a first set of multilevel pixels, filtering the binary pixels with a second digital filter producing a second set of multilevel pixels, sampling the second set of multilevel pixels at a preset sample rate identifying a set of sampled multilevel pixels, inputting the set of sampled multilevel pixels to a lookup table to create an output that is a threshold level for the set of sampled multilevel pixels, using the first multilevel pixels and comparing to the threshold level for the set of sampled multilevel pixels and generating a binary pixel output, and collecting the binary output and forming an adjusted halftone binary bitmap.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method for generating stochastic dither matrix
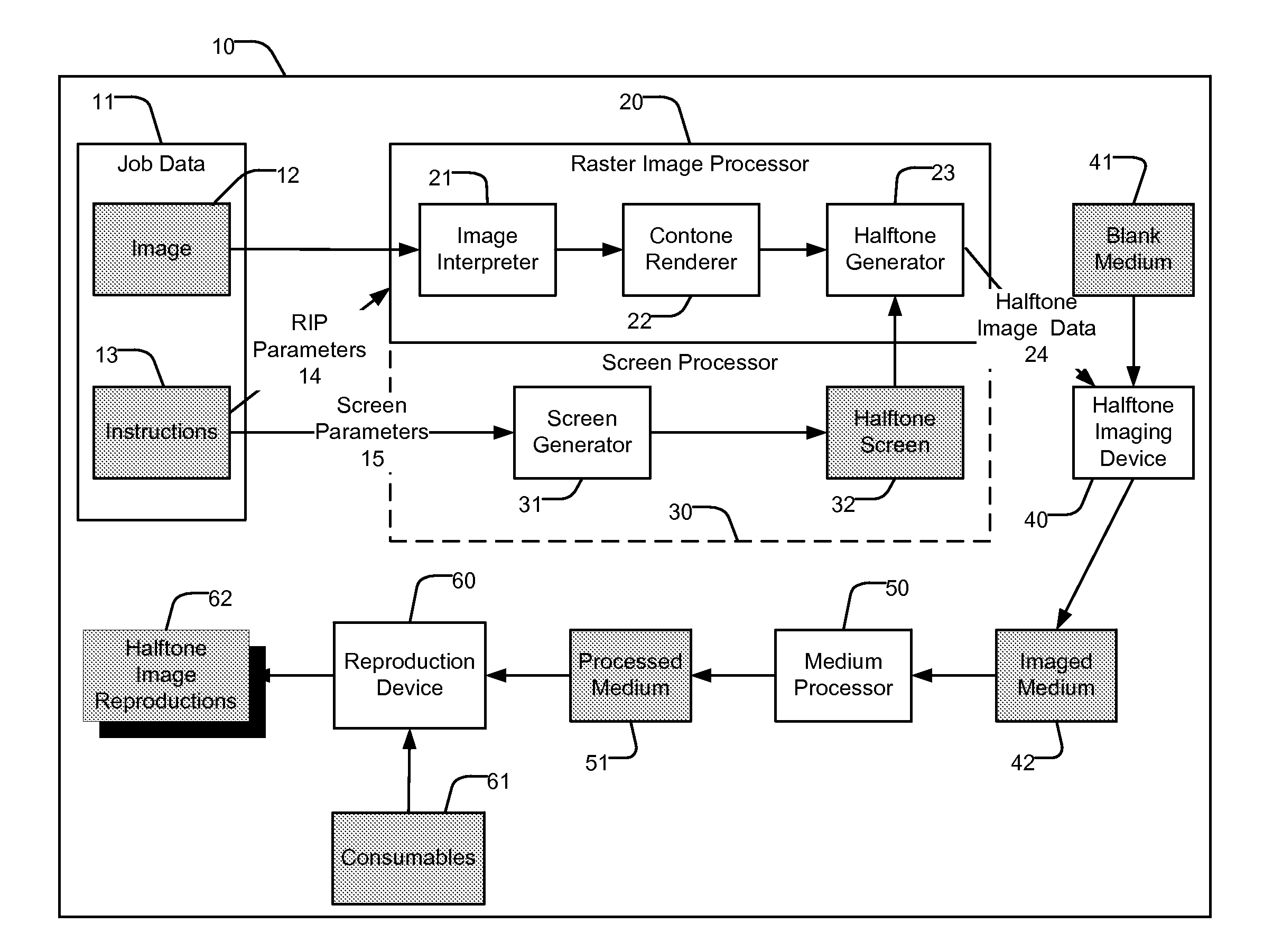
InactiveUS20090034008A1Wide rangeMore visually pleasing halftone representationVisual presentationPictoral communicationDot gainParameter control
A method for generating a stochastic halftone screen (32) includes a parameterized screen generator (31) whose parameters (15) control aspects of the generated screen (32). Some parameters (15) control the size of a generated threshold array (300). A variety of threshold array sizes can be generated quickly including larger arrays (300) wherein the generation time is proportional to the natural logarithm of the threshold array size. Some parameters control a set of shaping functions used to determine the distribution of minority pixels (302) for a wide variety of printing conditions. These include controls for edge-to-area ratio, cluster size, anticipated dot gain and modeled human visual response.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Color simulation method for digital proofing
ActiveCN103079027ARealize the effect of "what you see is what you get"Easy to operatePictoral communicationComputer graphics (images)Dot gain
The invention discloses a color simulation method for digital proofing, which comprises the following steps that color information and a dot gain value in actual printing process conditions are measured, the dot gain value is utilized to directly perform dot gain on an electronic file before RIP (Raster Image Processing), during RIP or after RIP, the electronic file after the RIP after the dot gain is used, and a digital printer without the dot gain during printing is used for digital proofing. The color simulation method for digital proofing has the advantages of easiness in operation and precise simulation, and the WYSIWYG (what you see is what you get) effect of digital proofing is achieved.
Owner:上海紫恩数码科技有限公司
Dot gain calibration method and apparatus
A method for providing in use estimation of dot gain in digital printing using digital printing plates, the method comprising: applying to a digital printing plate a calibration strip, the strip comprising at least one set of patches, each patch comprising a plurality of dots at a predetermined gray level within said dynamic range, gray levels of said set of patches being distributed over said dynamic range, printing from said calibration strip under a current set of printing conditions, measuring intensities of said printing, and interpolating from said measurements to generate a curve of dot gain over said dynamic range. The curve can then be used to compensate. When moving to a different set of printing conditions, a single test print is then carried out and a new dot gain estimation is available.
Owner:KODAK IL
Method of nonlinear calibration of halftone screen
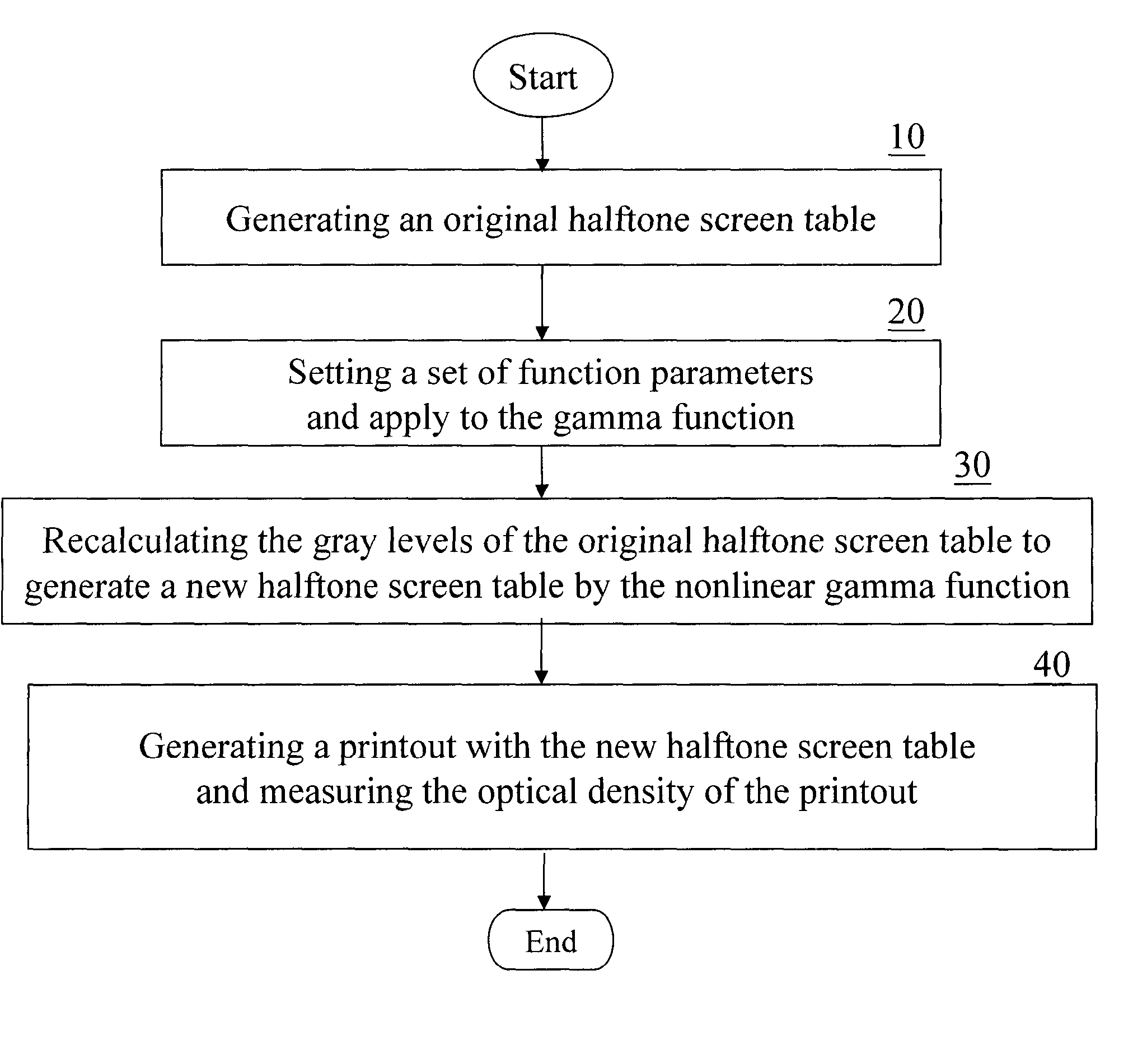
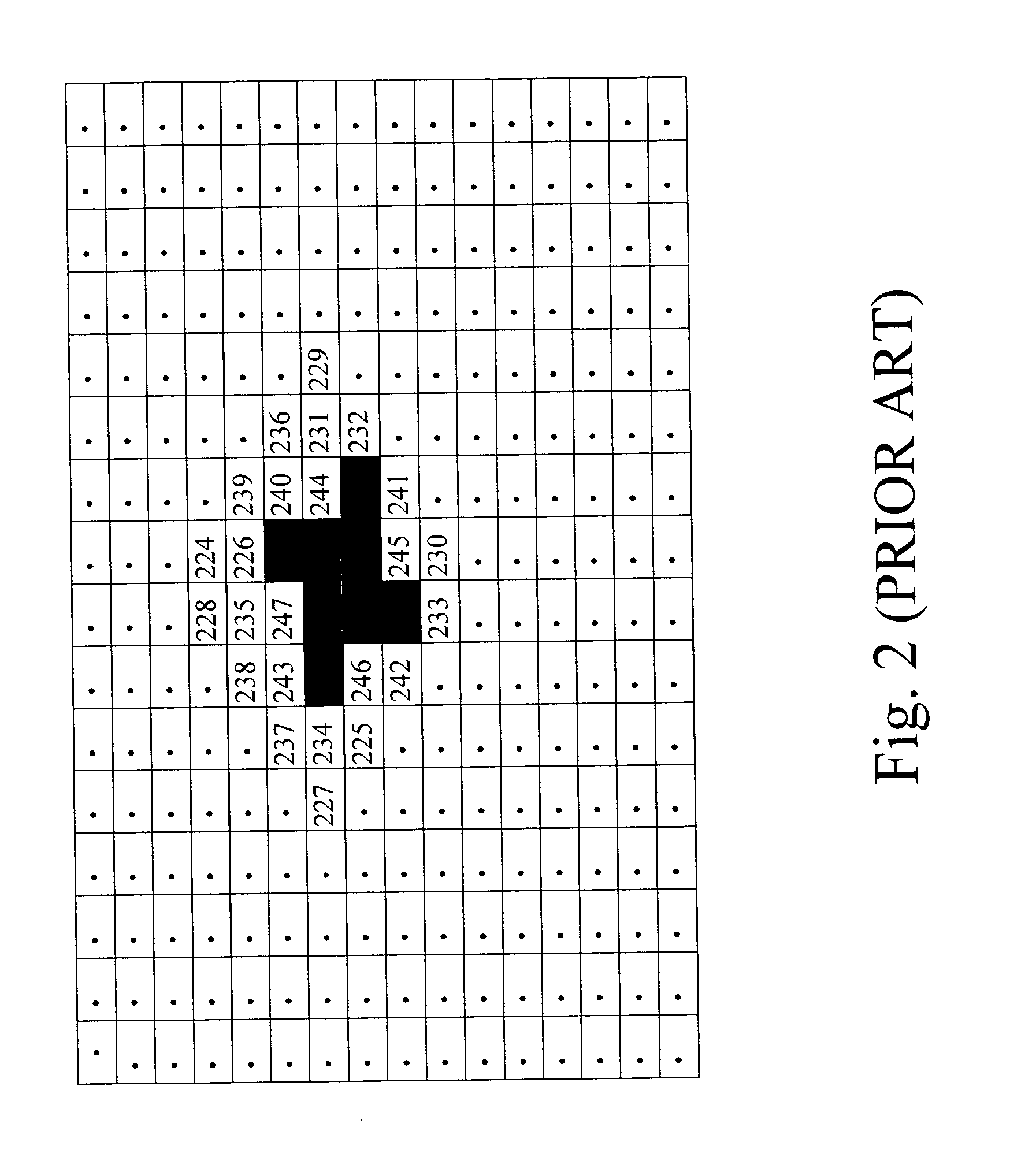
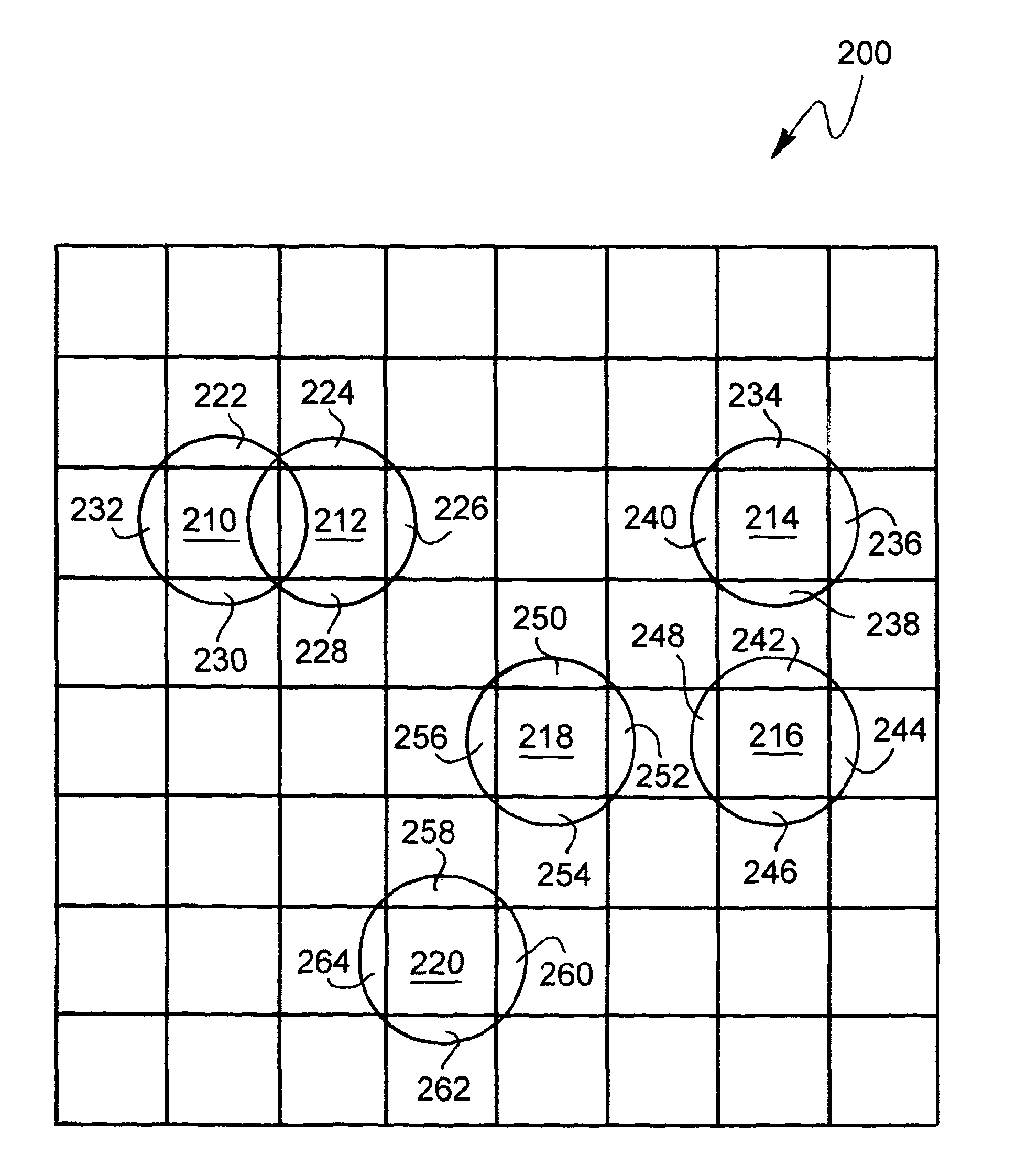
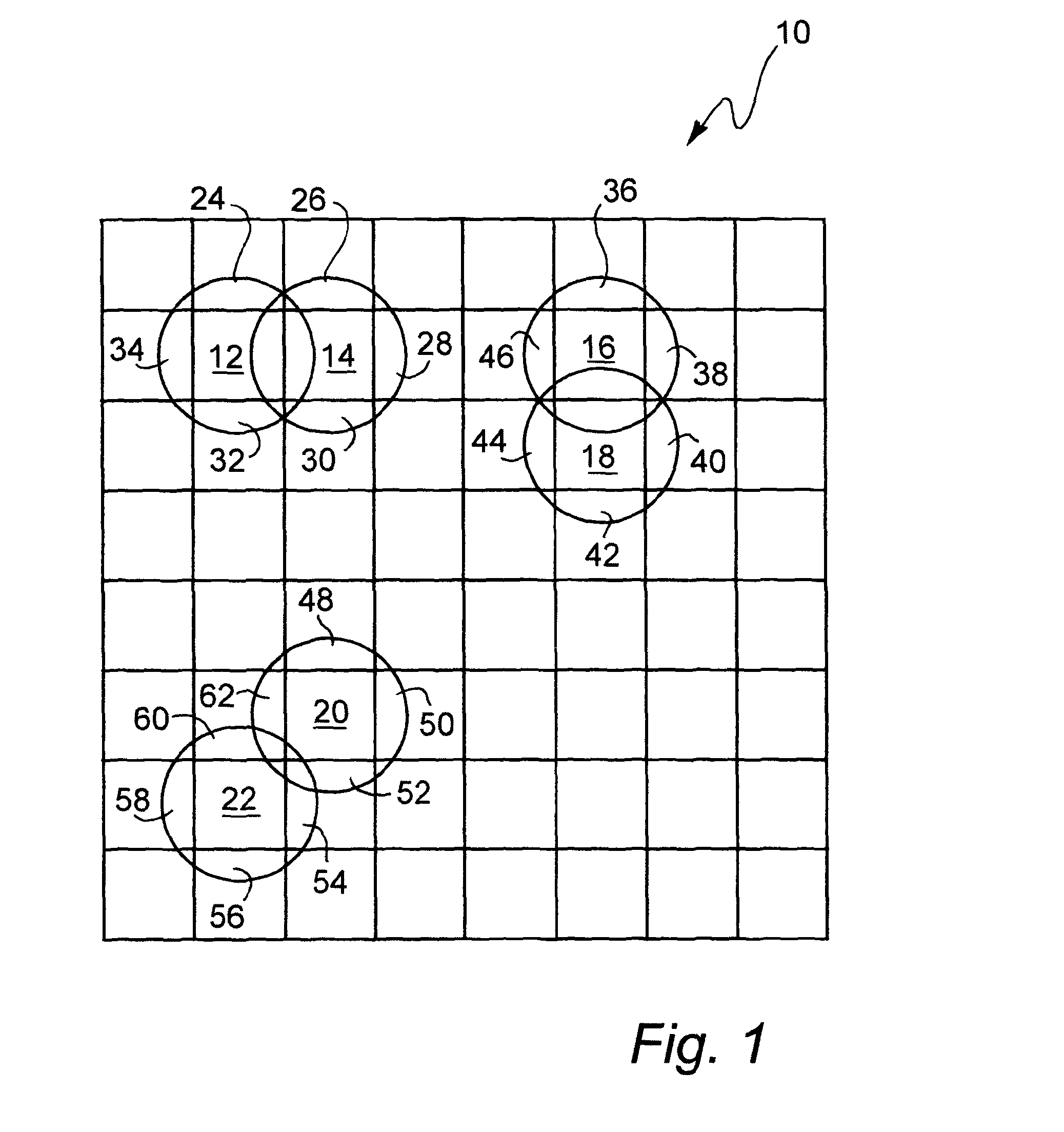
InactiveUS20050075813A1Easy CalibrationDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringDot gainNonlinear calibration
Calibration could be implemented in several stages during the color rendering processes. One possible and efficient place to put the calibration to work is in the screen table itself. In order to make the screen intelligent enough to adjust the factor results from output device characteristics, such as the dot gain, toner characteristics, etc., the method is introduced to create a gamma function with normalized gradation curve. Some color balance adjustment features (contrast, brightness, saturation and color strength) also have been taken into consideration.
Owner:PRIMAX ELECTRONICS LTD
Generating 1-bit image data from multiple-bit image data for producing when printed a dot image with reduced dot gain and appearance of patterning caused by isolated diagonally adjacent pixels
ActiveUS8654400B2Reliable printingSmall appearanceImage enhancementVisual presentationDot gainOutput device
A computer program for, or method of, generating 1-bit image data from multiple-bit image data, by a process which comprises the steps of: receiving multiple-bit image data comprising multiple-bit pixel values; and deriving from the multiple-bit pixel values 1-bit image data comprising “on” and “off pixel values, each pixel value of the 1-bit image data corresponding to a pixel of an output medium, which pixel an output device would attempt to mark when printing the 1-bit image data if the pixel value were “on”, the 1-bit image data producing when printed an image constituted by dots, each dot corresponding to a plurality of pixel values of the 1-bit image data, which pixel values correspond to a block of M*N horizontally and / or vertically adjacent pixels of an output is medium, at least one of M and N being greater than one, wherein for at least some of the dots, where M or N is equal to one, a pixel value corresponding to a first or last pixel of a row of horizontally adjacent pixels, or to a first or last pixel of a column of vertically adjacent pixels, is “off, and where both M and N are greater than one, at least one pixel value corresponding to a pixel of a first or last row of horizontally adjacent pixels is “off and / or at least one pixel value 20 corresponding to a pixel of a first or last column of vertically adjacent pixels is “off.
Owner:HAMILLROAD SOFTWARE LTD
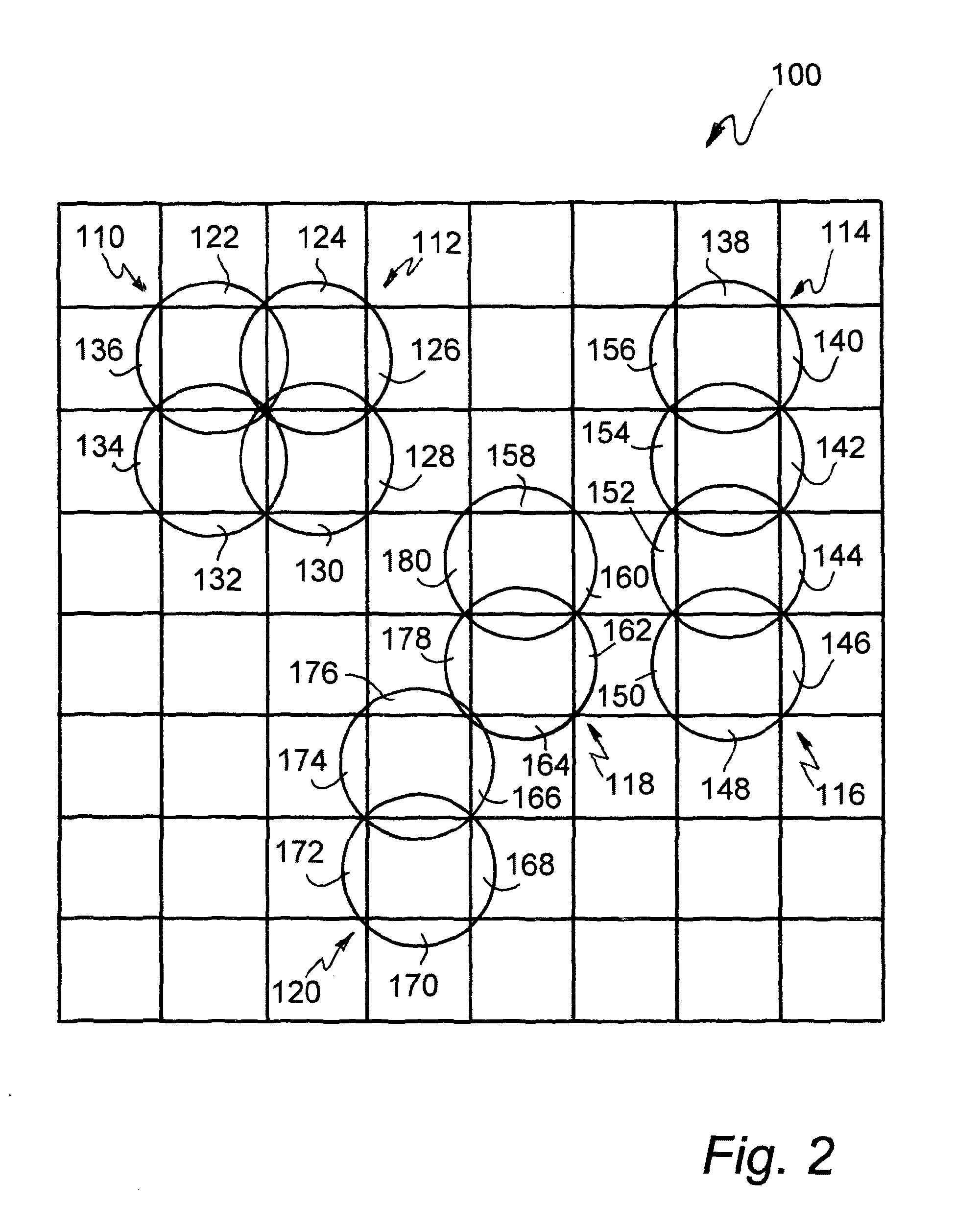
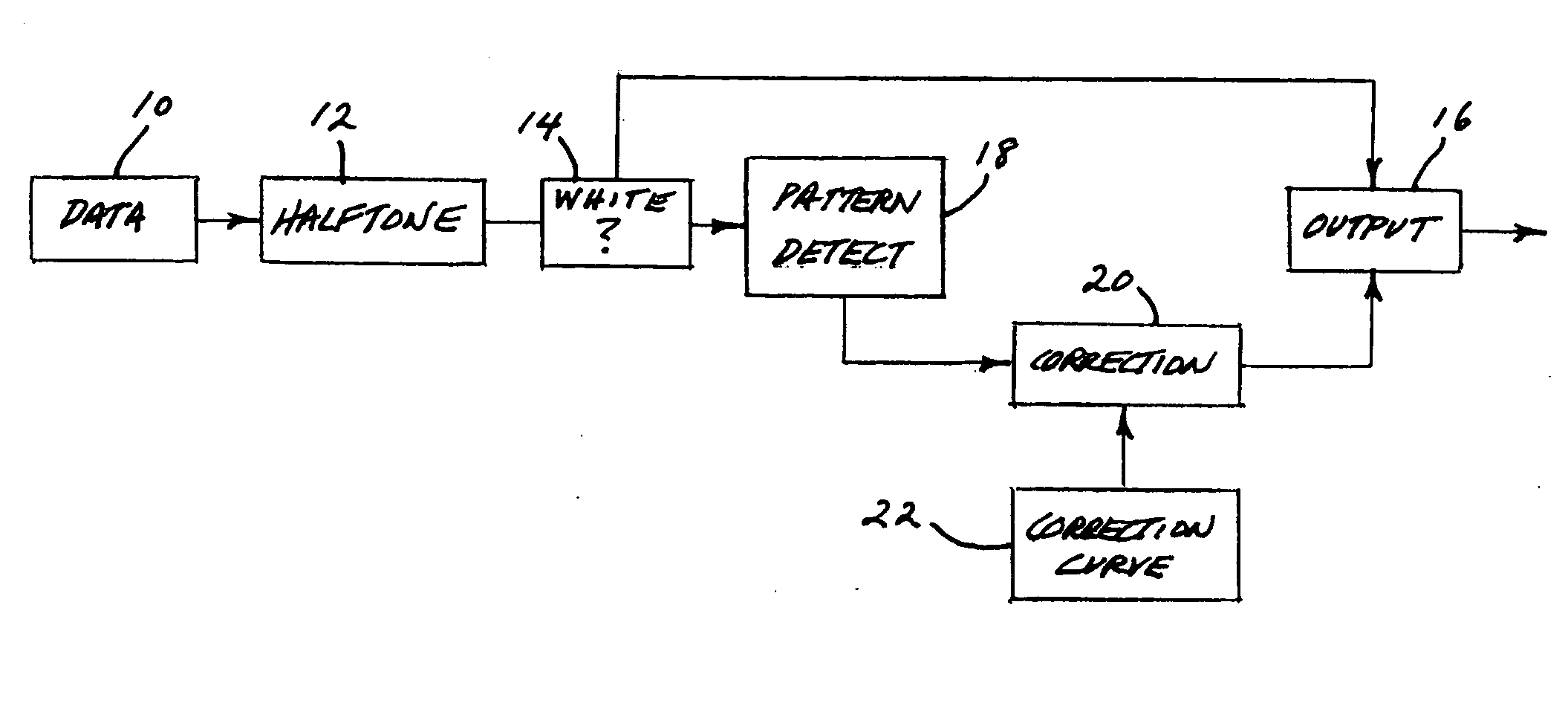
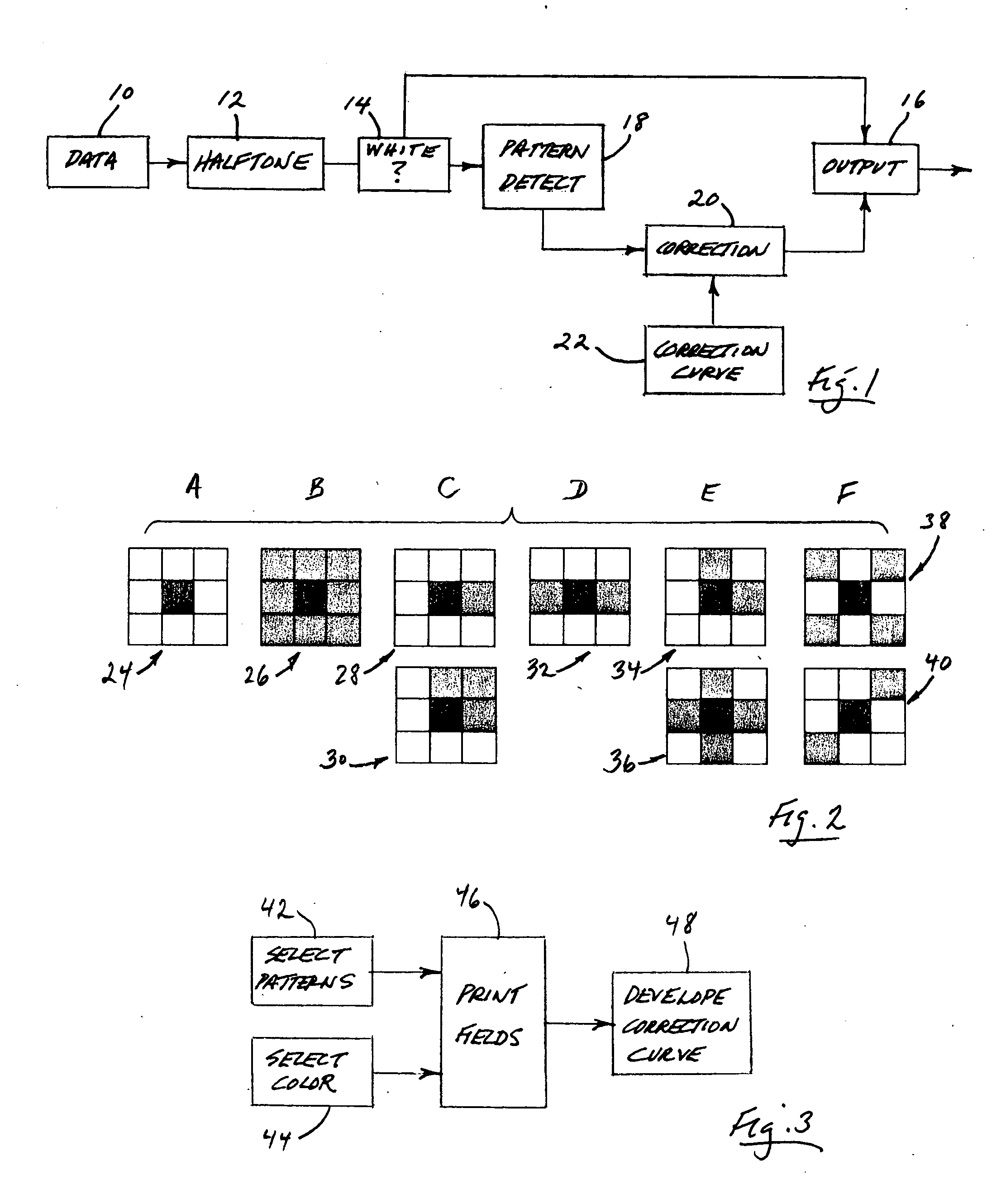
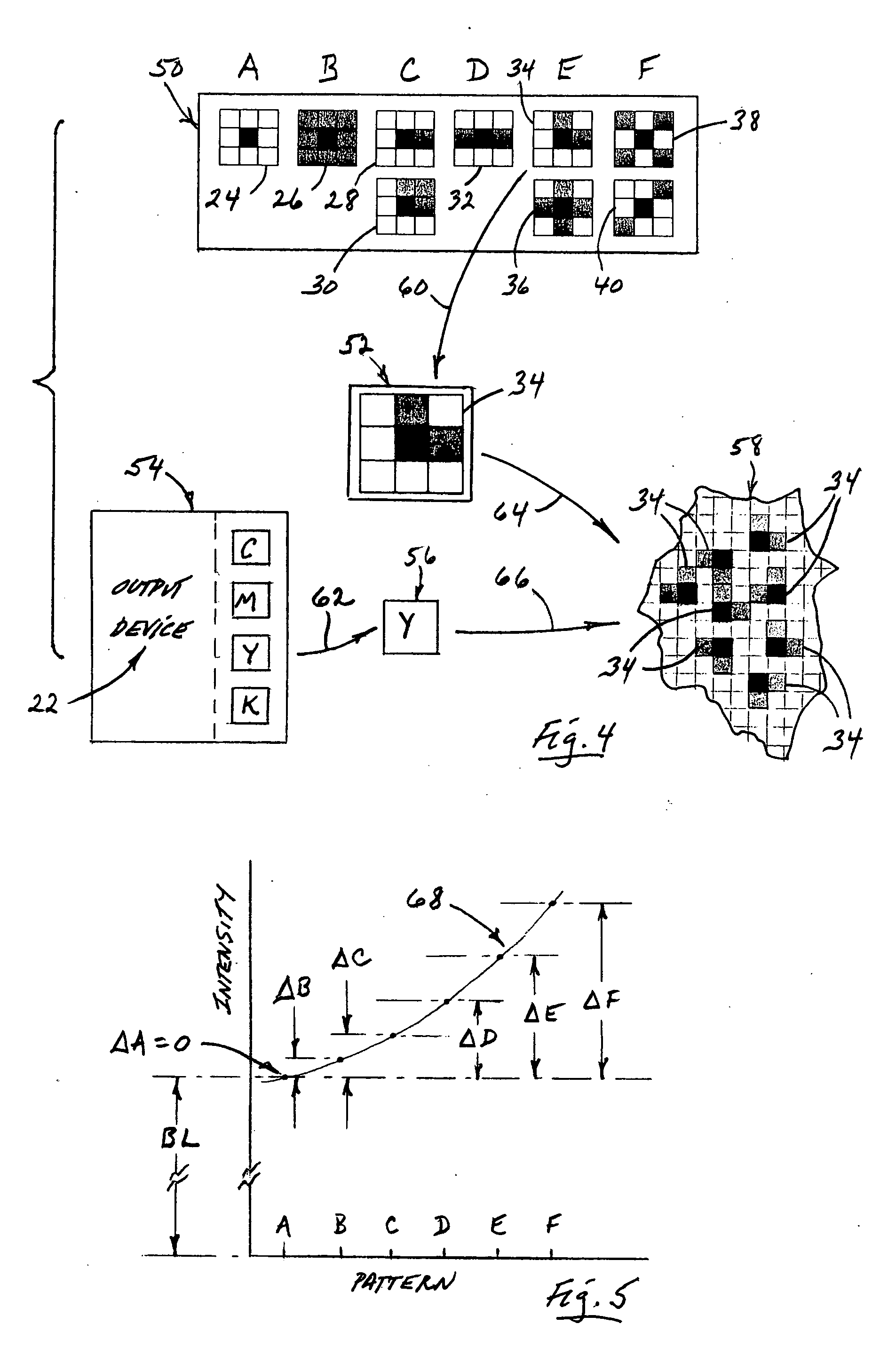
Dot-gain reduction method for multi-level halftoning
A method for minimizing color-image halftone dot-gain in the output of a multi-level halftone color-imaging output device. The method includes characterizing that device's halftone output, on a per-color basis, regarding pixel-pattern-specific dot gain which can be related to device pixel-infeed intensity levels, and from that characterizing, creating, and then applying to throughput color-image files, on a pixel-by-pixel basis, and for each output color producible by the device, a pixel-to-device infeed intensity correction value, thus to minimize device-output dot gain.
Owner:SHARP KK
Dot gain calibration method and apparatus
A method for providing in use estimation of dot gain in digital printing using digital printing plates, the method comprising: applying to a digital printing plate a calibration strip, the strip comprising at least one set of patches, each patch comprising a plurality of dots at a predetermined gray level within said dynamic range, gray levels of said set of patches being distributed over said dynamic range, printing from said calibration strip under a current set of printing conditions, measuring intensities of said printing, and interpolating from said measurements to generate a curve of dot gain over said dynamic range. The curve can then be used to compensate. When moving to a different set of printing conditions, a single test print is then carried out and a new dot gain estimation is available.
Owner:KOIFMAN IGAL +2
Lookup table for adjusting dot-gain on bitmap files based on average number of dots
A method for adjusting dot-gain for a halftone binary bitmap file by inputting a halftone binary bitmap file comprising binary pixels to a digital filter, filtering the binary pixels with the digital filter generating a weighted sum of the binary pixels producing a first set of multilevel pixels, filtering the binary pixels with a second digital filter producing a second set of multilevel pixels, sampling the second set of multilevel pixels at a preset sample rate identifying a set of sampled multilevel pixels, inputting the set of sampled multilevel pixels to a lookup table to create an output that is a threshold level for the set of sampled multilevel pixels, using the first multilevel pixels and comparing to the threshold level for the set of sampled multilevel pixels and generating a binary pixel output, and collecting the binary output and forming an adjusted halftone binary bitmap.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
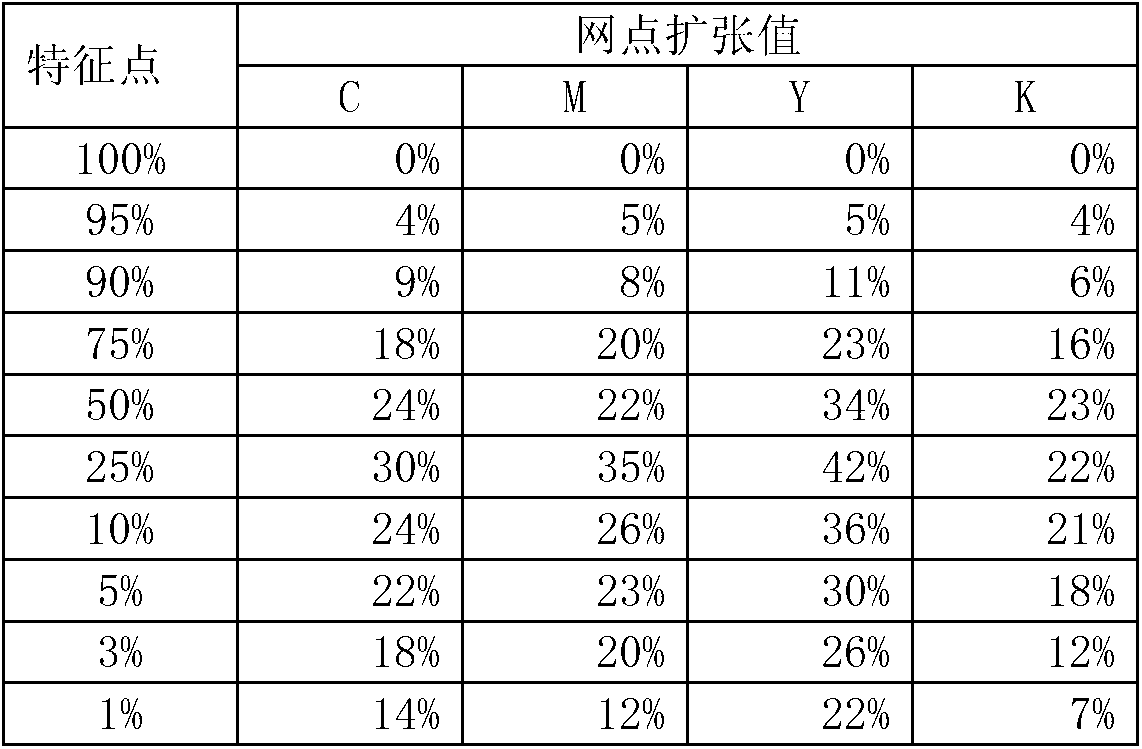
Gravure printing image quality control method
ActiveCN106379049AEnsure consistencyGuaranteed printing qualityPrinting press partsGerminating apparatusEngravingImaging quality
The invention provides a gravure printing image quality control method which comprises the following steps: first, manufacturing a CMYK color card; next, performing a printing test on the CMYK color card, so as to obtain a color reproduction curve under the premise that the dot gain is within a standard tolerance range; then, manufacturing a test version by utilizing the color reproduction curve, selecting three dots from each color on the color reproduction curve to control an image, and comparing the measured density values of the three dots with a standard value to judge whether each color meets the requirement within the tolerance range or not, wherein the three dots respectively correspond to dark tone, middle tone and highlight of the image; and finally, manufacturing a printing plate and a printing proof according to a standard sample, a color characteristic file and a standard color curve. By adoption of the gravure printing image quality control method provided by the invention, middle tone and shallow net control dots are added, so that direct engraving on the printing plate can be achieved and no other cost is needed; after a printing sample is obtained, whether the requirement is met or not can be determined through direct measuring, thereby avoiding the subjectivity in conventional visual sample measuring; the method is simple in judgement and easy to operate; and the accuracy and the standard property of gravure printing image quality control are improved.
Owner:上海紫江彩印包装有限公司
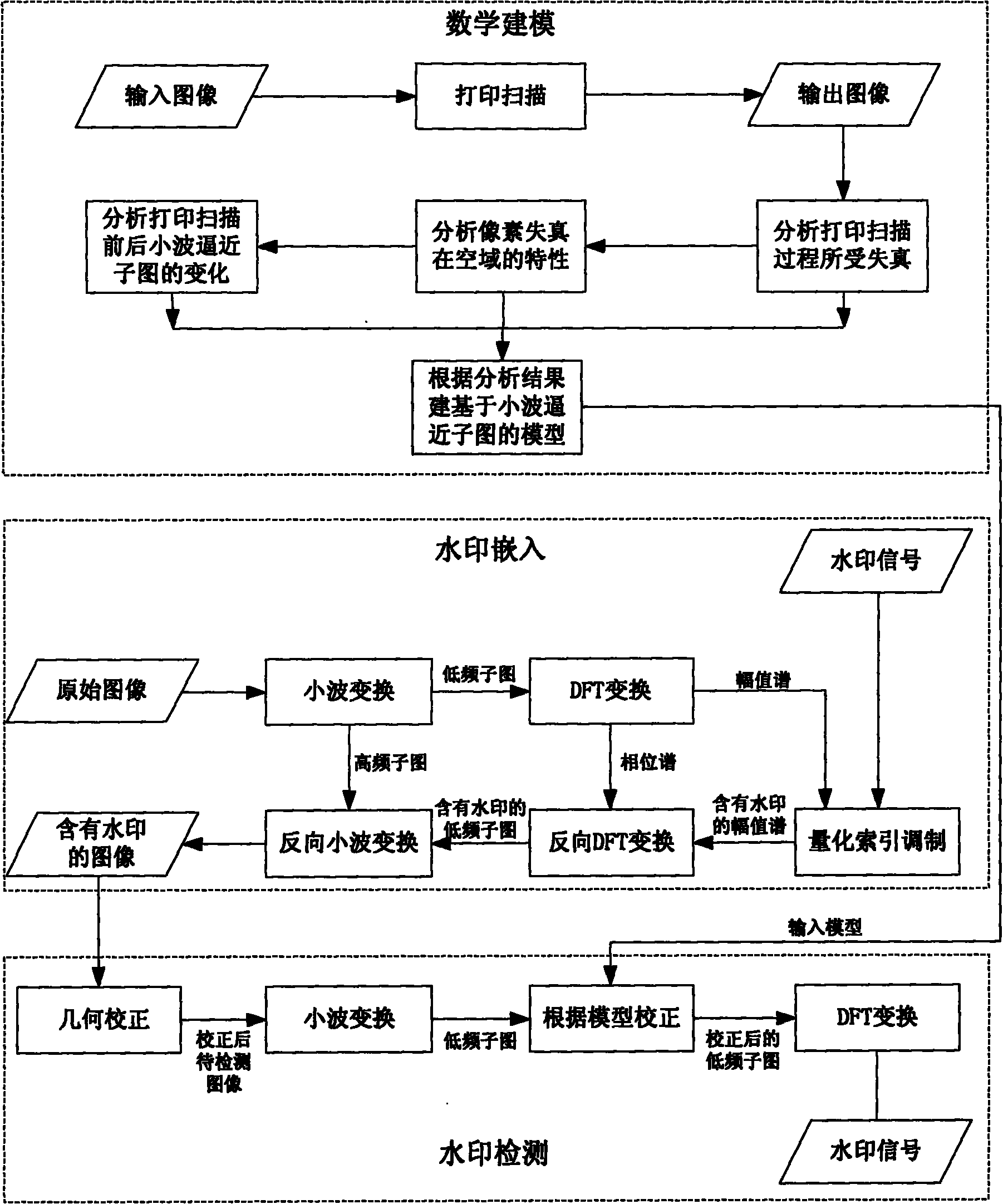
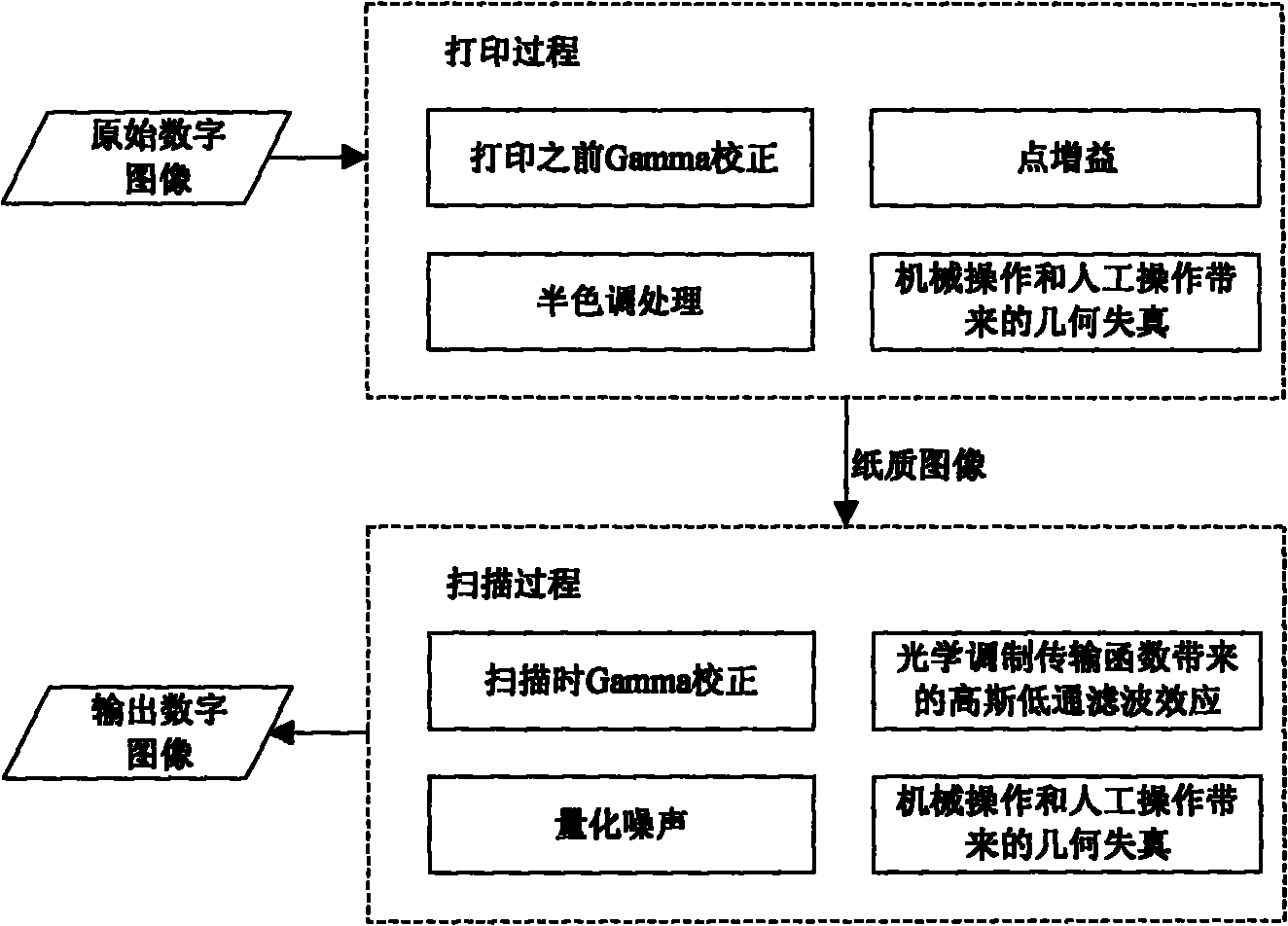
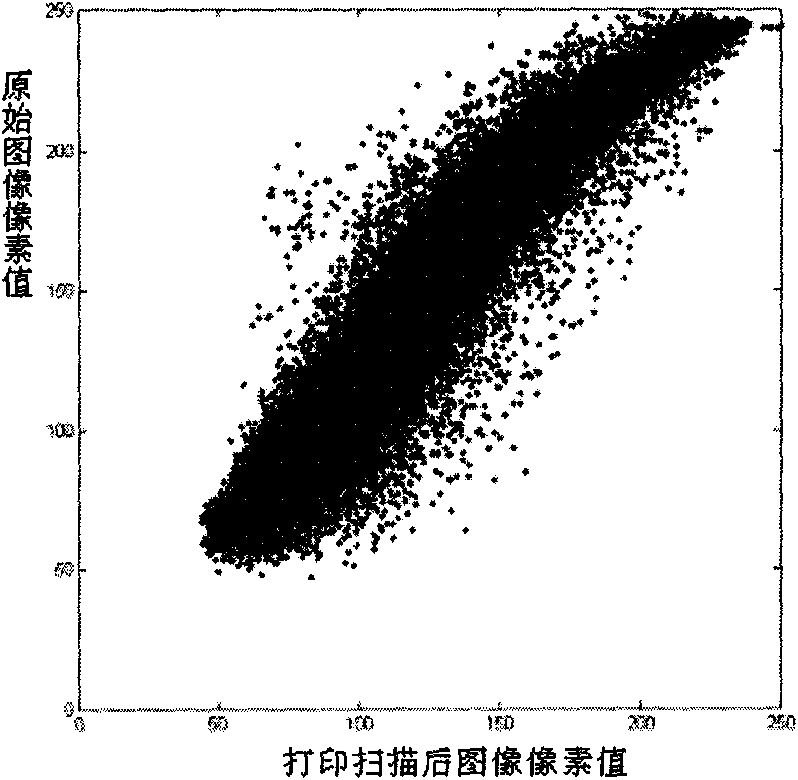
Printing and scanning resilient watermarking method based on mathematical modeling
InactiveCN101853483AReduce the impactImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage data processing detailsMathematical modelAlgorithm
The invention relates to a printing and scanning resilient watermarking method based on mathematical modeling, comprisng the mathematical modeling and correction of pixel distortion, watermark embedment and watermark detection. Mathematical modeling and correction of pixel distortion carries out mathematical modeling to the pixel distortion of an image brought by digital halftoning, dot gain, gamma correction, quantification and other links during a printing and scanning process and corrects the pixel distortion based on mathematical modeling so as to improve the watermark detection accuracy. Watermark embedment conducts analysis based on the mathematical modeling to determine an appropriate embedded domain, further investigate the impact of embedded watermarks at different positions in the embedded domain on the robustness and capacity of watermark algorithm and the fidelity of the image and determine the reasonable embedding positions of the watermarks. Watermark detection corrects the image to be detected and extracts the watermarks according to a model curve of the changed embedded domain before and after image printing and scanning obtained from mathematical modeling analysis. The invention corrects the pixel distortion that the printing and scanning process to the image by mathematical modeling, fits the model curve through a large amount of experimental data, corrects the printed and scanned image with the obtained model curve, detects the watermarks of the corrected image and can effectively improve the accuracy of watermark detection; and novel printing and scanning resilient digital image watermarking algorithm based on DWT and DFT is presented by integrating the pixel distortion mathematical modeling and correction, and the novel algorithm carries out pixel distortion mathematical modeling and correction on a wavelet approximation subgraph of the image.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Apparatus, system, and method for print quality measurements
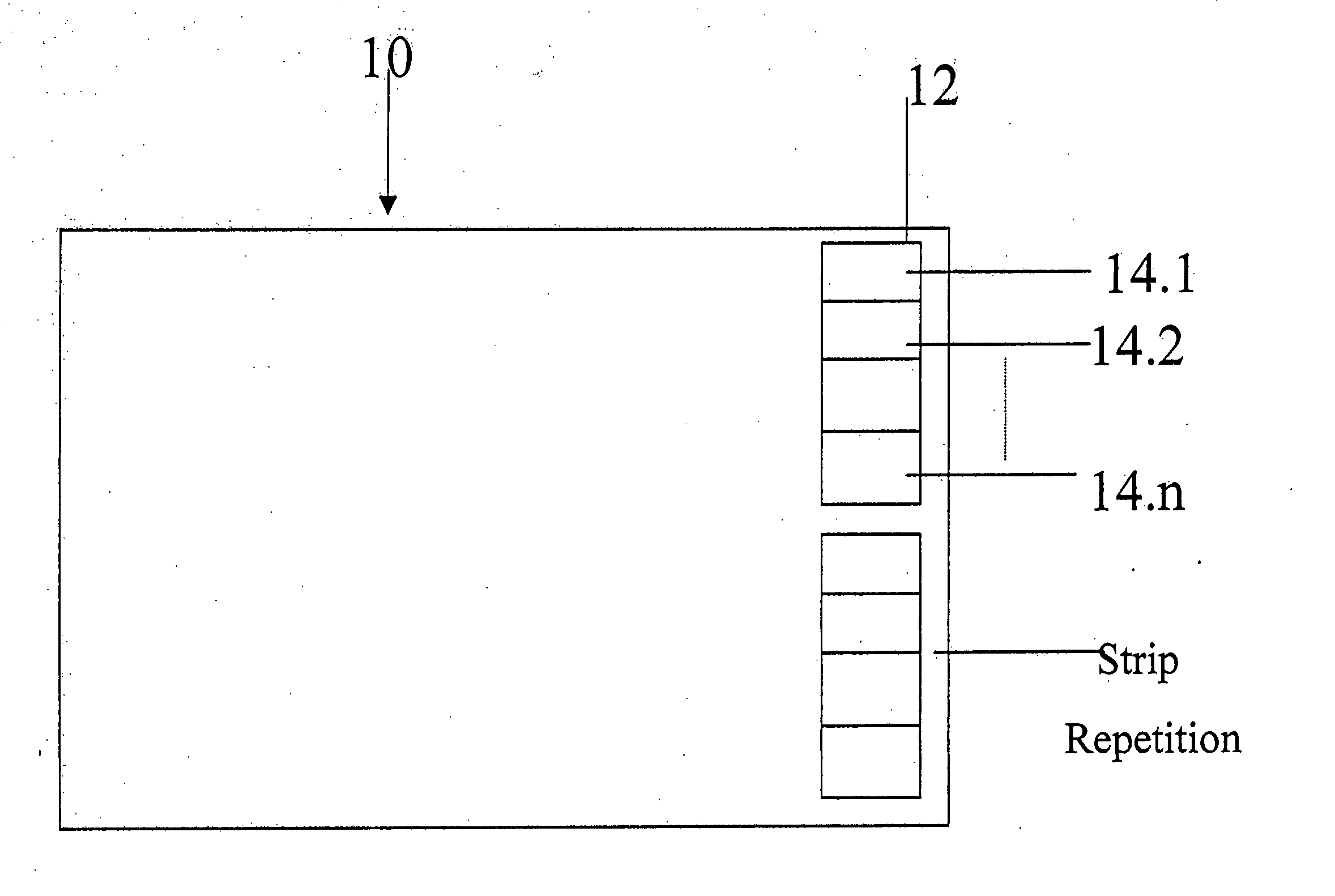
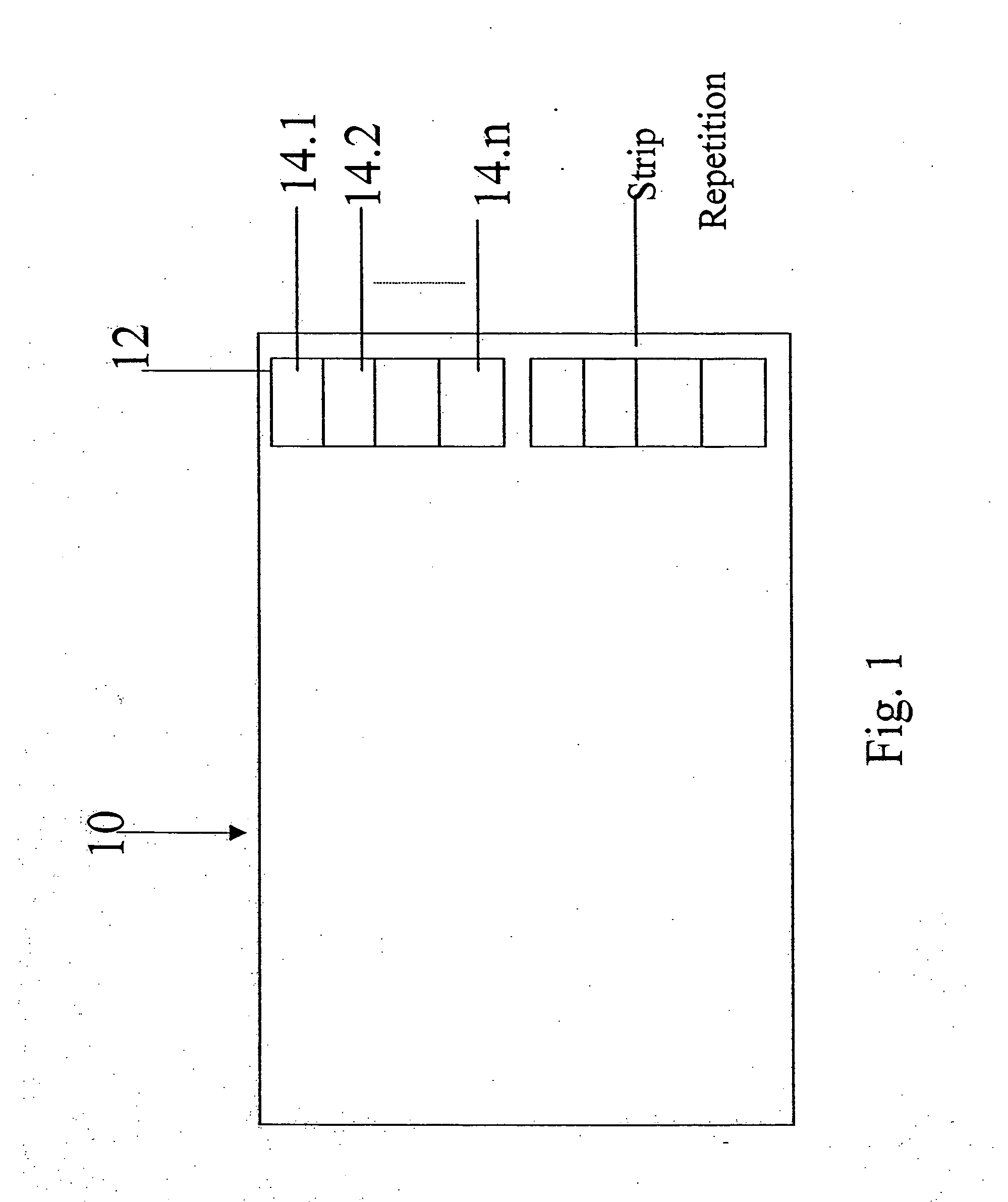
An apparatus includes at least one scanner. Each scanner includes a plurality of sensors, and each sensor is capable of measuring one or more characteristics associated with a portion of a substrate. The substrate has printing produced by a printing system. The apparatus also includes a controller capable of receiving at least some of the measurements from the plurality of sensors and determining a quality of the printing on the substrate using the received measurements. The substrate could represent paper, and the printing system could represent an offset printing system. At least one of the sensors may be in a fixed position and / or at least one of the sensors may be movable over part of a surface of the substrate. The determined quality of the printing could involve density, dot area, dot gain, contour sharpness, doubling, mottling, ghosting, misregister of different colored inks, slur, or improper positioning of the printing.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Digital customizer system and method
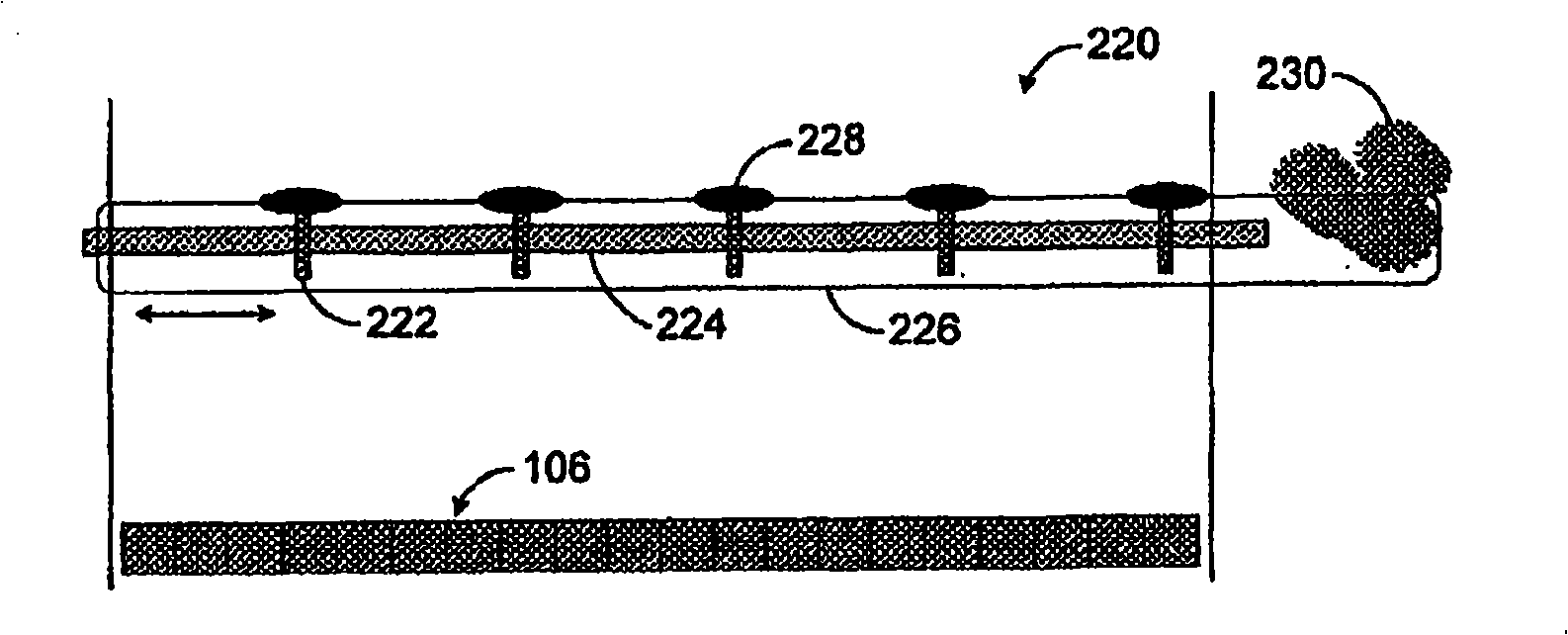
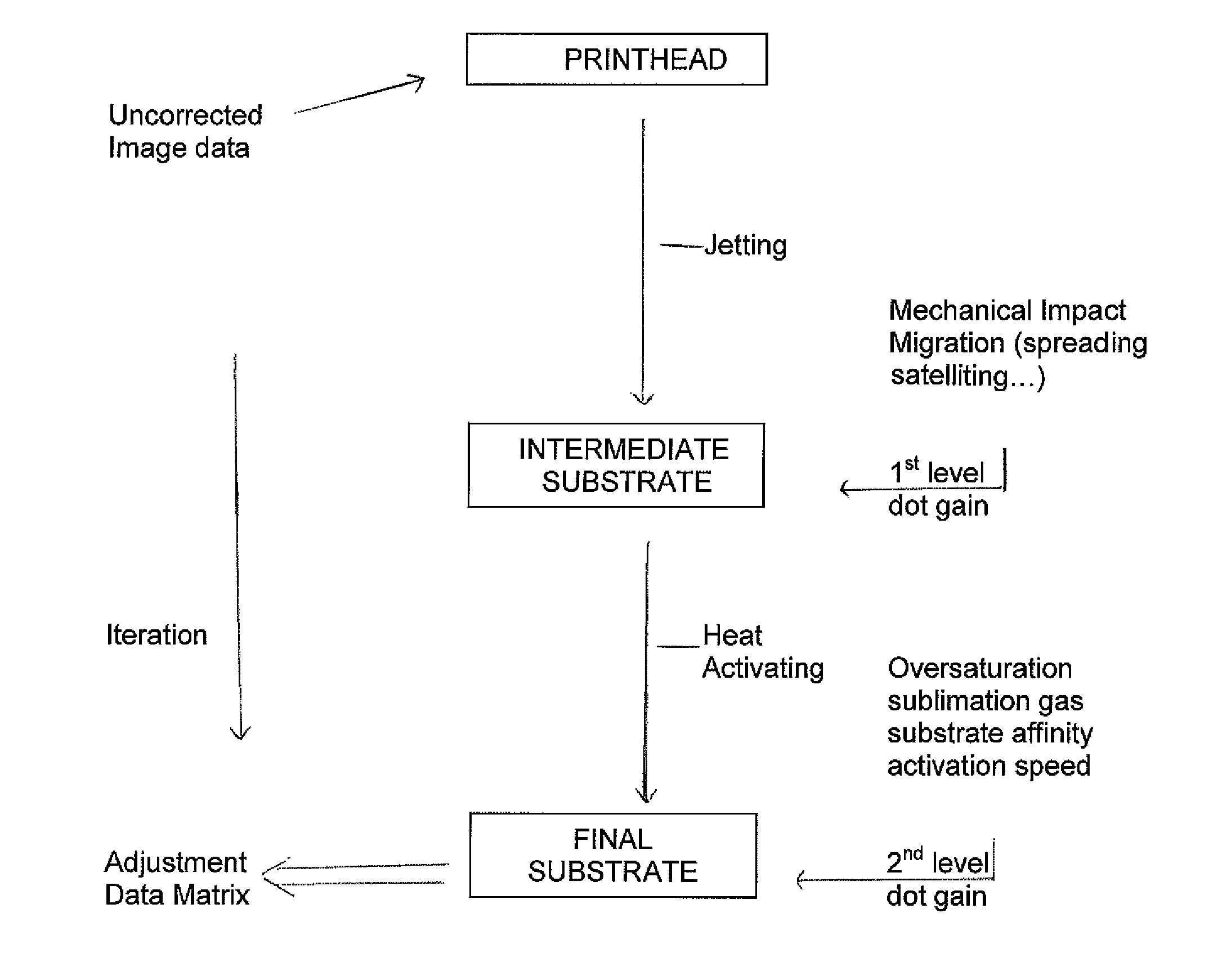
The present invention is a system and method for digitally customizing or decorating objects typically formed of substrates other than paper. The system includes a computer, color management software, and a full color inkjet printer designed for printing heat activatable ink. The ink comprises heat activatable colorant solids that are printed onto media in the form of an image that may be activated and / or transferred to a subsequent or final substrate by applying heat and intimate contact between the medium and the subsequent or final substrate. Control of first level dot gain upon printing and second level dot gain upon heat activation of the colorant provides an image that is of high quality, and even photographic quality, for most substrates that are usable with the system and method of the invention.
Owner:GOGIGIT LLC
Method for calculating a spot color database
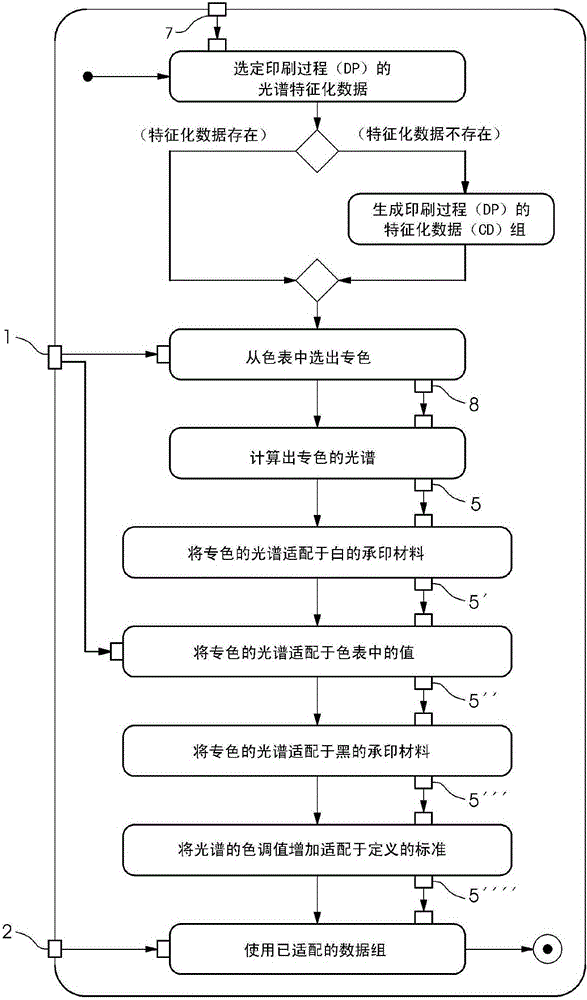
ActiveCN105522822ACalculations are simple and preciseRealize layoutPrinting press partsPictoral communicationDot gainHue
A method for calculating spectral data records for spot colors includes the steps of generating or selecting spectral characterization data of a printing process; selecting colorimetrically defined spot colors from a color table; calculating the spectrum of the spot colors based on the spectral characterization data on a white printing substrate and on a black printing substrate; calculating the spectrum of the halftone spot colors from the spectra of the spot colors on a white substrate and on a black substrate; adapting the spectra of the spot colors to a defined white printing substrate; adapting the spectra of the spot colors to the predetermined values from the color table; adapting the spectra of the spot colors to a defined black printing substrate; and adapting the spectral dot gains to a defined standard.
Owner:HEIDELBERGER DRUCKMASCHINEN AG
Flexographic printing original plate and water-developable photosensitive resin laminate
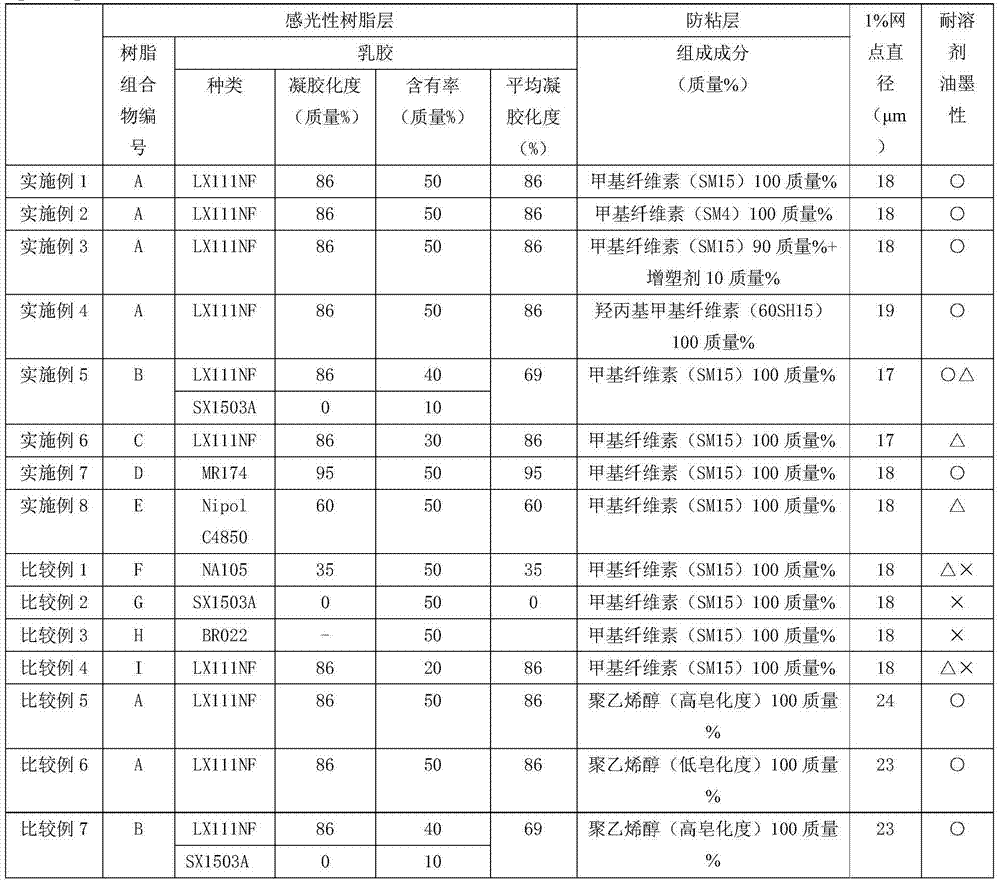
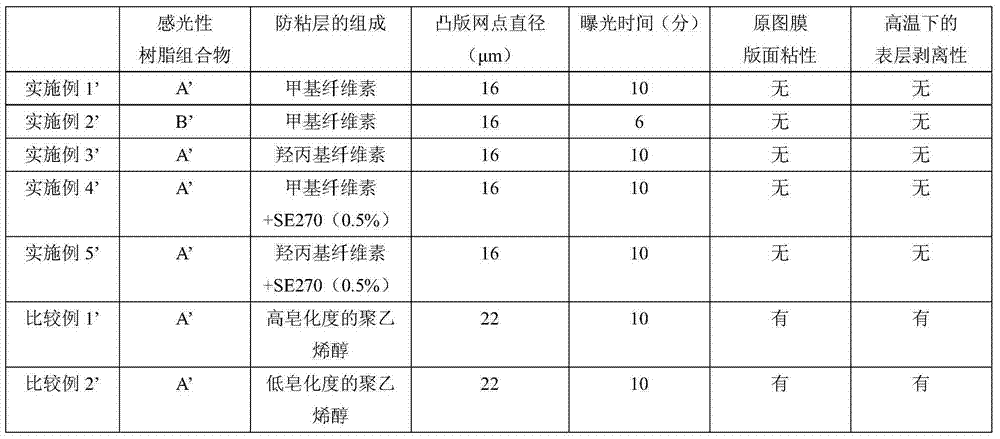
InactiveCN103782236AFine reproductionFine statePlate printingFoil printingLetterpress printingDot gain
A water-developable flexographic printing original plate, which uses a latex having a high degree of gelation in a photosensitive resin layer, and which has a good balance between resistance to solvent-borne inks and suppression of dot gain in a printing plate. Provided is a water-developable photosensitive resin laminate for letterpress printing original plates, which has excellent reproducibility of a fine pattern during the production of a printing plate and during the printing. A water-developable flexographic printing original plate of the present invention is characterized by being obtained by sequentially laminating at least a supporting body, a photosensitive resin layer that contains 25% by mass or more of a latex having a degree of gelation of 55% or more, and a bonding prevention layer, and is also characterized in that the bonding prevention layer contains a cellulose derivative. A water-developable photosensitive resin laminate of the present invention is characterized by being obtained by sequentially laminating at least a supporting body, an adhesive layer, a photosensitive resin layer that contains a water-soluble polymer compound, and a bonding prevention layer, and is also characterized in that the bonding prevention layer contains a cellulose derivative.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com