Methods and Compositions for Treating Prostate Cancer Using DNA Vaccines
a technology of plasmid dna and compositions, applied in the direction of dna/rna vaccination, antibody medical ingredients, genetic material ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of slow growth of prostate cancer, high risk of progressive disease for patients with stage d0 disease, and no accepted adjuvant treatment for patients undergoing radical prostatectomy or ablative radiation therapy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
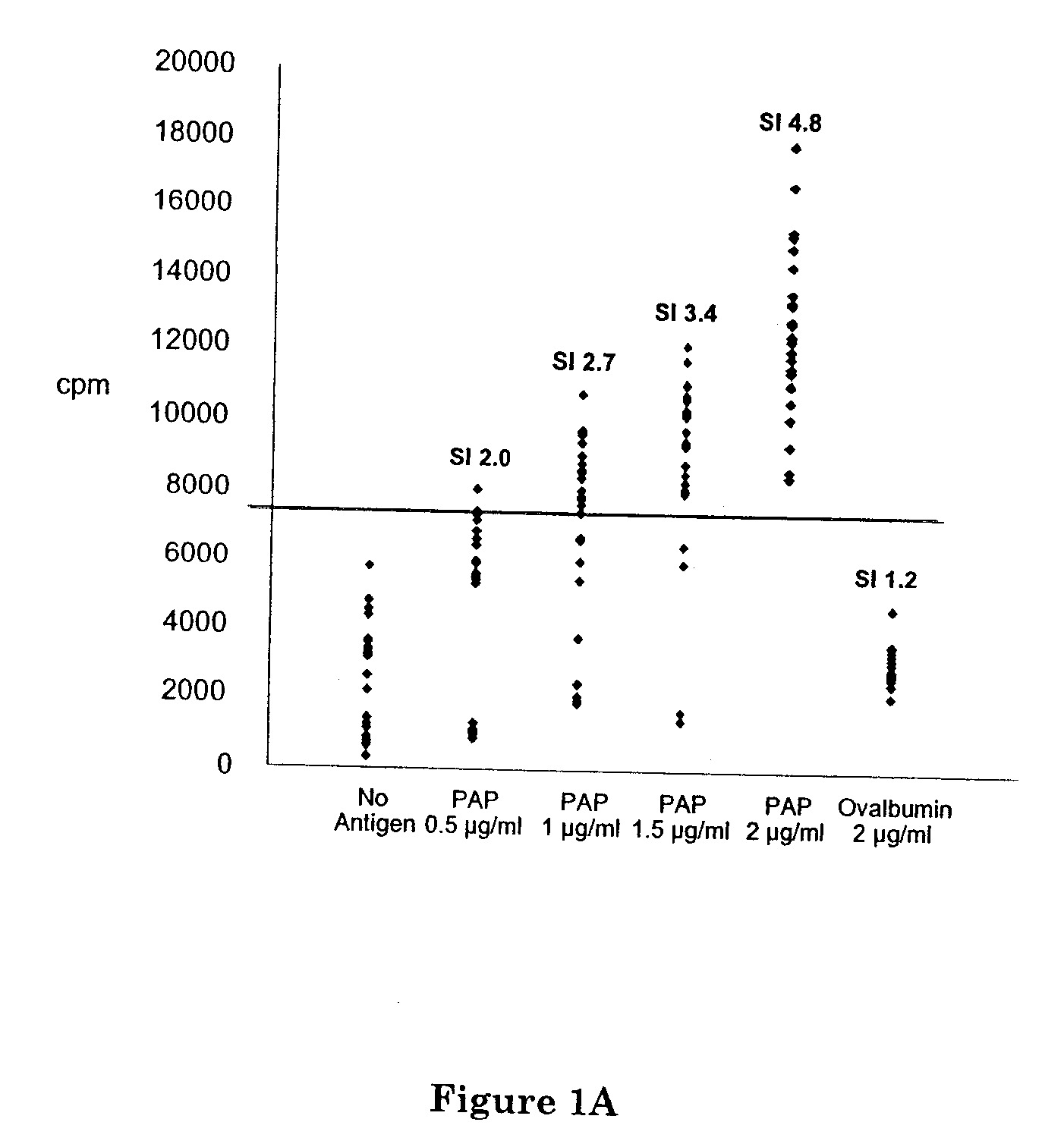
Rats Immunized with hPAP Protein Develop Cross-Reactive Immunity to rPAP and Immunization with hPAP Protein Elicits Helper T Cells and Antibodies but Not Prostate Inflammation
[0075] Lewis rats, when immunized with hPAP protein in Freund's adjuvant, developed a proliferative T cell and antibody response specific for hPAP (FIG. 1). Splenocytes from immunized rats were prepared by gradient centrifugation (Histopaque, Sigma). In FIG. 1A, human PAP (Research Diagnostics Inc., Flanders, N.J.) and ovalbumin, as a negative control protein, were used as test antigens for primed T cell responses in a 3H-thymidine incorporation assay. The numbers indicate stimulation indices compared with the no antigen control wells. In FIG. 1B, sera from an immunized rat were used to evaluate PAP-specific antibody responses in a Western blot experiment. Lane 1, protein standard; lane 2, human PAP (overexpressed from pQE-hPAP in E. coli); lane 3, rat PAP (overexpressed from pQE-rPAP in E. coli). The plasmids...
example 2
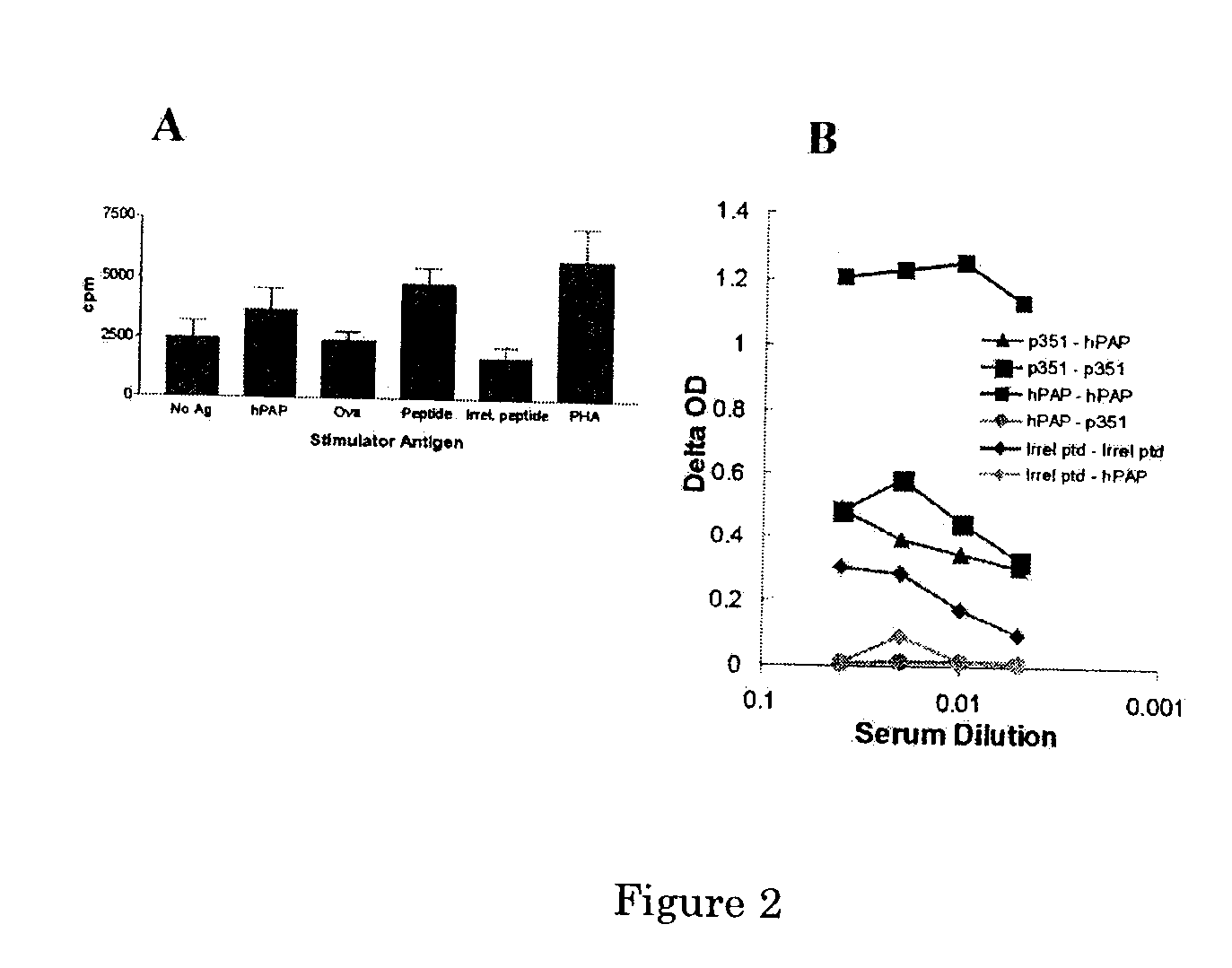
Male Lewis Rats Immunized with Peptides Derived from hPAP Develop PAP-Specific Immune Responses.
[0077] Male Lewis rats were immunized three times at 14-day intervals with 50 μg of one of ten distinct 15-mer peptides derived from the amino acid sequence of hPAP using Freund's adjuvant (McNeel et al. 2001, Cancer Res., 61:5161-5167). FIG. 2 demonstrates results from one such peptide, p351, compared with an irrelevant 15-mer peptide. Immunization with the p351 peptide elicited a peptide-specific and hPAP protein-specific T cell proliferative response (panel A). In addition, an antibody response specific for hPAP protein could be detected in p351-immunized rats (panel B). The absence of a peptide-specific antibody response in animals immunized with hPAP protein (panel B) suggests this may be a subdominant epitope of hPAP.
Example 3
DNA Vaccines Encoding Either Human or Rat PAP Elicit Potent Antigen-Specific Cellular Immunity in Rodent and Human In vitro Models
1. Preparation of mRNA En...
example 3
Lewis Rats Immunized with a Vaccinia Virus Expressing hPAP Develop PAP-Specific Cellular Immunity and Prostate Tissue Inflammation
1. Immunization with a Vaccinia Virus Vector
[0084] Immunization with vaccinia virus expressing hPAP, an immunization method permitting antigen expression in the MHC class I pathway, elicits a CTL / Th1 type of PAP-specific immune response and prostate tissue inflammation (Fong et al., 1997, supra; McNeel and Disis, 1999, supra).
[0085] As shown in FIG. 9A, Lewis rats immunized with vaccinia virus expressing human PAP develop evidence of autoimmune prostatitis. Lewis rats were immunized subcutaneously on day 1 with 2×107 pfu of vaccinia virus expressing PAP and then boosted on day 15 with either recombinant vaccinia virus (panel A), or 25 μg purified PAP administered s.c. in CFA adjuvant (panel B). Splenocytes from immunized animals were cultured for 96 hours in the presence of 2.0 μg / ml human PAP, 2.5 μg / ml PHA, or no antigen. Culture supernatants were th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| median time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com