Systems and methods for closing a vessel wound
a technology of wound closure and system, applied in wound clamping, medical science, surgery, etc., can solve the problems of hematoma risk, impaired patient comfort and physician efficiency, and use of external pressure techniques such as external pressure techniques,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
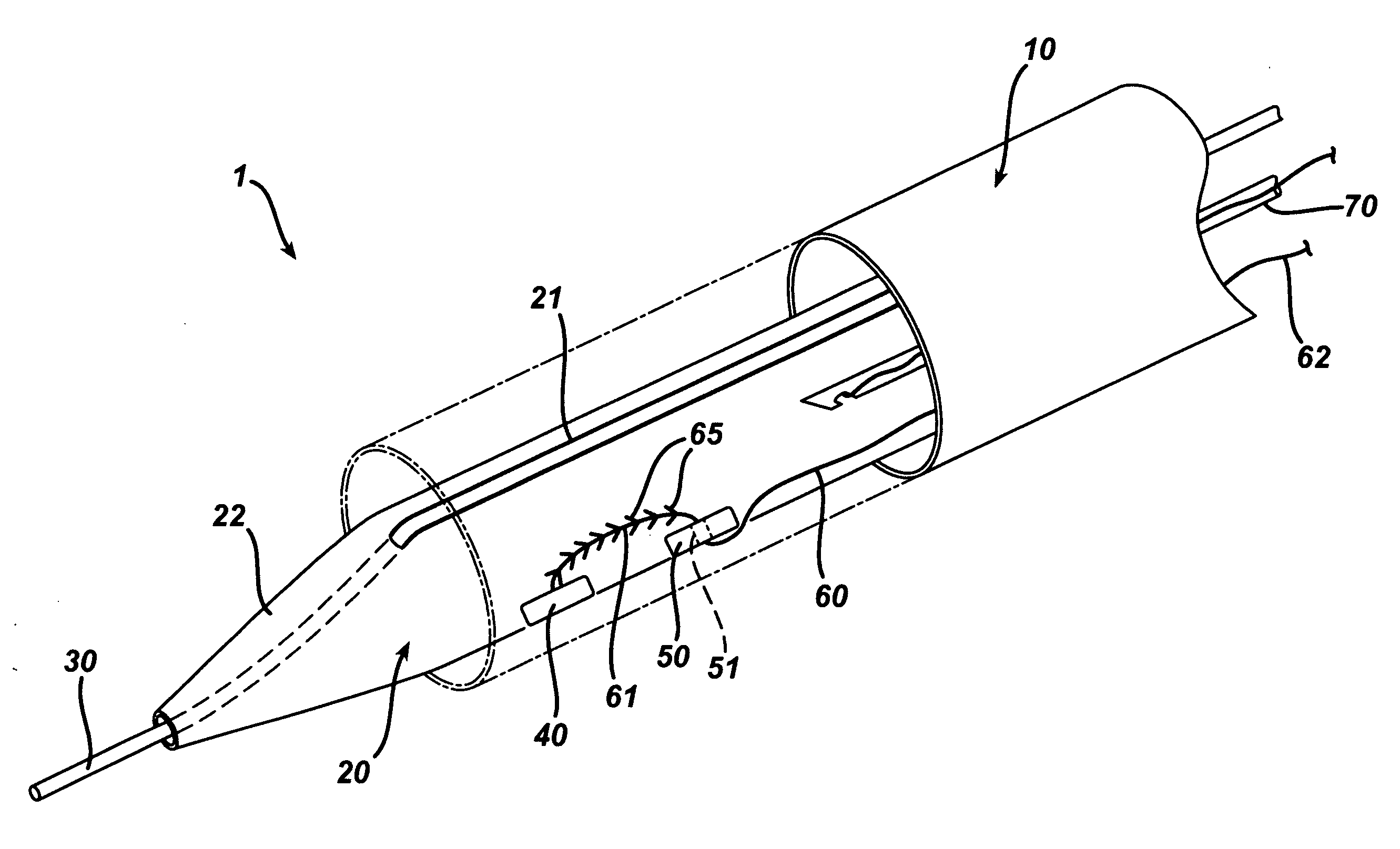
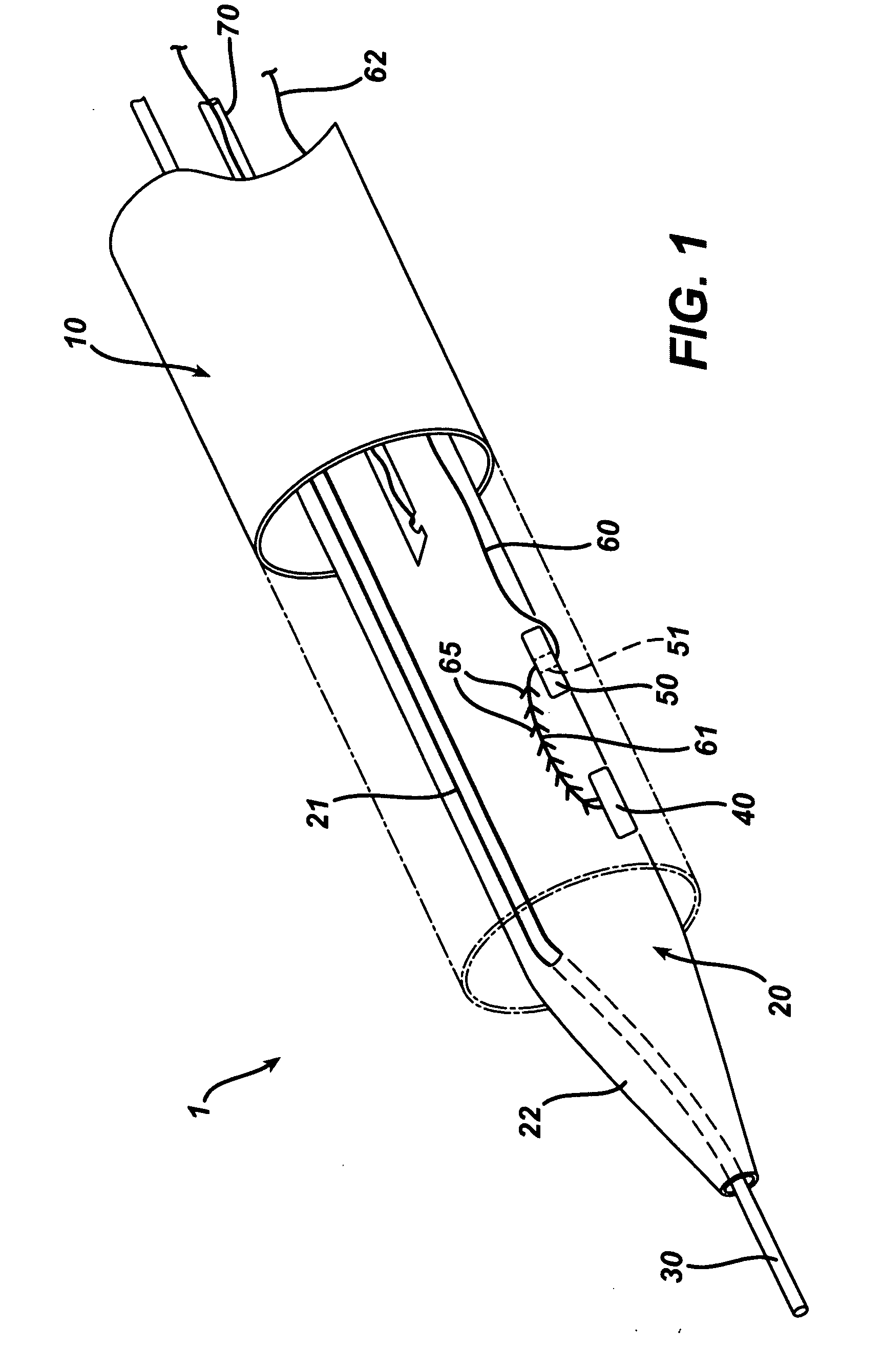
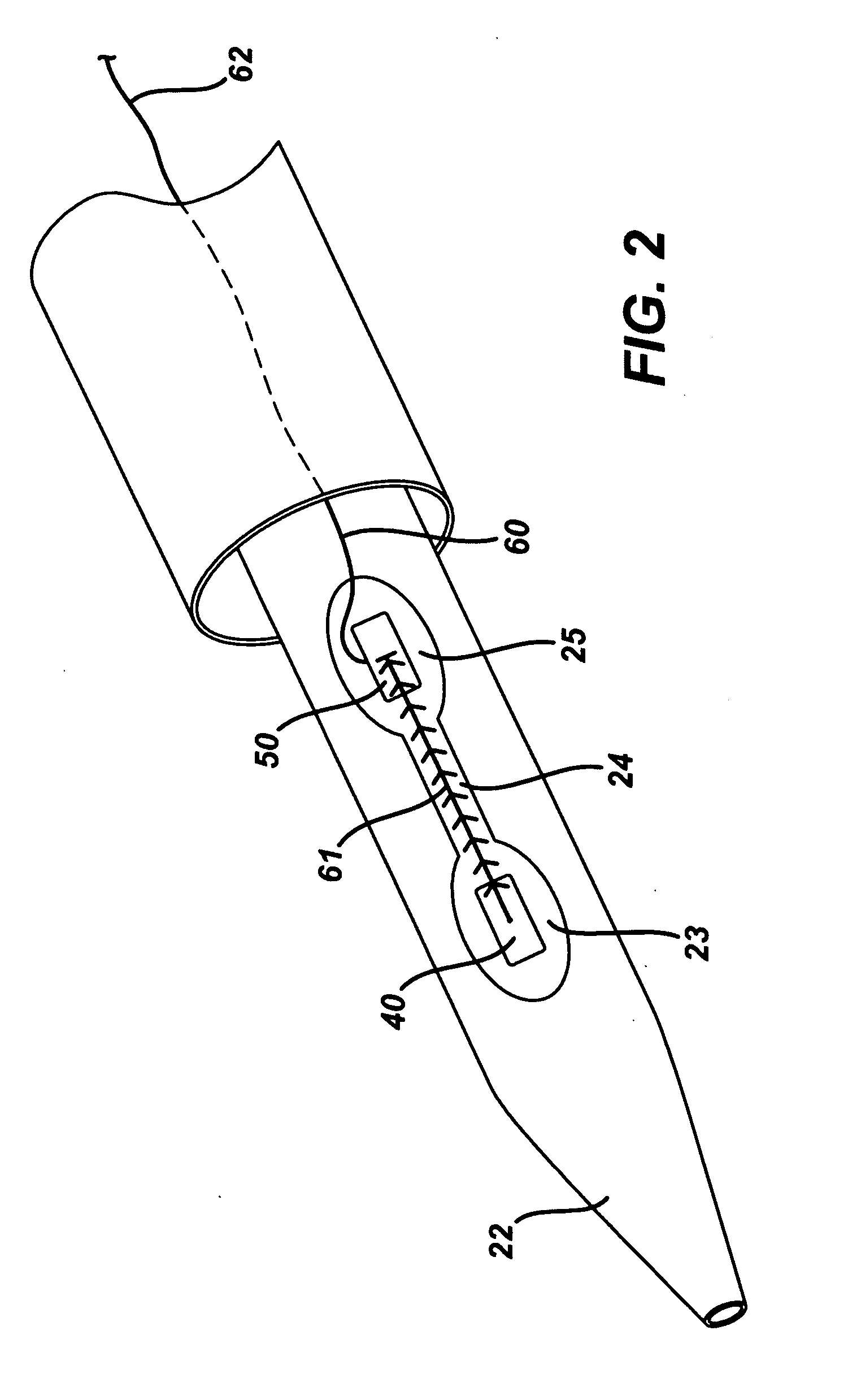
[0041]FIG. 1 illustrates one embodiment of a vessel wound closure system, wherein the term proximal, or variants thereof, is understood as closest to a medical practitioner operator, and the term distal, or variants thereof, is understood as furthest from a medical practitioner operator.
[0042] As shown in FIG. 1, the system comprises an outer sheath 10, a delivery rod 20 slidably disposed within the outer sheath 10, a guidewire 30 slidably associated with the delivery rod 20, a sealing member 40 deployably housed within the delivery rod 20, a anchor member 50 deployably housed within the delivery rod 20, and a suture 60 having a connecting portion 61 connecting the sealing member and the anchor member and an accessible portion 62 extending beyond a proximal end of the delivery rod 20 and the outer sheath 10, whereby the outer sheath 10 and the delivery rod 20 are configured such that at a first position the outer sheath 10 prevents the sealing member 40, the suture 60, and the anch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com