Method of Optimum Controlled Outlet, Impingement Cooling and Sealing of a Heat Shield and a Heat Shield Element
a technology of impingement cooling and sealing, which is applied in the direction of mechanical equipment, machines/engines, light and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of high brittleness of ceramic materials, limited operating temperature, and simple design, and achieve the effect of reducing the amount of compressor air extracted for cooling purposes, reducing the consumption of compressor air, and improving the power and efficiency of gas turbines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
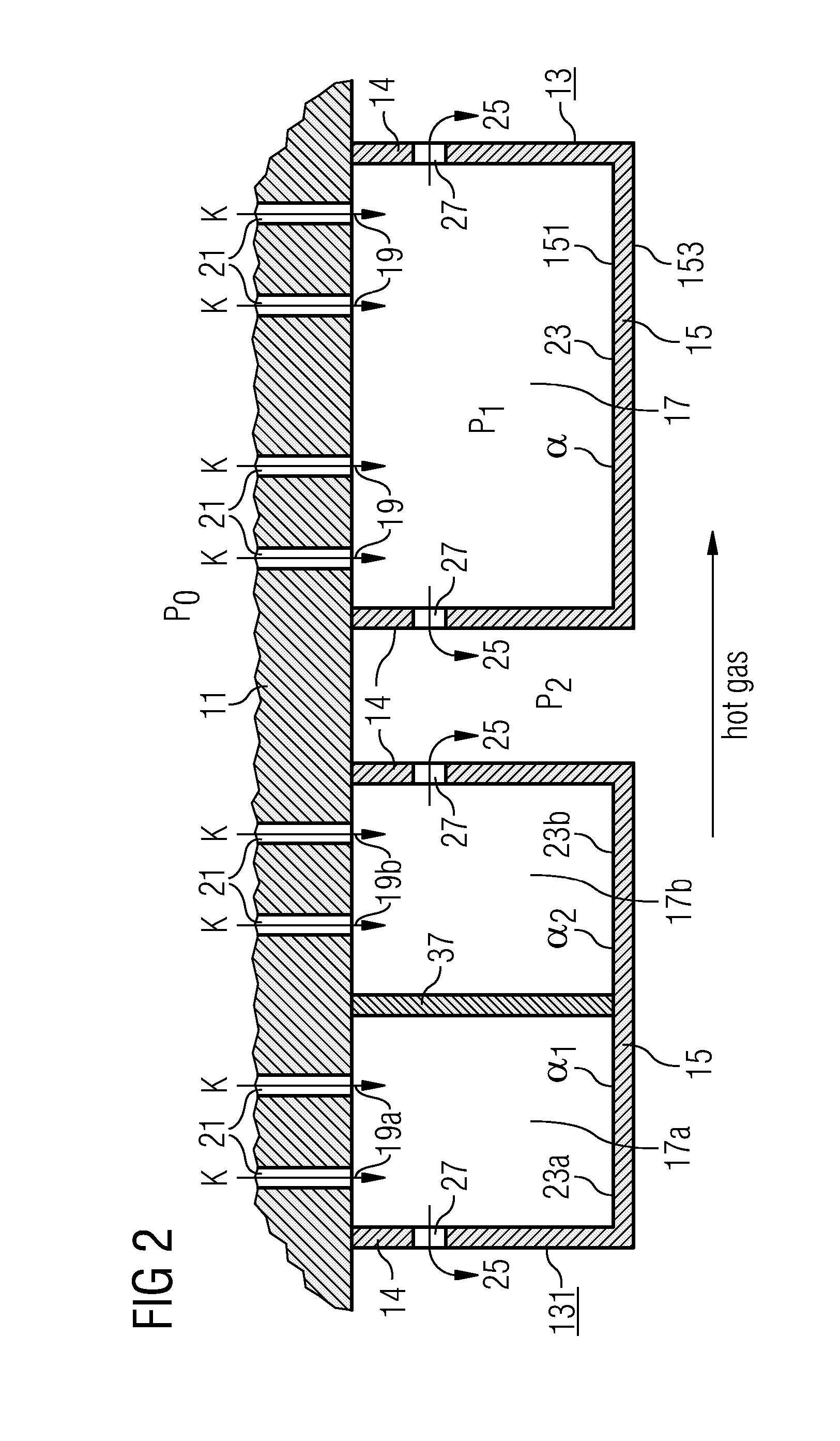
[0050] Identical reference indications have the same meaning in the figures.
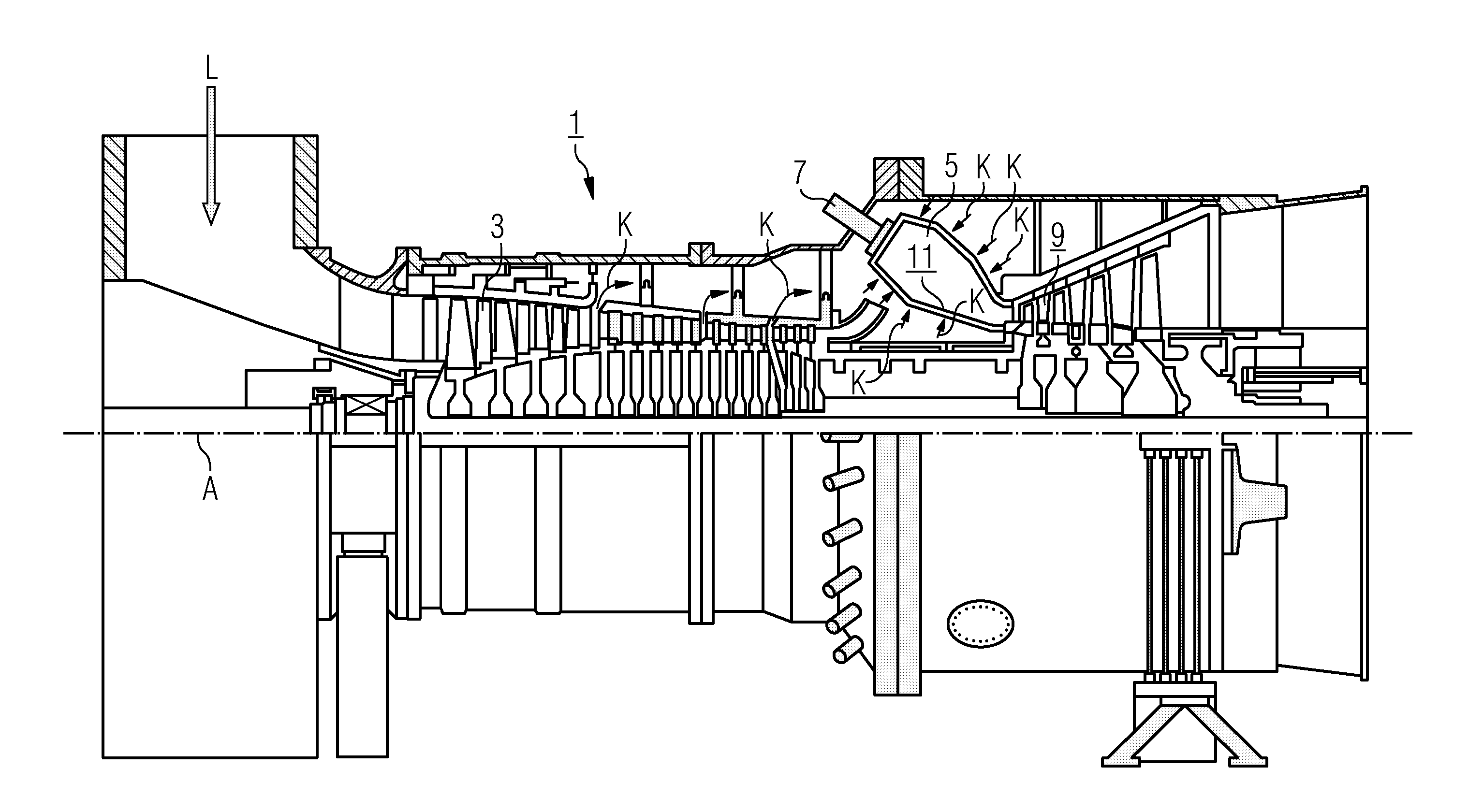
[0051] In the following an embodiment of a heat shield component in a gas turbine is depicted and explained with the accompanying drawings. The proposed designs principally do not necessarily need seals between the combustion chamber carrier wall 11 and the heat shield element 13.
[0052] In FIG. 1 a longitudinal cross section of a gas turbine installation is presented. The gas turbine installation 1 includes a compressor 3 for combustion air, a combustion chamber 5 with a burner 7 for liquid or gaseous fuel and a turbine 9 to drive the compressor 3 and a generator which is not shown in this figure. All components are lined on a common shaft along the axis A. In the compressor 3 combustion air L is compressed. This compressed air is fed into a number of burners 7, which are arranged on a circle around the annular combustion chamber 5. Fuel, which is not shown in the drawing, is mixed with a large part of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com