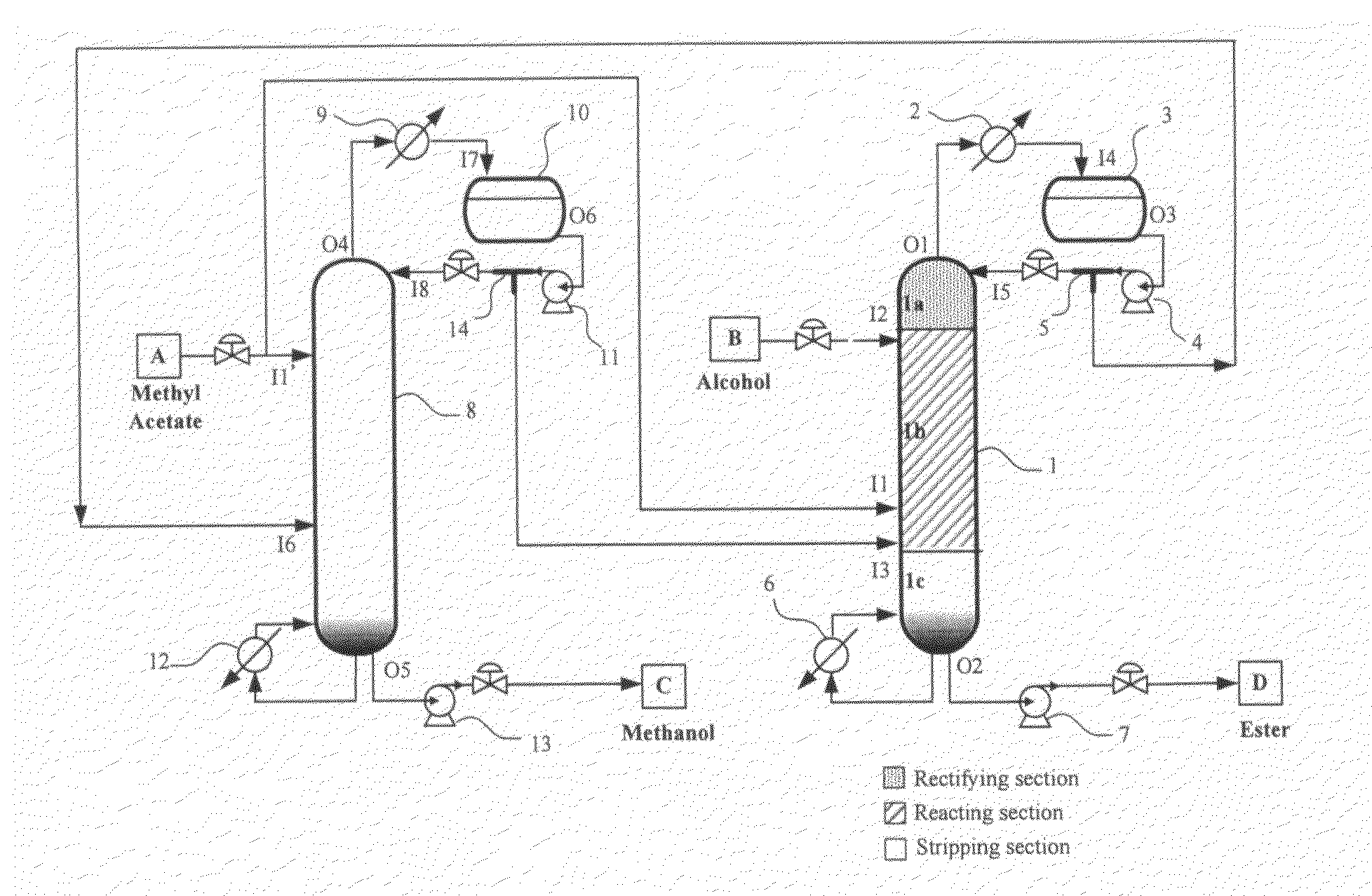
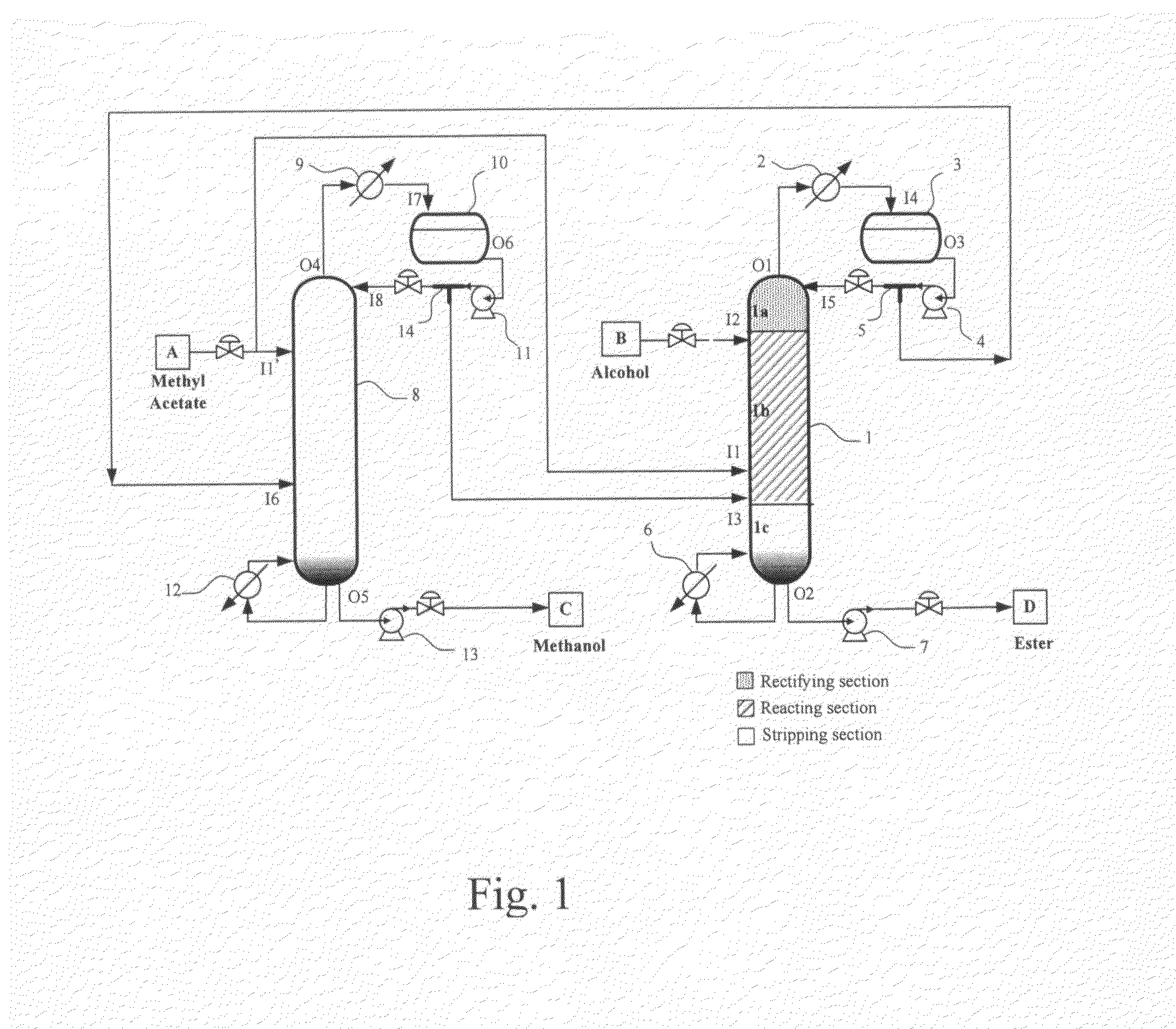
Transesterification process of methyl acetate
a technology of methyl acetate and esterification process, which is applied in the preparation of ester-hydroxy reactions, chemical apparatus and processes, and organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of reducing methyl acetate is a less valuable solvent, and the overall economic efficiency of the conventional polyvinyl alcohol plant is reduced. , to achieve the effect of economic and efficient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiments
[0053]
ItemsEmbodiment IEmbodiment IIMol. Composition of methyl60% methyl60% methylacetate solutionacetate +acetate + 40%40% methanolmethanolMol. Composition of100% n-butanol100% n-butanoln-butanol solutionThe reactive distillation device (1)No. of the reactive trays3548No. of the rectifying trays 5 5No. of the stripping trays 8 7No. of trays that n-butanol43th55thfeedsNo. of trays that methylX12thacetate feedsNo. of trays that a zeotrope feeds12th12thThe distillation device (8)No. of total trays1419No. of trays that methyl12thXacetate feedsNo. of trays that reflux feeds5th8thThe amount of reflux112.45 (kmol / hr)109.64 (kmol / hr)The purity of butyl acetate99 mol %99 mol %The purity of methanol99 mol %99 mol %
[0054]In the Embodiment I, the methyl acetate solution is fed to the distillation device (8); in the embodiment II, the methyl acetate solution is fed to the reactive distillation device (1).
[0055]In conclusion, although the reactive distillation system depends upon the plurality o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com