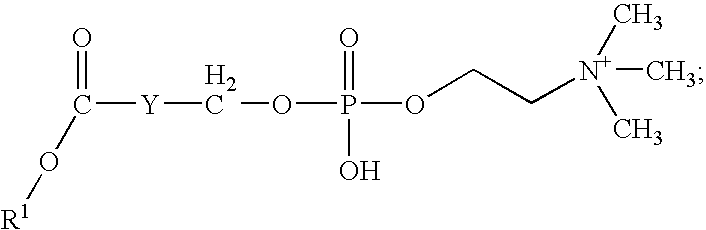
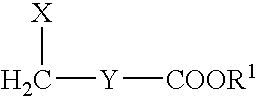Synthesis of phosphocholine ester derivatives and conjugates thereof
a technology of phosphocholine ester and phosphocholine ester, which is applied in the field of synthesizing phosphocholine ester derivatives and conjugates, can solve the problems that antibodies are not found to be protective against i>s. pneumoniae, and achieve the effect of preventing microorganism infections and being more efficient and cost-effectiv
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Step 1: Synthesis of 6-(O-Phosphocholine)Hydroxyhexanoic Acid
[0070]A sample of 6-bromohexanoic acid is combined with a catalytic amount of 1 8-crown-6 in formamide. To this combination, an equal molar amount of phosphorylcholine chloride calcium salt tetrahydrate is added. The resulting mixture is heated to 110-120° C. for about 3 hours. After incubation, the mixture is cooled to room temperature and is applied to a silica gel column (Emerck: 230-400 mesh silica gel; d2.5 cm×L35 cm). The product, 6- (O-phosphocholine)hydroxyhexanoic acid, is eluted from the silica gel column with methanol:water (4:1) solution.
Step 2: Synthesis of P-Nitrophenyl-6-(O-Phosphocholine)Hydroxyhexanoate
[0071]A sample of 6-phosphocholinehexanoic acid in dimethylformamide is stirred at room temperature for 5 min. To this mixture, approximately a three fold molar excess of p-nitrophenyl trifluoroacetate is added. While stirring the resulting mixture, approximately a 2 fold molar excess of 2,6-lutidine is adde...
example 2
[0073]Synthesis of 4-Nitrophenyl-6-(O-Phosphocholine)Hydroxyhexanoate from Ethyl 6-Bromohexanoate
Step 1: Synthesis of Ethyl 6-Phosphocholinehexanoic Acid
[0074]A sample of 9.1 g (41.2 mmol) of ethyl 6-bromohexanoate was combined with 1 .1 g (4.1 mmol) of 18-crown-6 in 40 ml of formamide. To this combination, 9.2 g (41.2 mmol) of phosphorylcholine chloride calcium salt tetrahydrate was added. The resulting mixture was heated to 110-120 ° C. for about 3 hours. After incubation, the mixture was cooled to room temperature and applied to a silica gel column (Emerck: 230-400 mesh silica gel; d2.5 cm×L35 cm). The product was eluted from the silica gel column with methanol:water (4:1) solution, which yielded 10 grams of ethyl 6-phosphocholinehexanoate with a percentage yield of 74%.
Step 2: Deprotection of Ethyl 6-Phosphocholinehexanoate to Yield 6-Phosphocholine Hexanoic Acid
[0075]A sample of 2.0 g (6.15 mmol) of ethyl 6-phosphocholinehexnoate was combined with 3.2 g (12.3 mmol) of tetrabuty...
example 3
Conjugation of PC Haptens
[0078]EPC haptens are conjugated to keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) (400,000 used as MW) dissolved in borate buffered saline (BBS), pH 8.5 at 10 mg / ml. EPC is dissolved in dry acetonitrile (100 mg / ml) just prior to addition to the KLH. Hapten and KLH are mixed overnight at 4° C. and then dialyzed to remove unbound hapten and the released p-nitrophenylate. Alternatively, the PC-KLH conjugate can be purified by gel exclusion chromatography on a Sephadex G-25 column. The conjugation efficiency is estimated by determining the phosphate bound to protein according to the method described in Ames, B. N., et al. (1960) J Biol. Chem. 235:769.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| covalent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| soluble | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com