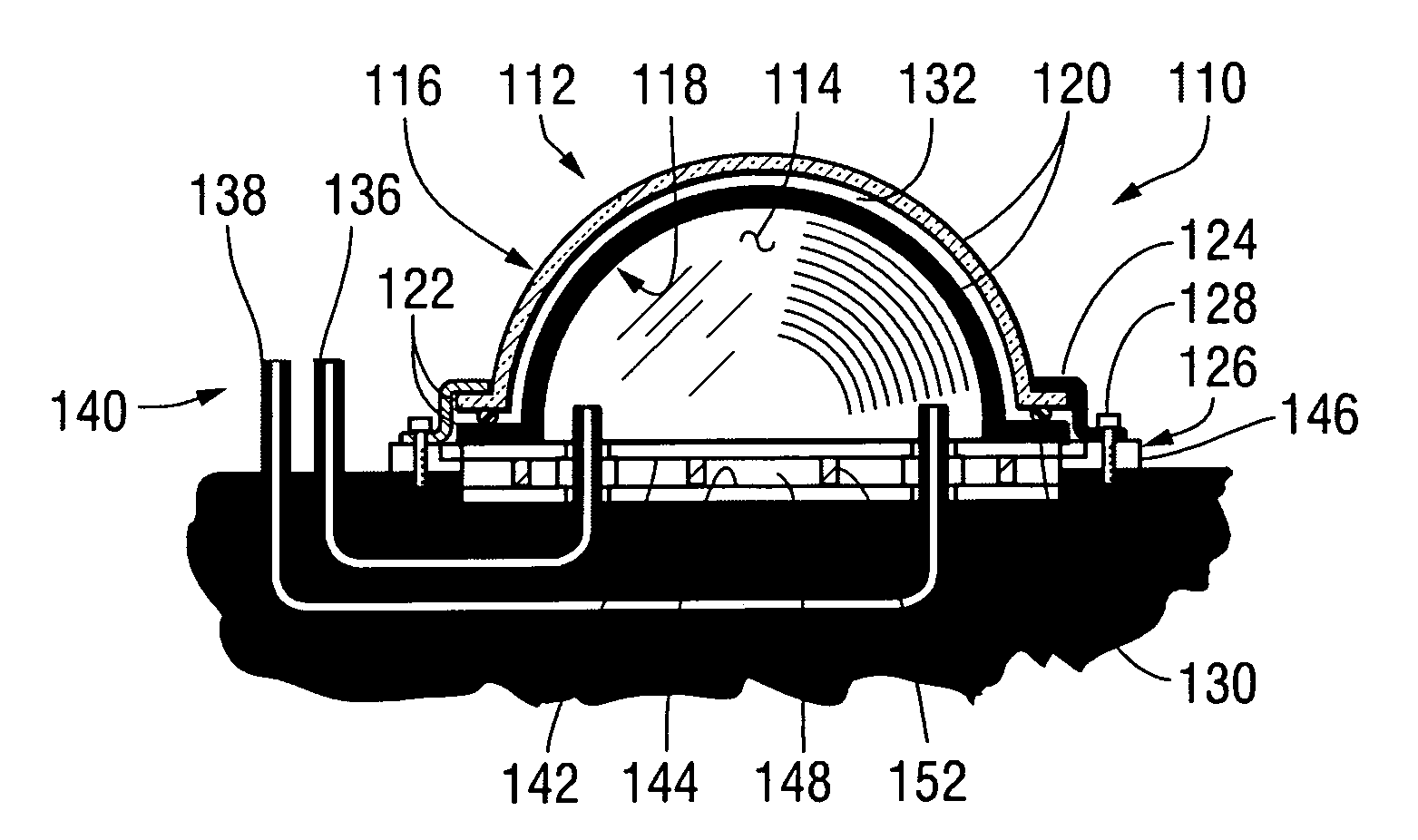
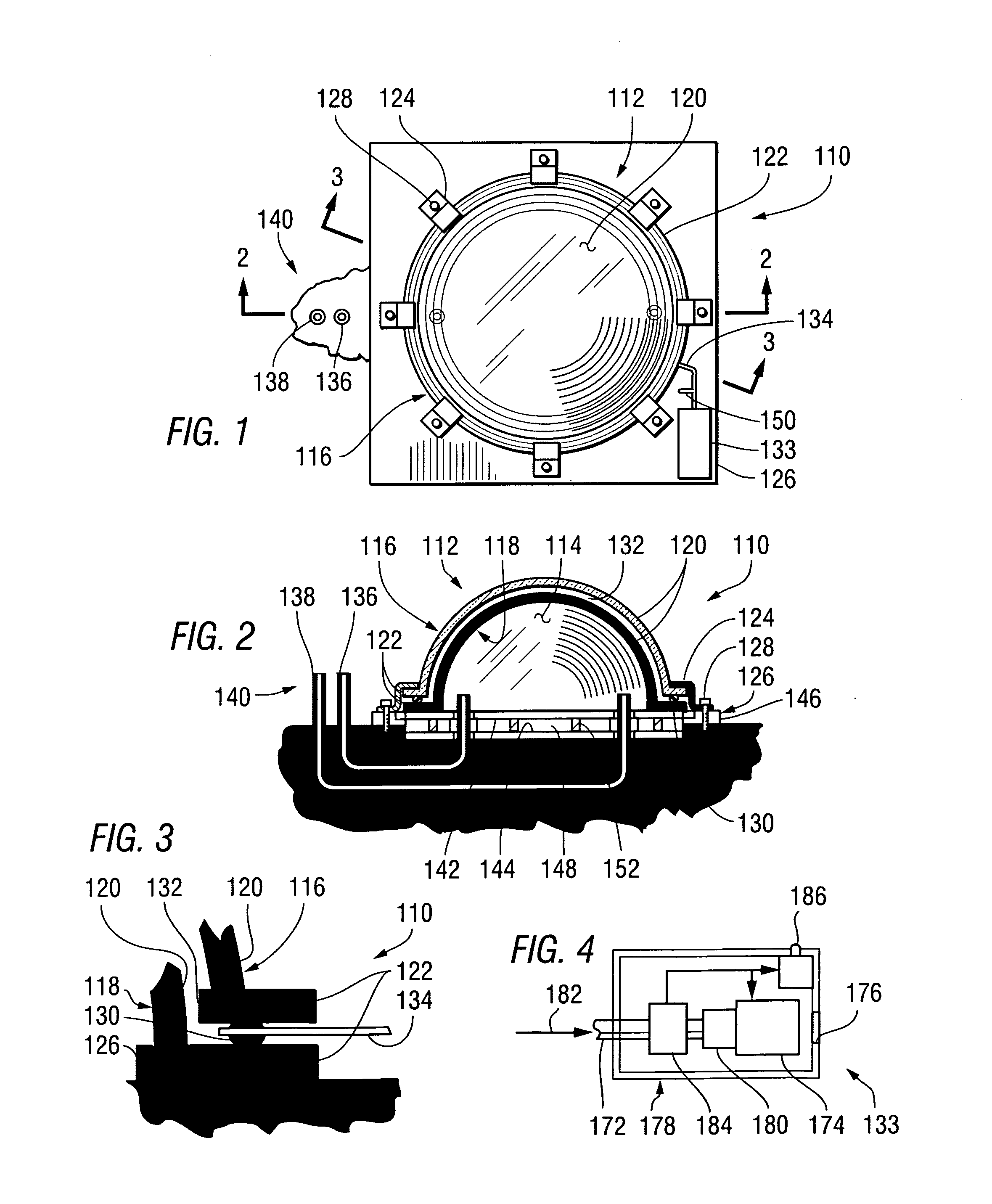
Active thermal insulation system including evacuated structures and a vacuum sustaining unit
a technology of active thermal insulation and evacuated structures, which is applied in the direction of solar ray transmission, domestic cooling devices, lighting and heating devices, etc., can solve the problems of loss of vacuum, low strength of glass materials generally used, and low reliability of such structures, so as to prevent heat loss to the atmosphere, reduce the overall efficiency of solar heat collectors, and reduce the effect of heat loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
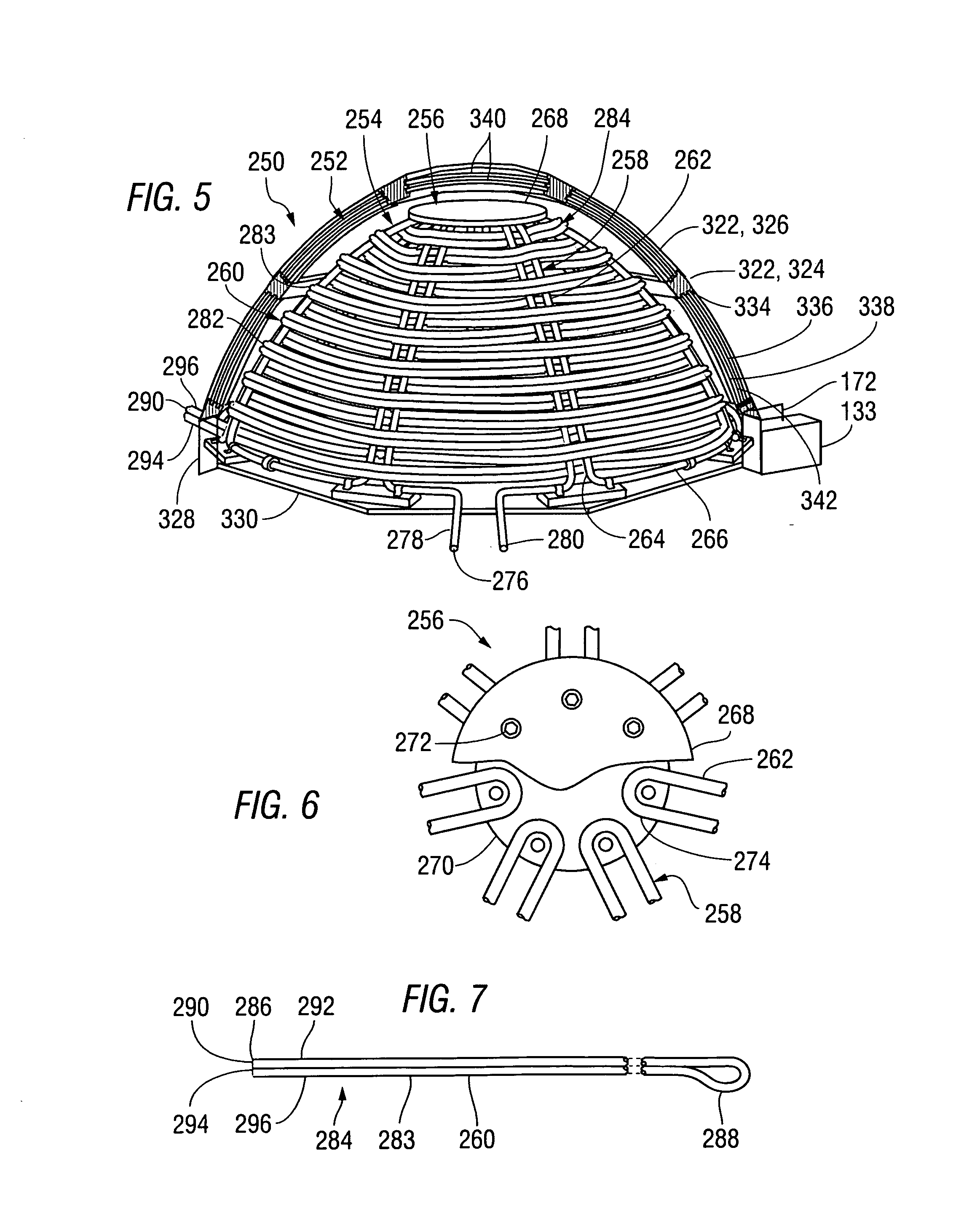
[0069]FIG. 5 is a perspective view of a thermal insulation system 250 including a dome-shaped structure 252 built in accordance with a second version of the invention to extend around and over a dome-shaped solar heat collector 254 built as described in detail in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 12 / 009,092, the disclosure of which has been incorporated herein by reference. A front portion of the dome-shaped structure 252 has been cut away to show the structure of the solar heat collector 254, which includes a frame 256, having a plurality of frame elements 258, and a plurality of transverse elements 260. Each of the frame elements 258 includes a pair of rigid tubular elements 262, extending parallel to one another. The lower ends 264 of rigid tubular elements 262 within adjacent frame elements 258 are connected to one another by peripheral tubular elements 266 within the frame 256.
[0070]FIG. 6 is a fragmentary plan view of the frame 256, showing a central portion thereof, including ...
second embodiment
[0092]FIG. 27 is a cross-sectional end elevation of a thermally insulating panel 610 built for use within a thermally insulating structure built in accordance with the invention, which to include a plurality of such insulating panels 610 attached to a vacuum sustaining unit 133, as described above in reference to FIG. 4.
[0093]The insulating panel 610 includes a pair of side panels 612 held in a spaced-apart condition within a frame 614. An evacuation tube 616 extends through the frame to provide for the evacuation of air from the interior space 618 between the side panels 612, and seals 620 prevent, or at least minimize, the return of air into the interior space 618 following evacuation. In the example of FIG. 27, the side panels 612 are composed of an opaque material, such as a metal, plastic, or composite material including wood chips. Spacers 622 may be attached to extend between the side panels 612, preventing deflection and possible breakage of the side panels 612 due to atmosp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com