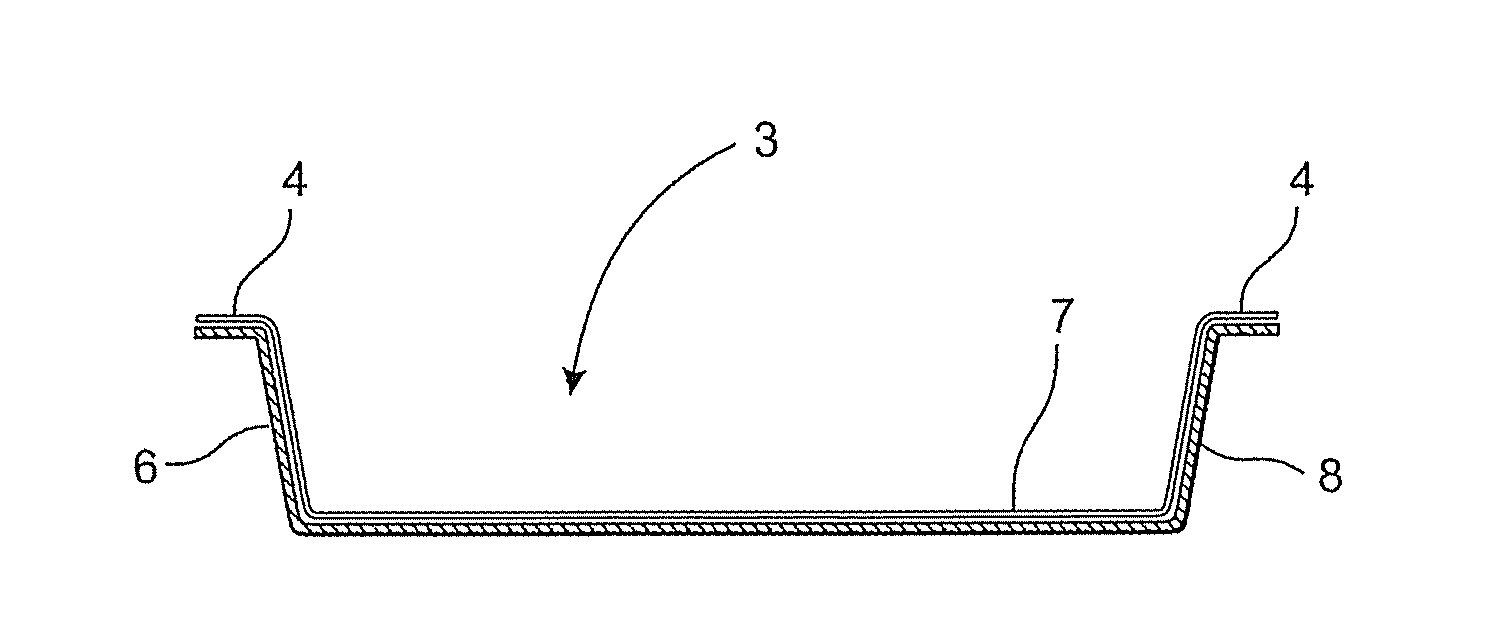
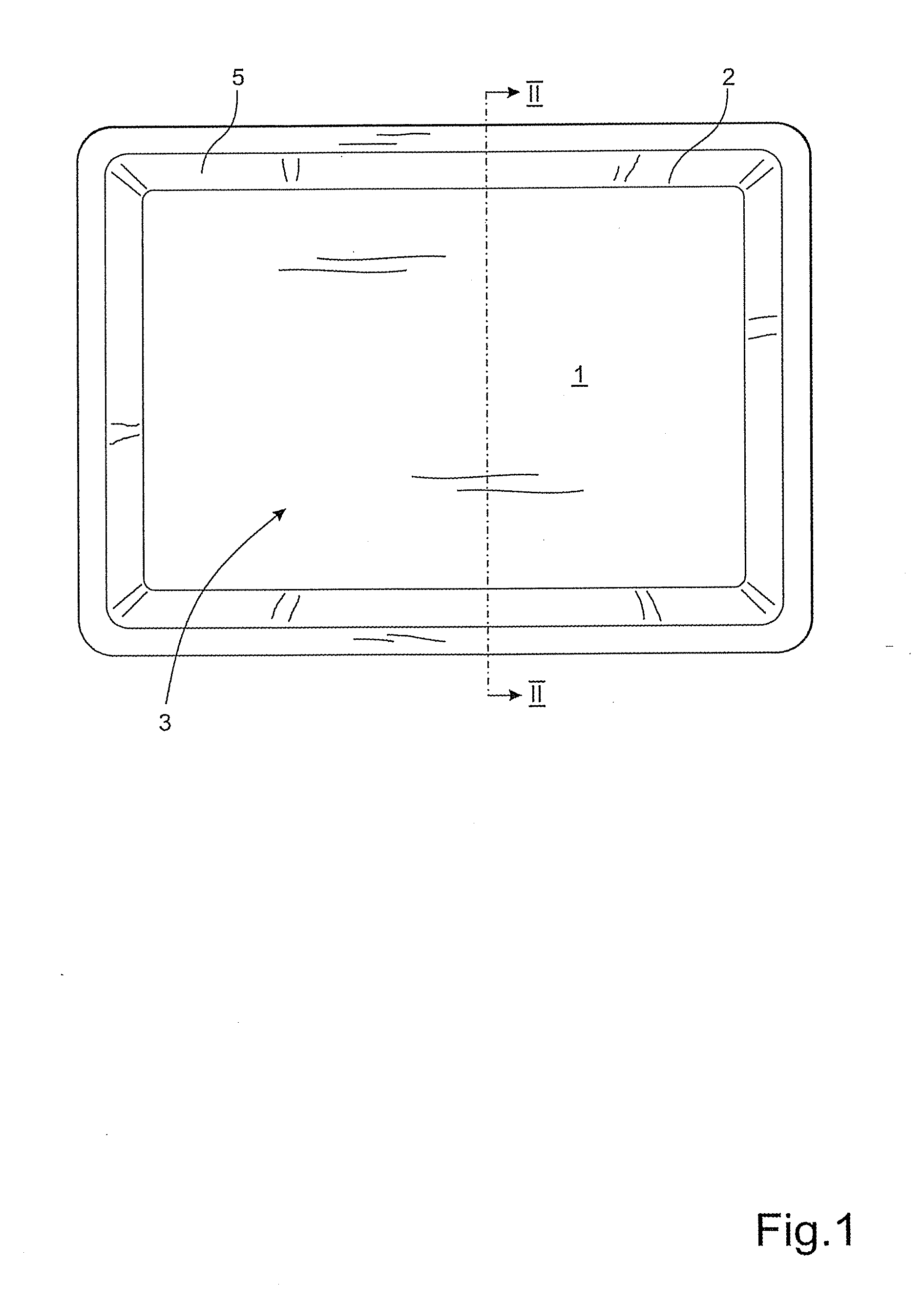
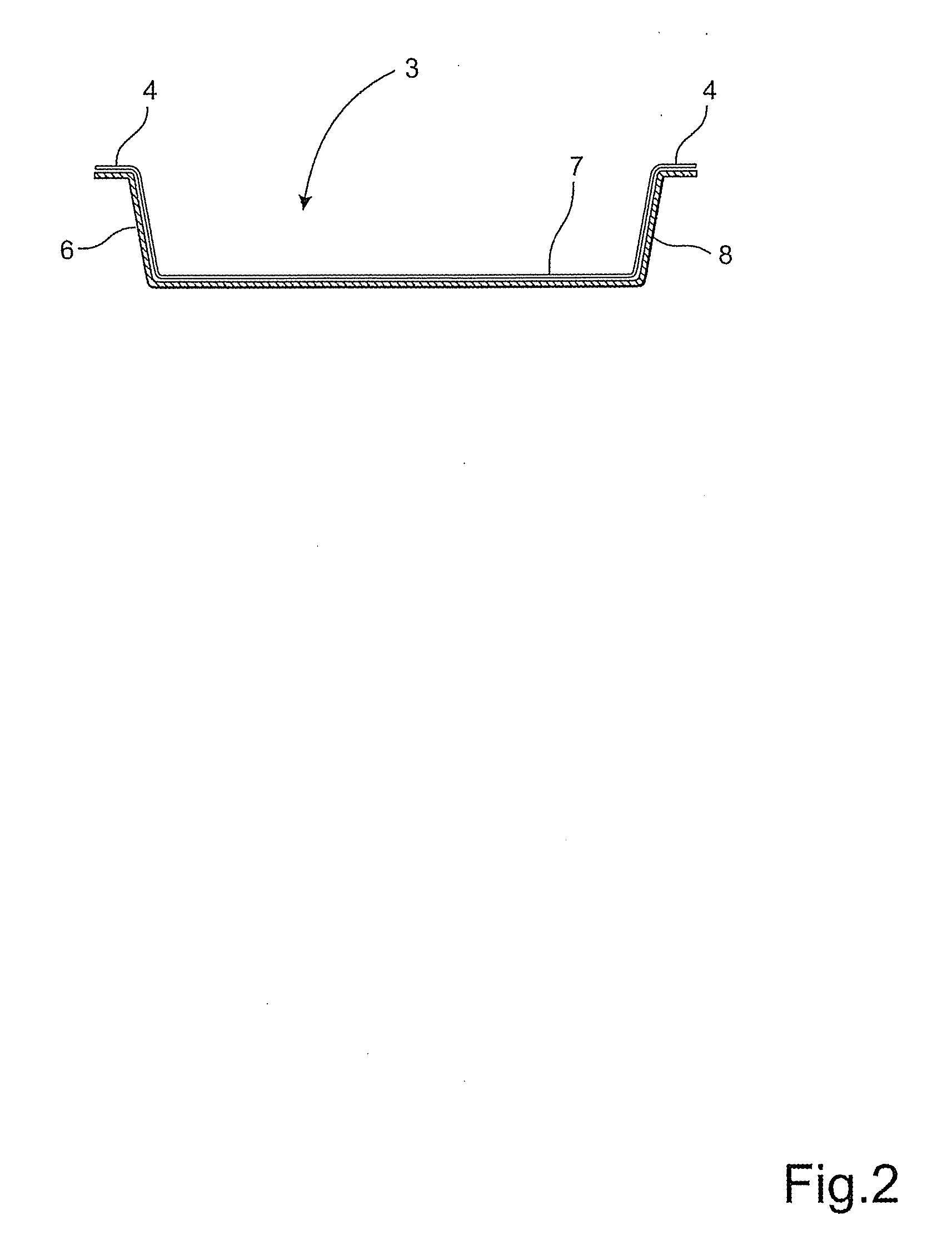
Compression-moulded tray and method of producing a fibre tray
a technology of compression moulding and fibre material, which is applied in the direction of packaging foodstuffs, packaging goods types, containers for heating food, etc., can solve the problems of bacteria and flavouring agents not being able to migrate through the packages, being very hot, and sometimes even impossible to hold in your hands, etc., to achieve the effect of improving function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Tested Materials
[0055]Polyester-laminated fibre trays formed of CTMP from a suspension. The dimensions of the trays were 173×117×30 mm.
Testing
[0056]Surface weight measurements were performed according to ISO 536:1995. Samples were taken from the bottom and the side walls of the trays.
[0057]Measurements of the thickness and density were performed according to ISO 534:1998. Samples were taken from the bottom and the side walls of the trays.
[0058]Measurements of the tear strength were performed according to ISO 1974:1990. Samples were taken from the bottom and the side walls of the trays.
[0059]A. The weights of the trays were measured, after which the whole tray was submerged under water for 60 seconds. After drainage of the water and drying in air for 1 minute, the tray was weighed again. The gain in weight was reported.
[0060]B. The weights of the trays were measured, after which they were filled with 5 dl of water and were left to stand in room temperature for 24 h...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com