Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Herbicide Resistant Sorghum
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Herbicide Resistance in Wild Sorghum Genotype
[0085]Seeds of 83 wild sorghum populations from Bolivia were planted in a greenhouse for comparison with Tx2783, an herbicide susceptible elite sorghum genotype. Wild sorghum genotypes were planted in flats containing MetroMix 360 potting soil (Sun Gro) and greenhouse grown. Tx2783 was planted with the wild accessions in each flat for comparison. In one selection using clethodim, plants were sprayed with 0.09 lb ai clethodim acre−1 at 18 days after planting. Tx2783 and many of the wild sorghums died, but the herbicide tolerant entries were transplanted to pots for seed increase. In one selection using fluazifop-P, flats with Tx2783 and wild accessions were sprayed with a rate of 0.12 lb ai fluazifop-P acre−1 at 18 days after planting and with 0.36 lb ai fluazifop-P acre−1 at 32 days after planting. Tx2783 and many of the wild sorghums died, but the herbicide tolerant entries were transplanted to pots for seed increase. In a third experime...
example 2
Crosses of Bol-71 Wild Sorghum Genotype with Elite Sorghum Lines and Inheritance Determination
[0086]Bol-71 was crossed with elite sorghum parent lines including Tx430, 00MN7645, BTx623, and ATx623. Seed set was excellent in every cross indicating that the wild genotype was sexually compatible with cultivated sorghum and could be used in a plant breeding program to produce herbicide tolerant sorghum varieties.
[0087]The mode of inheritance of herbicide tolerance was determined by planting seeds of Bol-71, F1 generation of cross ATx623 x Bol-71, and Pioneer 84G62 (herbicide susceptible control) in flats containing MetroMix 360 potting soil in a greenhouse using a randomized complete block design (n=3). The plants were sprayed with 0.045 lb ai fluazifop-P acre−1 at 14 days after planting. Pioneer 84G62 died between 12-16 days after spraying. The ATx623 x Bol-71 and Bol-71 genotypes showed no herbicide damage, indicating that the herbicide tolerance trait was transmitted to cultivated so...
example 3
Gene Sequencing for ACC Resistance Gene
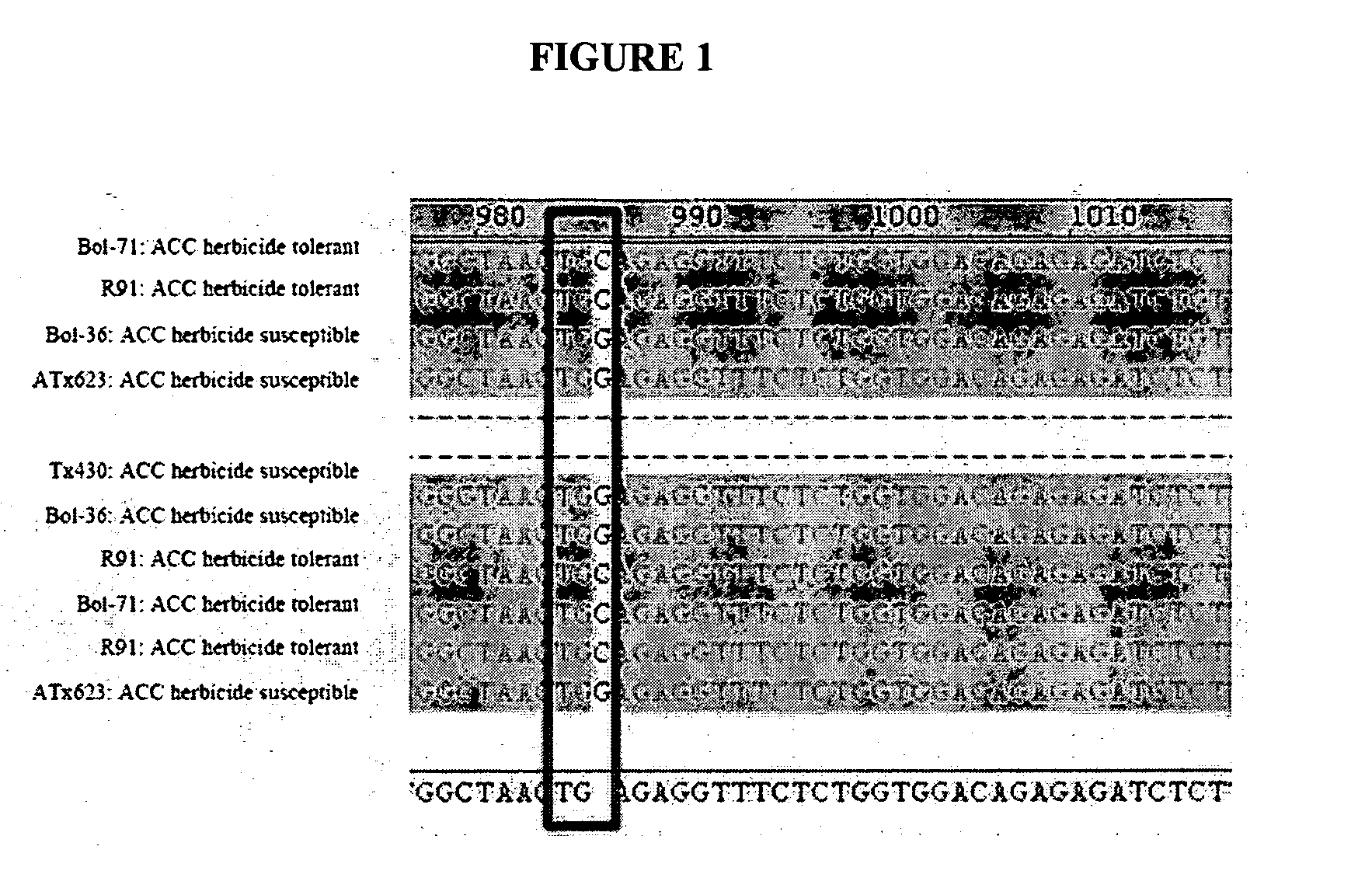
[0088]Gene sequencing efforts were initiated to determine if a genetic mutation might explain the herbicide tolerance phenotype. DNA was extracted from herbicide tolerant genotypes Bol-71 and R91 and herbicide susceptible genotypes Bol-36, ATx623, and Tx430. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using primers described by Delye and Michel (Weed Research, 2005, 45: 323-330; incorporated herein in its entirety) were used to amplify regions of the ACC gene associated with expression of herbicide tolerance. DNA sequencing (Kansas State University DNA sequencing facility) of resultant PCR products from herbicide tolerant and susceptible sorghum genotypes revealed that the susceptible genotypes contained the wild type sequence for the ACC gene as reported for sorghum (The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR) Plant Transcript Assemblies database sequence designated TA3768—4558; incorporated herein in its entirety, see also table 1 below) and other cere...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| herbicide resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| morphological characteristics | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com