Methods and systems for generating transition probability matrices through an optimization framework
a technology of transition probability and optimization framework, applied in the field of credit migration, can solve the problems of affecting the validity and usefulness of these transition probability matrices, monotonicity and/or smoothness of the resultant etpms, and not generating matrixes by smoothing techniques that accurately predict transition probabilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
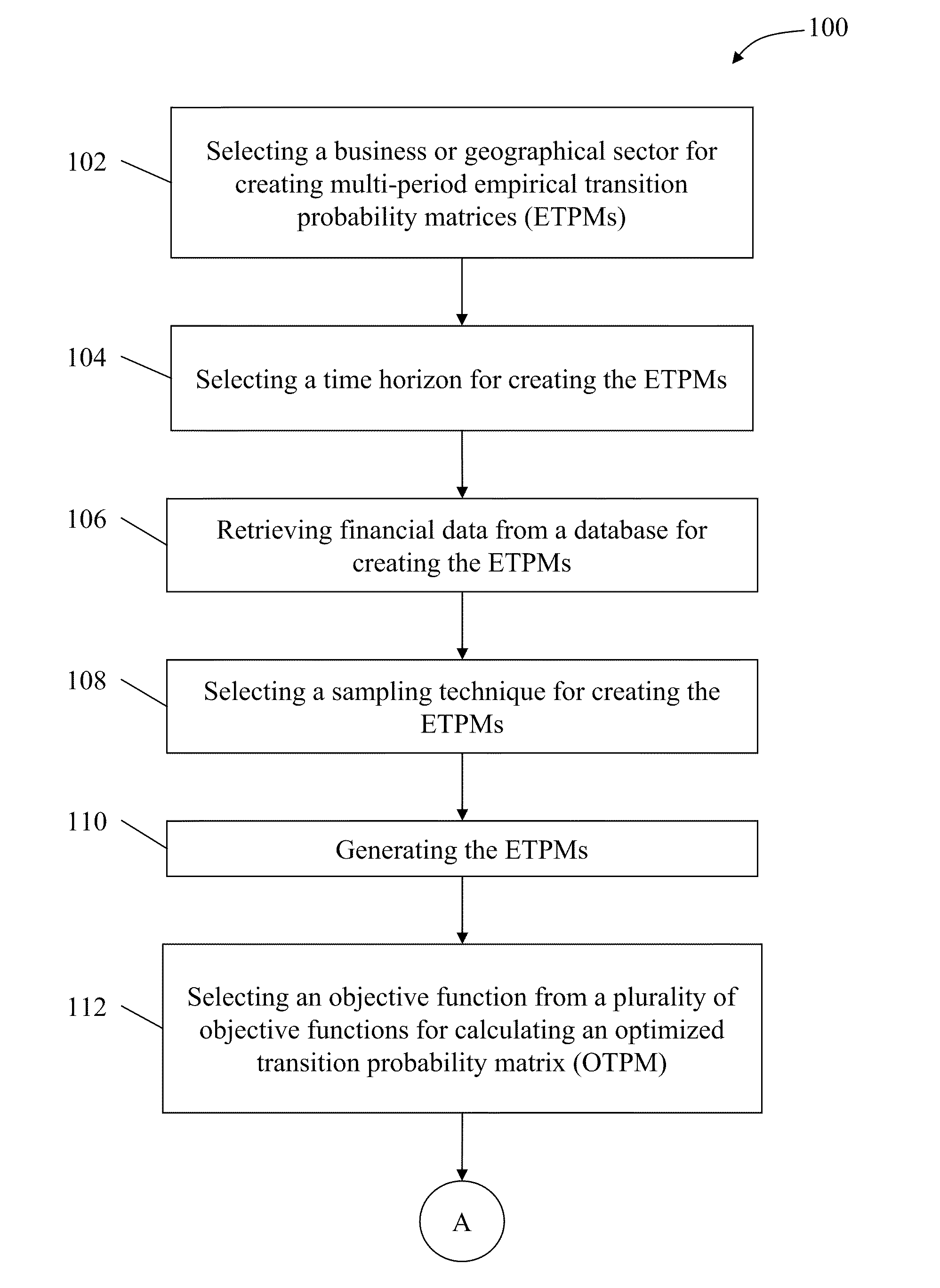
[0046]As a matter of background, credit migration patterns have received increasing amounts of attention in recent years, primarily from two types of market participants. First, for example, by those financial and commercial entities involved in creating or investing in structured products that include collateralized debt obligations (CDOs), TPMs have been used to forecast credit deterioration for a given pool of obligations. These iterated forecasts are used for assigning an appropriate criteria for tranching (i.e., a likelihood that structural requirements will be violated), and a potential accumulation of defaults and losses in the pool over multi-year time horizons. The availability of agency-published transition matrices has facilitated this type of application, particularly when pooled assets are agency-rated obligations.
[0047]As used herein, a CDO is an investment-grade security backed by a pool of bonds, loans, and other assets, wherein these bonds, loans, and assets are oft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com