Method for Eliminating Spikes of Mercury Emissions
a mercury emission and emission reduction technology, applied in waste heat treatment, special form destructive distillation, coking carbonaceous materials, etc., can solve the problems of large increase in emissions of several of these compounds, and achieve the effects of reducing emissions, reducing variability in emissions, and reducing emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
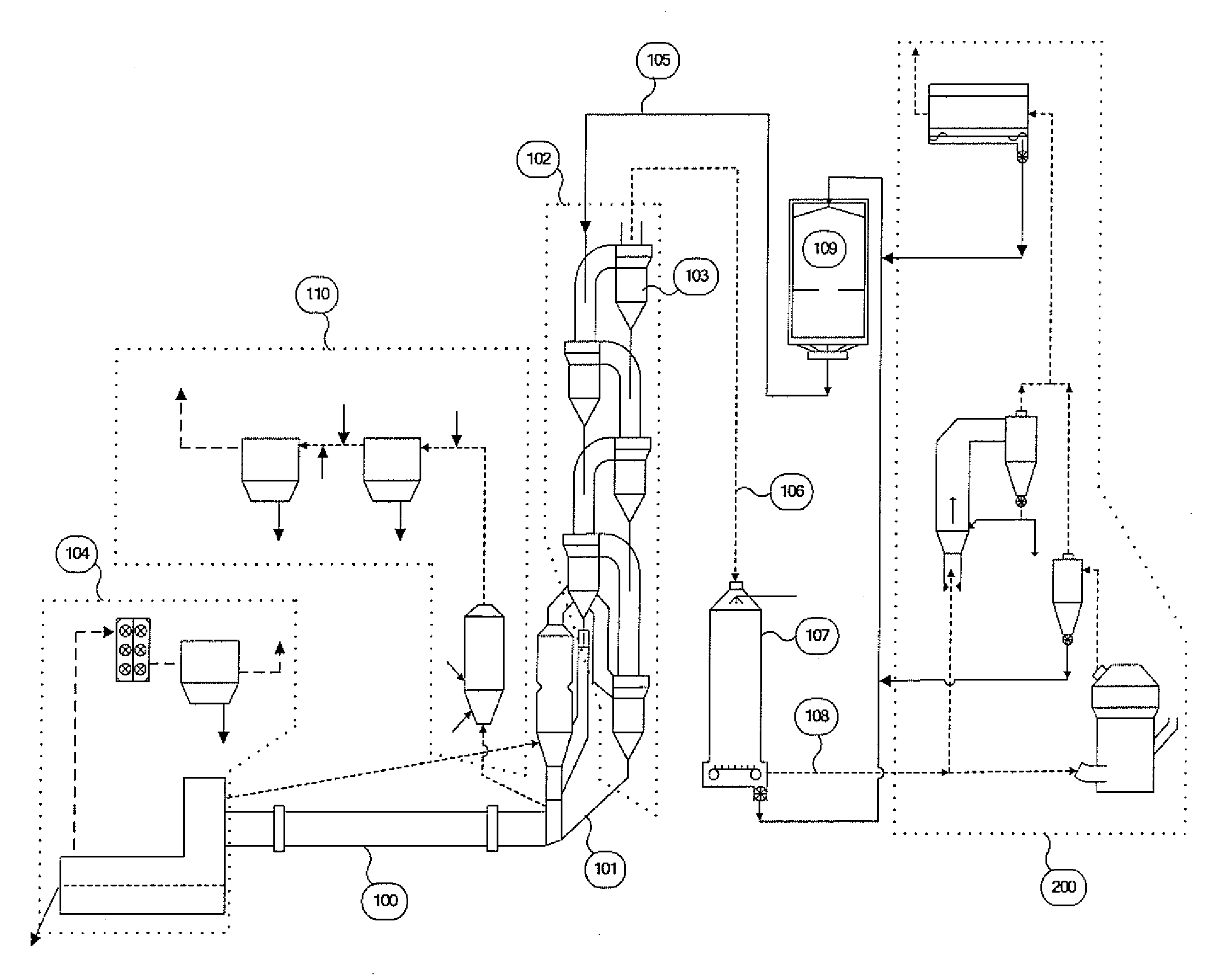
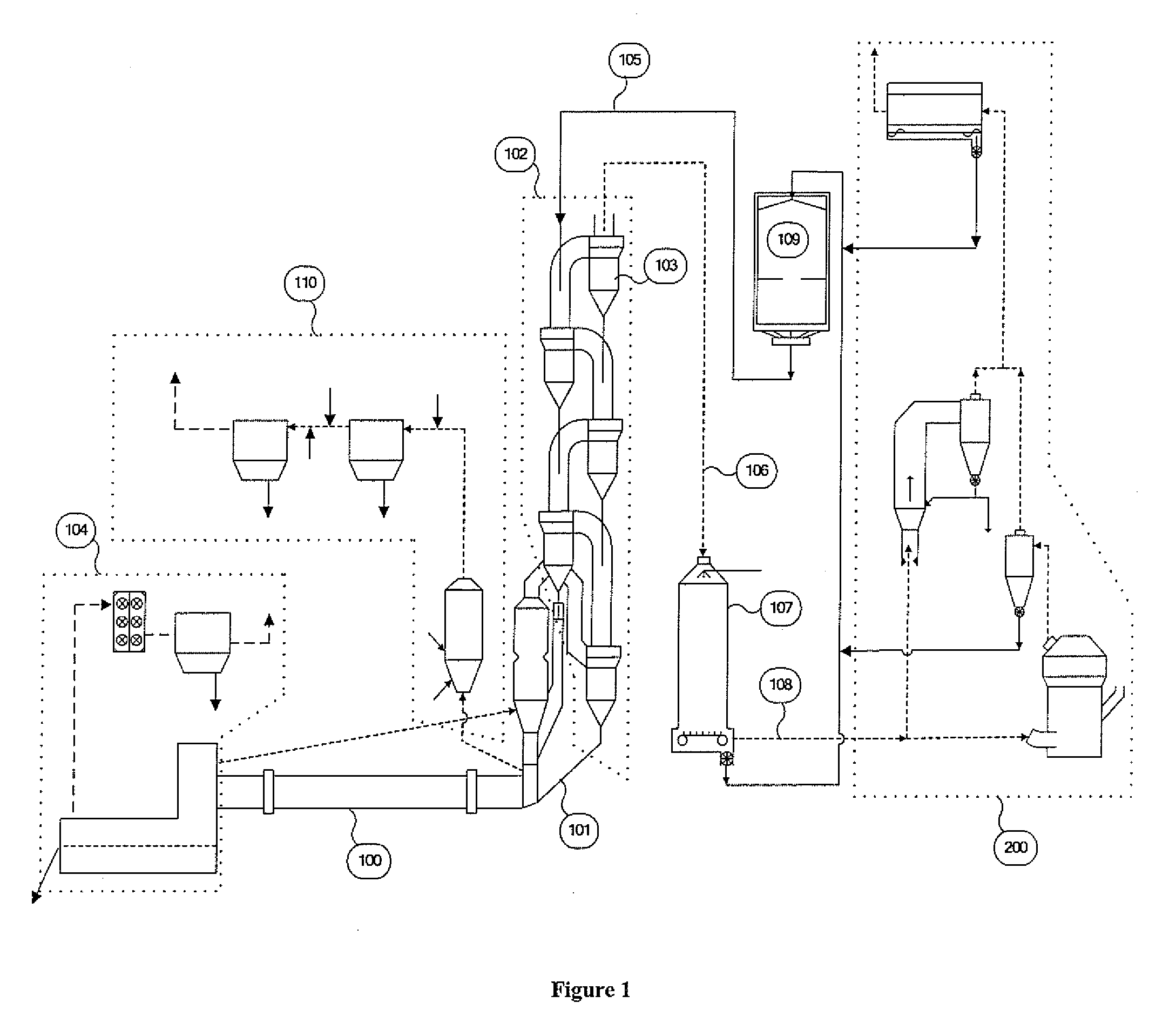
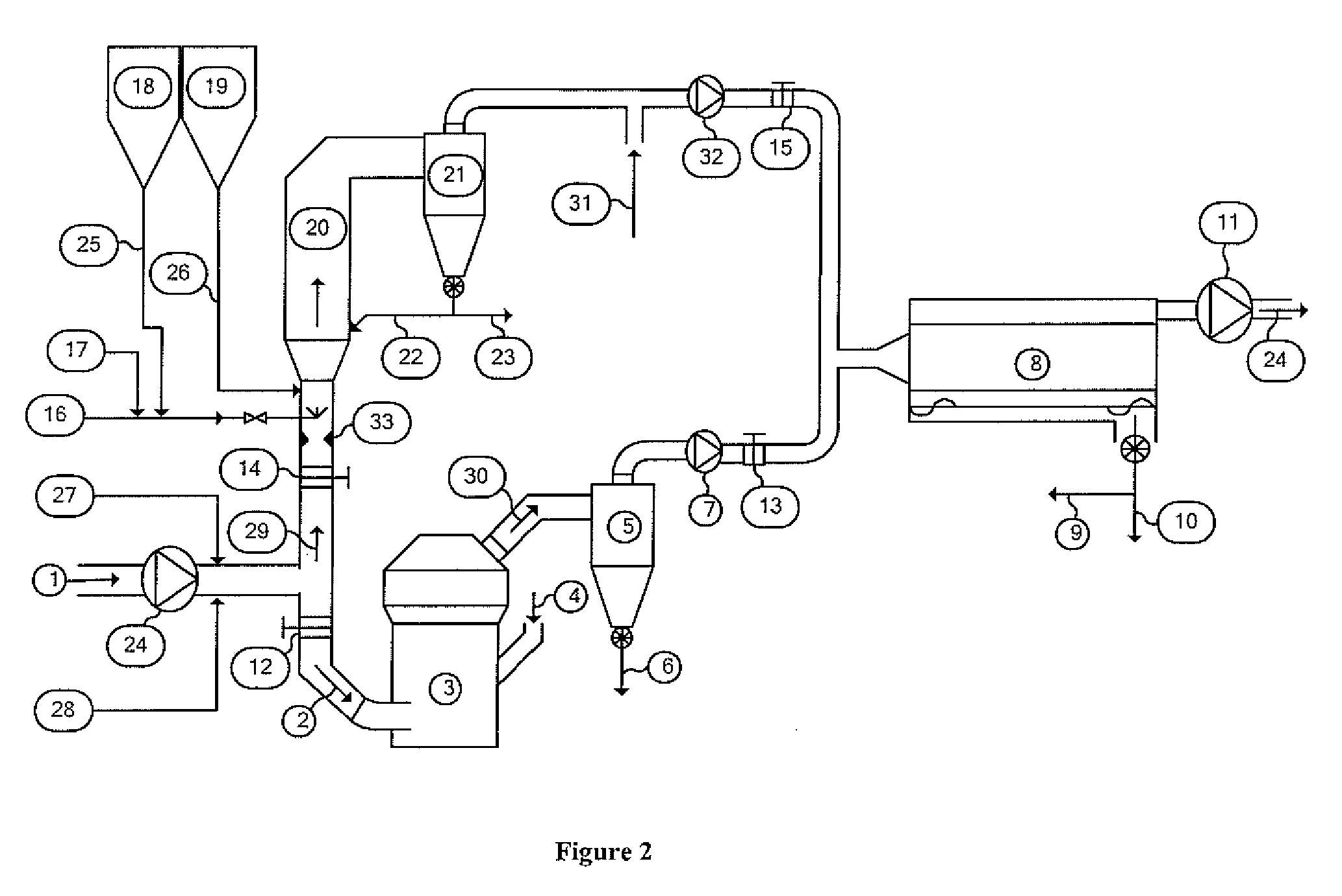
[0033]FIG. 3 shows the present invention which may be utilized depending on the specifications of the particular plant in which the invention is being applied. The embodiment of FIG. 3 is substantially equivalent to the embodiment of FIG. 2, with the notable exception that the off gases, which contain fine product and exhaust gases, from both mill 3 and GSA 20 are directed to the same separation cyclone (or series of cyclones) 21 in which the coarse fraction of the product is collected and conveyed via conduit 6 (or a series of conduits) to other locations in the plant for storage, blending and / or feed to the kiln system. The exhaust gases from the raw mill collection cyclones 21 contain a portion of the final product from the mill and any fine dust from the various gas sources that have not been captured in the mill collection cyclone or cyclones. A portion of exhaust gas from the main air pollution device 8 may also be recycled to the inlet 4 of the mill 3 for the purpose of tempe...
third embodiment
[0035]FIG. 4 shows the application of the present invention which may be appropriate depending on the specifications of the particular plant in which the invention is being applied. The embodiment of FIG. 4 is substantially equivalent to the embodiment of FIG. 3, with the notable exception that the off gases from mill 3 are directed to main air pollution control device 8 without being directed to an intervening collection cyclone or series of cyclones. The fine product and the exhaust gases of the mill 3 are pulled through a main air pollution control device 8 by means of a fan 11 prior to venting to the atmosphere or to subsequent air pollution control devices via exit conduit 24. A portion of exhaust gas from the main air pollution device may also be recycled to the inlet 4 of the mill 3 for the purpose of temperature control or to supplement gas volume through the mill.
[0036]FIG. 5 shows yet another embodiment of the present invention which is substantially equivalent to the embo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| residence time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com