Method And Apparatus For Compressive Imaging Device Having Startle Reflex
a compression imaging and startle reflex technology, applied in the field of imaging devices, can solve the problems of missing an important event entirely, reducing the computational complexity of the video encoding process, and acquiring large amounts of raw image or video data (large n)
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Still Image Acquisition
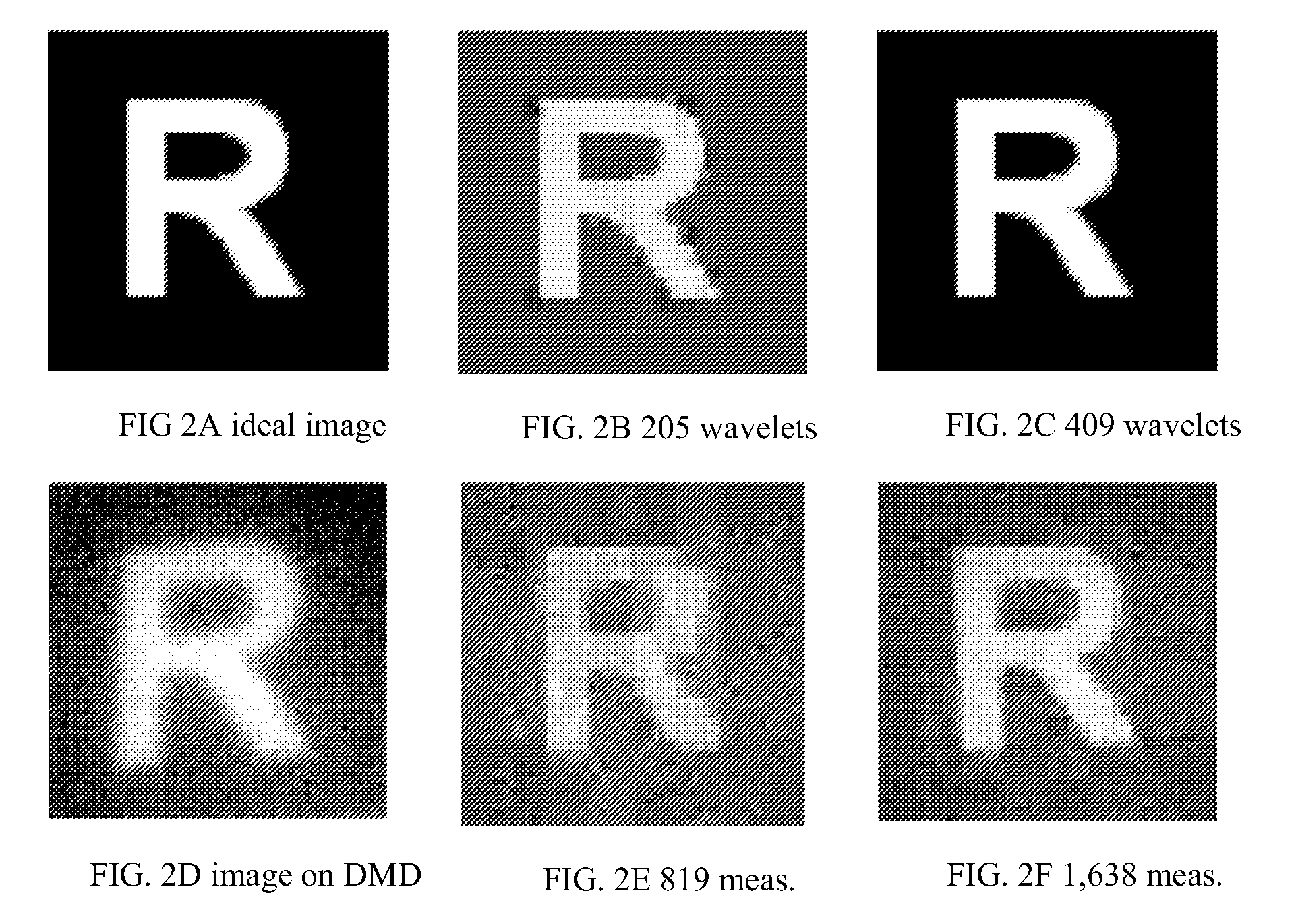
[0071]For an imaging experiment, we displayed a printout of the letter “R” in front of the camera; FIG. 2A shows the printout. For acquisition and reconstruction, we use an imaging resolution of N=64×64=4096. Since our test image is piecewise constant (with sharp edges) it can be sparsely represented in the wavelet domain. FIGS. 2B and 2C show the best K-term Haar wavelet approximation of the idealized image in FIG. 2A with K=205 and 409, respectively. Using M=819 and 1,638 measurements (roughly 4× the K used in B and C), we reconstructed the images shown in FIGS. 2E and 2F using the Dantzig Selector (see Candès, E., Tao, T., “The Dantzig selector: Statistical estimation when p is much larger than n,” (2005) Preprint), a robust scheme for CS reconstruction. In all cases Haar wavelets were used for approximation or reconstruction. This preliminary embodiment confirms the feasibility of the CI approach; resolution of minor calibration and noise issues will impro...
example 2
Video Simulation
[0072]To demonstrate the potential for applications in video encoding, we present a series of simulations for video measurement / reconstruction. Column (a) in FIG. 3 shows a single frame taken from our F=64 frame video sequence that consists of P=64×64 images; in total the video contains N=FP=262,144 3D voxels. The video shows a disk moving from top to bottom and growing from small to large. We measure this video sequence using a total of M measurements, either 2D random measurements (with M / F measurements / frame) or 3D random measurements. (For the 2D measurements, we make the simplifying assumption that the image remains constant across all snapshots within a given frame.) To reconstruct the video from these measurements we compare two approaches: 2D frame-by-frame reconstruction using 2D wavelets as a sparsity-inducing basis and 3D joint reconstruction using 3D wavelets as a sparsity-inducing basis.
[0073]FIG. 3 shows Matching Pursuit reconstruction results using M=2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com