Single Inductor Serial-Parallel LED Driver
a technology of led driver and serial parallelization, which is applied in the direction of electroluminescent light source, lighting apparatus, light source, etc., can solve the problems of reduced life, failure in operation, and overall quality of display images, and achieve the effect of increasing the tolerance of the overall system to led mismatch due to manufacturing processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025]An LED driver circuit is disclosed for an LED display system that includes the ability to control the current in each LED string and the voltage output. The present invention also provides improved power efficiency and scalability. In the following description, specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough understanding of the present invention. It will be understood, however, to one skilled in the art, that the present invention may be practiced without some or all of these specific details. In other instances, well known process operations have not been described in detail, as they are well known to those skilled in the art.
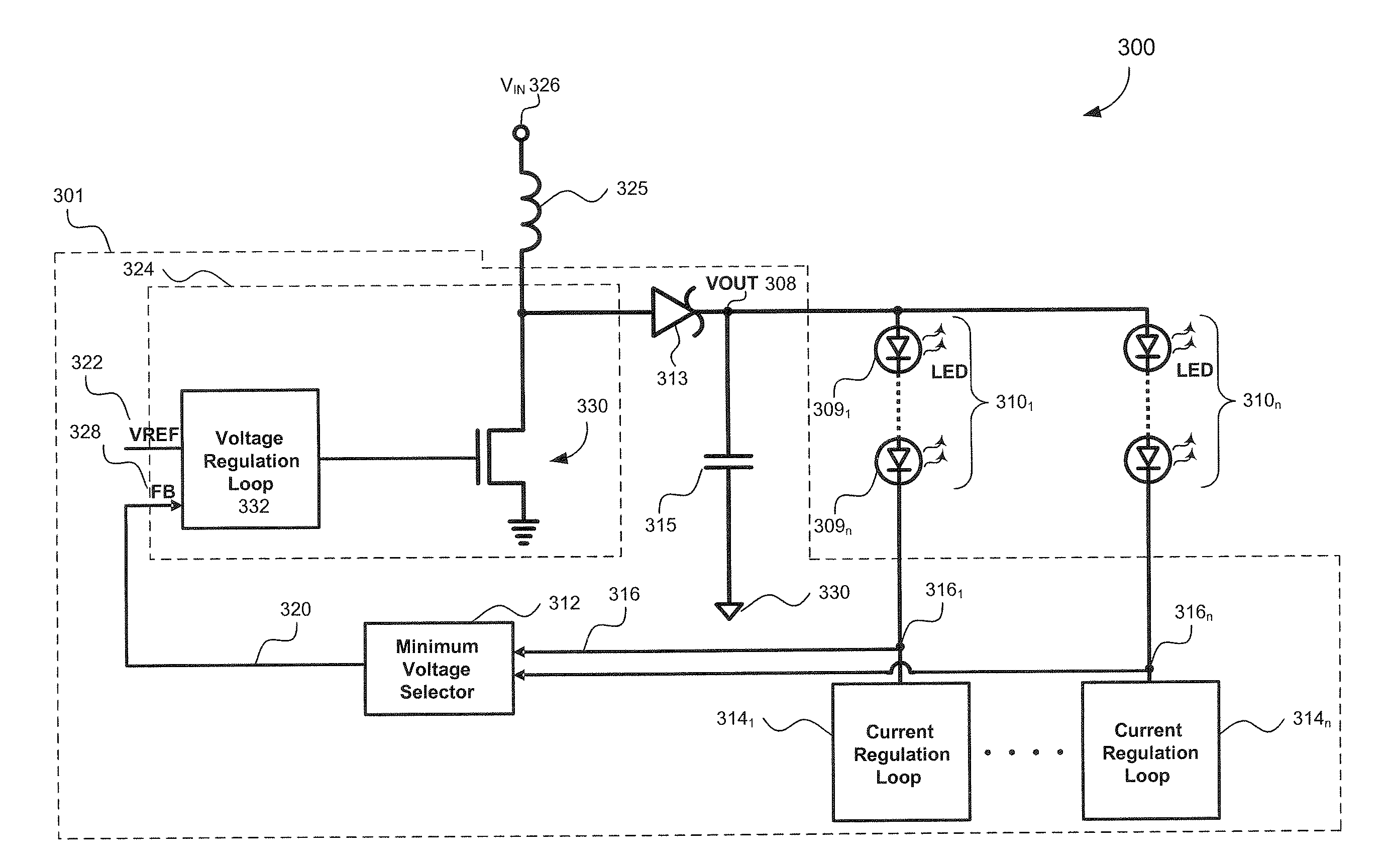
[0026]FIG. 3 illustrates a LED display system 300 having an LED driver 301 driving a plurality LED strings 3101 to 310n according to embodiments of the invention, where each LED string 310 includes a plurality of LEDs 309. As shown, the LED strings 3101 to 310n are connected in parallel with each other, but the LEDs 309 in each LED string ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com