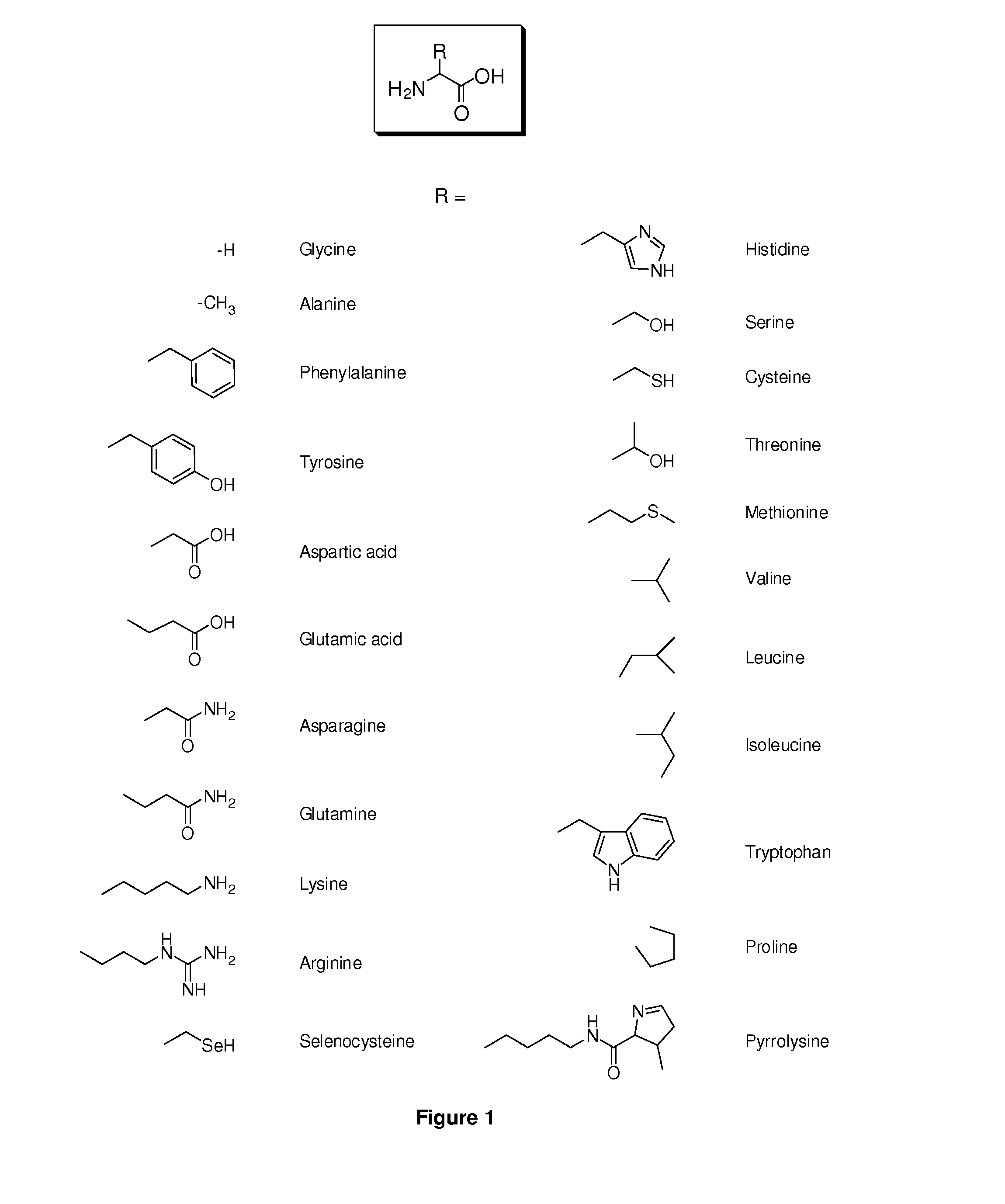
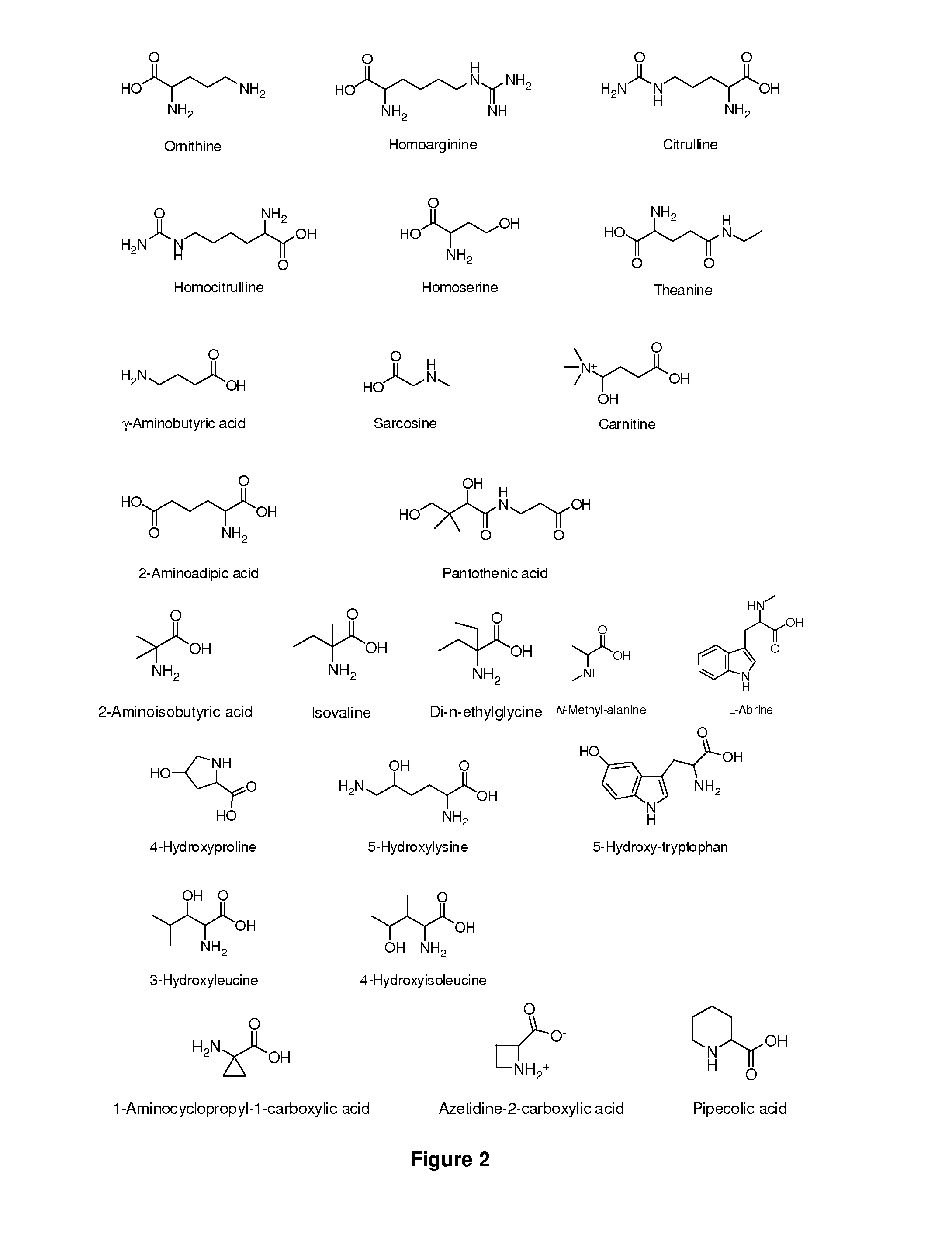
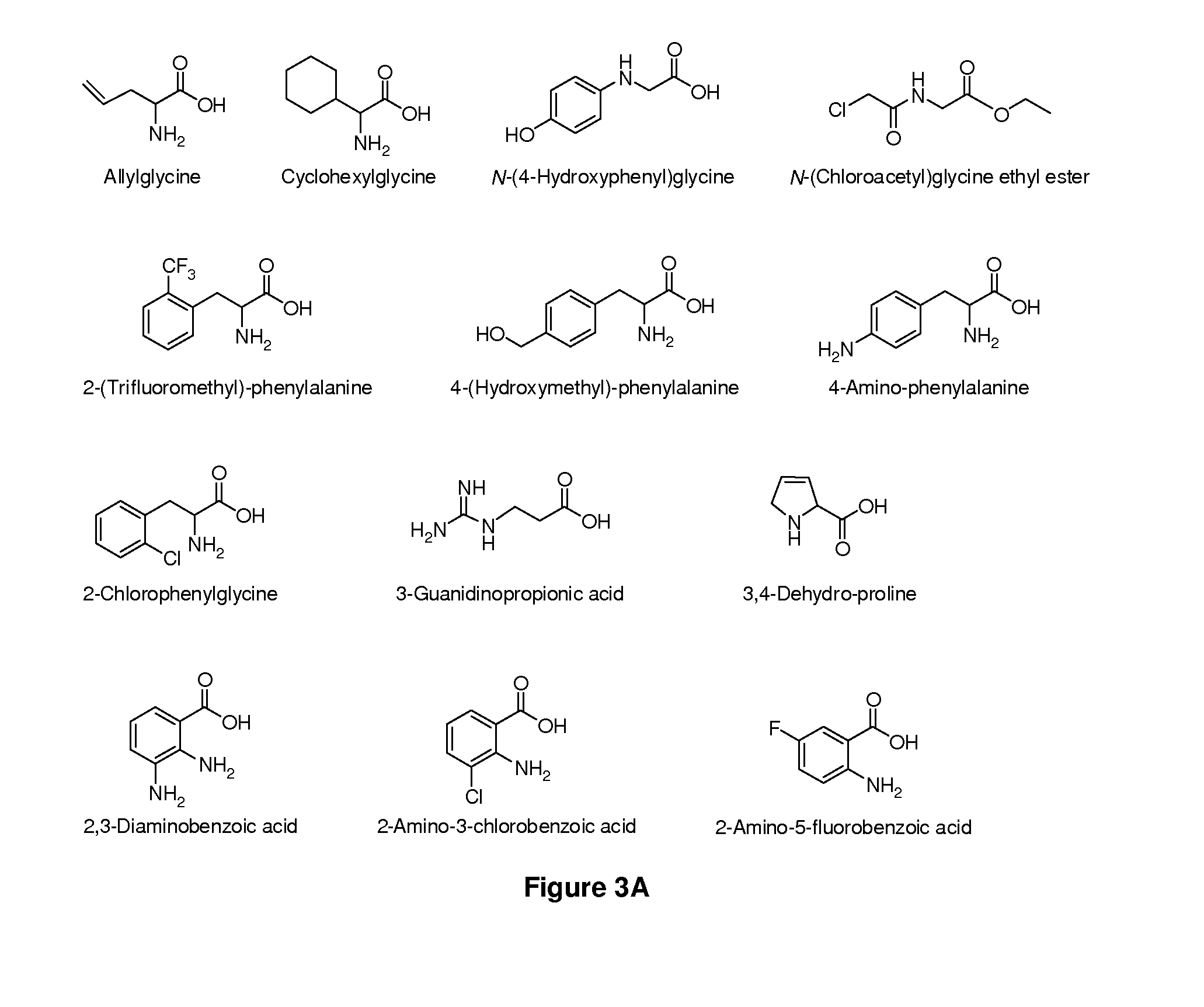
Amino Acid Conjugates of Quetiapine, Process for Making and Using the Same
a technology of quetiapine and amino acid conjugates, which is applied in the field of amino acid conjugates of quetiapine, process for making and using the same, and can solve the problem of difficult tabletops containing such a high concentration of active pharmaceutical ingredients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
formulation examples
The prodrugs provided in the compositions and methods herein are primarily geared towards oral dosage forms. These dosage forms include but are not limited to tablet, capsule, caplet, troche, lozenge, powder, suspension, syrup, solution or oral thin film (OTF). Embodiments of oral administration forms are capsule, tablet, solutions and OTF. The film dosage forms provide an inexpensive, convenient and immediate method for delivery of the compositions described herein without the undesirable aspects associated with certain oral or nasal delivery methods, while providing versatility, safety and patient comfort. Any effective edible “thin film” or “strip” may be used in accordance with the present invention. Unless otherwise specified or required by the context, the edible films of the present invention may be manufactured in any effective manner.
In certain embodiments, the film layer can be produced using a highly water-soluble polymer comprising a natural or synthetic water-soluble po...
example 1
Oral Pharmacokinetic Data
Plasma concentrations of quetiapine released from prodrug conjugates as described herein were dosed as oral solutions in rats and compared to an equimolar solution of quetiapine dihydrochloride. Although the commercial form of quetiapine (Seroquel®) is a fumarate salt, the dihydrochloride salt was used as comparator because the fumarate is not soluble enough to be dosed efficiently via oral gavage in rats.
Generally and as shown in FIGS. 4-6, plasma concentrations of released quetiapine varied depending on the attached amino acid. For the provided examples, the systemic exposure of released quetiapine ranged from 99-175% (%-AUC compared to quetiapine dihydrochloride). Valine-quetiapine showed the highest relative %-AUC value of 175%. Cmax values varied between 61-189% (%-Cmax compared to quetiapine dihydrochloride) with valine-quetiapine producing the highest relative %-Cmax value of 189%. Tmax values were similar for all examples.
example 2
General Synthesis of Amino Acid-Quetiapine Conjugates
A general synthetic scheme for the synthesis of a prodrug of this invention typically consists of the following steps:1. Protection of the amino acid, if applicable.2. Activation of the carboxylic group, if not already in activated form.3. Addition of activated amino acid to quetiapine or vice versa in the presence of base4. Removal of amino acid protecting groups, if applicable.
To a solution of quetiapine (1 mmol) in THF (10 mL) was added LiN(TMS)2 (1.5 mmol) at room temperature. The solution was stirred for 30 min. at room temperature. N-protected amino acid succinimidyl ester (1.05 mmol) in THF (10 mL) was added dropwise. The mixture was stirred for an additional 30 min. at room temperature, subsequently poured into an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride (200 mL) and extracted with EtOAc (2×200 mL). The organic layer was washed with aqueous NH4Cl (2×100 mL) and brine (2×100 mL), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and evaporated to d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com