Processes for controlling afterburn in a reheater and for controlling loss of entrained solid particles in combustion product flue gas
a technology of combustion product flue gas and afterburner, which is applied in the direction of combustible gas purification/modification, vortex flow apparatus, single direction vortex, etc., can solve the problems of ash build-up in the reheater, reduce the operating efficiency of the reheater, and reduce the volume available for combustible gas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016]The following detailed description of the invention is merely exemplary in nature and is not intended to limit the invention or the application and uses of the invention. Furthermore, there is no intention to be bound by any theory presented in the preceding background of the invention or the following detailed description of the invention.
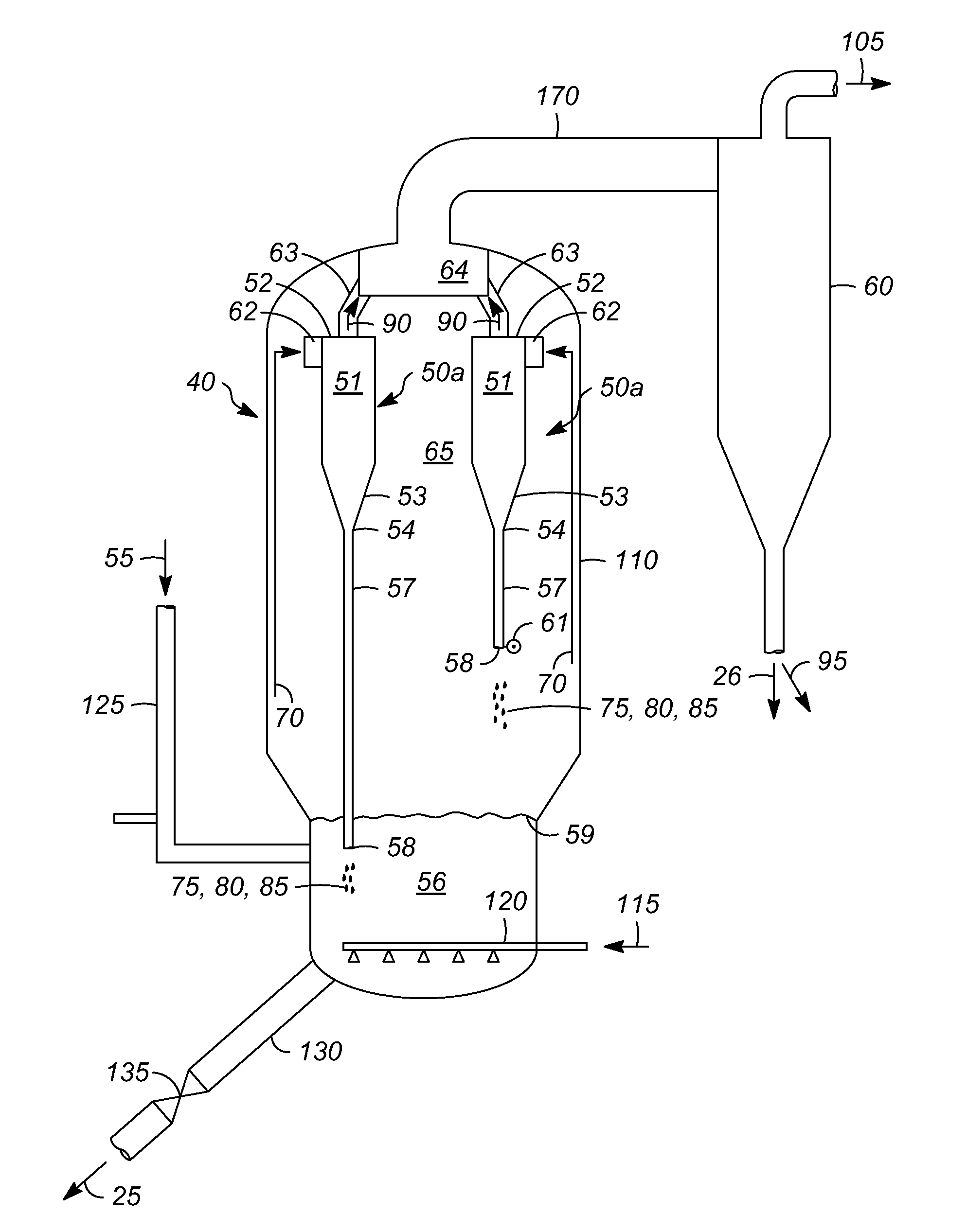
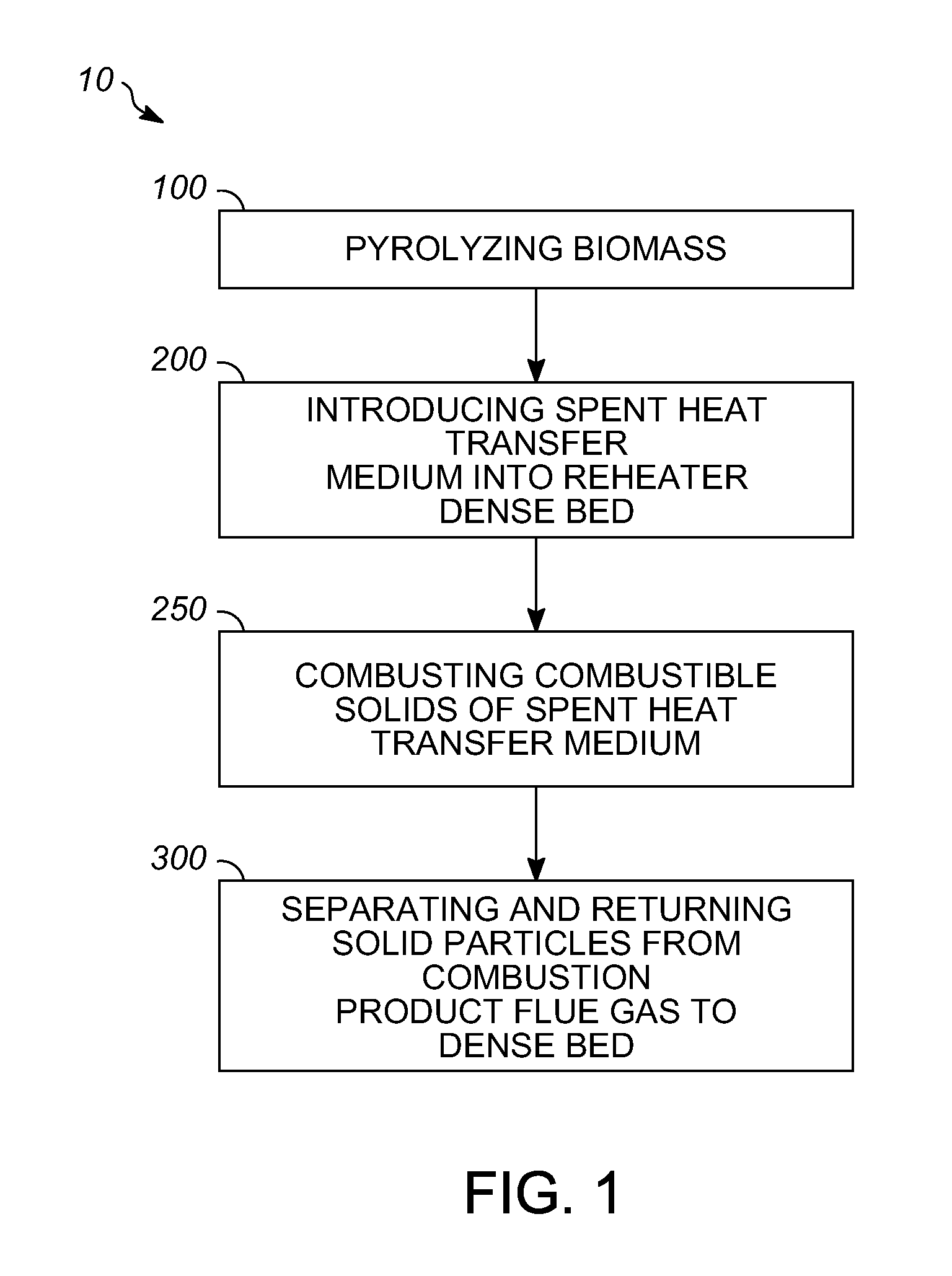
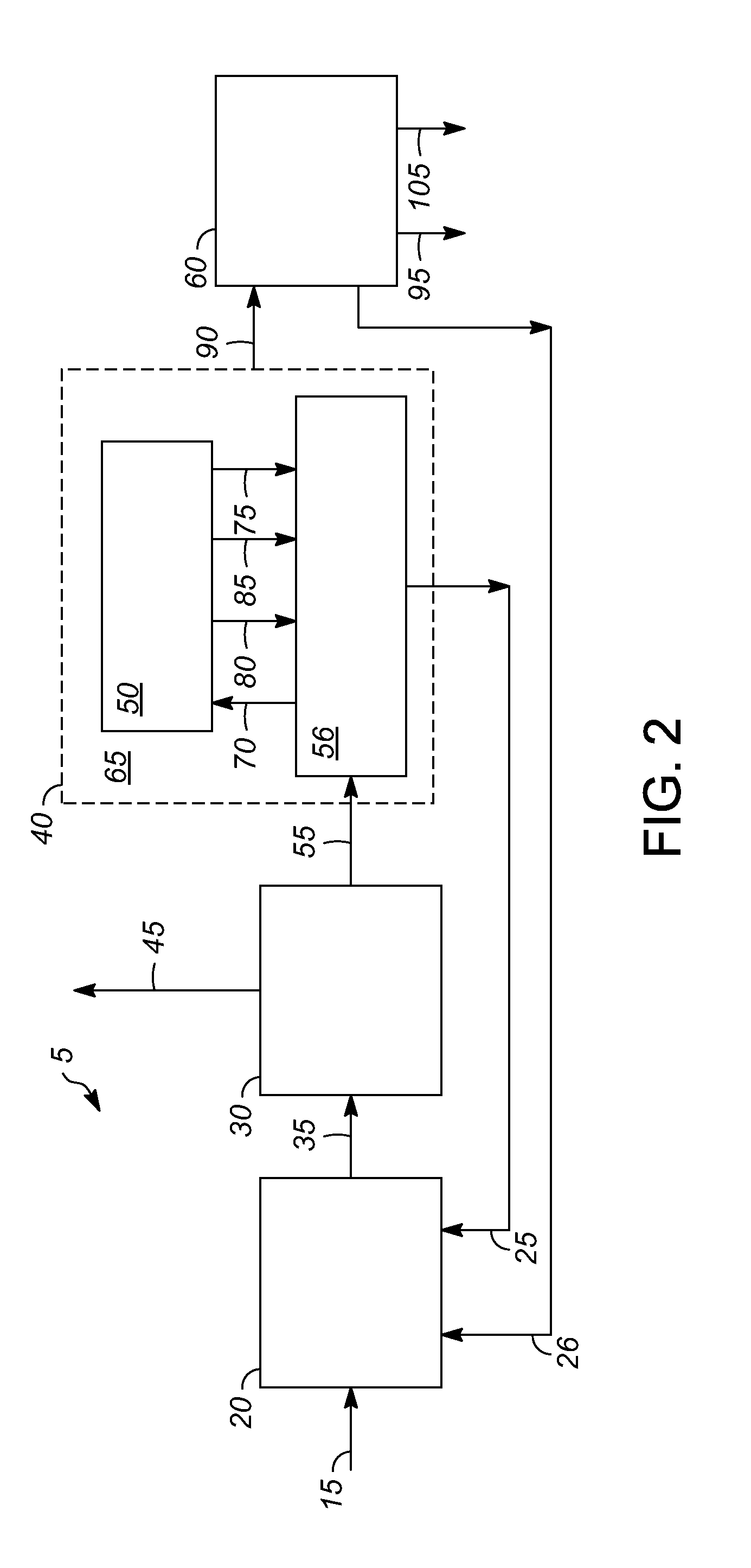
[0017]Various exemplary embodiments of the present invention are directed to processes for controlling afterburn and loss of entrained solid particles in combustion product flue gas during regeneration of a heat transfer medium in a reheater of a pyrolysis system. The “reheater” may be a reheater zone of a pyrolysis reactor or a reheater separate from the pyrolysis reactor. The reheater is equipped with an internal gas-solids separator, such as a cyclone separator, a vortex separator, or both, as hereinafter described. Controlling afterburn and loss of entrained solid particles increases the amount of heat transferred to the reheater dense b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com