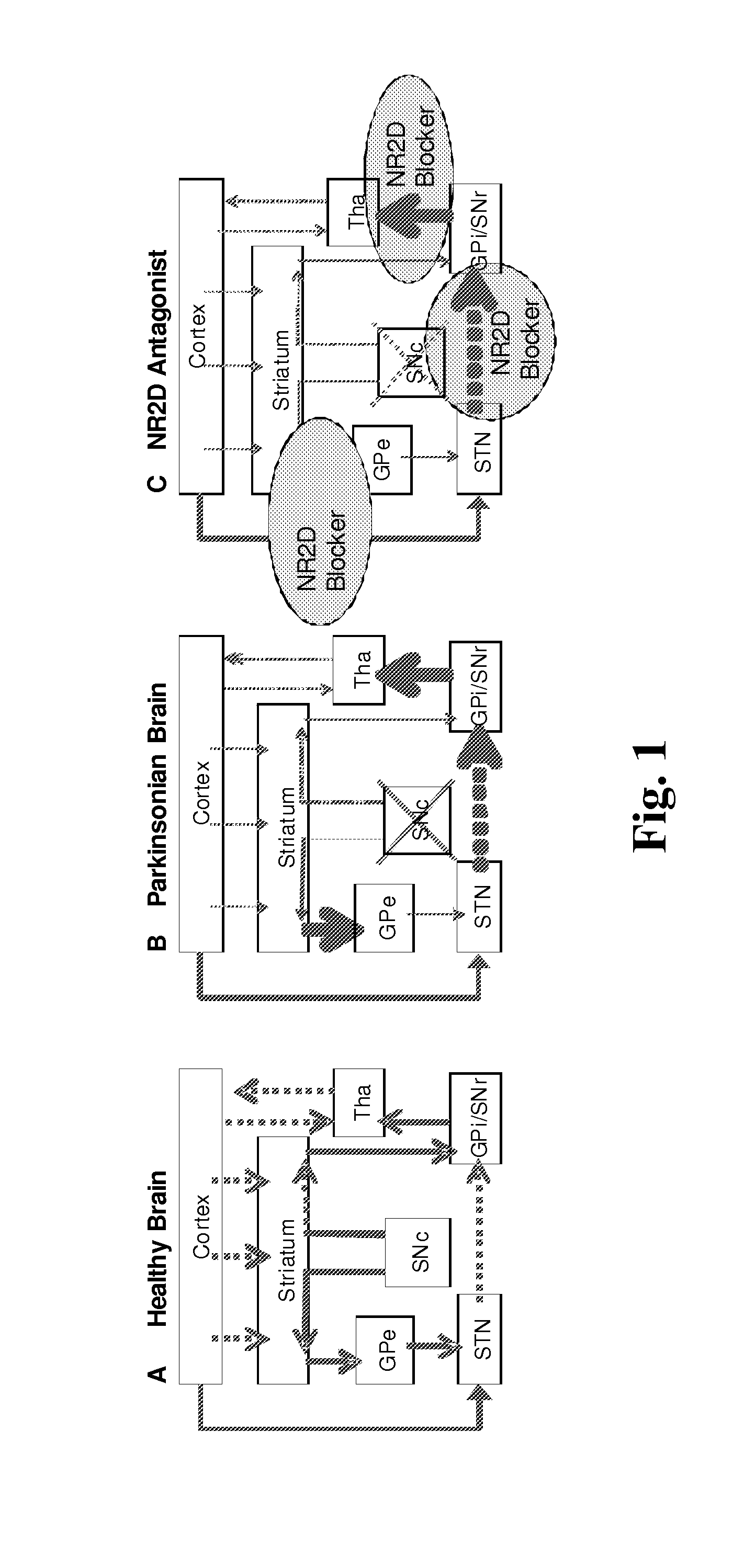
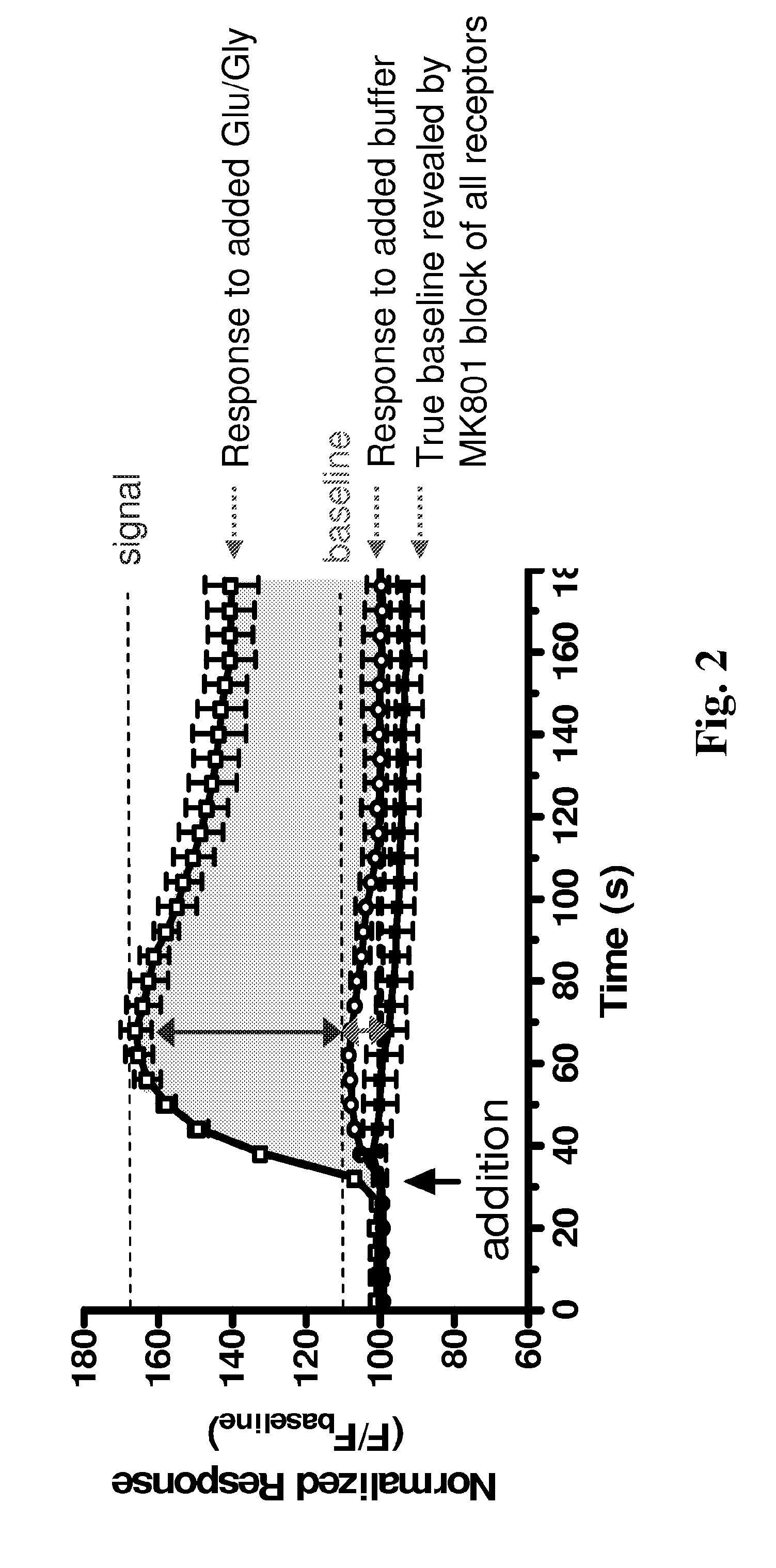
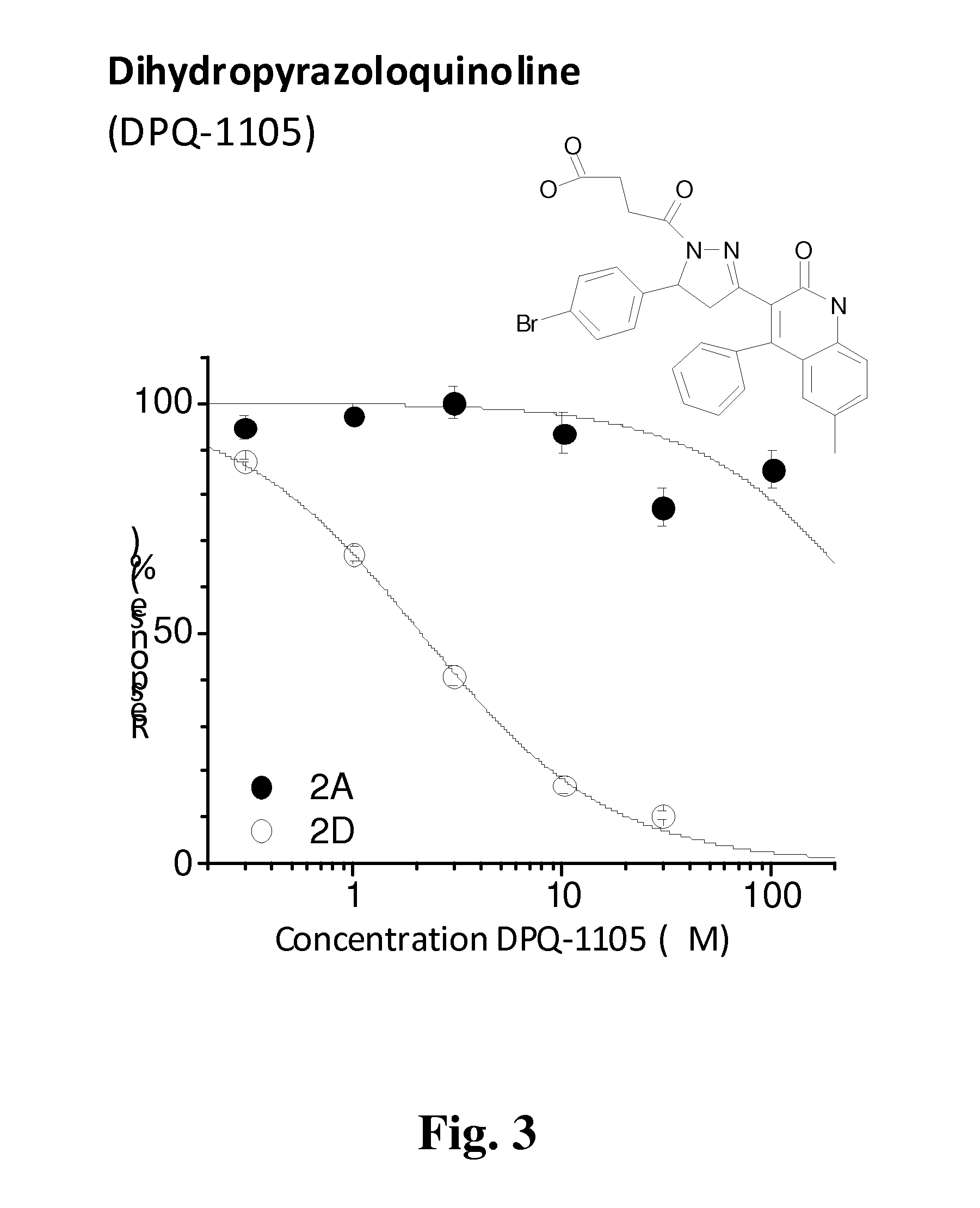
Subunit Selective NMDA Receptor Antagonists For The Treatment Of Neurological Conditions
a neurodegenerative condition and subunit selective technology, applied in the field can solve the problems of difficult treatment of chronic pain, including neuropathic pain, central nerves, and dose-limiting side effects that have prevented clinical use of nmda receptor antagonists, etc., to stimulate osteoblast differentiation, enhance bone formation, and increase bone density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Evaluation of Compounds of Formula A as Potential NMDA NR2C / D Antagonists
Cell Based Screening for NR2C and NR2D Antagonists
[0270]To evaluate potential lead compounds, we used a BHK cell line expressing NR1 under control of the Tet-On system (Clontech) (Hansen et al 2008) to create two cell lines that constitutively express either NR2C or NR2D. It is known from previous work that stable expression of NMDA receptor subunits is cytotoxic. To avoid this toxicity, the culture media was supplemented with NMDA receptor antagonists (200 μM DL-APV and 200 μM 7-Cl-kynurenate), and functional NR1 expression was induced by doxycyclin 48 hours prior to assay. Fura-2 Ca2+ imaging of the functional response of the NR1 / NR2D cell line produced a glutamate EC50 value (340 nM) that was similar to that measured from two-electrode voltage-clamp assay (460 nM), suggesting this cell line faithfully reproduces NR1 / NR2D properties.
[0271]The BHK cell line expresses a low affinity glutamate transporter system...
example 2
NMDA Receptor Activity of the Compounds of Formula C
[0278]Using the methodology in the above examples, compounds of Formula C were evaluated. The data is shown in Table 3 below.
997 P Compounds2A2B2C2DGluR1IC50IC50IC50IC50IC50#Structure(uM)(uM)(uM)(uM)(uM) 99778195311052187473109117912322421176243074118514059169120979352213118320117821118487% at 100 μM903322121085% at 100 μM2093327114932124979% at 30 μM125081% at 30 μM117780% at 100 μM112890% at 100 μM1248>300
[0279]No compounds tested inhibited homomeric GluR6 kainate receptor responses. When no inhibition IC50 value is given, the percent response at the maximum tested concentration is given. Concentration effect data was fitted with the logistic equation with the minimum forced to 0.
[0280]Additional compounds of the various formulae described herein were also screened, and the results are shown in the tables below.
1063 S Compounds2A2B2C2DGluR1IC50IC50IC50IC50IC50#Structure(μM)(μM)(μM)(μM)(μM)10631365122821105% at 100 μM1063-0101% at...
example 3
In Vitro Binding Studies for Secondary Effects
[0284]Compounds can be evaluated for binding to the human ether-a-go-go potassium channel (hERG) expressed in HEK293 cells by displacement of 3[II]-astemizole according to the methods by Finlayson et al. (K. Finlayson., L. Turnbull, C. T. January, J. Sharkey, J. S. Kelly; [3H]Dofetilide binding to HERG transfected membranes: a potential high throughput preclinical screen. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 430, 147-148). Compounds can be incubated at 1 or 10 μM final concentration, in duplicate, and the amount of displaced 3[H]-astemizole determined by liquid scintillation spectroscopy. In some cases, a seven concentration (each concentration in duplicate) displacement curve can be generated to determine an IC50. Binding to the rat alpha-1 adrenergic receptor in rat brain membranes can be determined by displacement of 3[H]-prazosin (P. Greengrass and R. Bremner; Binding characteristics of 3H-prazosin to rat brain a-adrenergic receptors. Eur. J. Ph...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| enantiomeric excess | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| enantiomeric excess | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| enantiomeric excess | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com