High temperature stabilizer for well treatment fluids and methods of using same
a technology of stabilizer and well treatment fluid, which is applied in the direction of fluid removal, wellbore/well accessories, chemistry apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the viscosity of the fluid, and exceeding the maximum operating limits of conventional well treatment fluid, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing the viscosity and facilitating hydration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
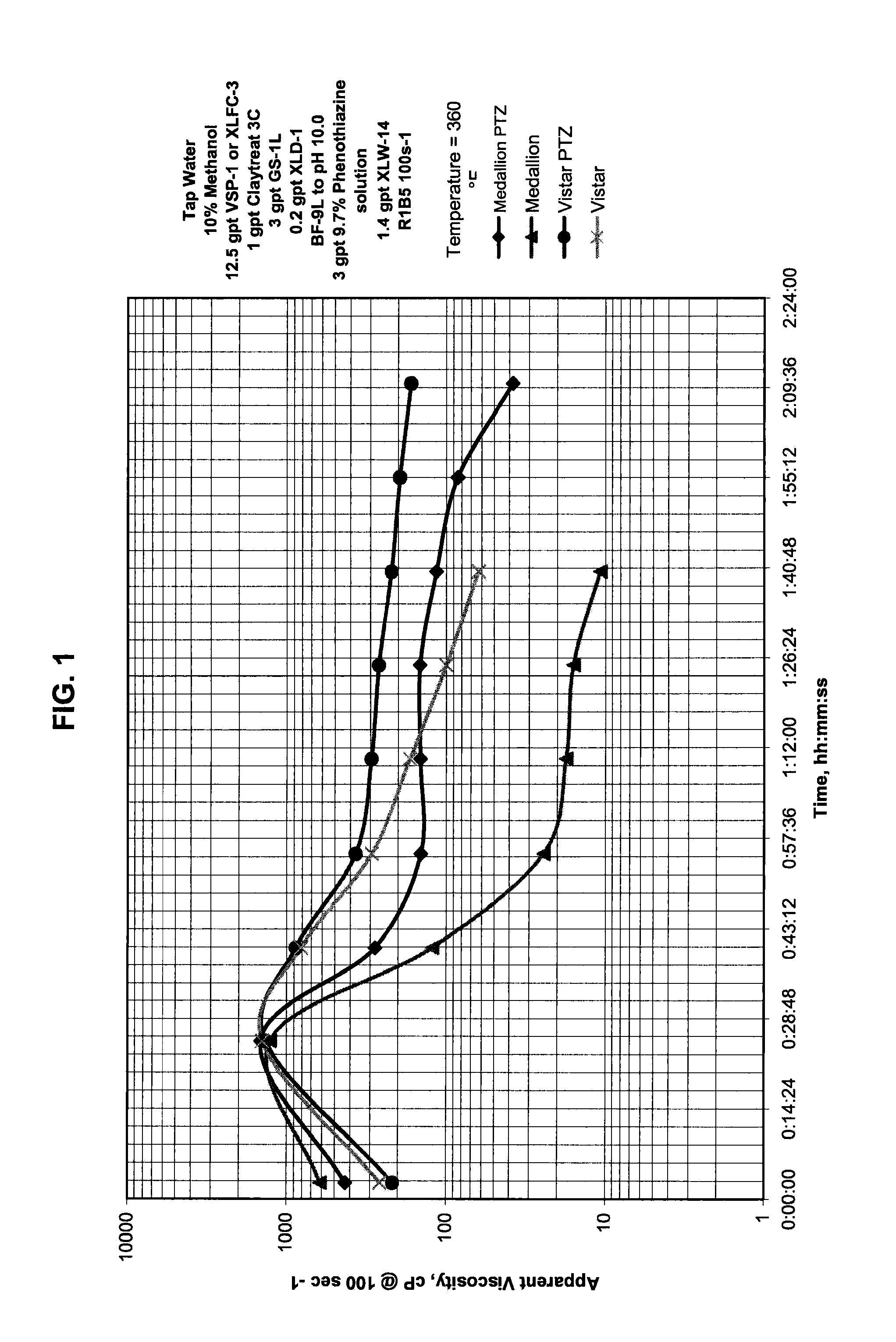
[0043]The electron donating compound comprising phenothiazine was mixed at 360° F. (182.2° C.) with two guar-based fracturing fluids that are commercially available under the commercial names Medallion Frac HT® and Vistar® from BJ Services Company. In addition order, tap water, 10 wt. % methanol, 12.5 gpt of the (slurried polymer XLFC-3 or VSP-1 by BJ Services Company respectively for Medallion Frac HT® and Vistar®) 1 gpt Claytreat-3C clay stabilizer (CT-3C) by BJ Services Company, 3 gpt stabilizer (GS-1L) by BJ Services Company, 0.2 gpt crosslink delay agent (XLD-1) by BJ Services Company, and 1.4 gpt zirconate-based crosslinker (XLW-14) by BJ Services Company were mixed with 50 ppt of the fracturing fluid to produce the samples. The pH of the Medallion Frac HT® system was about 10 and the pH of the Vistar® system was about 10.25. The concentration of the electron donating compound comprising phenothiazine was 120 ppm in the fracturing fluid, i.e., 3 gpt 9.7 wt. % in dipropylene gl...
example 2
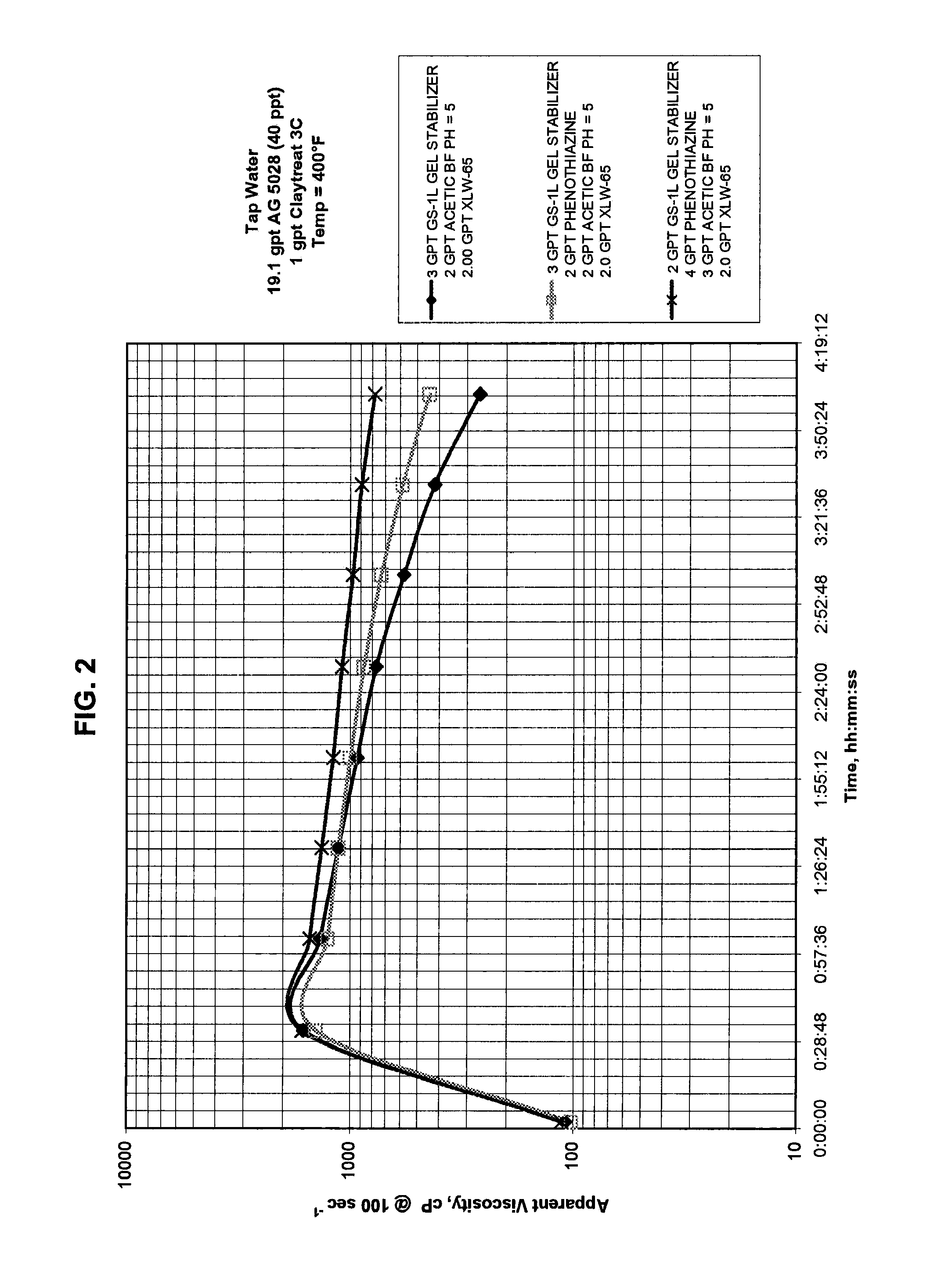
[0044]Three samples were prepared in this example. The first sample was the control sample. In the second and third samples, the electron donating compound stabilizer comprising phenothiazine was mixed at varying amounts at 400° F. (204.4° C.) with 40 ppt high molecular weight polymer-based fracturing fluid comprising a copolymer derived from acrylamide. A suitable copolymer that was used in this example is commercially available as Allessan® AG 5028P from Allessa Chemie. The pH of the samples prepared in this example was about 5. In addition order, tap water, 10 wt. % methanol, 19.1 gpt of the polymer emulsion, 1 gpt Claytreat-3C clay stabilizer (CT-3C) by BJ Services Company, 3 gpt stabilizer (GS-1L) by BJ Services Company, 2.0 gpt zirconate-based crosslinker (XLW-65) by BJ Services Company and 2 gpt low pH buffer (BF-65L) by BJ Services Company were mixed to produce the samples. The high molecular weight polymer-based fracturing fluid was made in accordance with co-pending U.S. p...
example 3
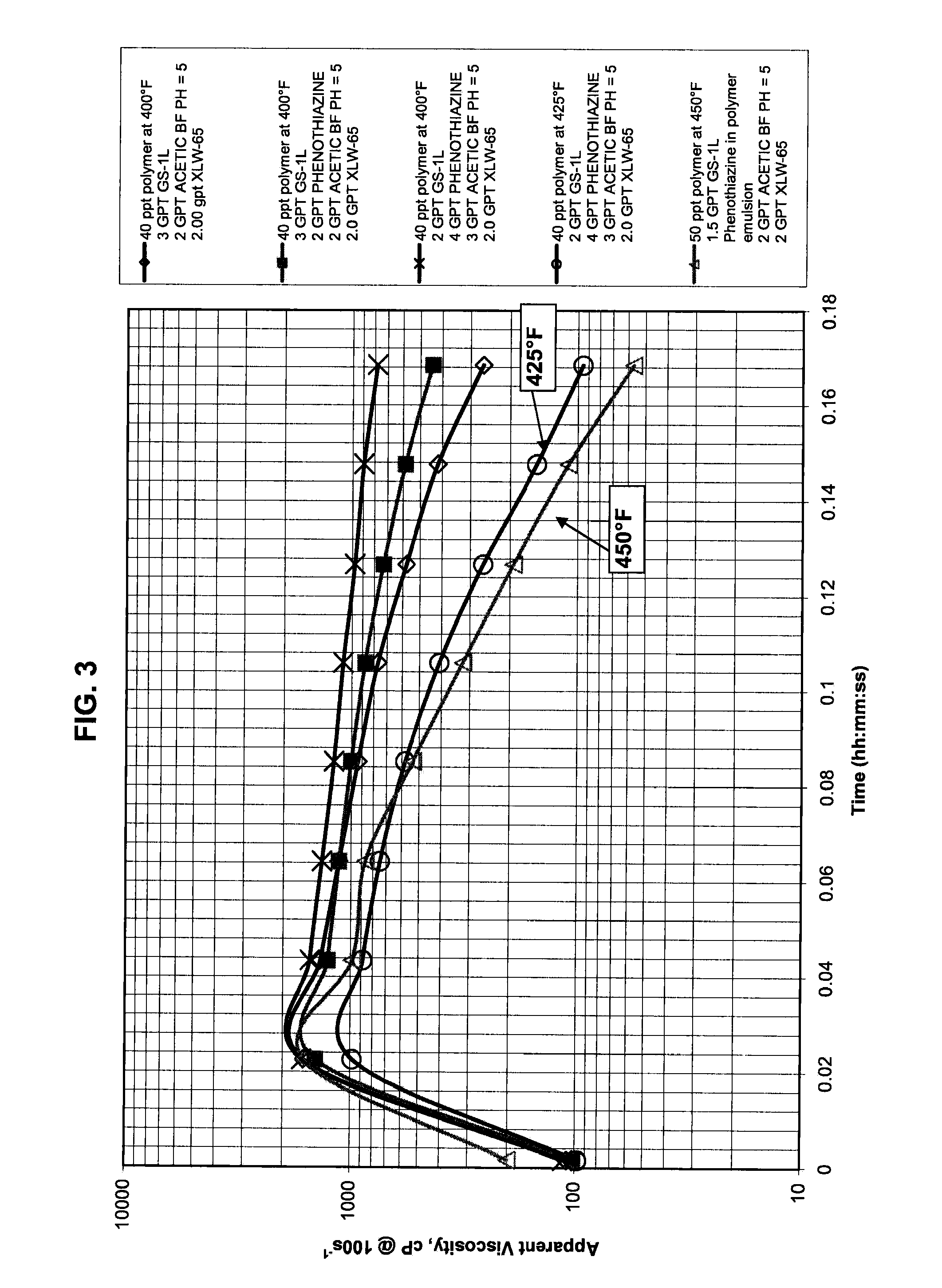
[0047]Five samples were prepared in this example. The first top sample was the control sample at 400° F. (204° C.). In the remaining samples, the electron donating compound stabilizer comprising phenothiazine was mixed at varying amounts at 400° F. (204.4° C.) with 40 ppt or 50 ppt high molecular weight polymer-based fracturing fluid comprising a copolymer derived from acrylamide, as indicated in Table 1. A suitable copolymer that was used in this example is commercially available as Allessan® AG 5028P from Allessa Chemie. The components, addition order, and conditions in this example are as follows:
TABLE 1Sam-Sam-Sam-Sam-Sam-Component / Conditionple 1ple 2ple 3ple 4ple 5Copolymer (AG 5028P),4040404050pptGel stabilizer (GS-1L),33221.5gptBuffer, gpt22332Crosslinking agent22222(XLW-65), gptStabilizer, gpt—2444Temperature, ° F. (° C.)400400400425450
The samples were allowed to hydrate for 30 minutes. The pH of the samples prepared in this example was about 5. The high molecular weight pol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com