Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
a technology of optical devices and electronic devices, applied in semiconductor devices, instruments, computing, etc., can solve problems such as the fluctuation of the holding potential of the gate, and the difficulty of influencing the noise of the holding capacity, so as to prevent the deformation of the display quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
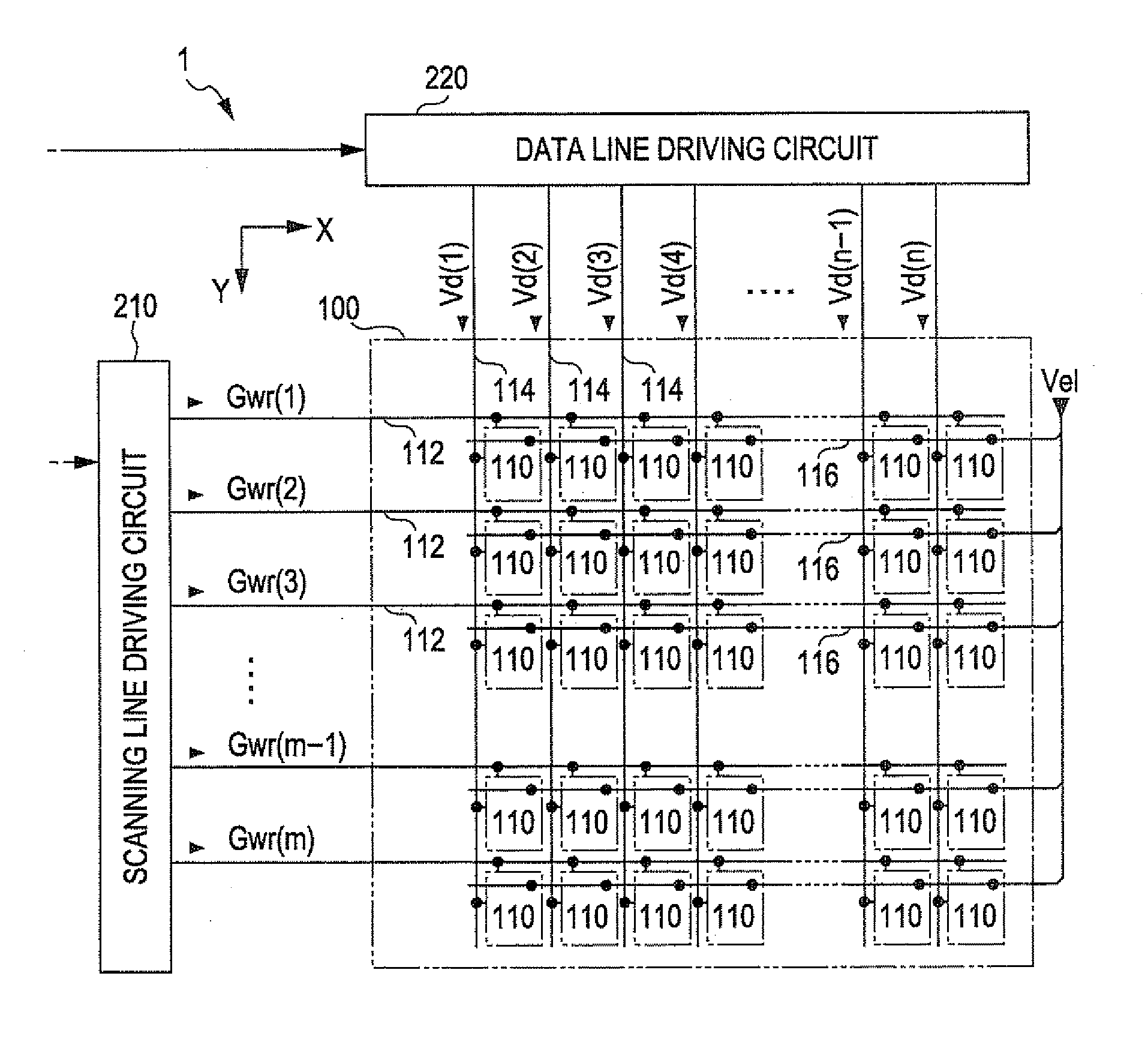
[0039]FIG. 1 is a block diagram which shows a configuration of an electro-optical device according to a first embodiment of the invention. The electro-optical device 1 is a device for displaying an image using a plurality of pixel circuits 110.
[0040]As shown in the drawing, the electro-optical device 1 includes an element unit 100, a scanning line driving circuit 210 and a data line driving circuit 220.
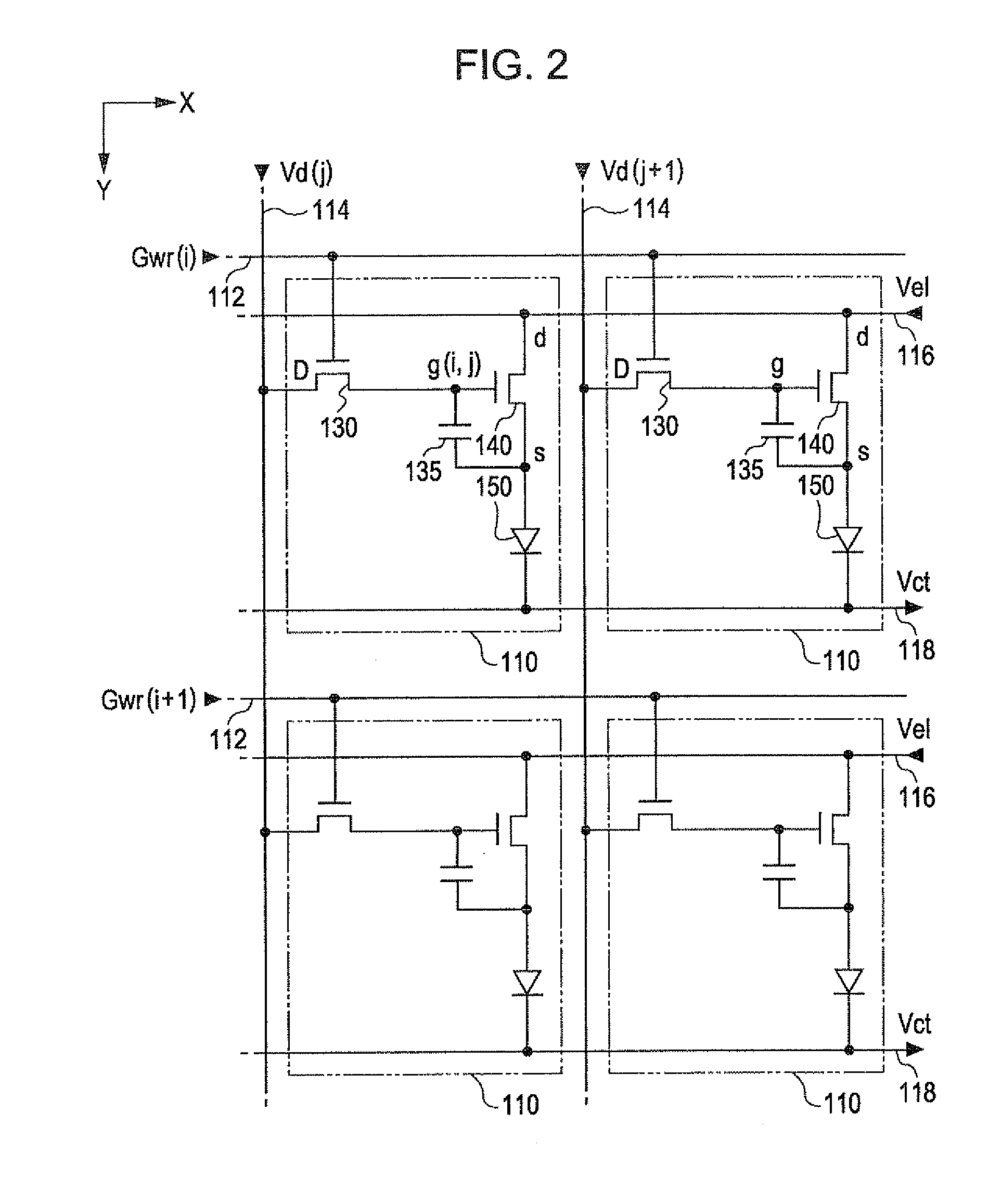
[0041]Among these, in the element unit 100, m rows of scanning lines 112 are provided in the row (X) direction, and n columns of data lines 114 are provided in the column (Y) direction in the drawing so as to maintain electrical insulation with respect to each of the scanning lines 112, each other. The pixel circuit 110 is respectively arranged corresponding to each intersection between the m rows of scantling lines 112 and the n columns of data lines 114. Accordingly, in the embodiment, the pixel circuit 110 is arranged in matrix of vertical m rows x horizontal n columns. In addition...
second embodiment
[0125]According to the first embodiment, the shield wires 81a and 81b were formed, by patterning the same wiring layer as that of the data line 114, however, the shield wires may be formed of a wiring layer different from that of the data line 114. Therefore, subsequently, as a second embodiment, an example will be described, in which the shield wires 81a and 81b are formed of the same wiring layer as that of the relay electrodes 61 and 62 which are on the lower side of the data line 114, and the power supply line 116.
[0126]FIG. 10 is a plan view which shows a configuration of a pixel circuit 110 of an electro-optical device in the second embodiment. FIG. 11 is a partial cross-sectional view of the pixel circuit shown in FIG. 10 which is cut along line XI-XI.
[0127]When forming shield wires 81a and 81b from the same wiring layer as that of relay electrodes 61 and 62, and a power supply line 116, it is necessary to avoid interference (electrical contact) from the shield wire 81a and t...
third embodiment
[0135]FIG. 12 is a plan view which shows a configuration of a pixel circuit 110 of an electro-optical device according to a third embodiment. FIG. 13 is a partial cross-sectional view of the pixel circuit in FIG. 12 which is cut along line XIII-XIII.
[0136]As shown in FIG. 12, in the third embodiment, a part of a shield wire 81a is extended toward the right side, and is formed to cover a relay electrode 43 when seen in the plan view. A holding capacity 135 is a region where the relay electrode 43 and a gate electrode layer 21 are overlapped with each other when seen in the plan view. The relay electrode 43 is the other electrode in the holding capacity 135, and also is a source node of the transistor 140. For this reason, in the third embodiment, the shielding function is further strengthened compared to the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com