Ifn-gamma inhibitors in the treatment of motoneuron diseases
a technology of ifn-gamma inhibitors and motoneuron diseases, which is applied in the field of treatment of motoneuron diseases, can solve the problems of preventing the development of effective therapies, unable to reverse the damage already done to motoneurons, and unable to achieve effective treatments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
IFNγ-Induced Motoneuron Death
[0110]In order to support the role of IFNγ in motoneuron death in ALS, the following preliminary tests were conducted.
In Healthy Motoneurons
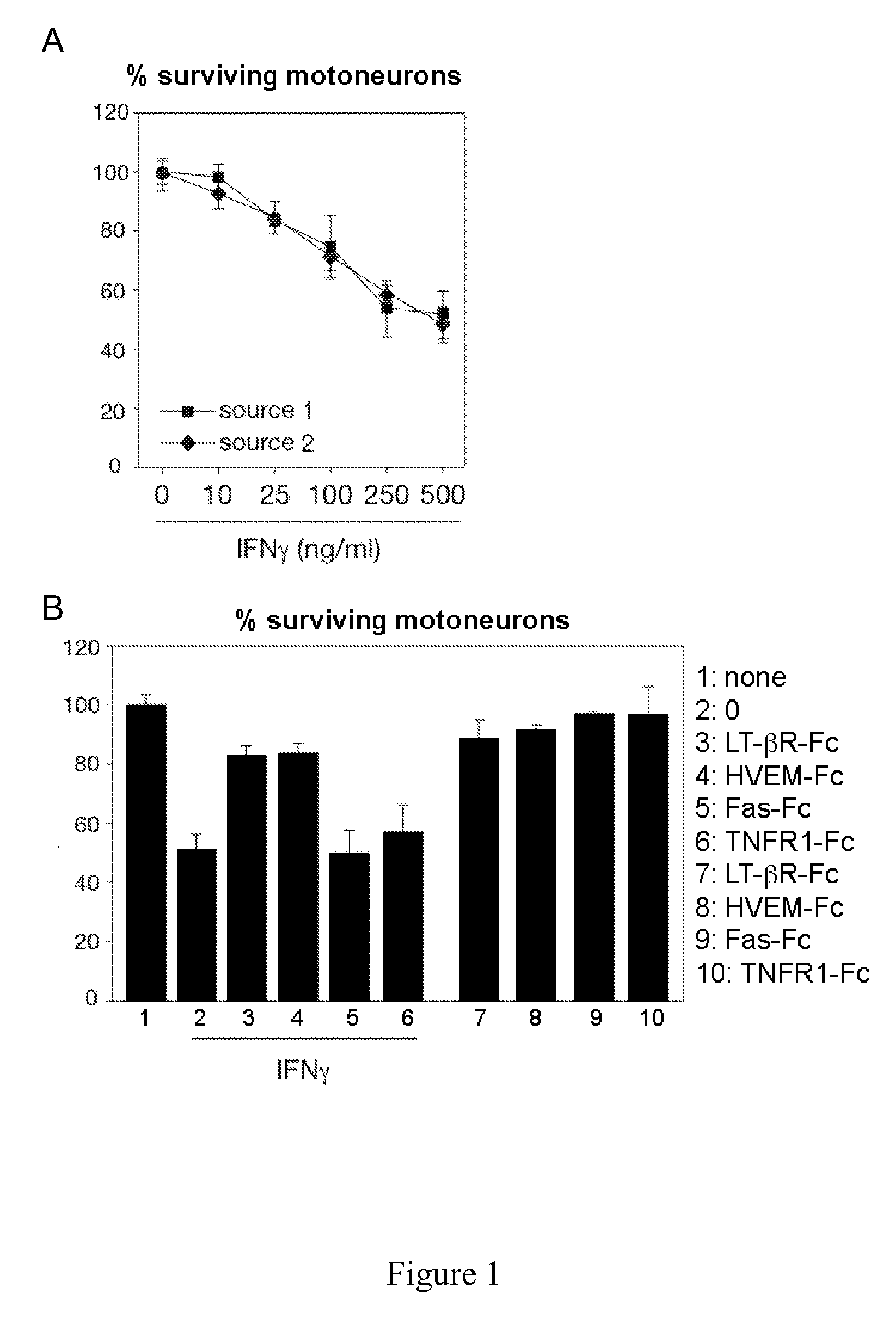
[0111]IFNγ receptor chain 1 (IFNγR1) and chain 2 (IFNγR2) are expressed in nearly all Hb9::GFP motoneurons (embryonic motoneurons (E12.5) isolated from transgenic mice expressing the green fluorescent protein (GFP) under the control of the motoneuron-selective Hb9 promoter (Hb9::GFP) to facilitate motoneuron tracing) in vitro as shown by immunostaining 24 hours after seeding with antibodies directed against IFNγR1 or IFNγR2 as described below.
[0112]The exposure of motoneurons to a suboptimal dose of sLIGHT and increasing doses of IFNγ shows that IFNγ substantially enhances the LIGHT killing effect and that this synergetic lethal effect is specific to LIGHT since IFNγ had no effect on sFasL-induced death (FIG. 1B). Recombinant IFNγ induced death of about 50% of motoneurons in a dose-dependent manner (FIG. 1A). The syn...
example 2
IFNγ Levels in Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid are Increased in ALS
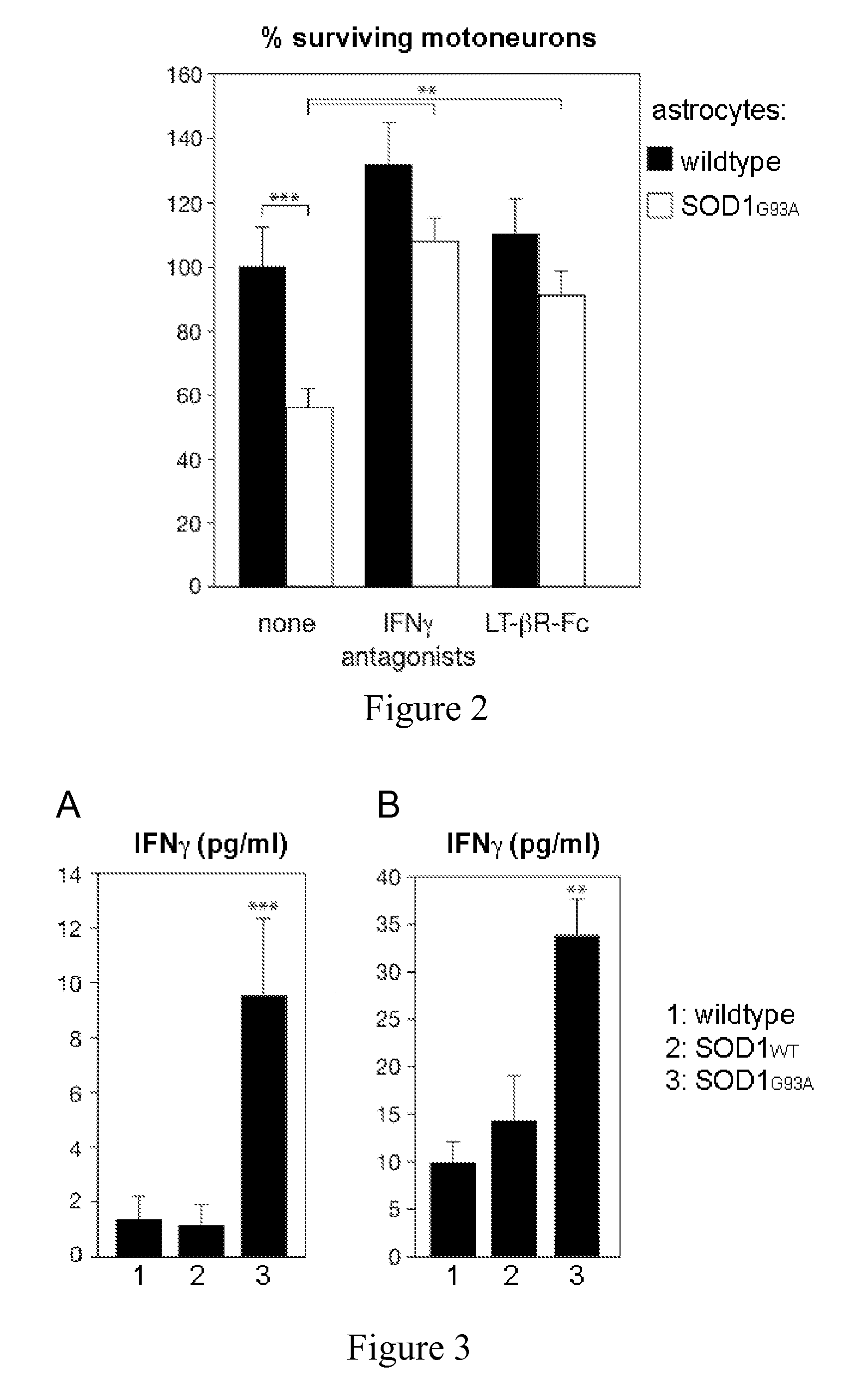
[0119]The efficacy of a method for detection and / or prognosis of ALS and disease progression according to the invention are tested through the measure of IFNγ levels in serum and spinal cord of SOD1G93A mice and ALS patients, at different disease stages.
IFNγ Levels in Serum and Lumbar Spinal Cord of Sod1G93A Mice Compared to Age-Matched Wildtype and SOD1WT Mice
[0120]An enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent (ELISA) analysis was carried out to titer for IFNγ levels wherein mice of indicated genotype were bled at 13 weeks of age. Lumbar spinal cords were dissociated in 50 mM Tris-Hcl pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl containing a cocktail of protease inhibitor (complete EDTA-free tabs, Roche Diagnostic). Spinal cord homogenates were centrifuged at 10,000×g for 10 min at +4° C. and protein concentration was determined in supernatants using Bradford assay (BioRad). Levels of IFNγ were then determined using mouse IFNγ ELISA kit II OptEIA™ (BD Bio...
example 3
Rescue from Neurotoxicity of Astrocytes by Antagonizing the IFNγ-Induced LIGHT-Triggered Death Pathway
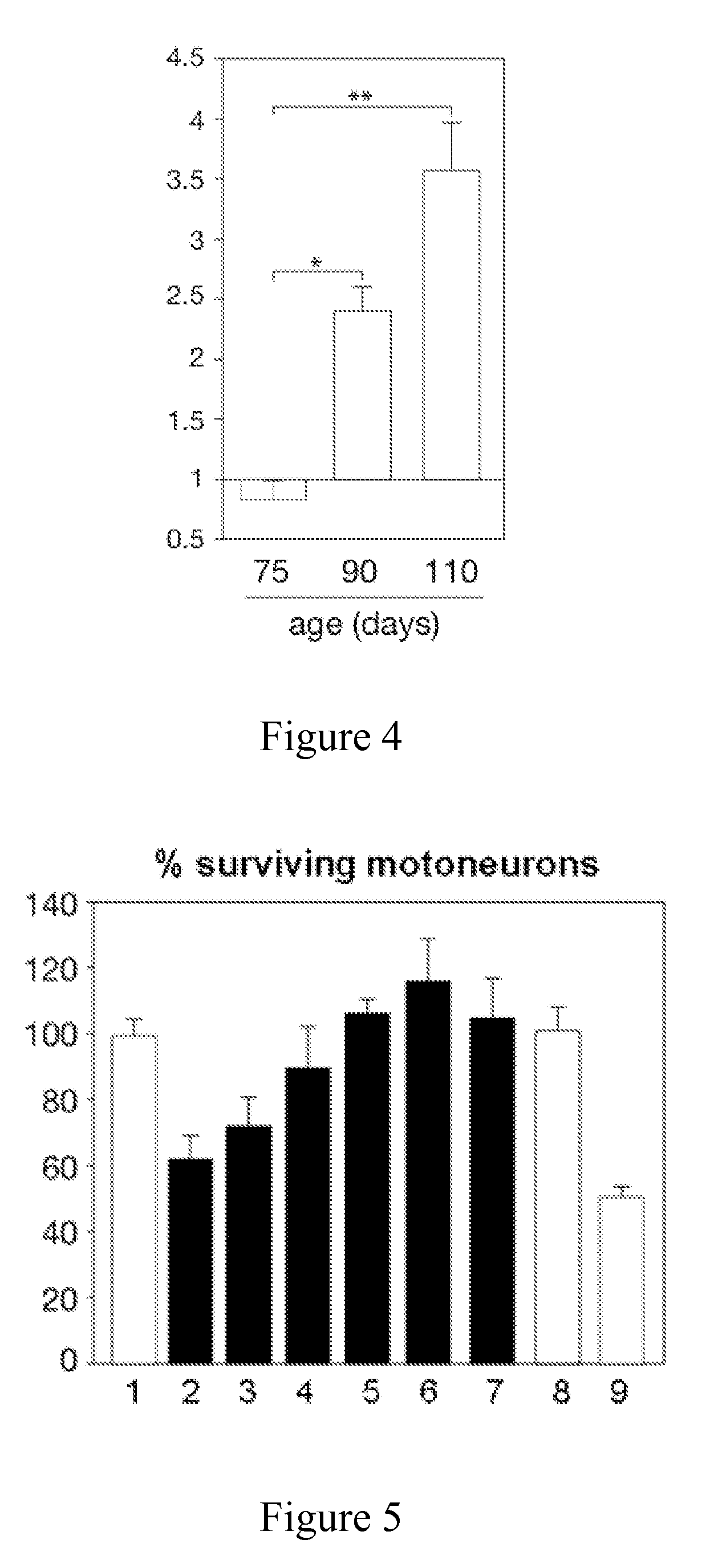
[0134]The efficacy of a method according to the invention are tested through the therapeutic impact of the inhibition of IFNγ, by using an antagonizing antibody in vitro and in vivo. Disease progression and lifespan is determined by behavioural and histopathological analysis as described in Example 2.
Purified Motoneurons Rescued with Neutralizing Anti-IFNγ Antibodies
[0135]The potential of anti-IFNγ antibodies to protect motoneurons from death induced by recombinant mouse IFNγ was first assessed in vitro in cultured motoneurons (FIG. 5). As described in Example 1, recombinant IFNγ, or sLIGHT, or agonistic anti-LT-βR antibodies, induced death of about 50% of motoneurons. Neutralizing goat polyclonal anti-IFNγ antibodies (15027, Sigma-Alrich) efficiently blocked IFNγ- or LIGHT-induced death of cultured motoneurons. IFNγ in combination with irrelevant rat IgG did not rescue motoneurons ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com