Cognitive radio sensing method and system
a radio sensing and cognition technology, applied in the field of radio systems, can solve the problems of non-trivial system complexity, difficult practical implementation, high computational complexity, etc., and achieve the effects of improving the sensing quality, enhancing cognition, and enhancing the sensing capability of the receiver
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
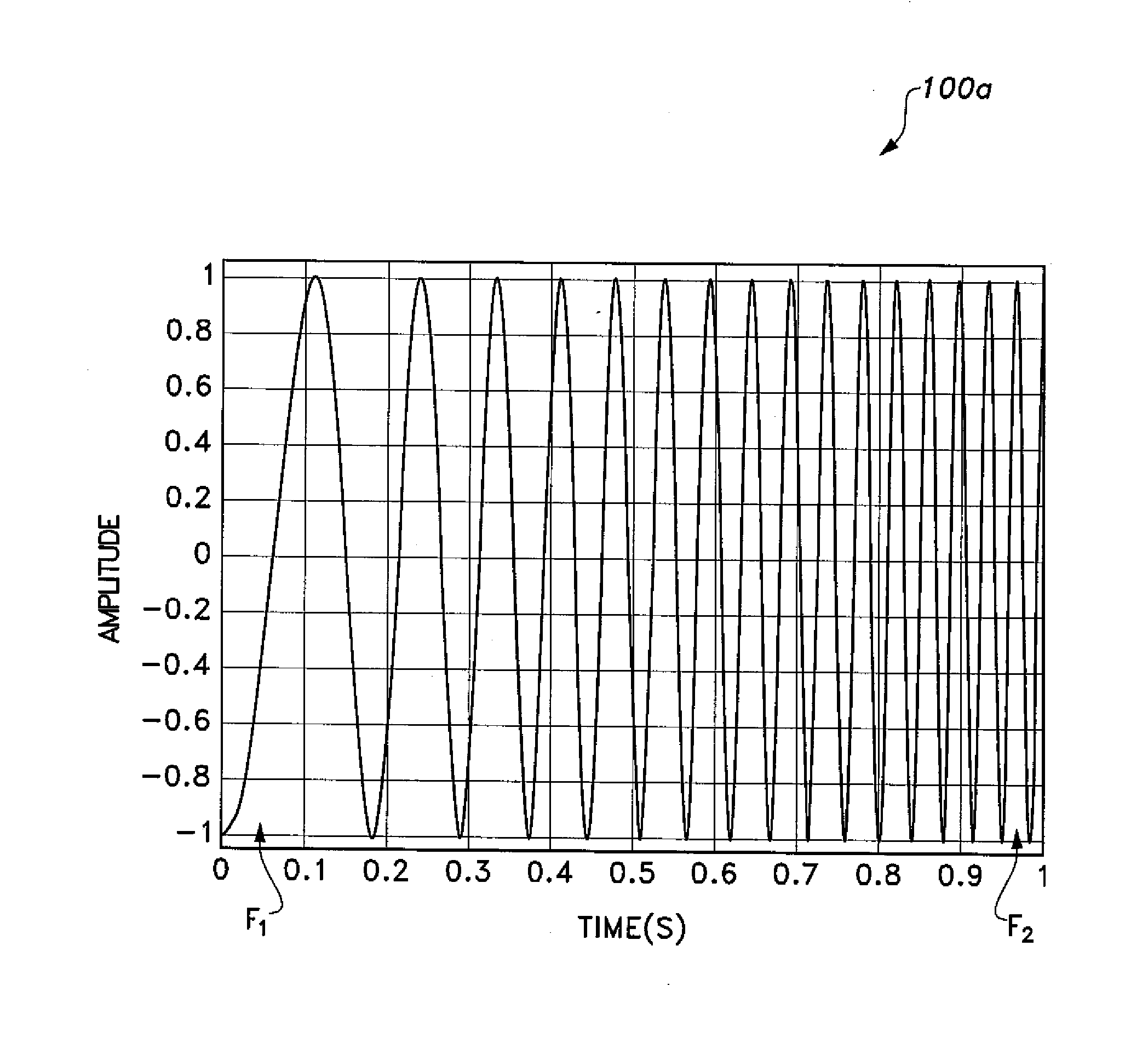
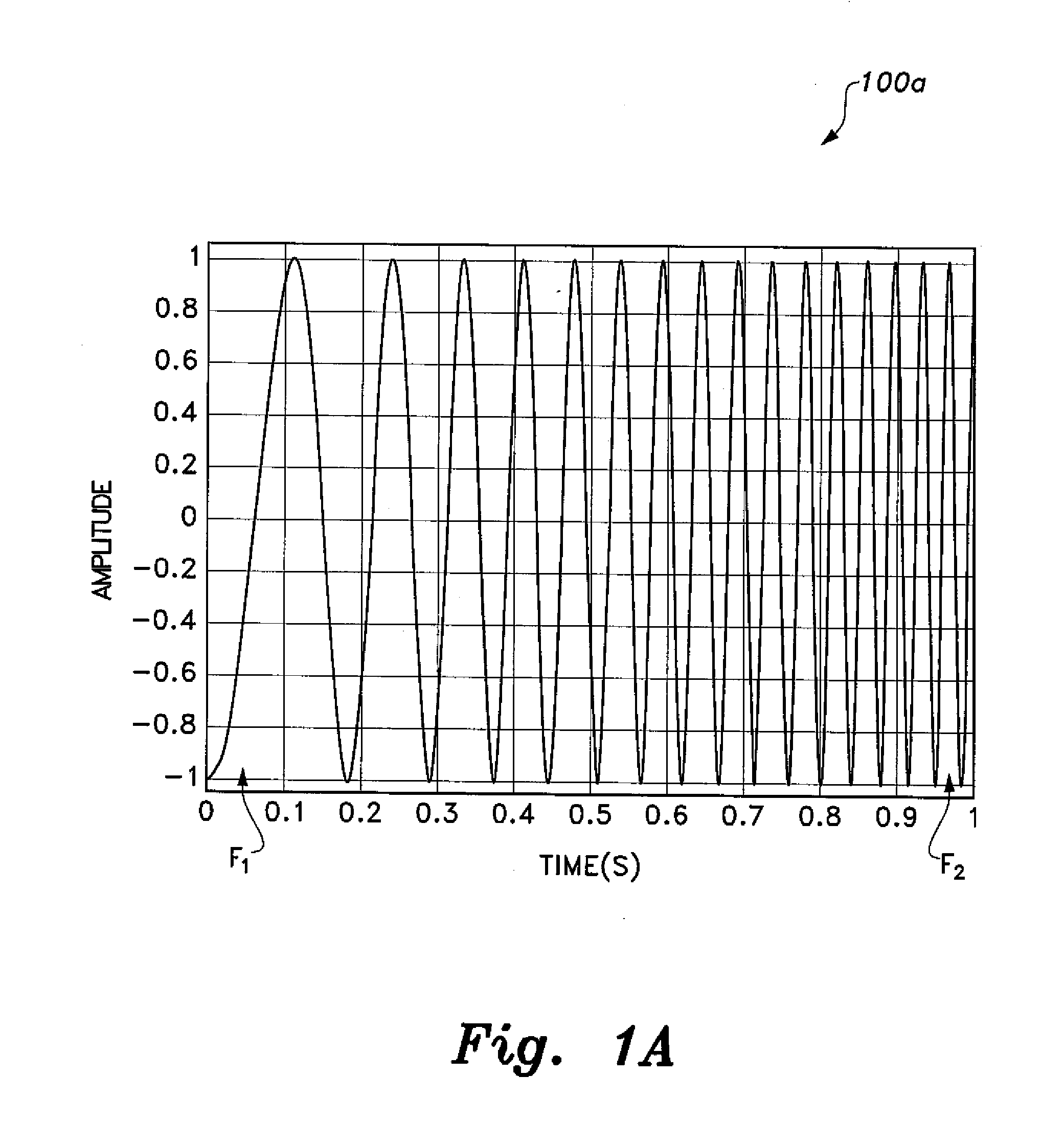
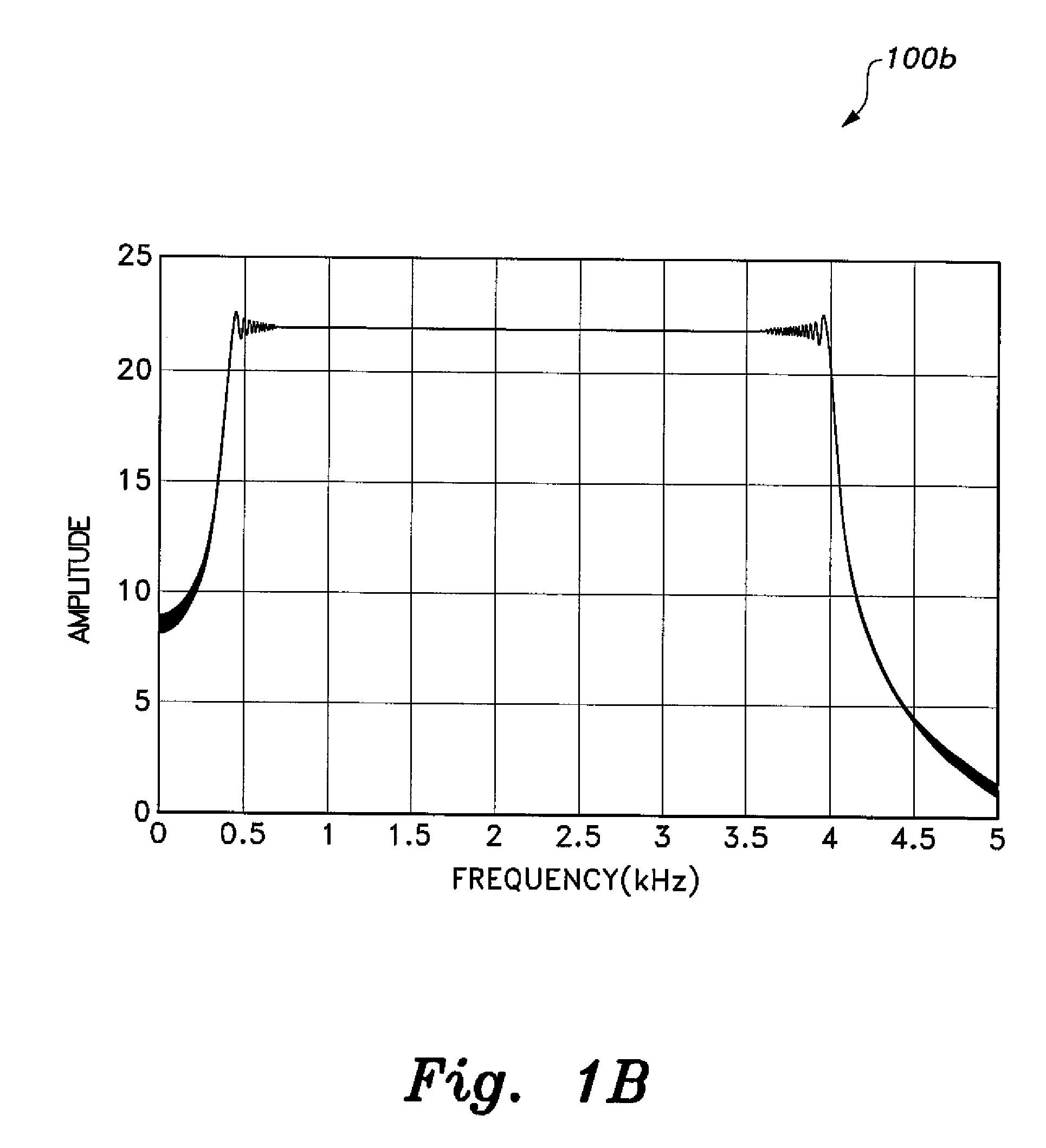
[0027]The cognitive radio sensing method employs wideband chirp signal frequency modulation for a digital signal, which is used in sensing the operable spectrum of the cognitive radio. The chirp signal is inherently wideband, as its bandwidth spread over a range of frequencies exceeds the signaling frequency of the cognitive radio. The chirp signal is generated by linear frequency modulation of a digital signal. Thus, the instantaneous frequency of the chirp signal increases or decreases linearly with time. As shown in FIG. 1A, the bandwidth of a chirp signal 100a extends from the starting frequency sweep f1 to the final frequency sweep f2. With a proper choice for processing gain, i.e., the FT product, where T is the bit period, is such that the spectrum of the chirp signal has a distinctive, nearly square shape 100b, as shown in FIG. 1B.
[0028]As shown in FIG. 2, the system architecture is a hybrid network 200, comprising a primary radio network 312a and a cognitive “adaptive” radi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com