Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Improve sensing quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
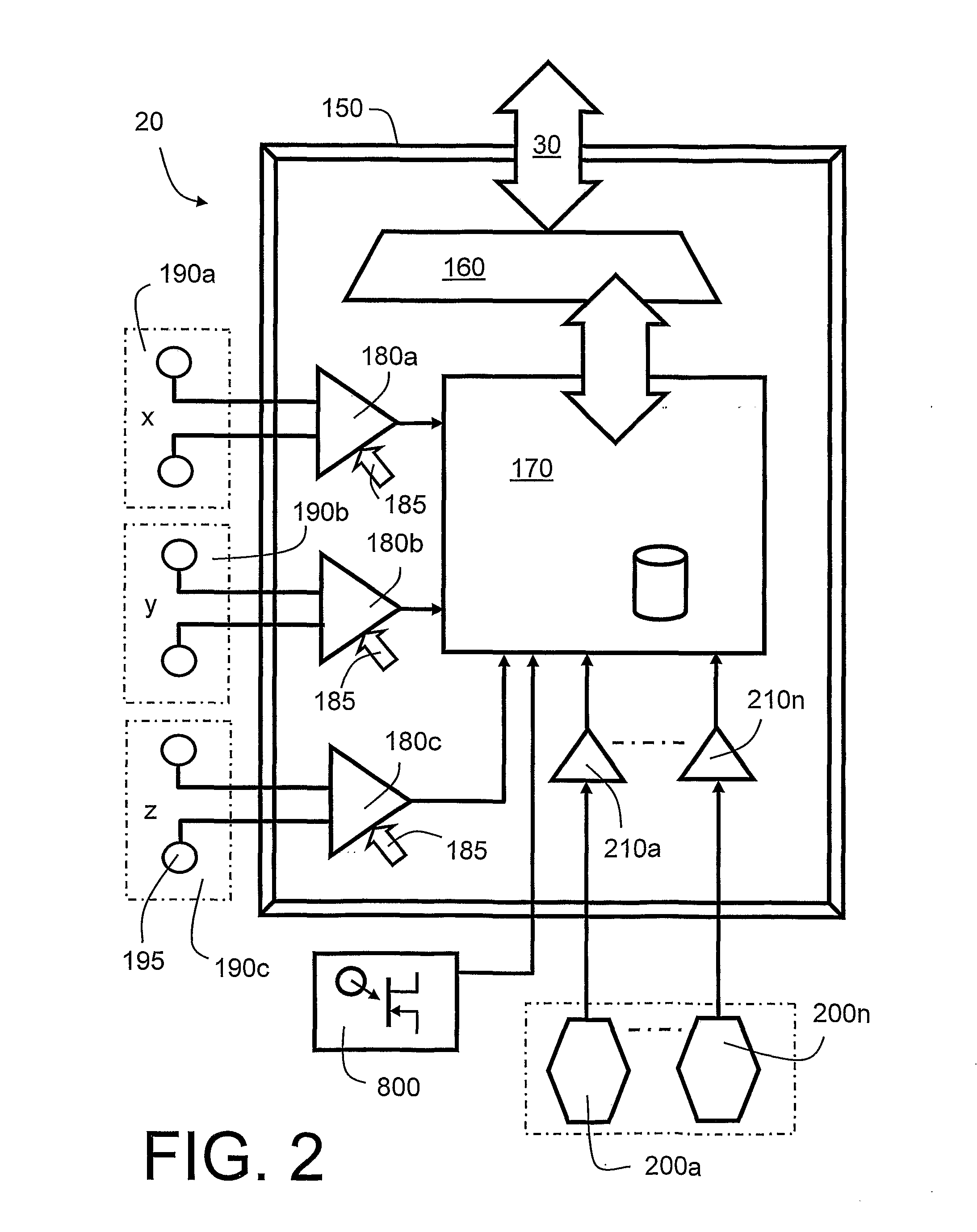
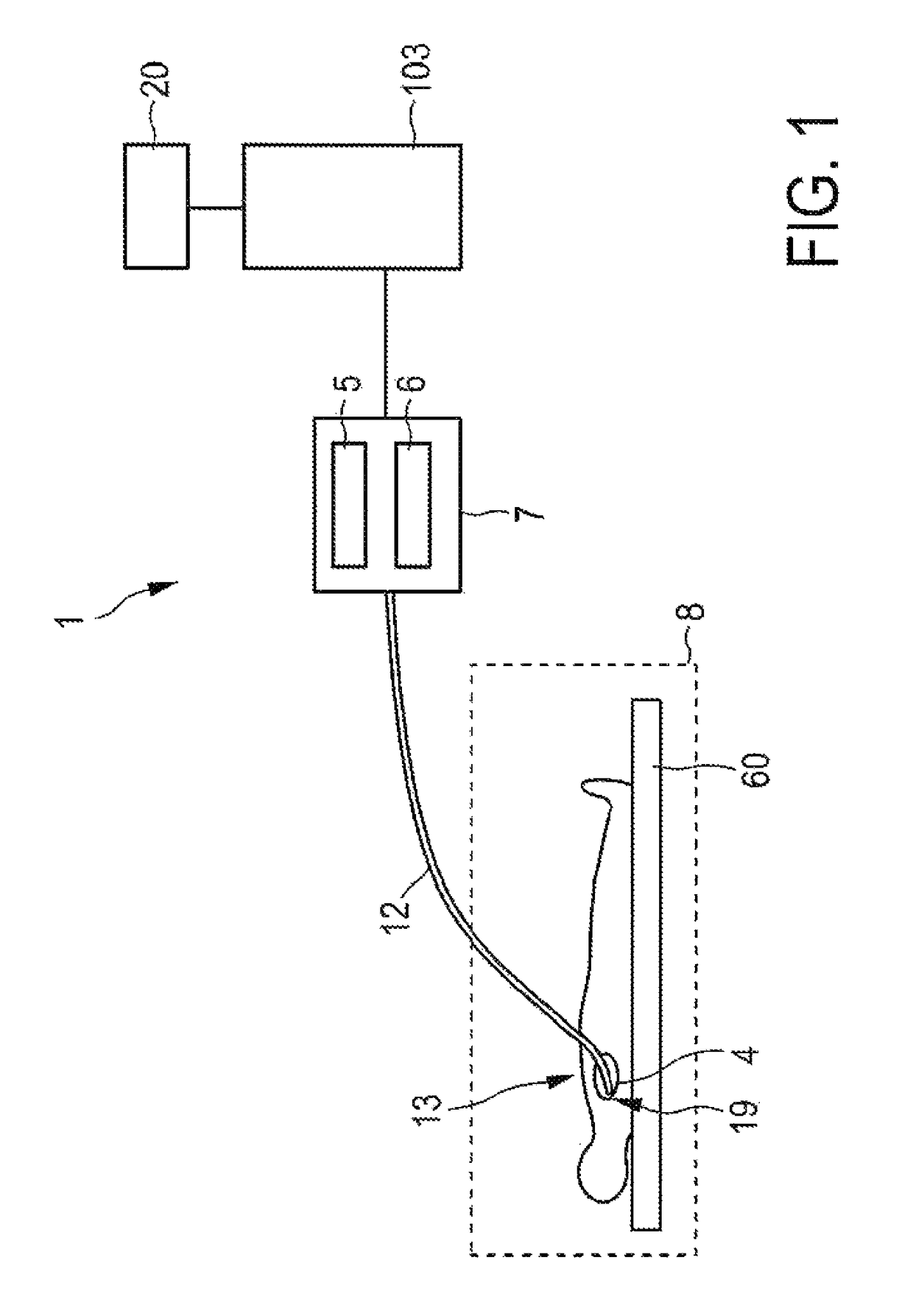
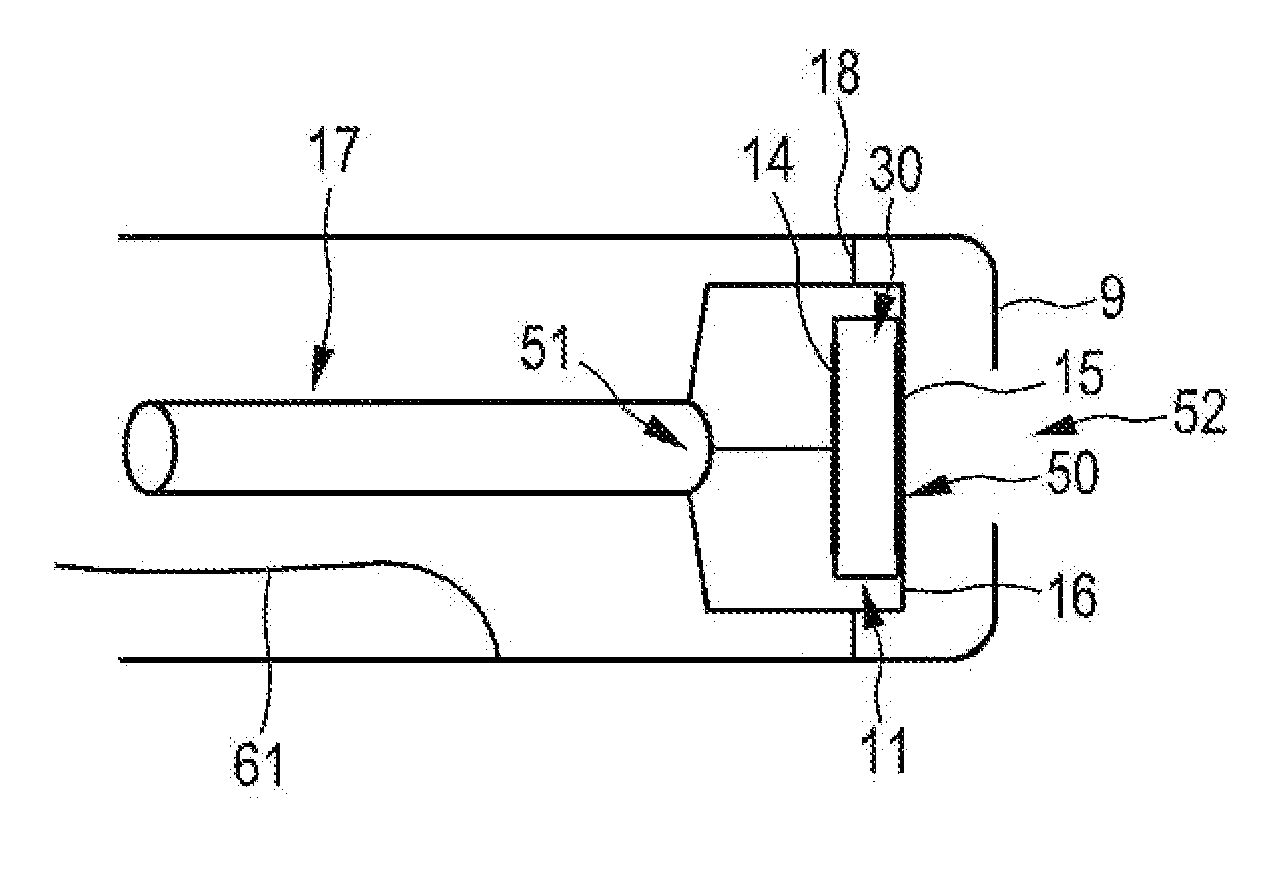
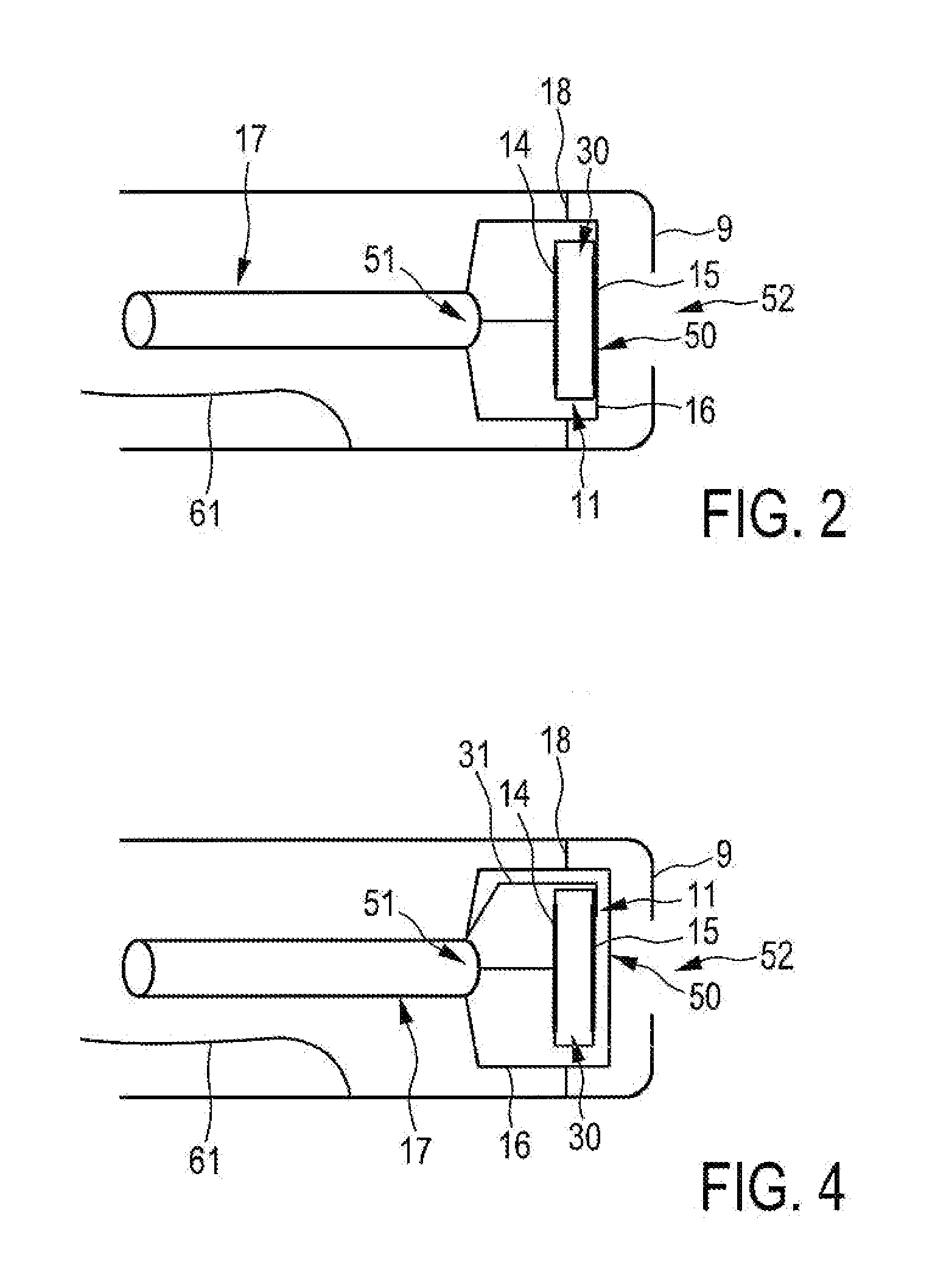
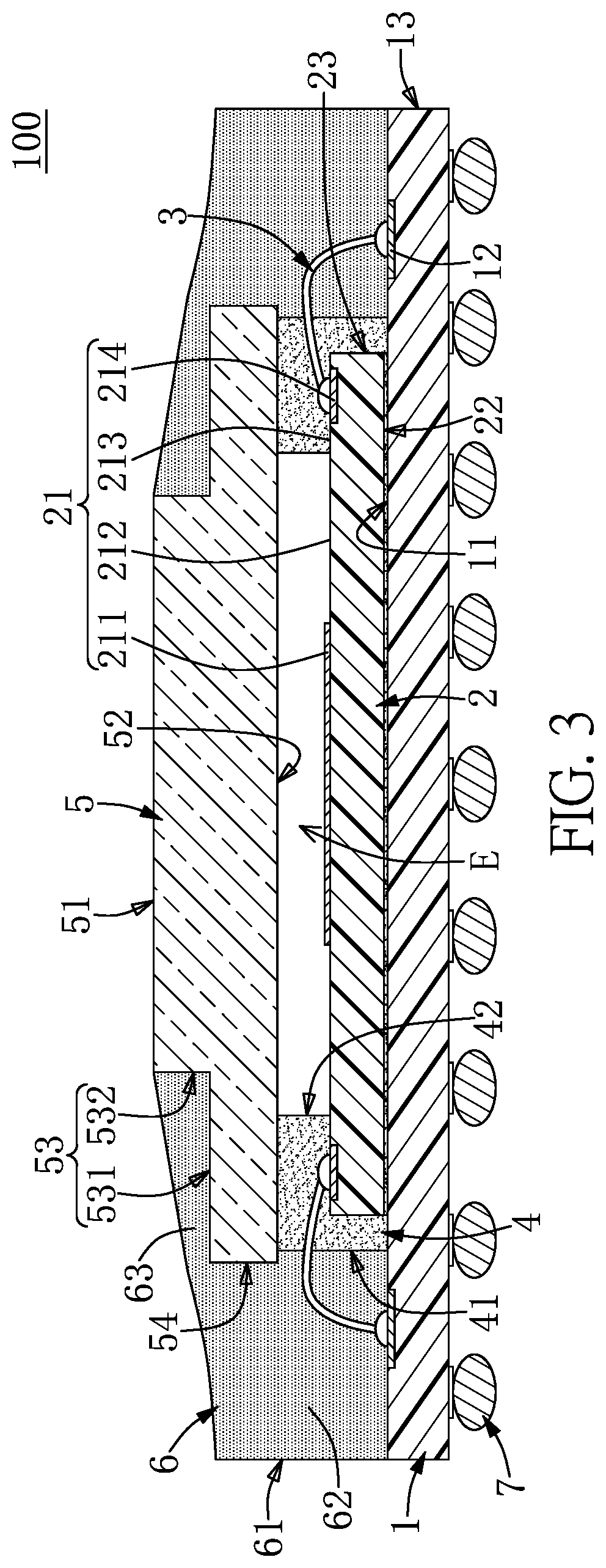
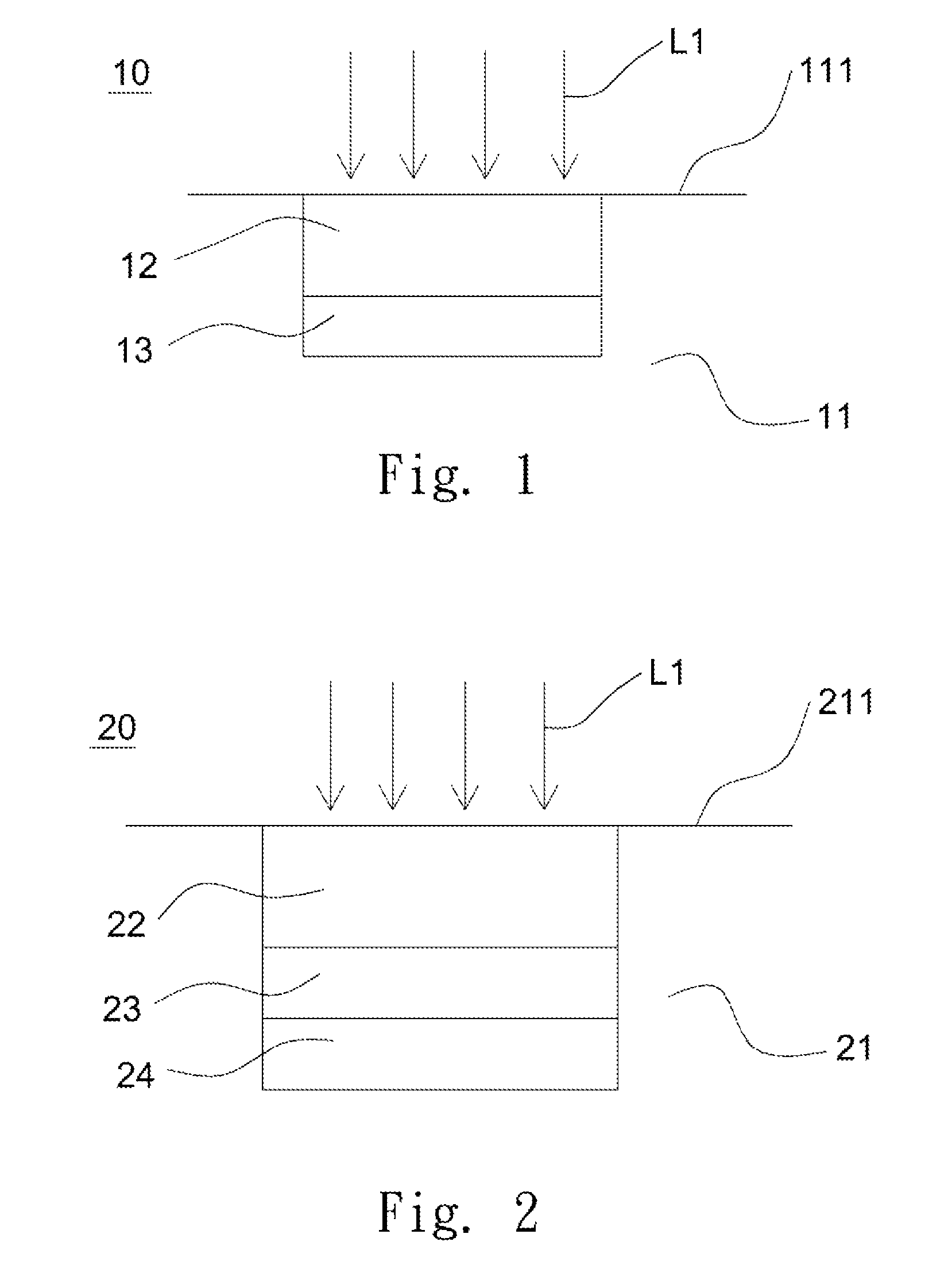
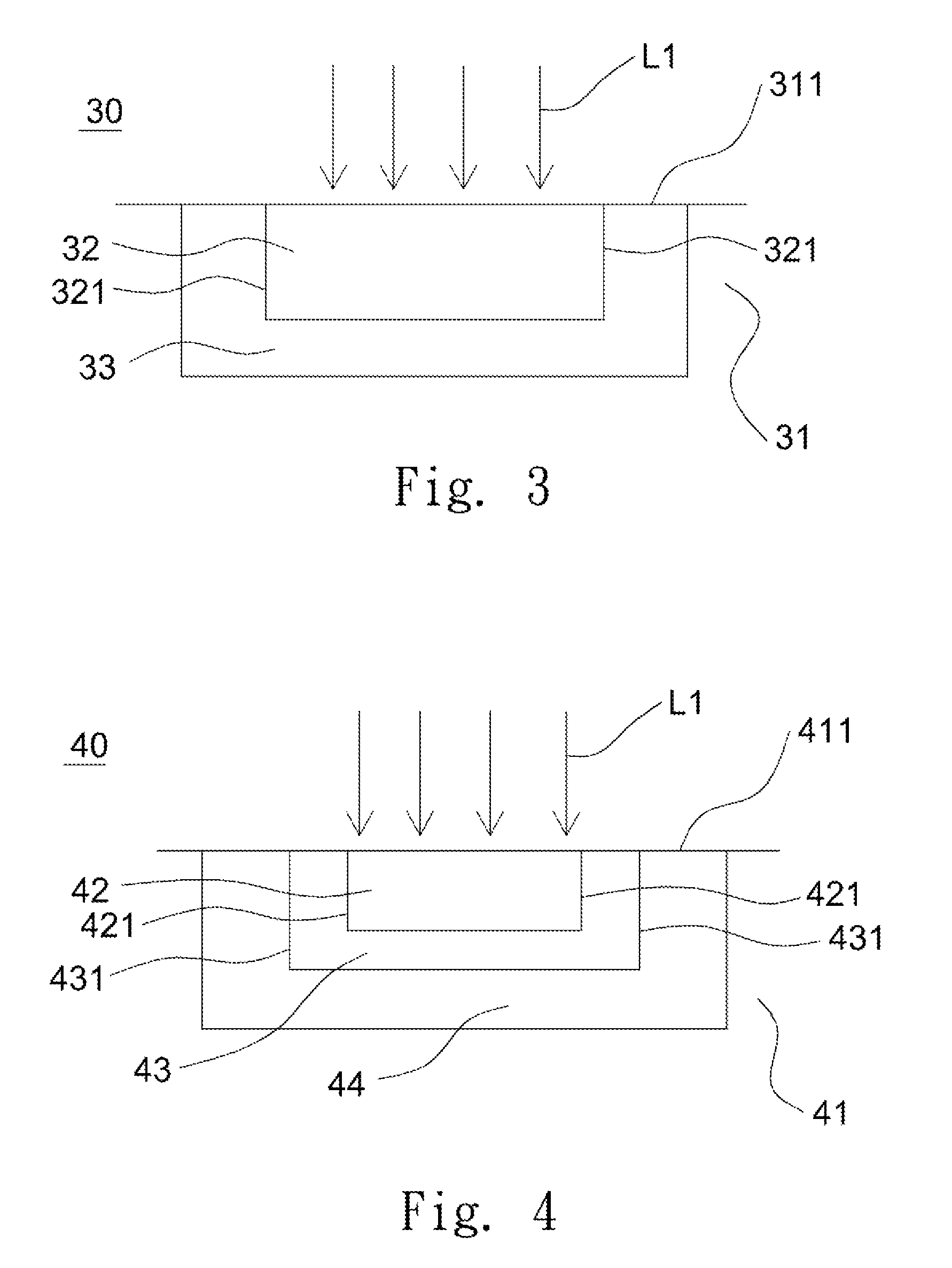
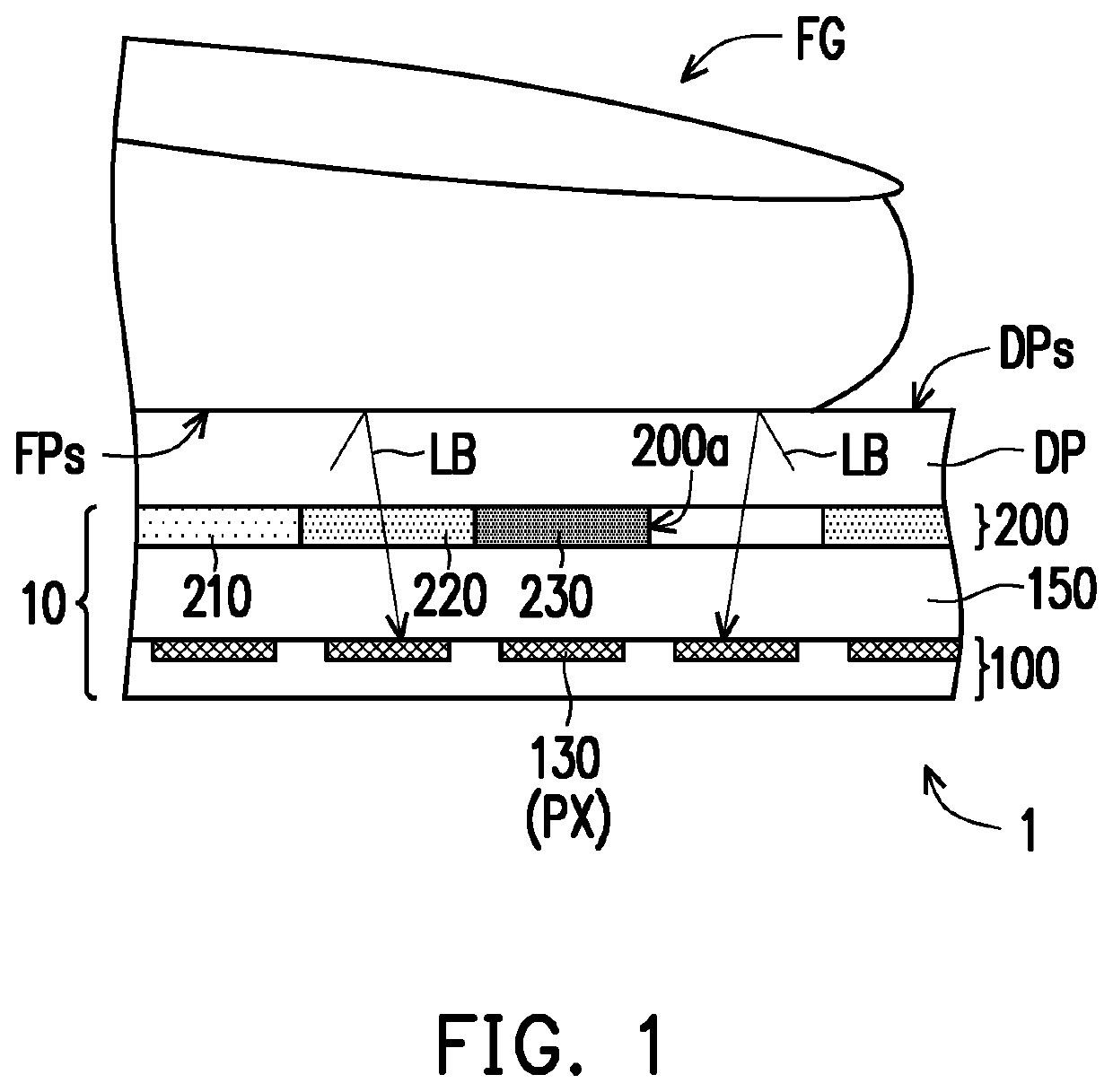
Underwater measurement system
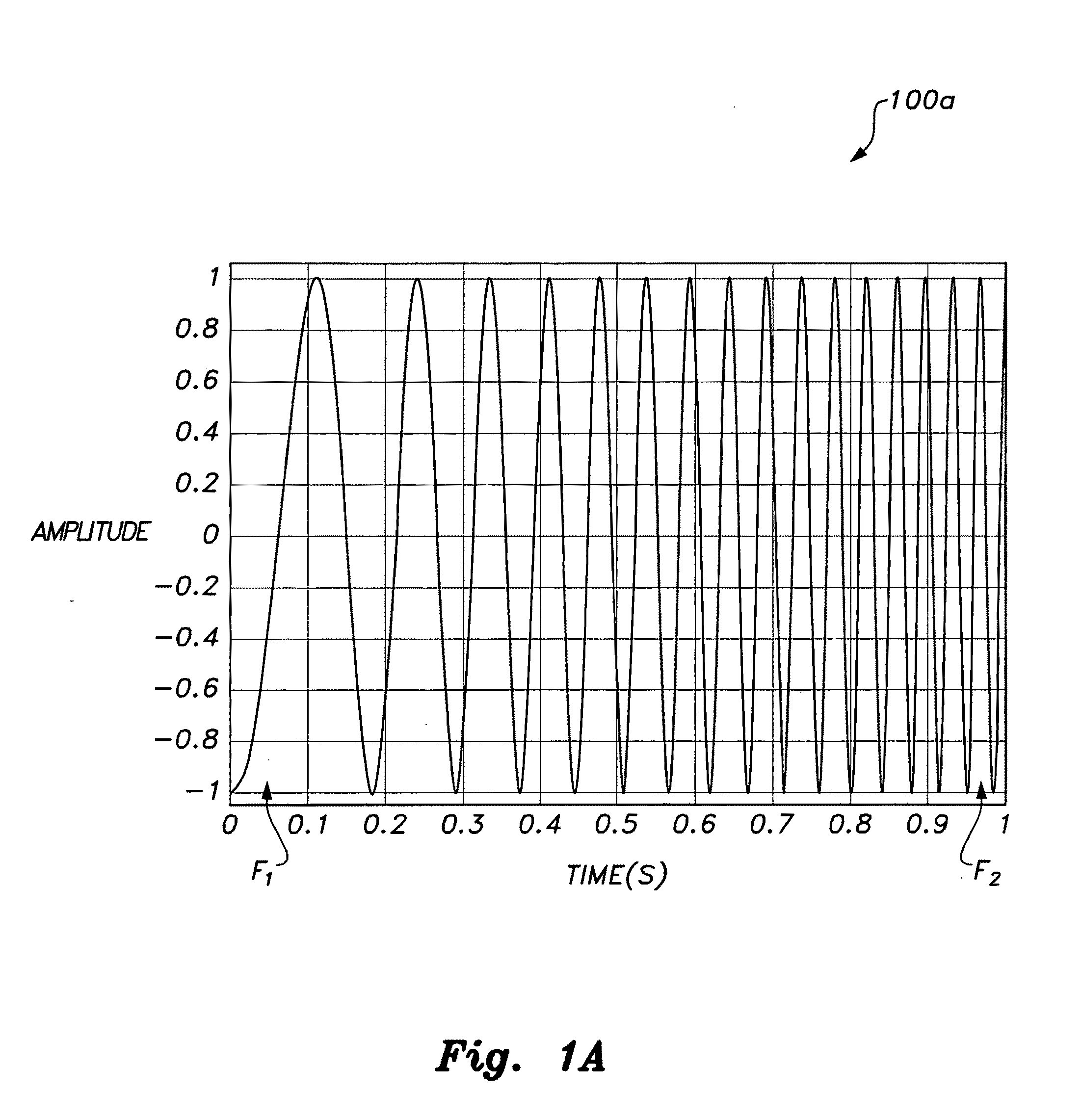
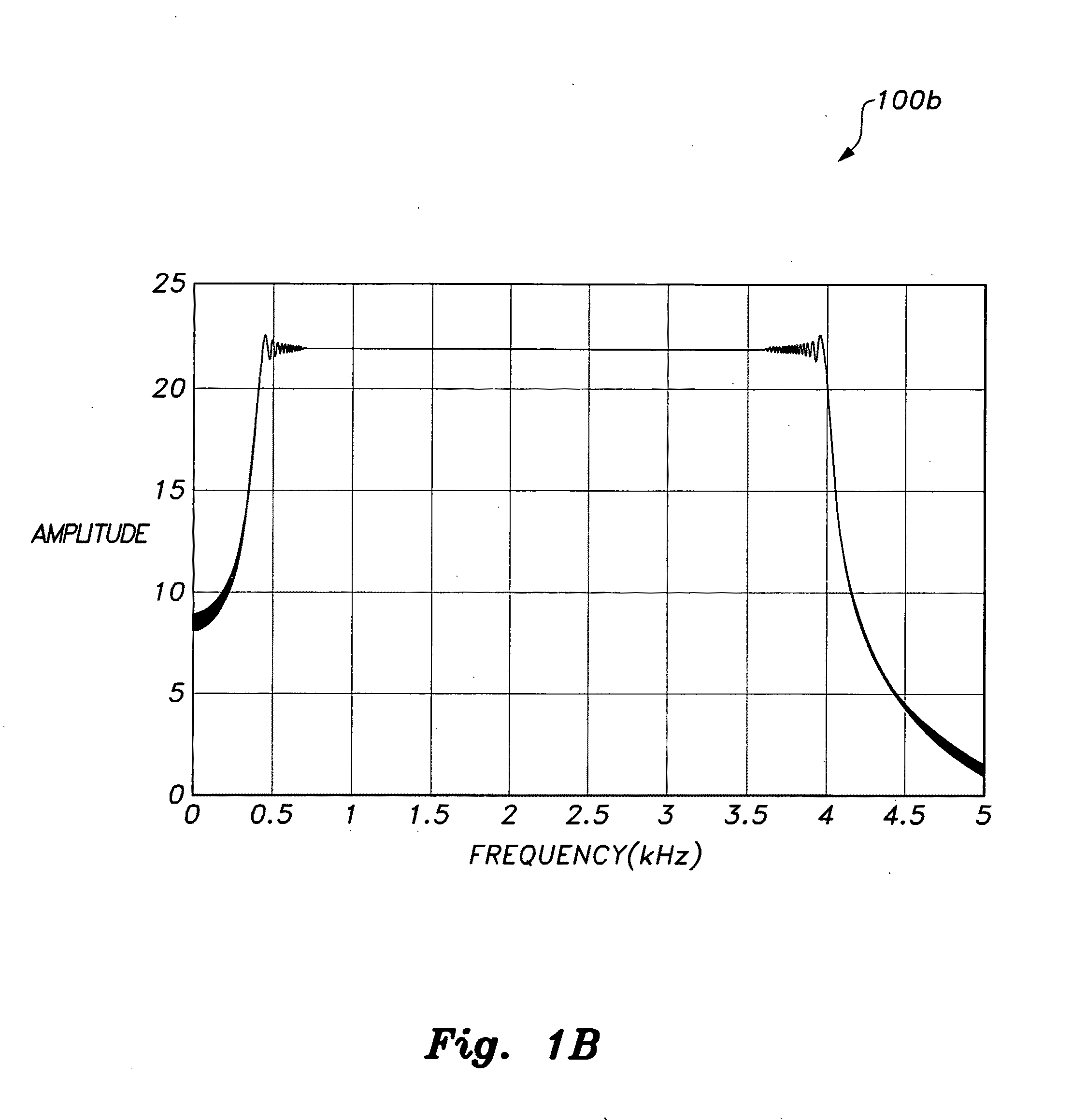
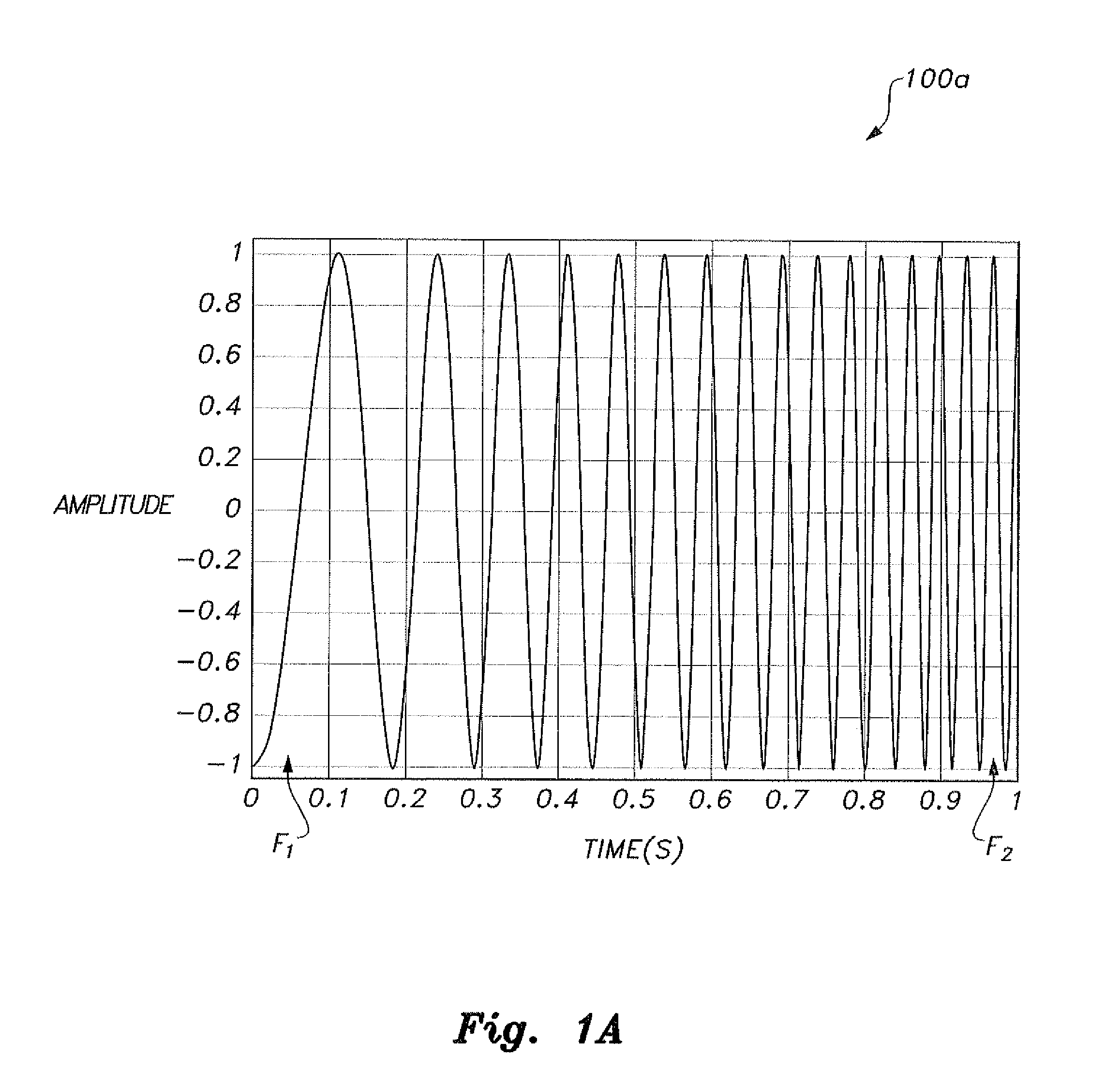
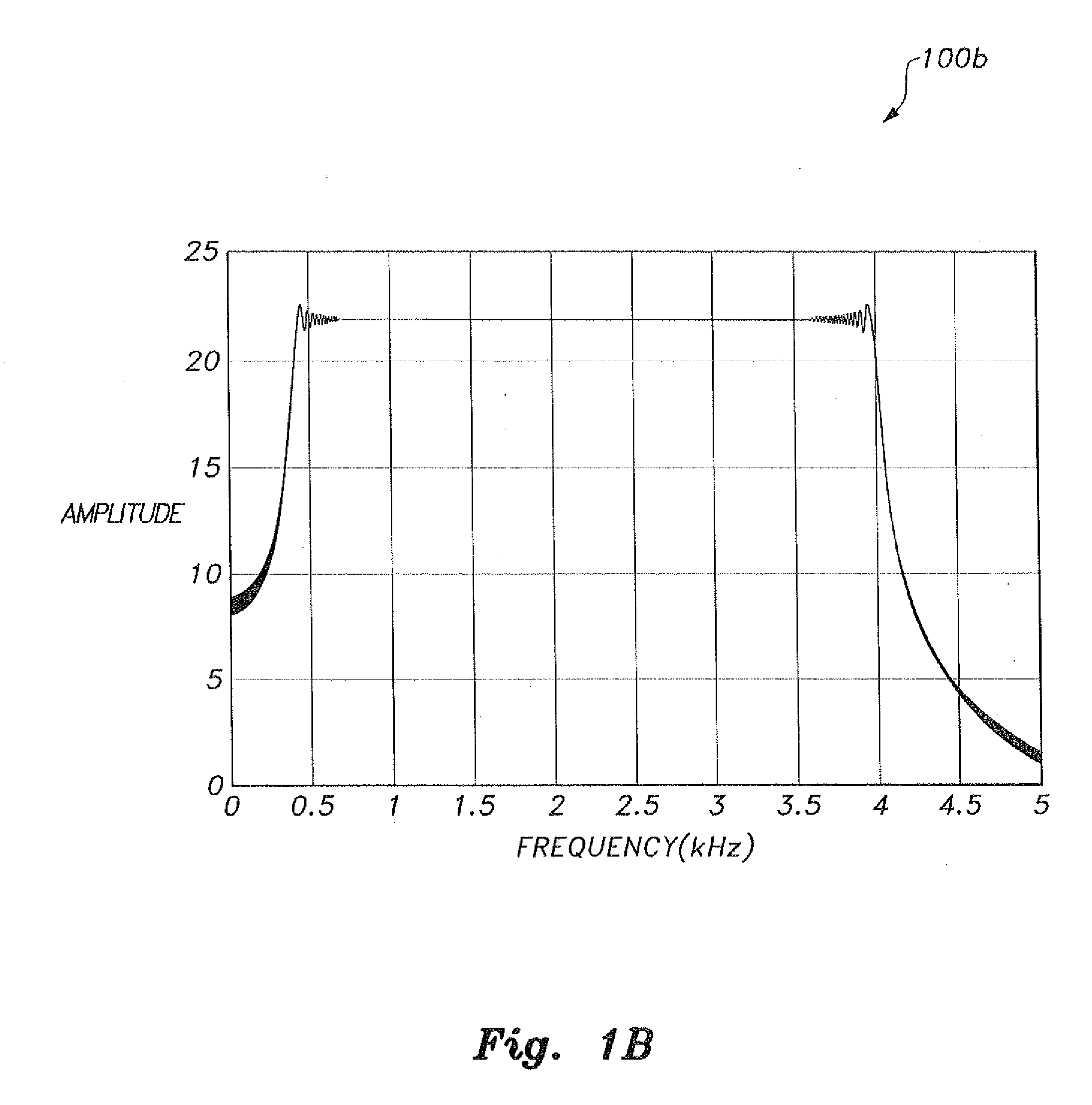
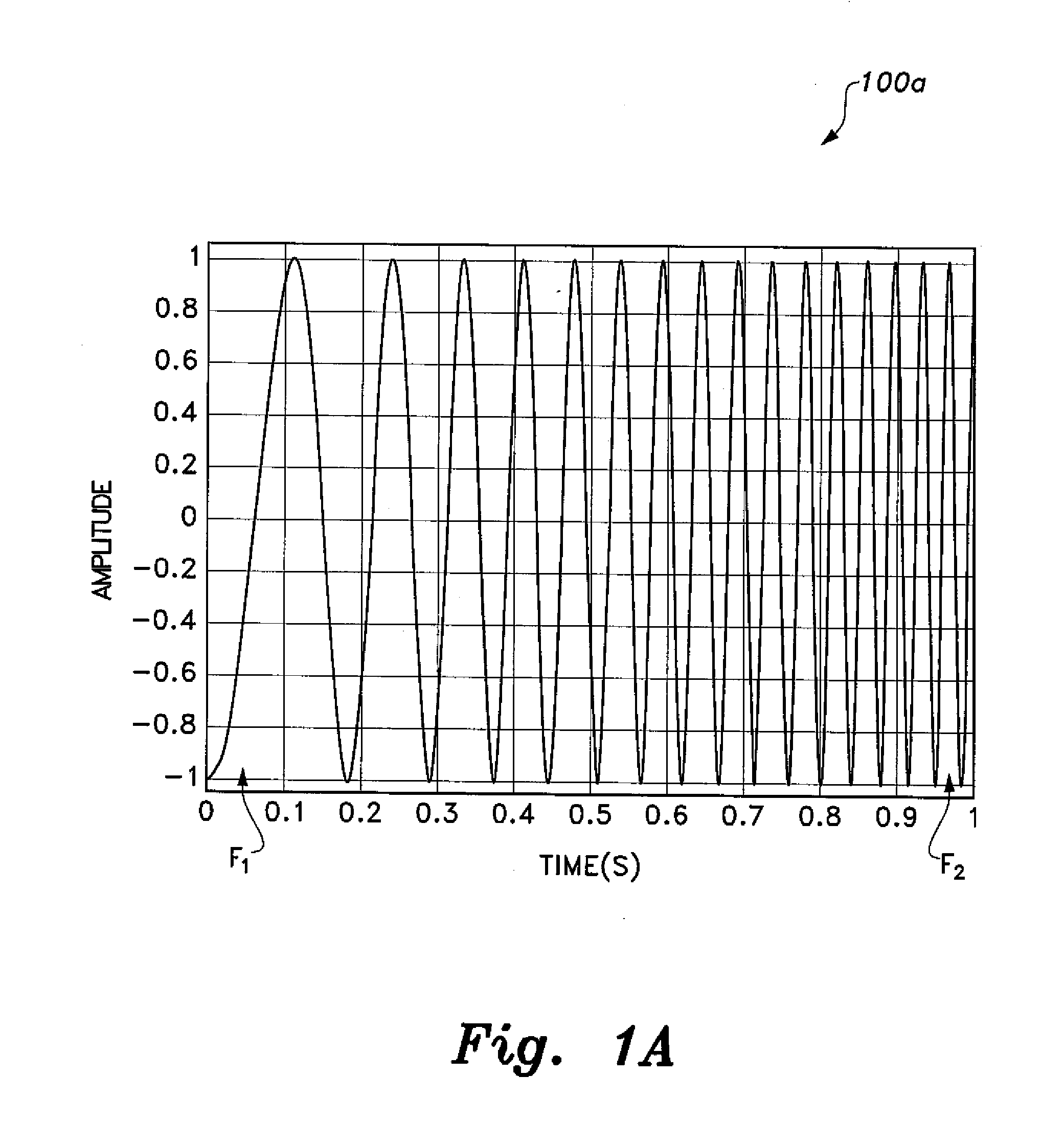
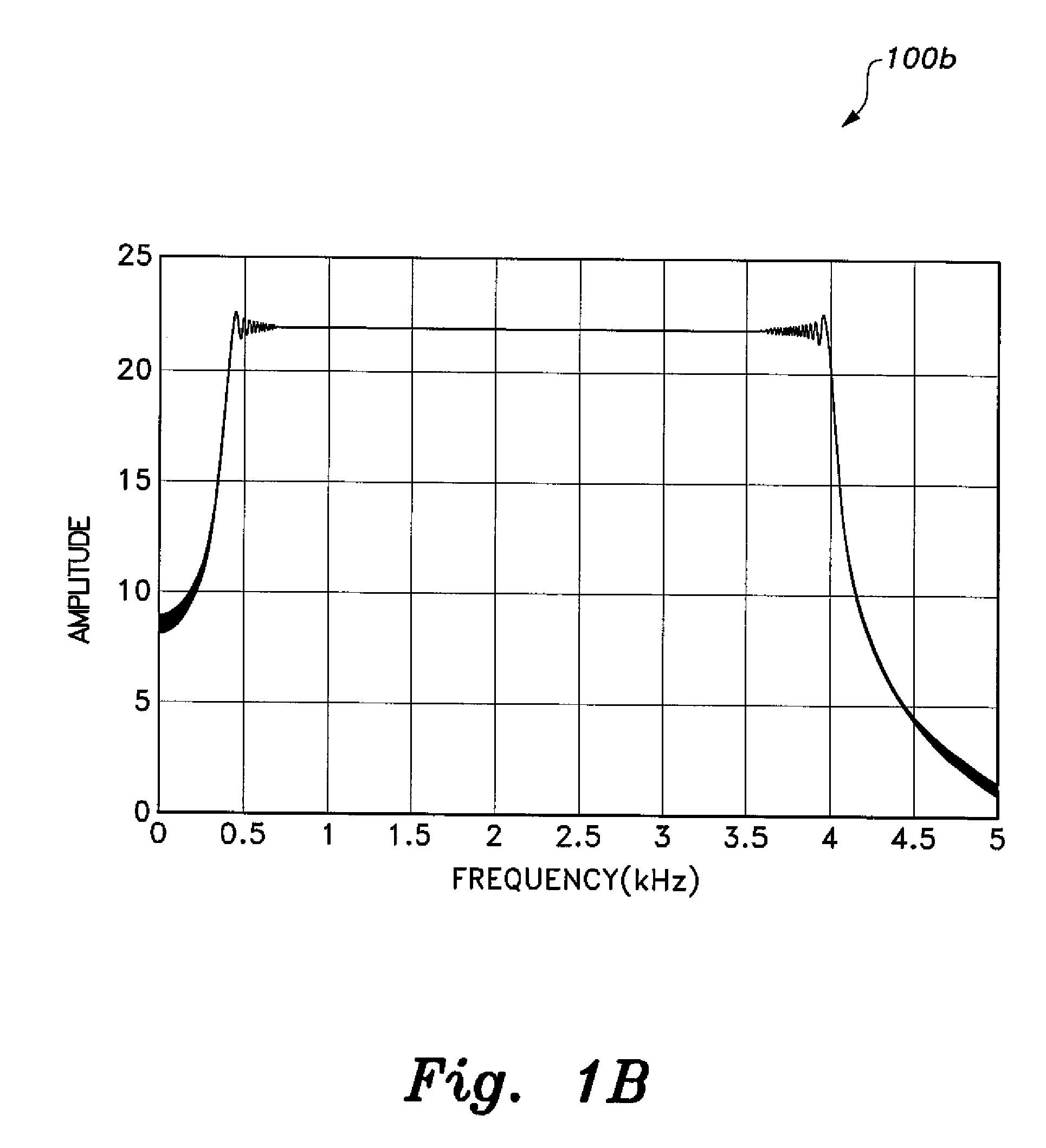
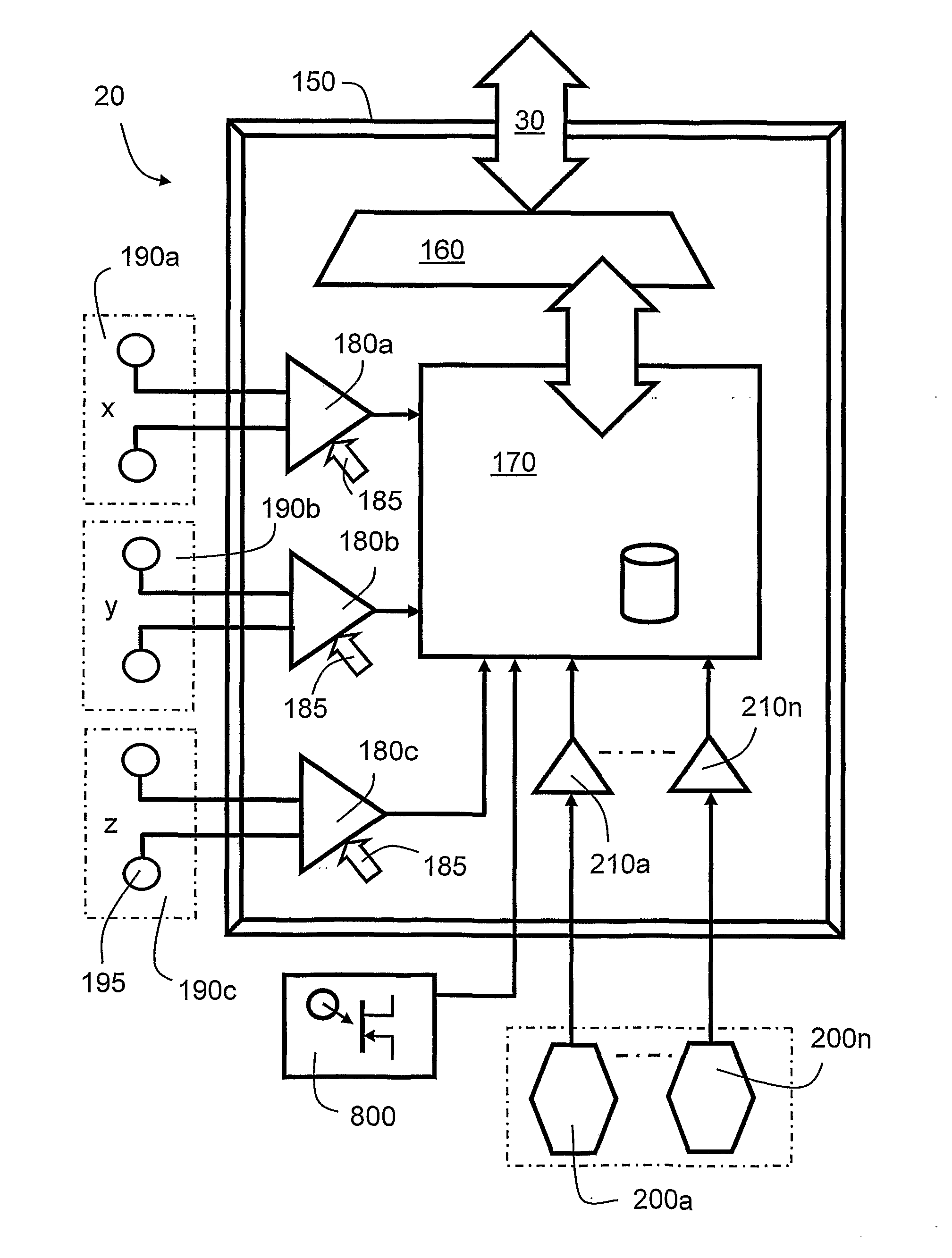
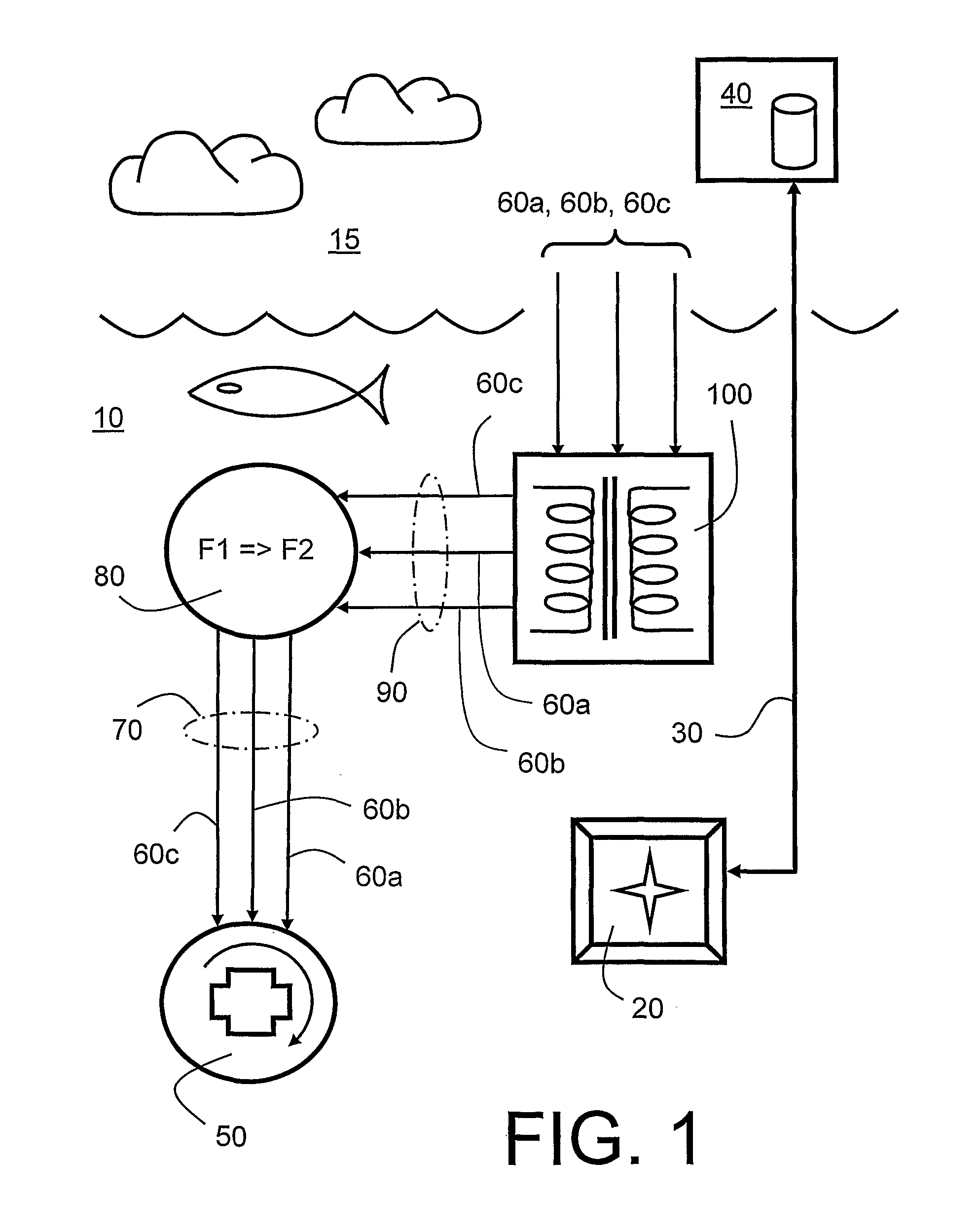
ActiveUS20100280773A1Reliably and accurately identifiedImprove sensing qualityTesting dielectric strengthFault location by conductor typesHydrophoneEngineering
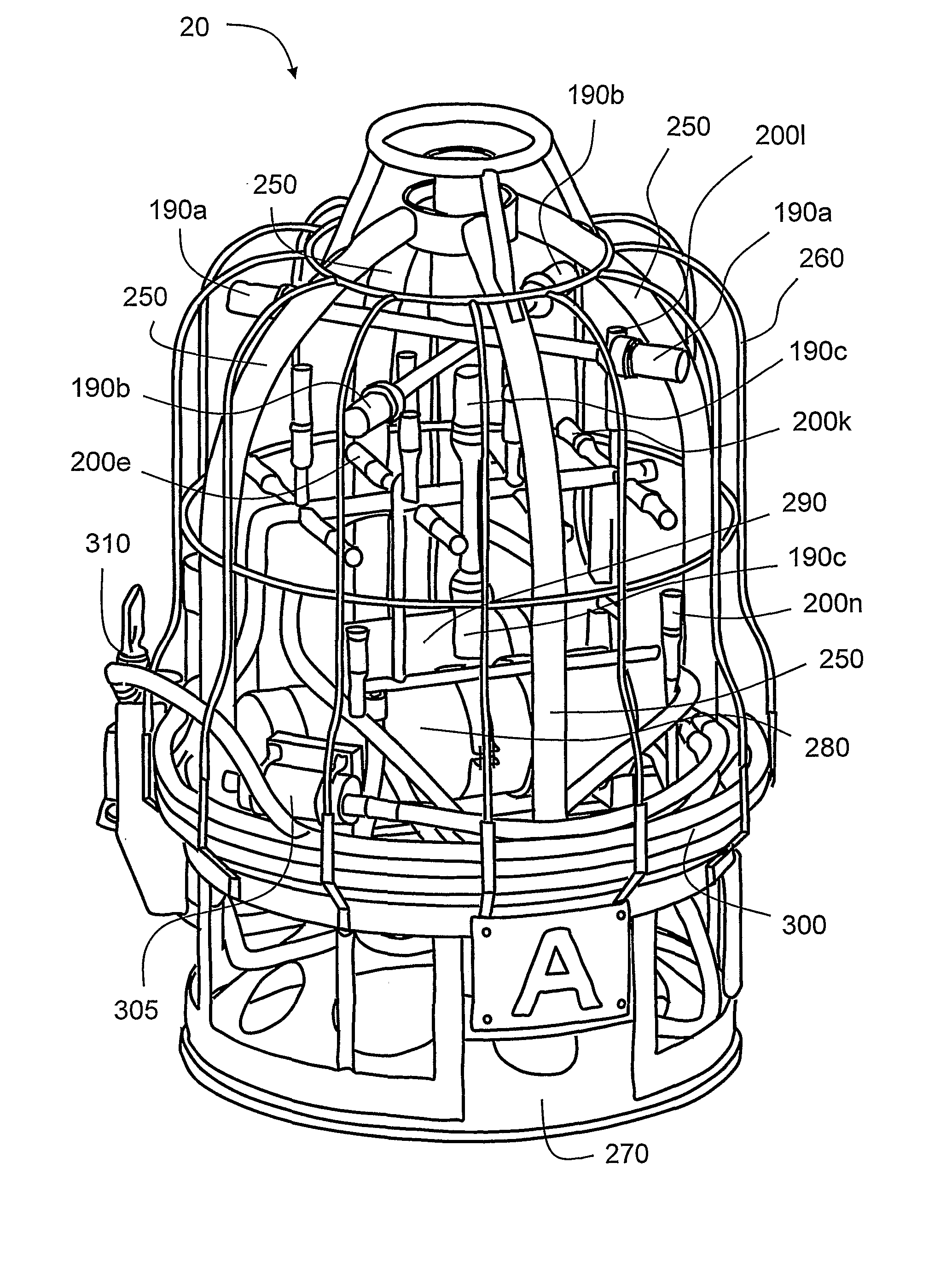
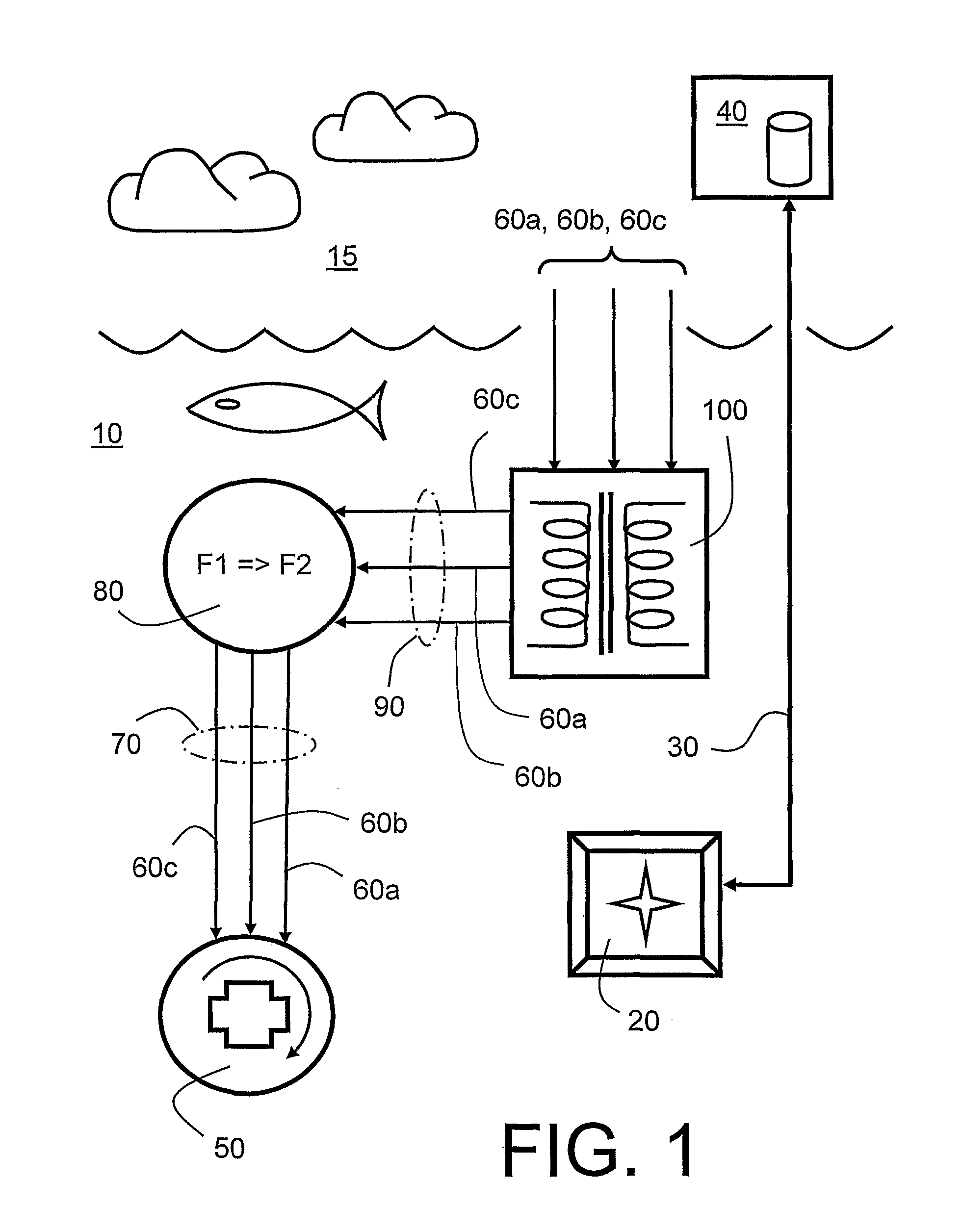
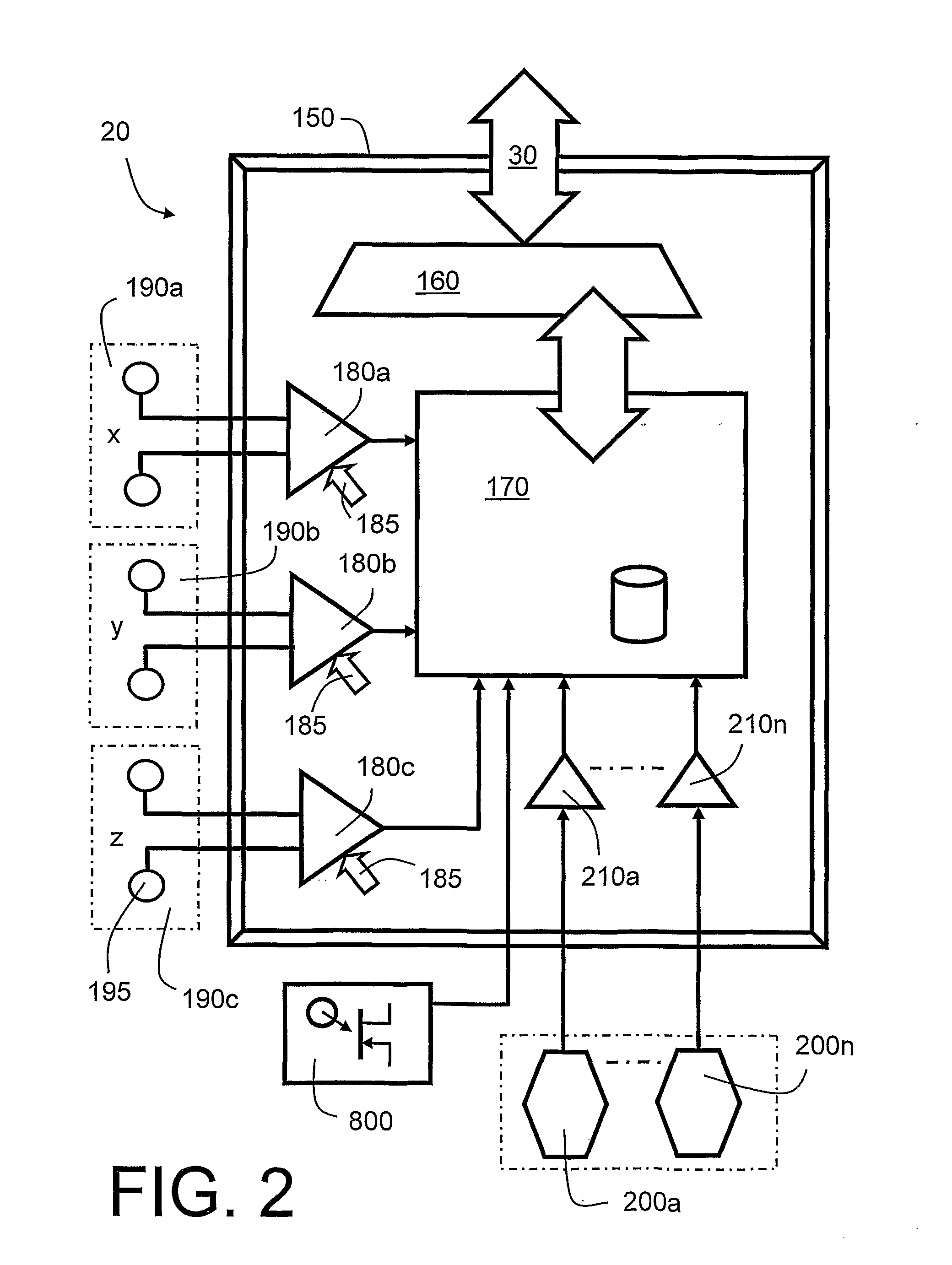
There is provided an underwater measurement system (20, 30, 40) for monitoring an underwater region (10). The system (20, 30, 40) includes a sensor assembly operable to sense at least one physical variable in the region (10) for generating at least one corresponding sensor signal, and a data processing arrangement (170, 510, 520) for processing the at least one sensor signal to generate processed data for presentation and / or logging. The sensor assembly (20) includes one or more voltage sensors (190) configured to sense electric fields present in the underwater region (10) and provide information in the at least one signal indicative of the electric fields. Moreover, the sensor assembly (20) includes one or more hydrophones (200) operable to receive sonic energy generated in the underwater region (10) and to include corresponding information in the at least one sensor signal for communicating to the data processing arrangement (170, 510, 520).
Owner:NAXYS
Cognitive radio sensing method and system
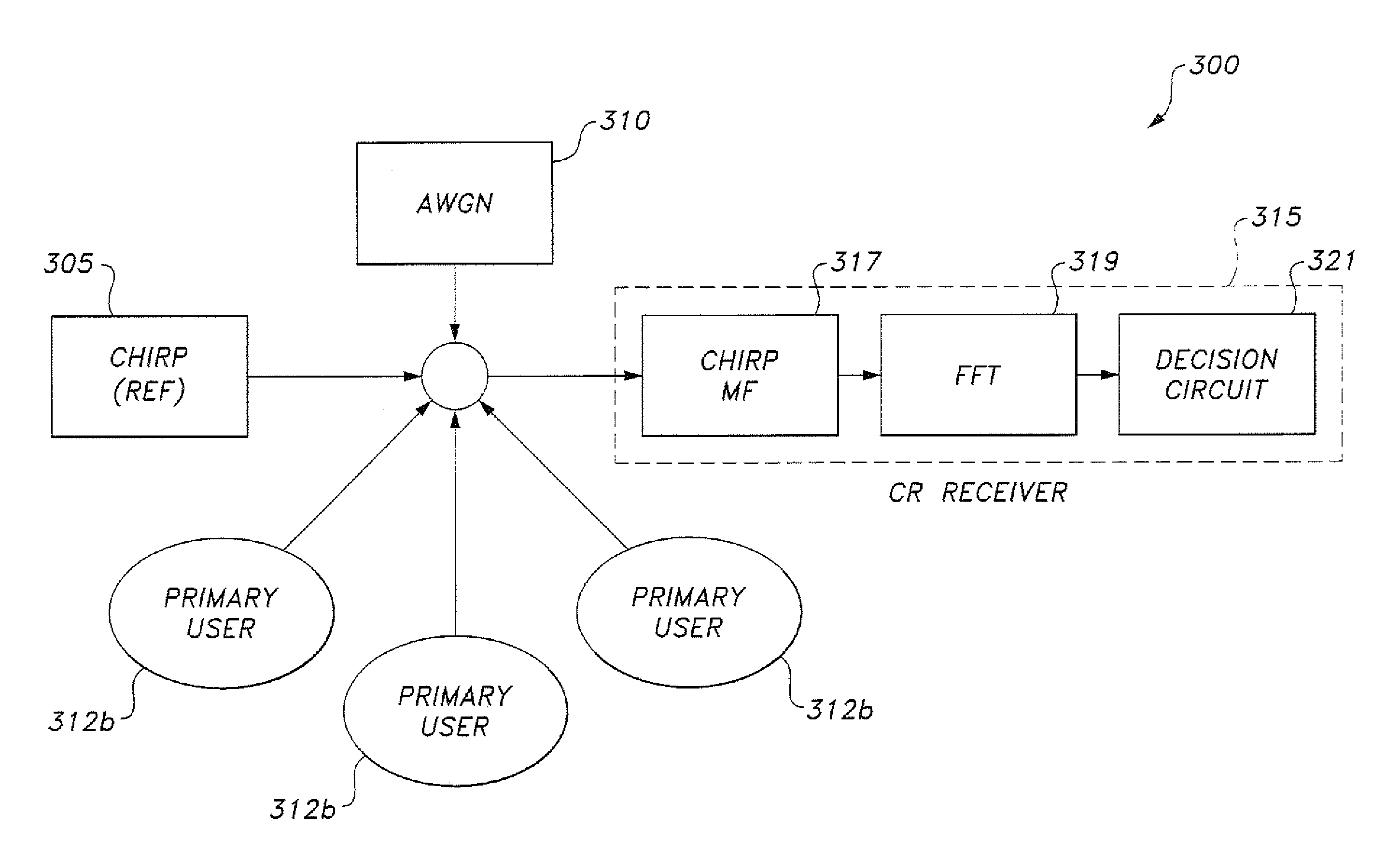
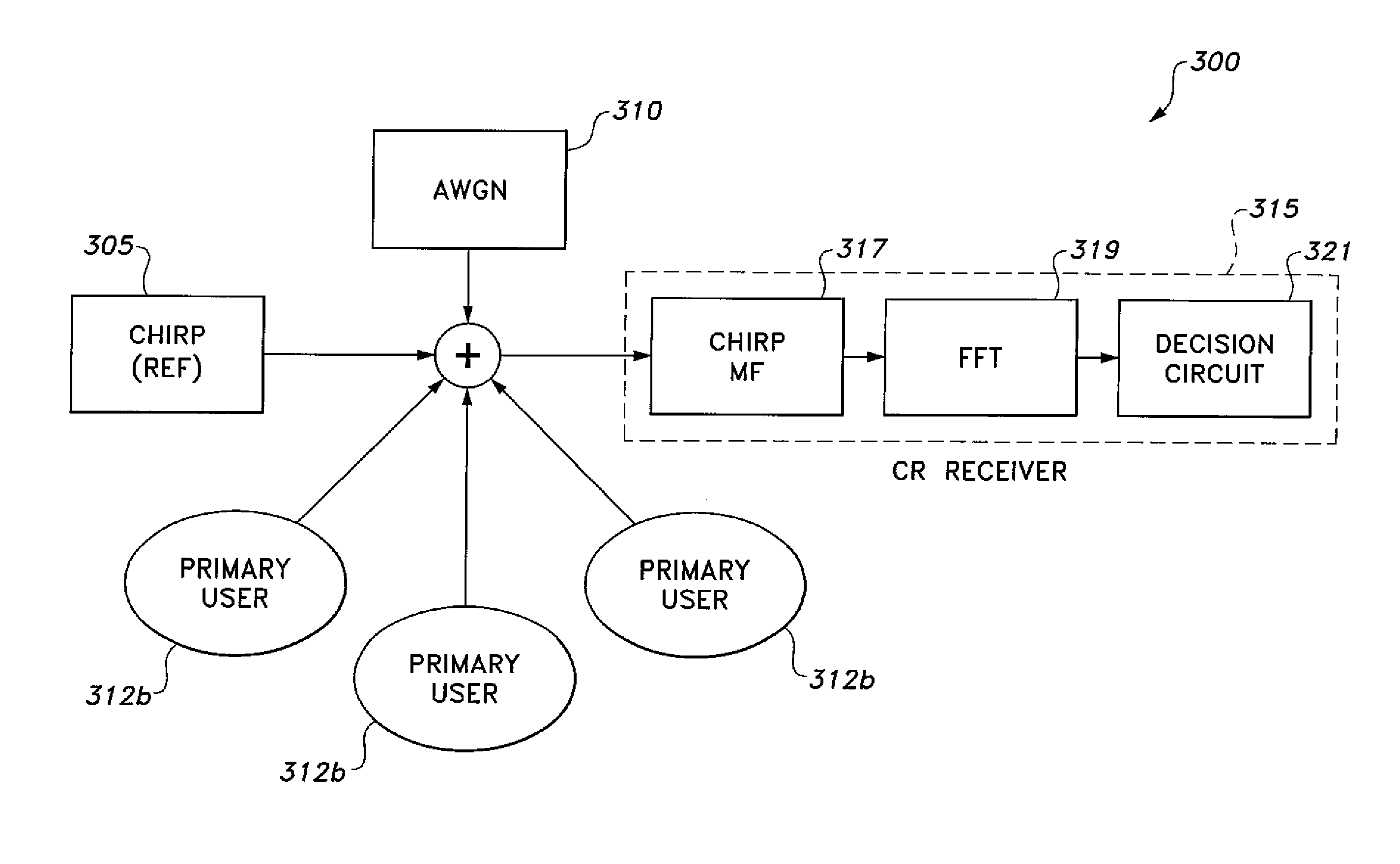
InactiveUS20110263208A1Sensing computational complexityImprove the sense of qualityTransmission monitoringHigh level techniquesFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
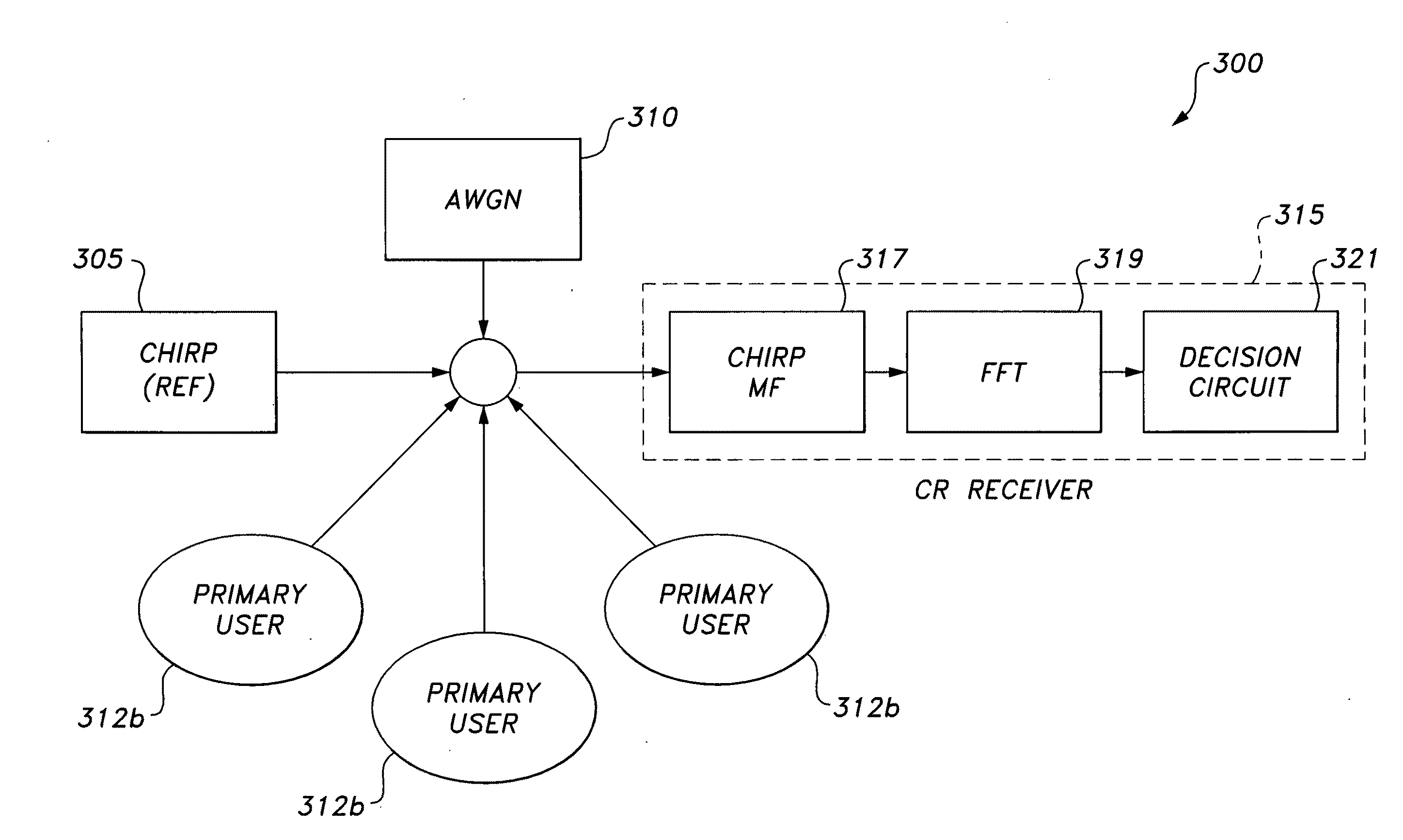
The cognitive radio system and method uses a wideband chirp signal. A cognitive radio base station broadcasts the low power reference wideband chirp signal with bandwidth covering the sensed spectrum. At the receiver, a Fast Fourier Transform is applied to the output of a chirp signal matched filter. The filter output is fed to decision circuitry, where a threshold value is set to decide the minimum spike's amplitude to determine frequencies utilized by primary users. Using reference chirp signal and its matched filter eases sensing computational complexity and improves the quality of sensing, thereby offering enhanced cognition at the CR receiver.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
Image sensing apparatus for fingerprint identification and related decoder circuit
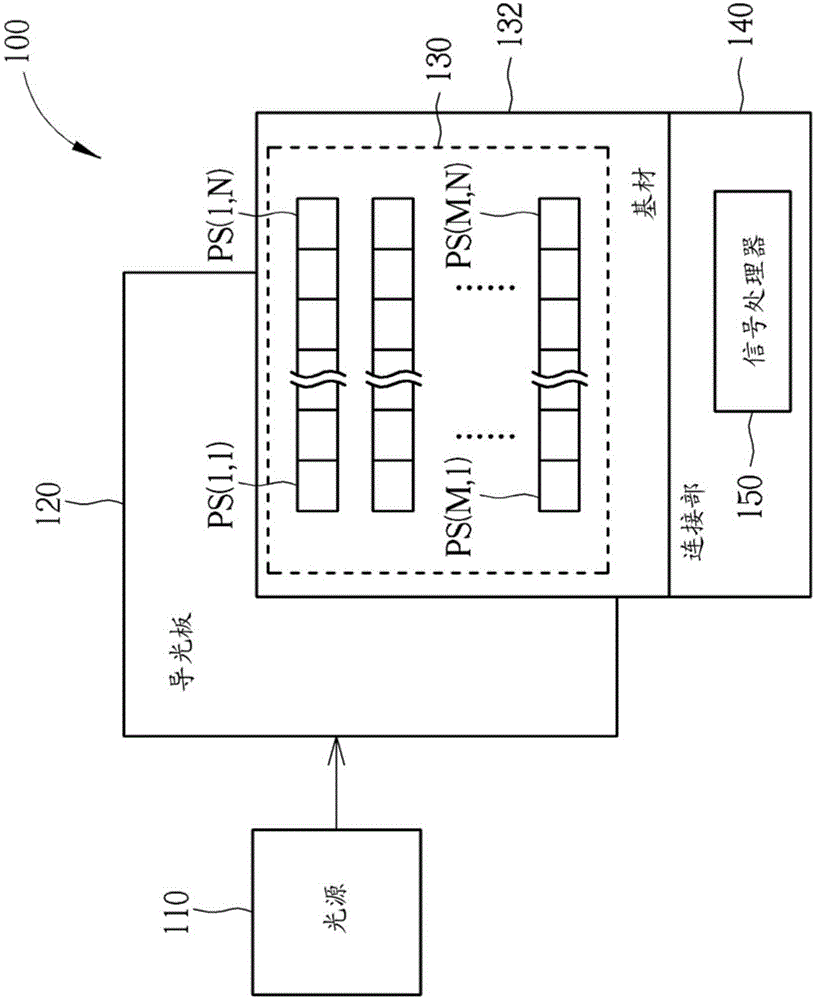
InactiveCN103942559ASimple processLow costSolid-state devicesPrint image acquisitionTotal internal reflectionPhotodetector
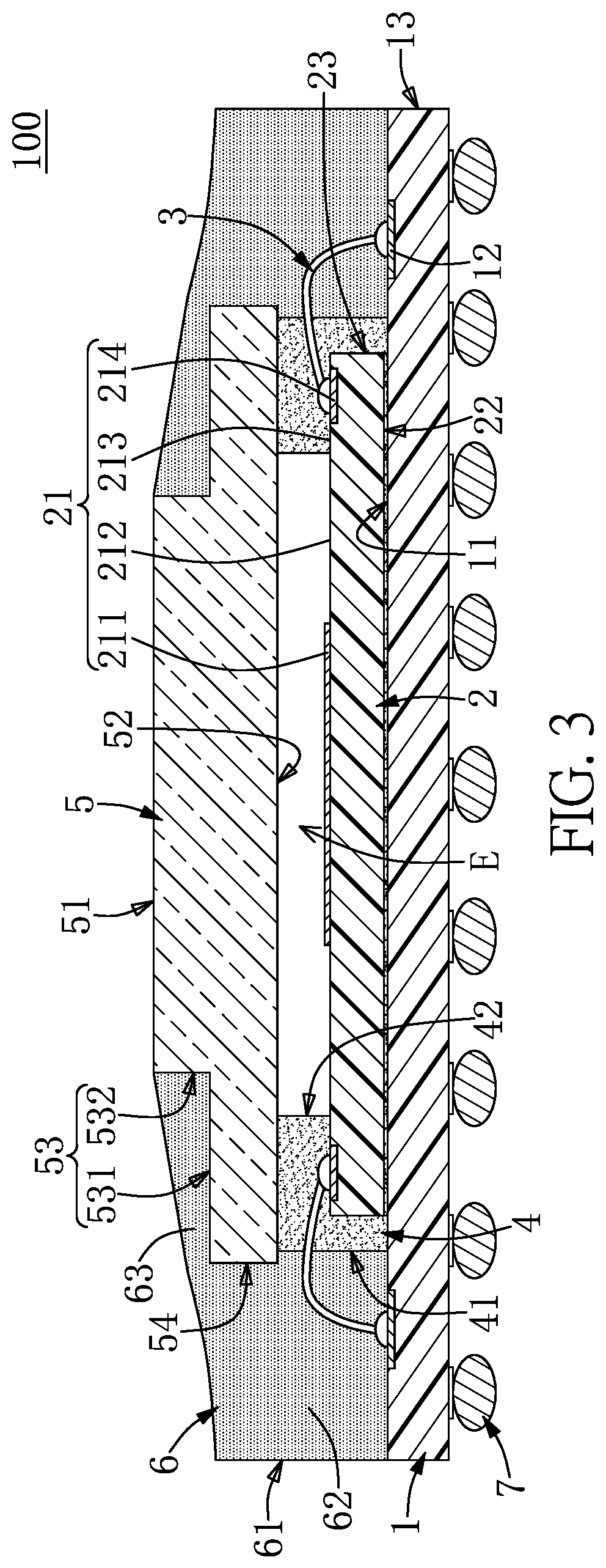
An image sensing apparatus includes a substrate, a light guide plate, a plurality of photosensors and a light source. The substrate has a first side. The light guide plate has a light exit surface and a light entry surface, wherein the light exit surface faces the first side of the substrate. The photosensors are disposed on the first side of the substrate. The light source is disposed near the light entry surface of the light guide plate, wherein light generated from the light source enters the light guide plate through the light entry surface. After entering the light guide plate, the light generated from the light source is incident to the substrate through the light exit surface of the light guide plate, or travels in the light guide plate by total internal reflection.
Owner:EMINENT ELECTRONICS TECH
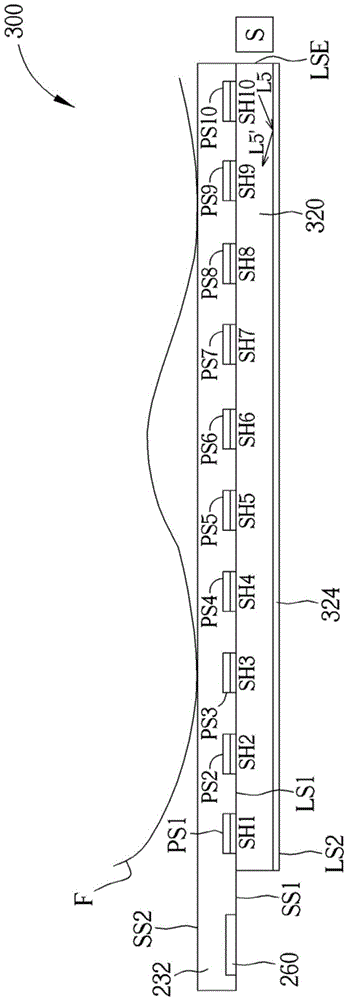
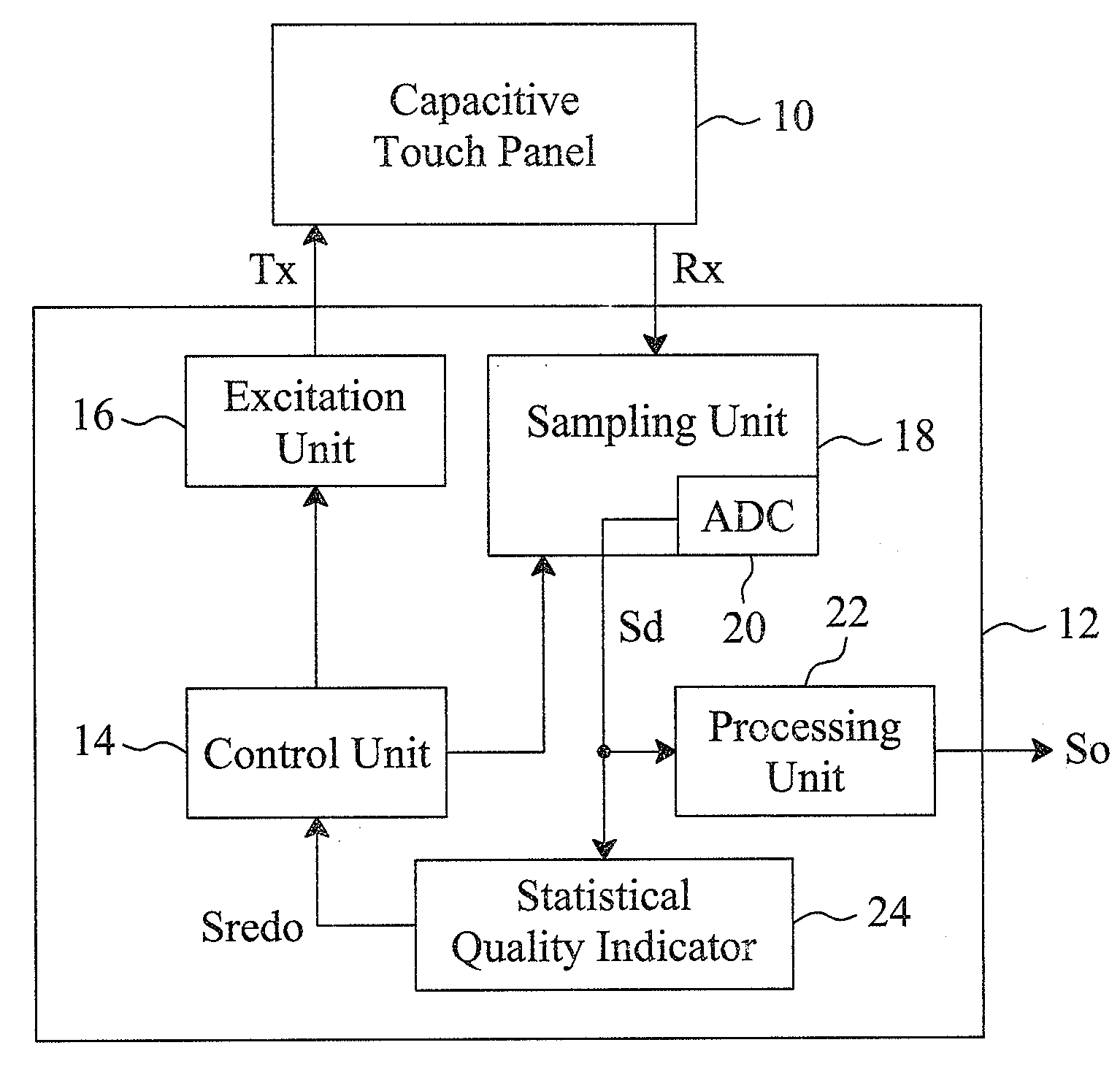
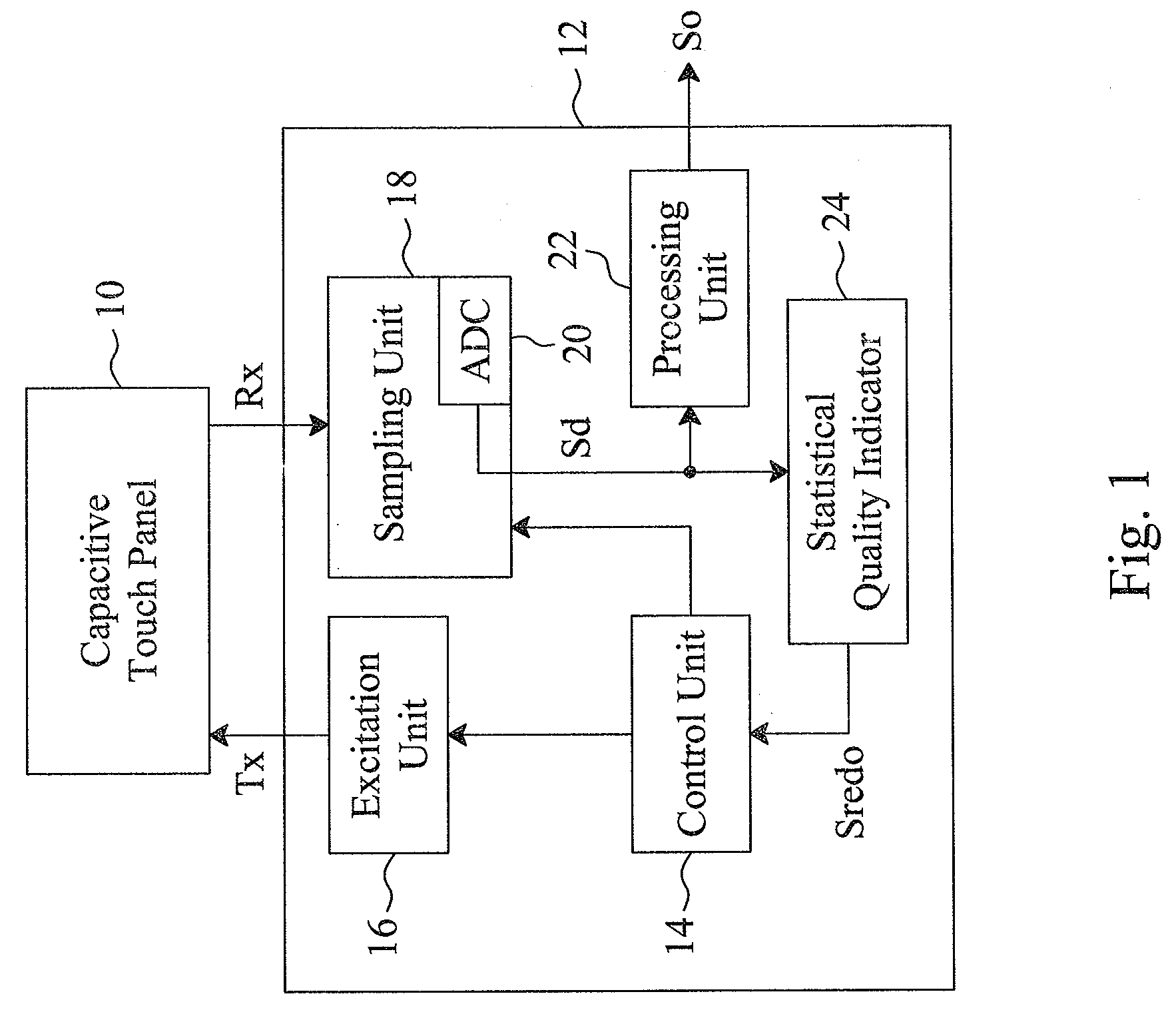
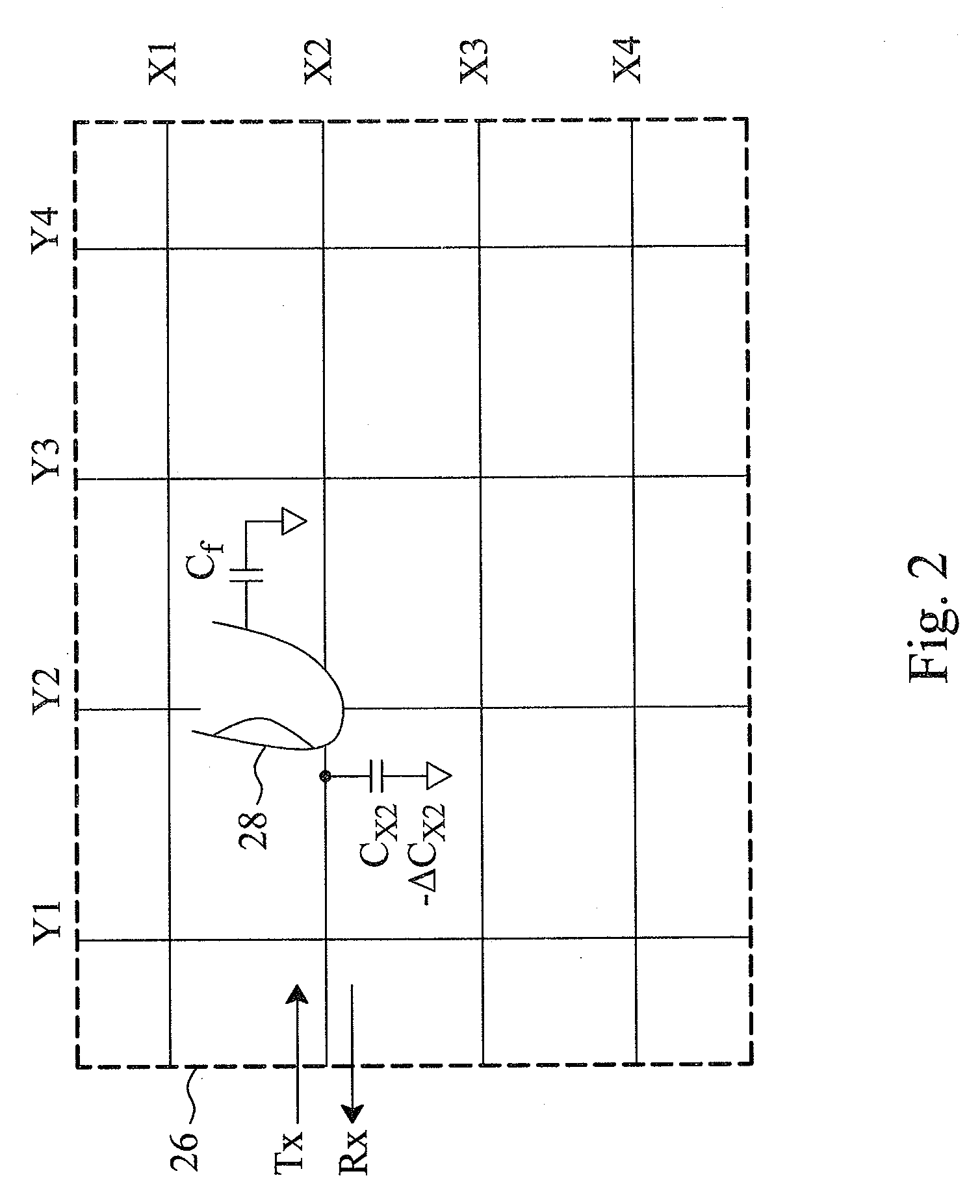
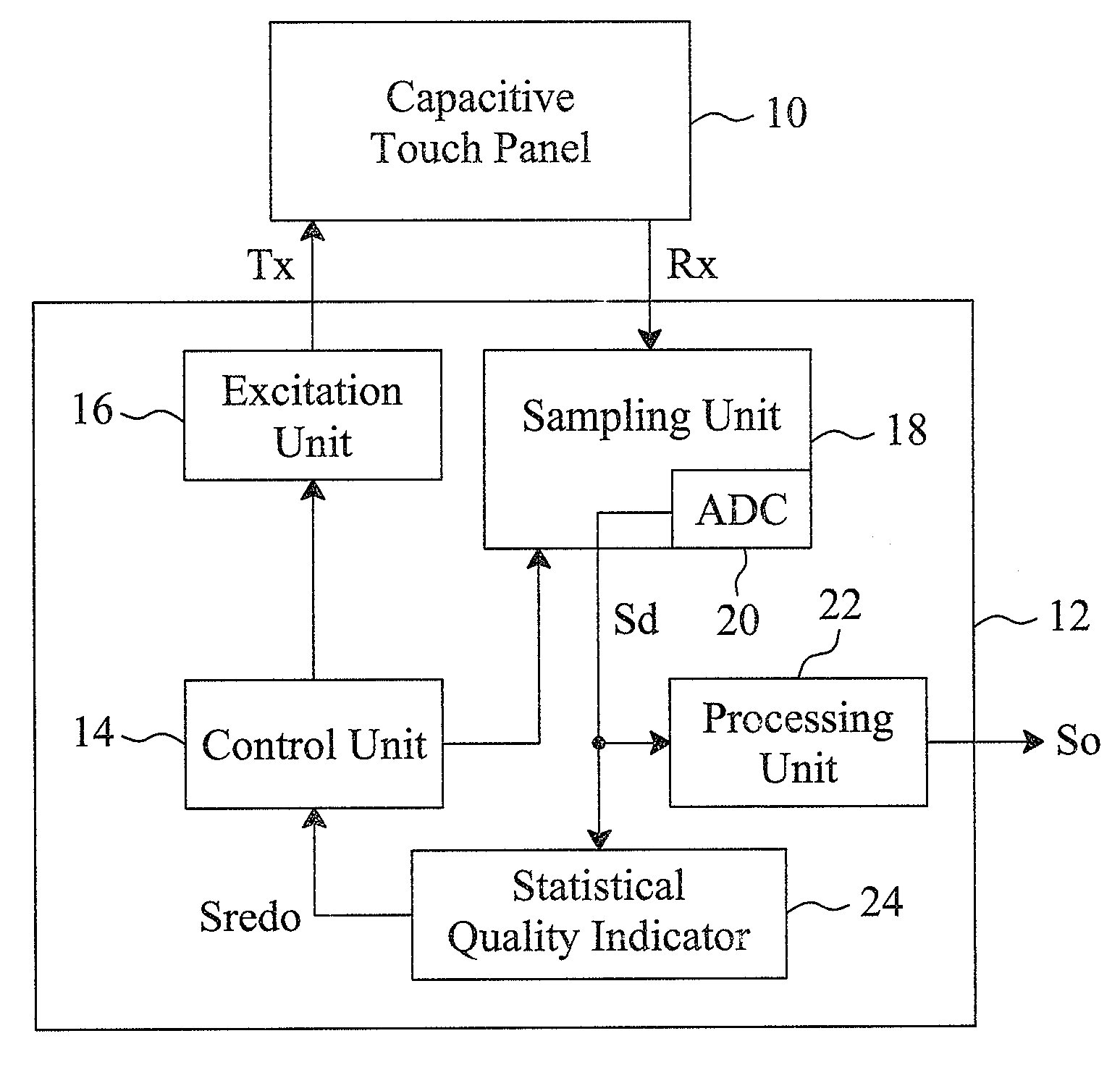
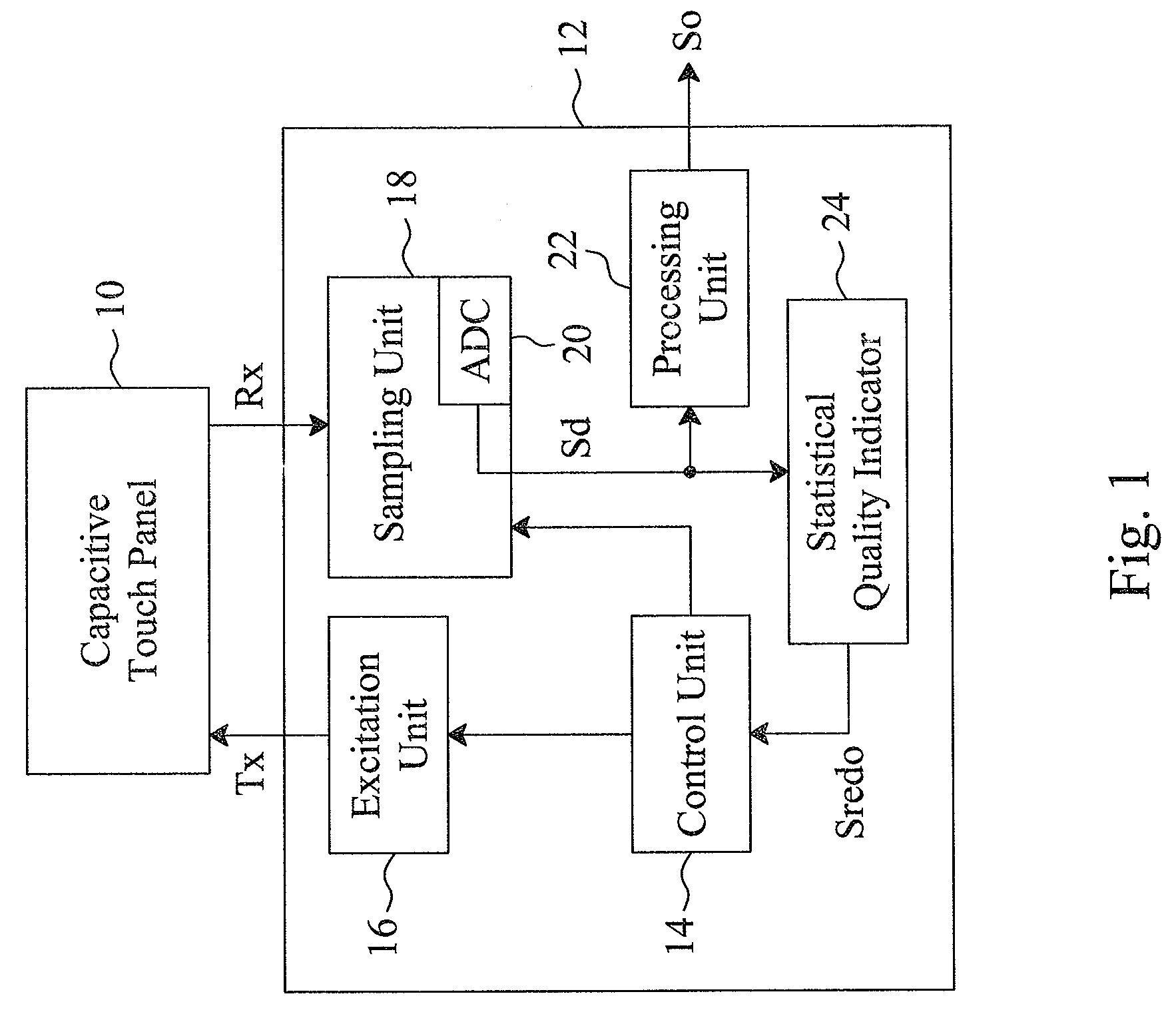
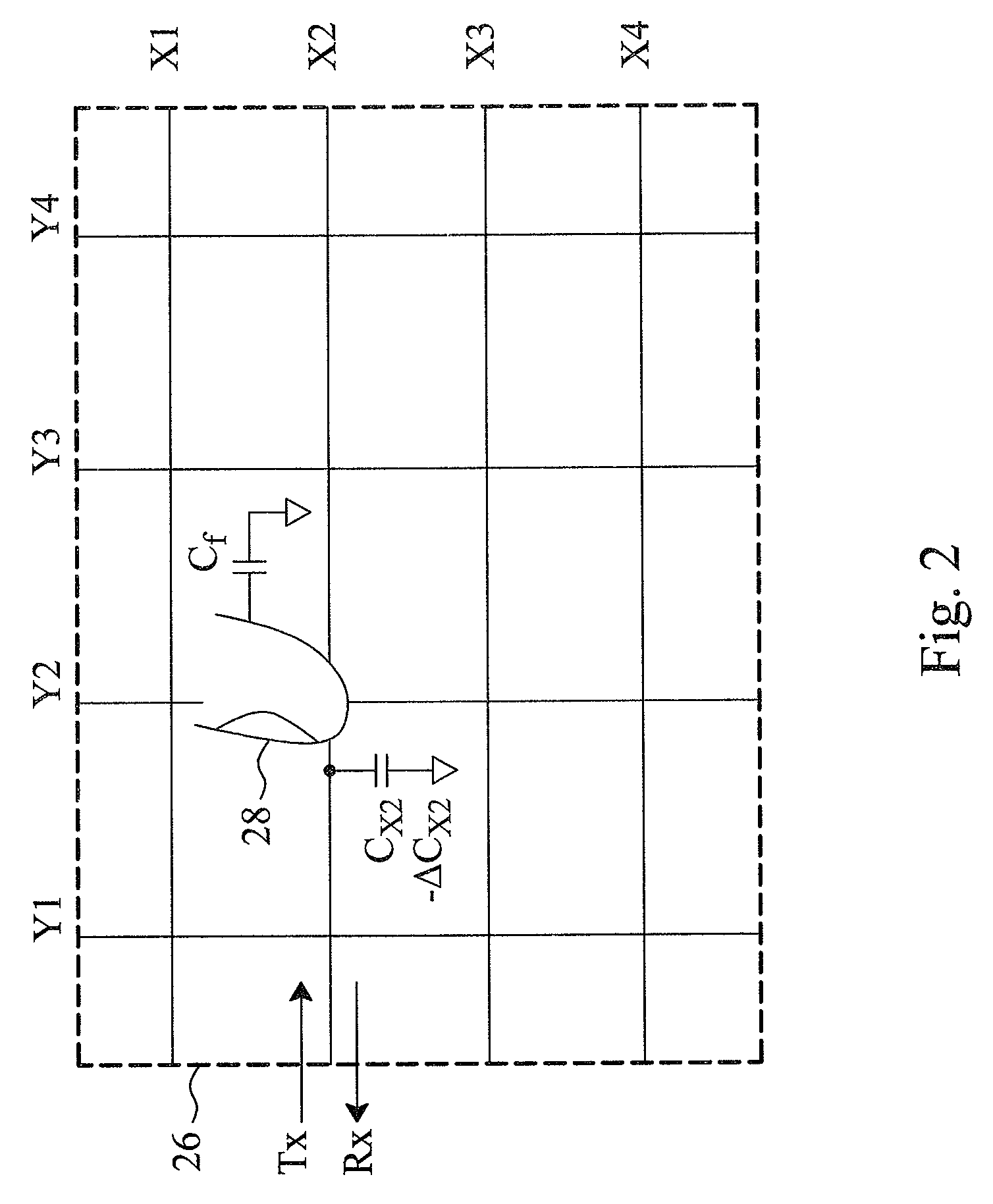
Statistical analyzing method and statistical quality indicator for reliability improvement of a capacitive touch device
InactiveUS20130249852A1Improve sensing qualityInput/output processes for data processingStatistical analysisStatistical quality
For a capacitive touch device having a capacitive touch sensor to be sensed to generate sensed values, a sensing apparatus and method statistically analyze the sensed values generated in a certain time period to evaluate the sensing quality thereof, discard the poor reliable sensed values, and re-sense the capacitive touch sensor to generate new sensed values, by which the resultant output signal will have improved reliability.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Sensing devices
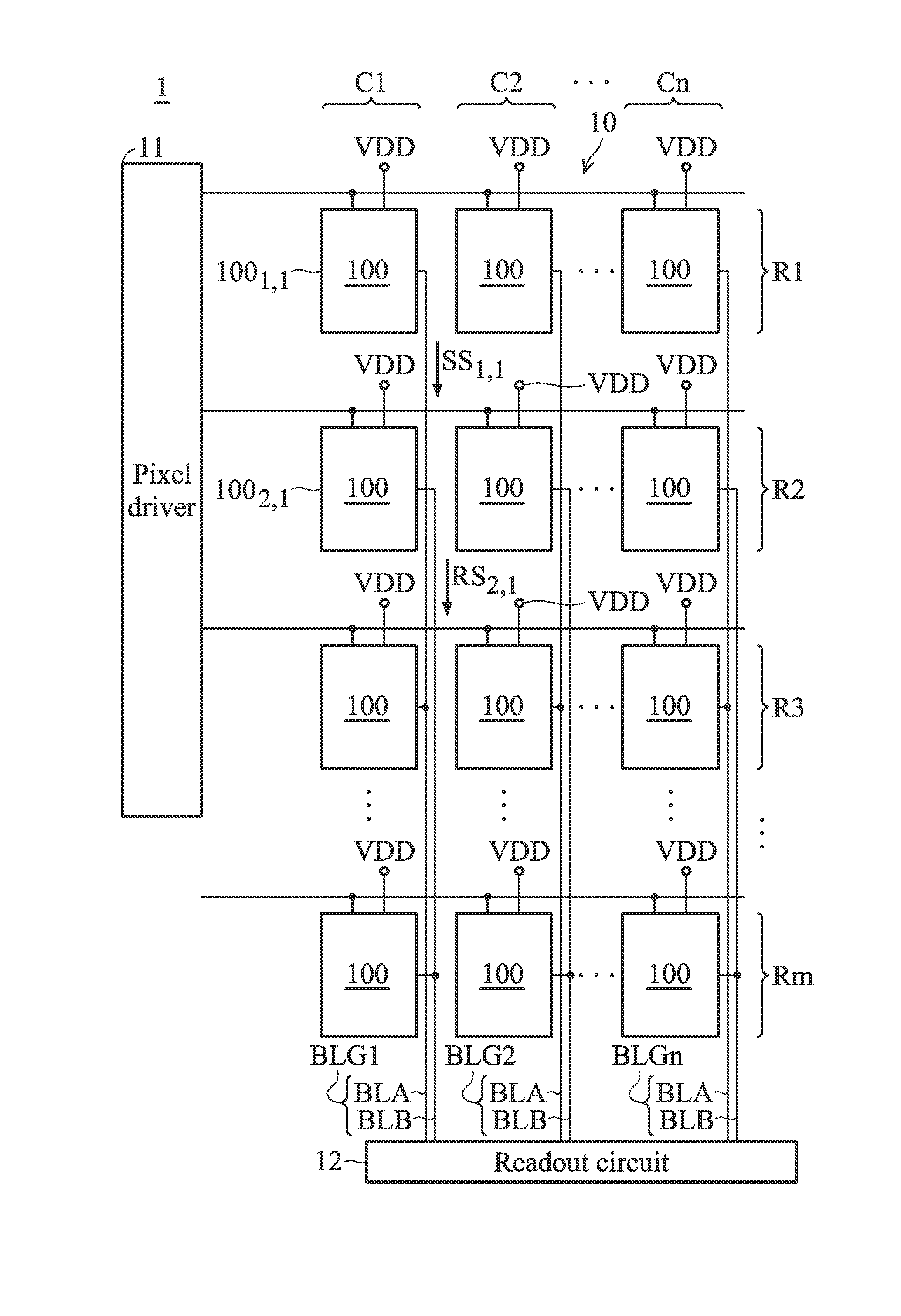
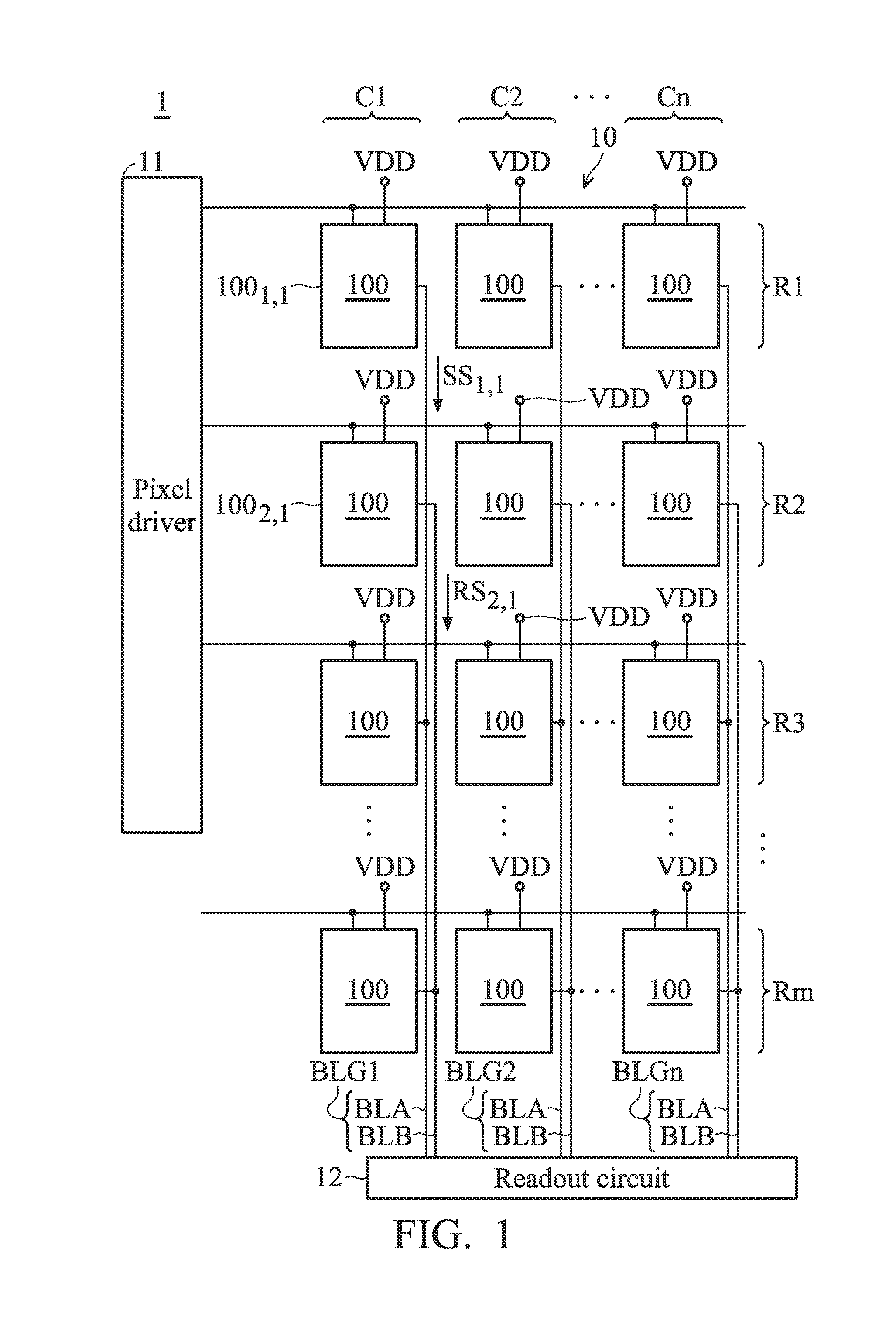
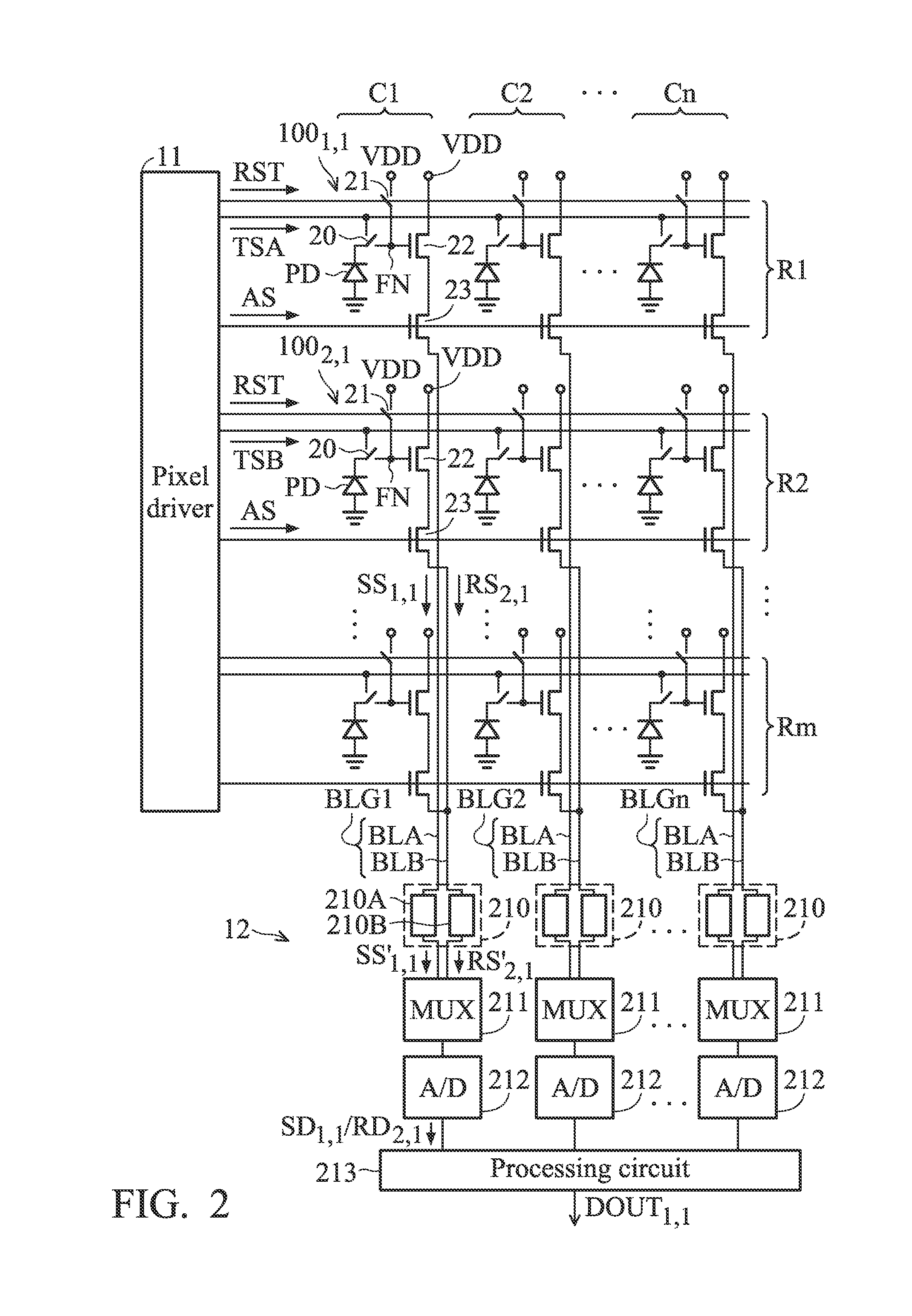
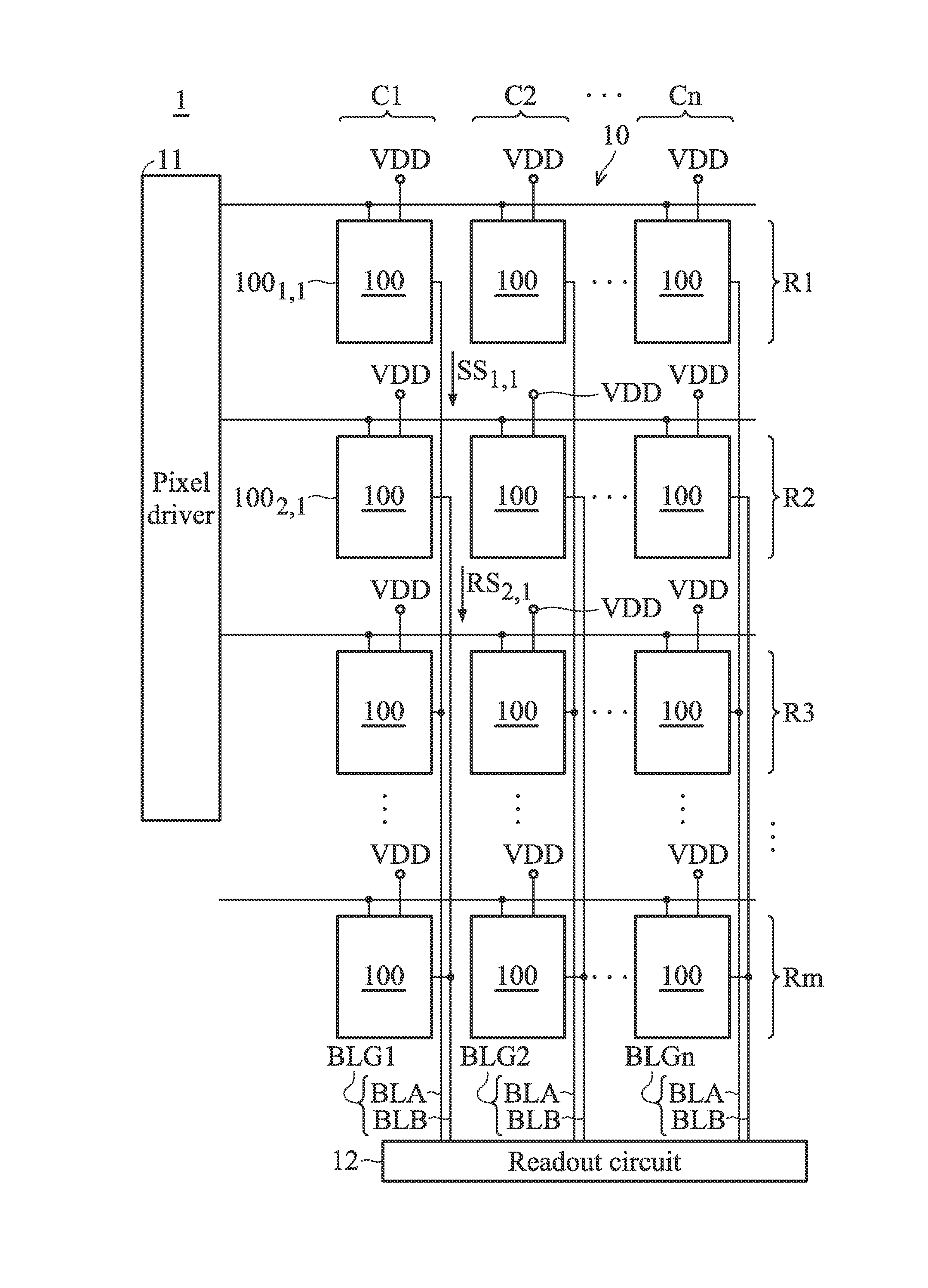
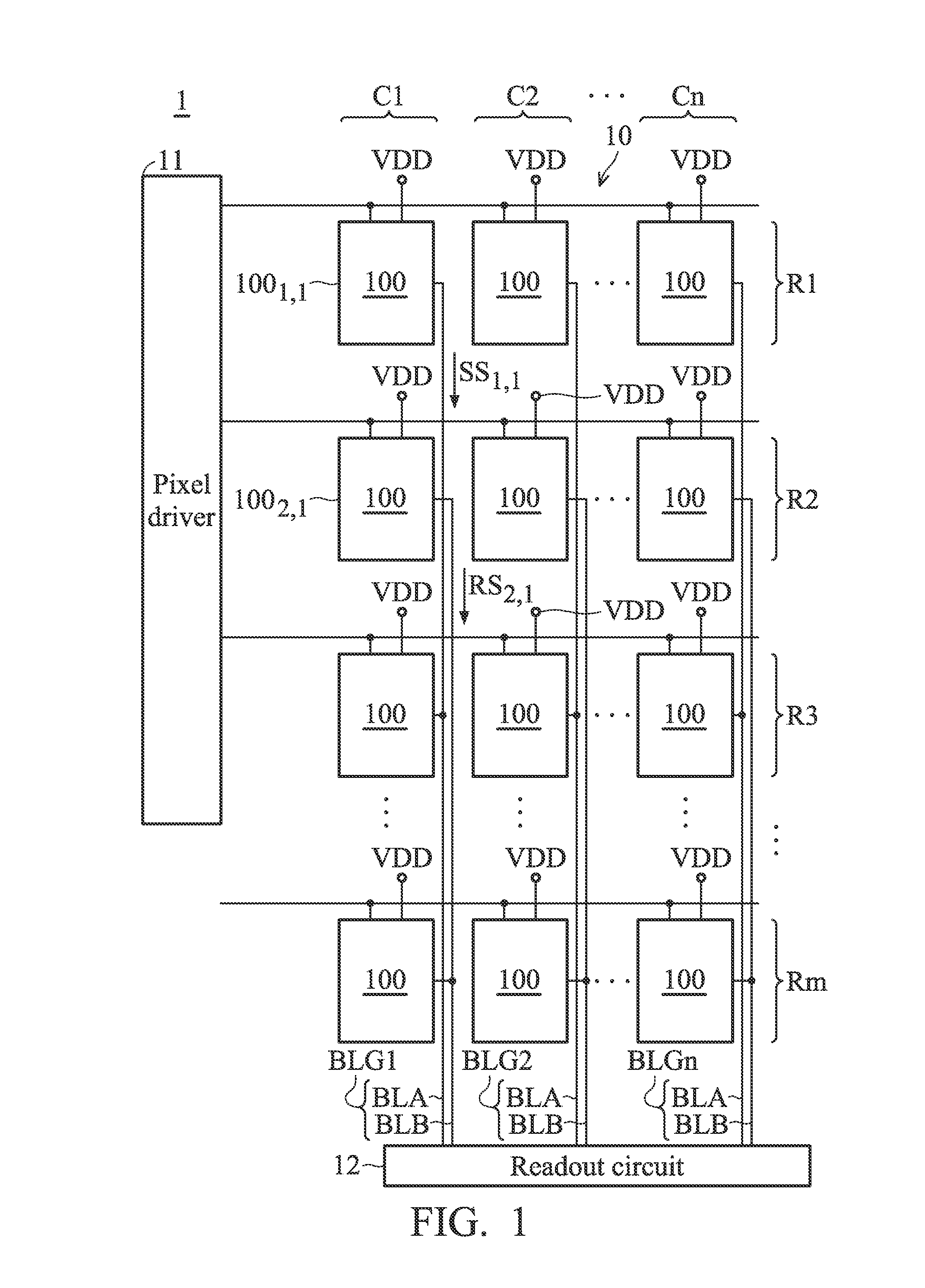
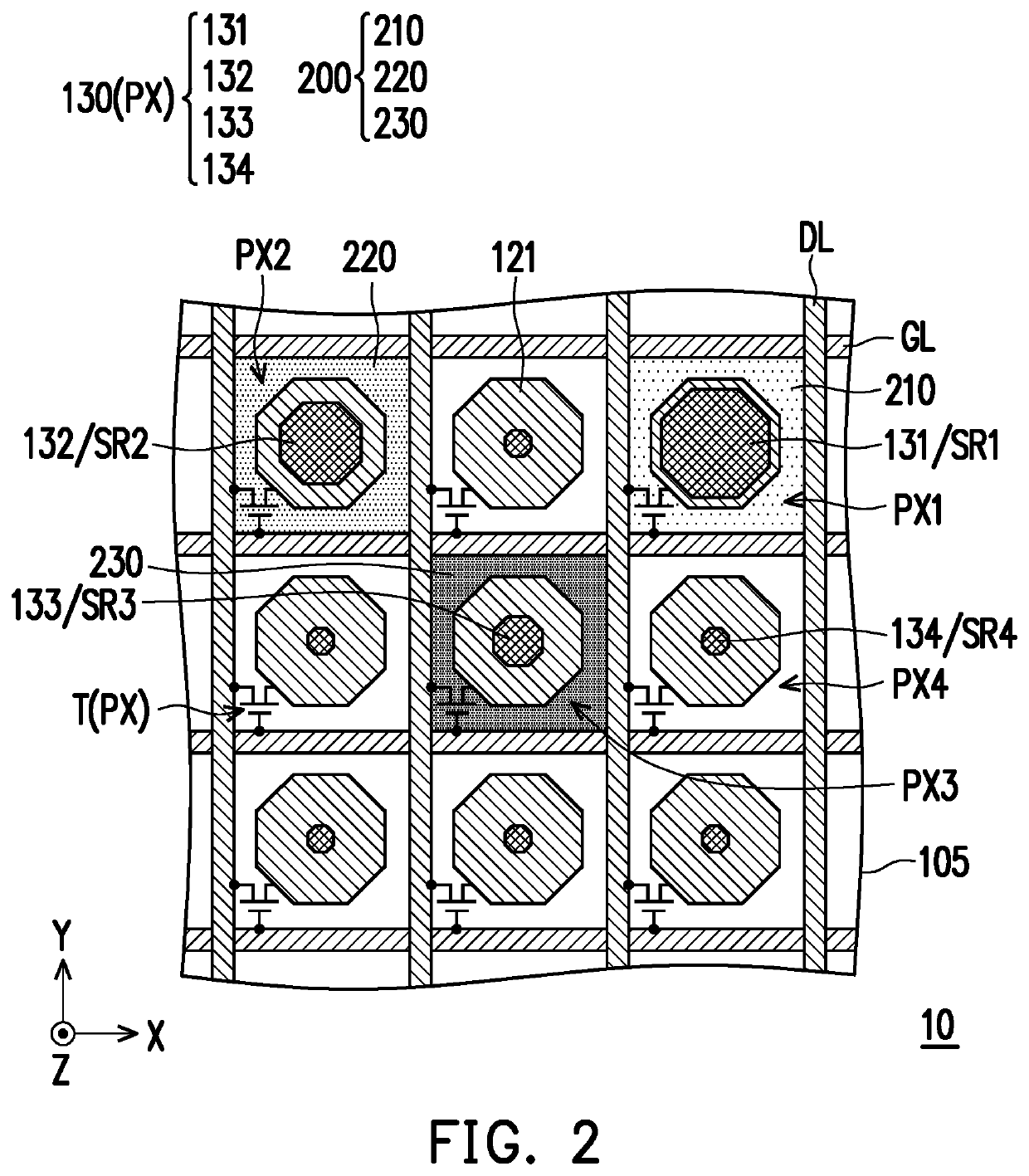
ActiveUS9148605B1Improve the sense of qualityReduce Power NoiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer sciencePixel array
A sensing device is provided. The sensing device includes a plurality of pixel groups and a readout circuit. The pixel groups are arranged on a plurality of rows and a plurality of columns to form a pixel array. The pixel groups include a first pixel group and a second pixel group which are arranged on the different rows and the same column. The readout circuit is coupled to the pixel groups. When the first pixel group is triggered to perform a readout operation to generate a first sensing signal, the second pixel group performs a coupling operation to generate a reference signal. The readout circuit performs a subtraction operation based on the first sensing signal and the reference signal to generate a first readout data corresponding to the readout operation of the first pixel group.
Owner:HIMAX IMAGING LIMITED
Cognitive radio sensing method and system
InactiveUS20120294333A1Improve sensing qualityEases sensing computational complexityTransmission monitoringHigh level techniquesFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
Sensing devices
ActiveUS20150304580A1Reduce Power NoiseImprove sensing qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer sciencePixel array
A sensing device is provided. The sensing device includes a plurality of pixel groups and a readout circuit. The pixel groups are arranged on a plurality of rows and a plurality of columns to form a pixel array. The pixel groups include a first pixel group and a second pixel group which are arranged on the different rows and the same column. The readout circuit is coupled to the pixel groups. When the first pixel group is triggered to perform a readout operation to generate a first sensing signal, the second pixel group performs a coupling operation to generate a reference signal. The readout circuit performs a subtraction operation based on the first sensing signal and the reference signal to generate a first readout data corresponding to the readout operation of the first pixel group.
Owner:HIMAX IMAGING LIMITED
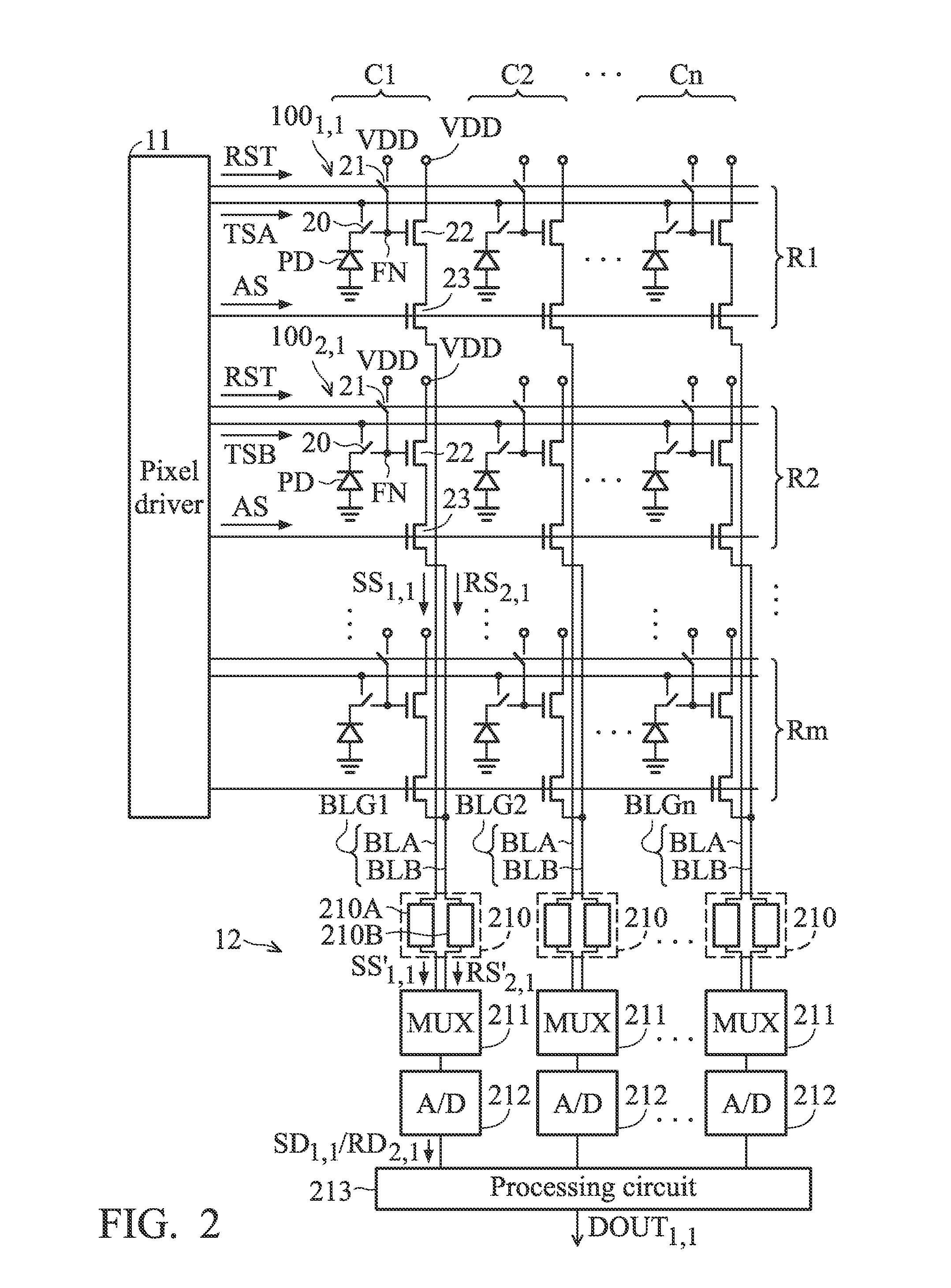
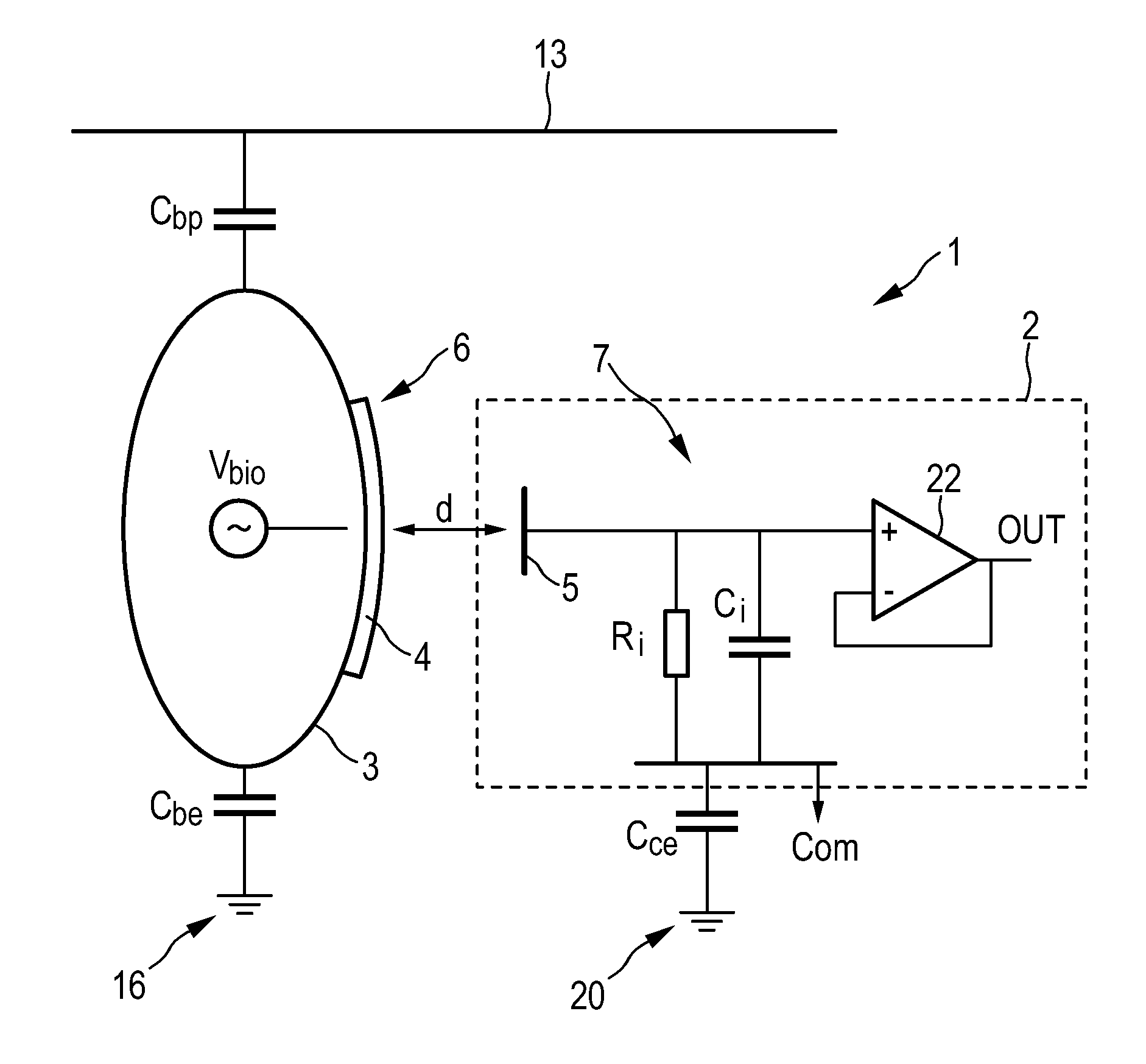
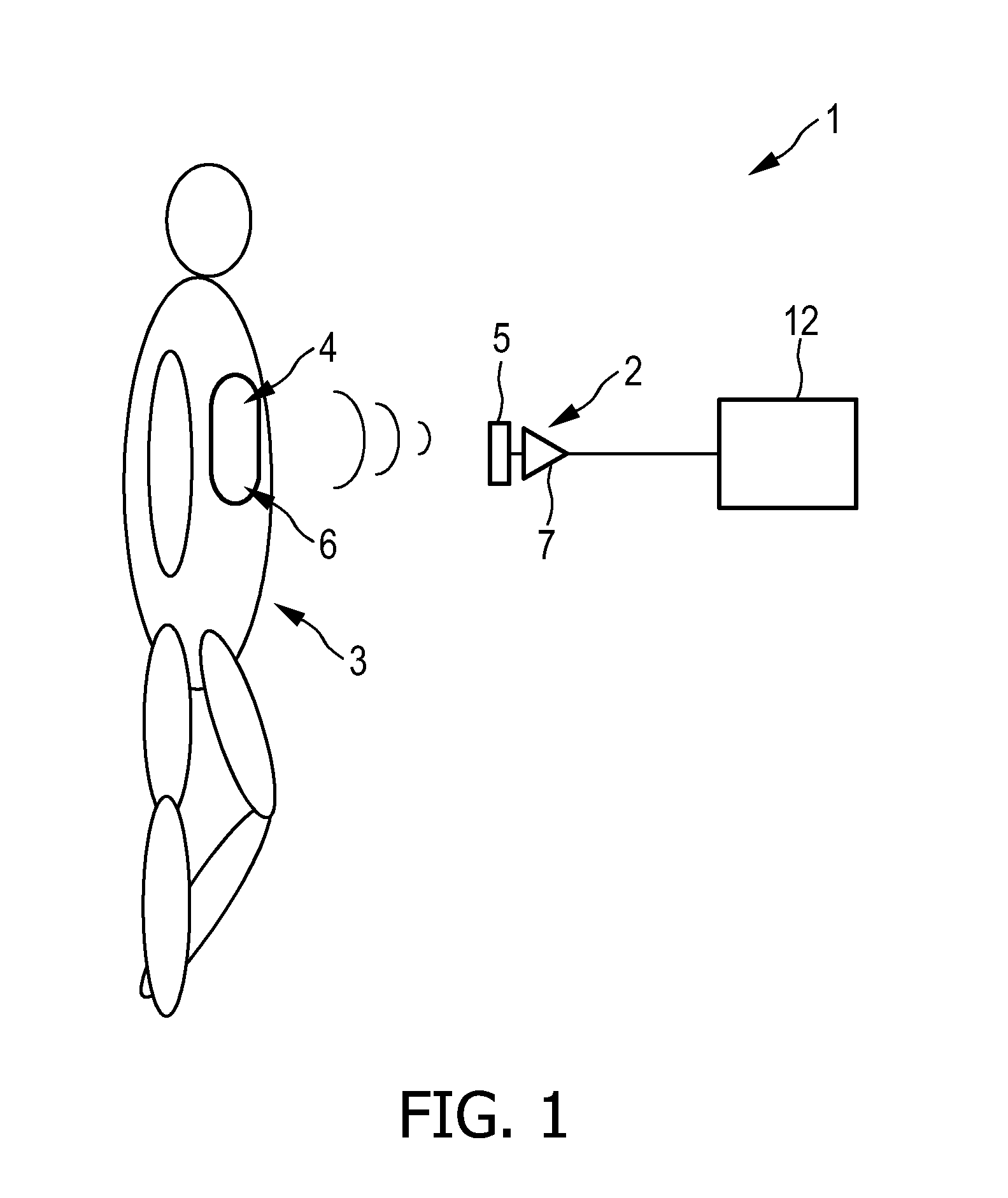
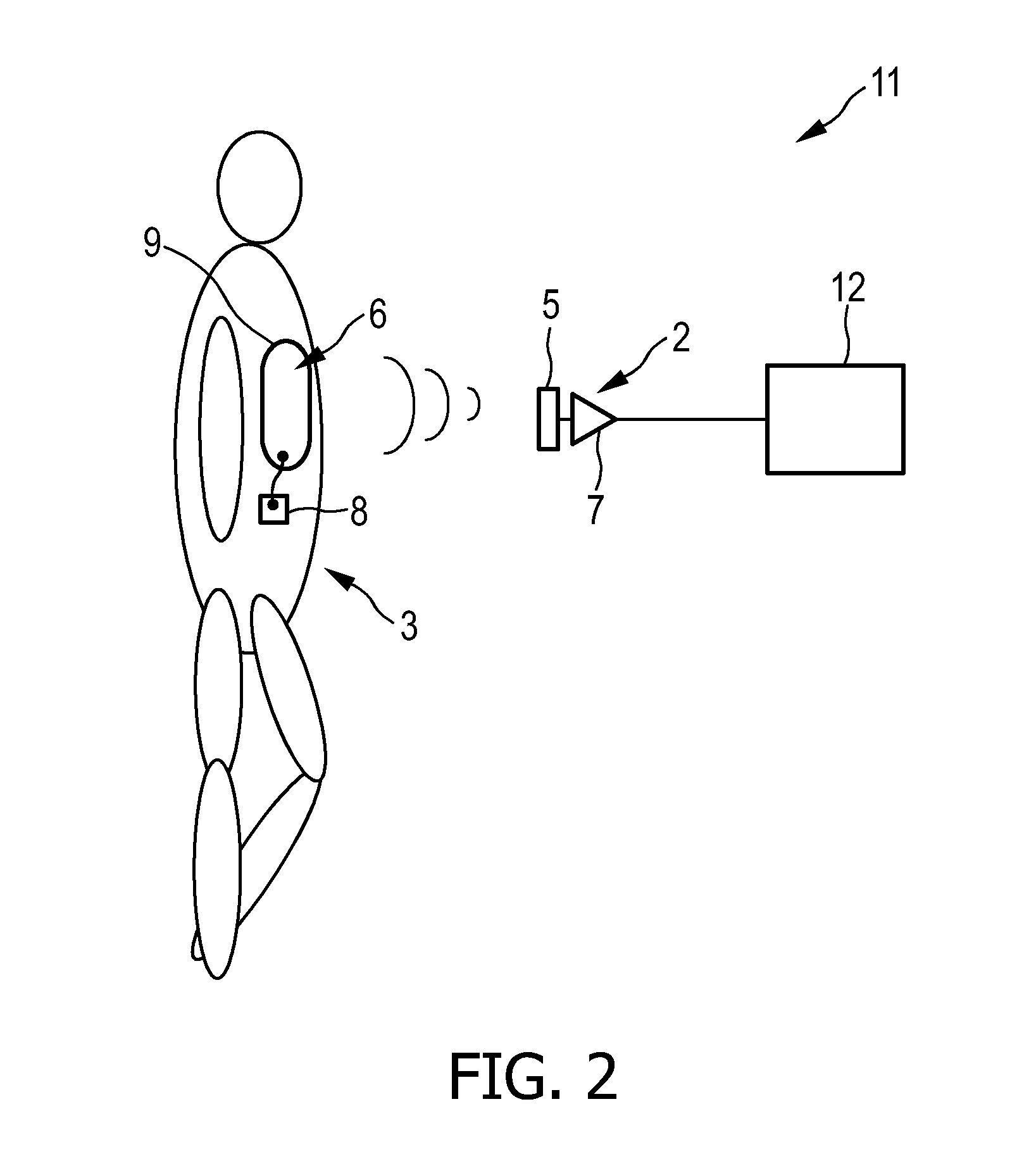
Capacitive sensing system
ActiveUS20120062253A1Improve sensing qualityQuality improvementResistance/reactance/impedenceSensorsCapacitive sensingEngineering
The invention relates to capacitive sensing system (1) for sensing an object. The capacitive sensing system (1) comprises an electrical charge providing unit (4) like an electret foil for providing a permanent electrical charge at a sensing site (6) of the object (3) and a capacitive sensor (2) comprising a sensing electrode (5) for generating a sensing signal by capacitively sensing the object (3) at the sensing site (6) of the object (3). By providing a permanent electrical charge at the sensing site (6) of the object (3), the bias between the object (3) and the sensing electrode (5) of the capacitive sensor (2) is intentionally preferentially made large, thereby increasing the sensitivity towards mechanical motions. The resulting sensing signal substantially caused by these mechanical motions between the object (3) and the sensing electrode (5) is generally larger than a signal generated substantially by an electrophysiological field.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
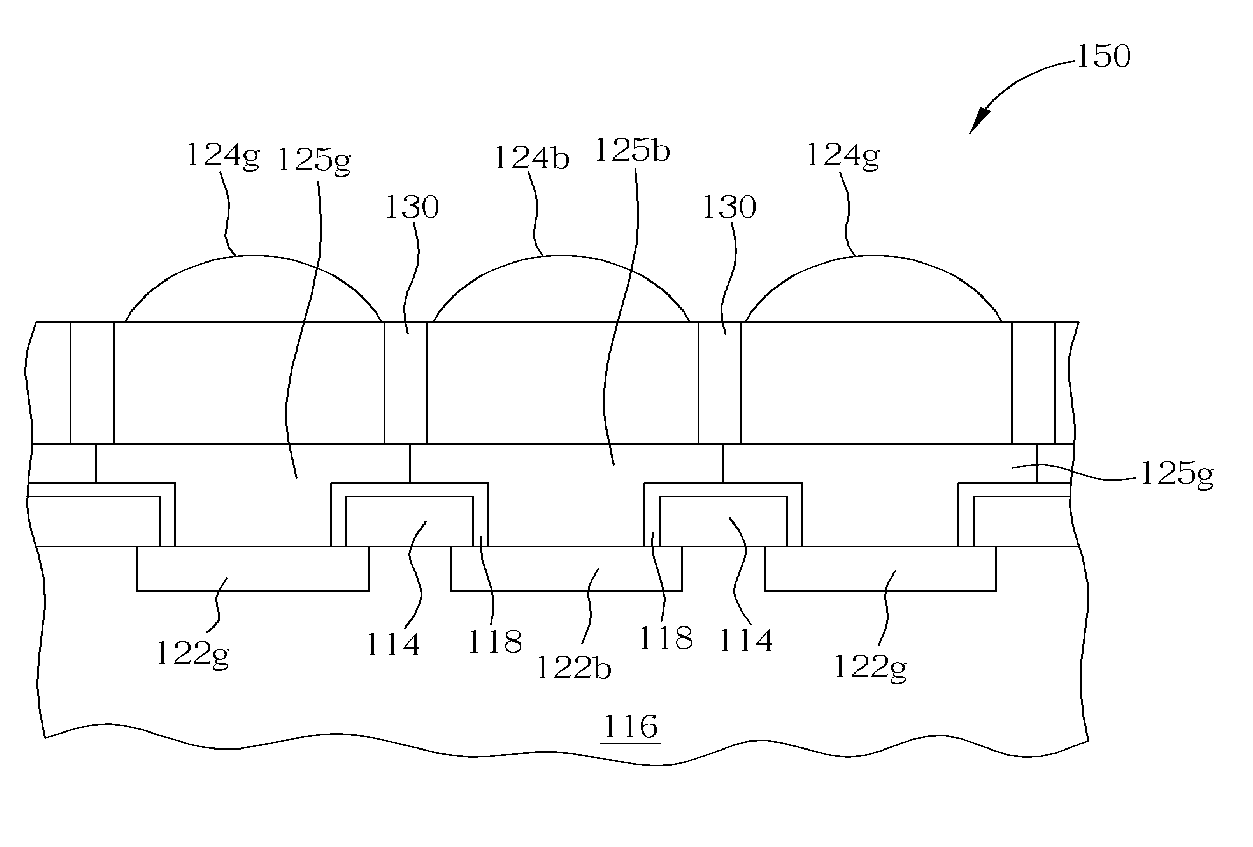
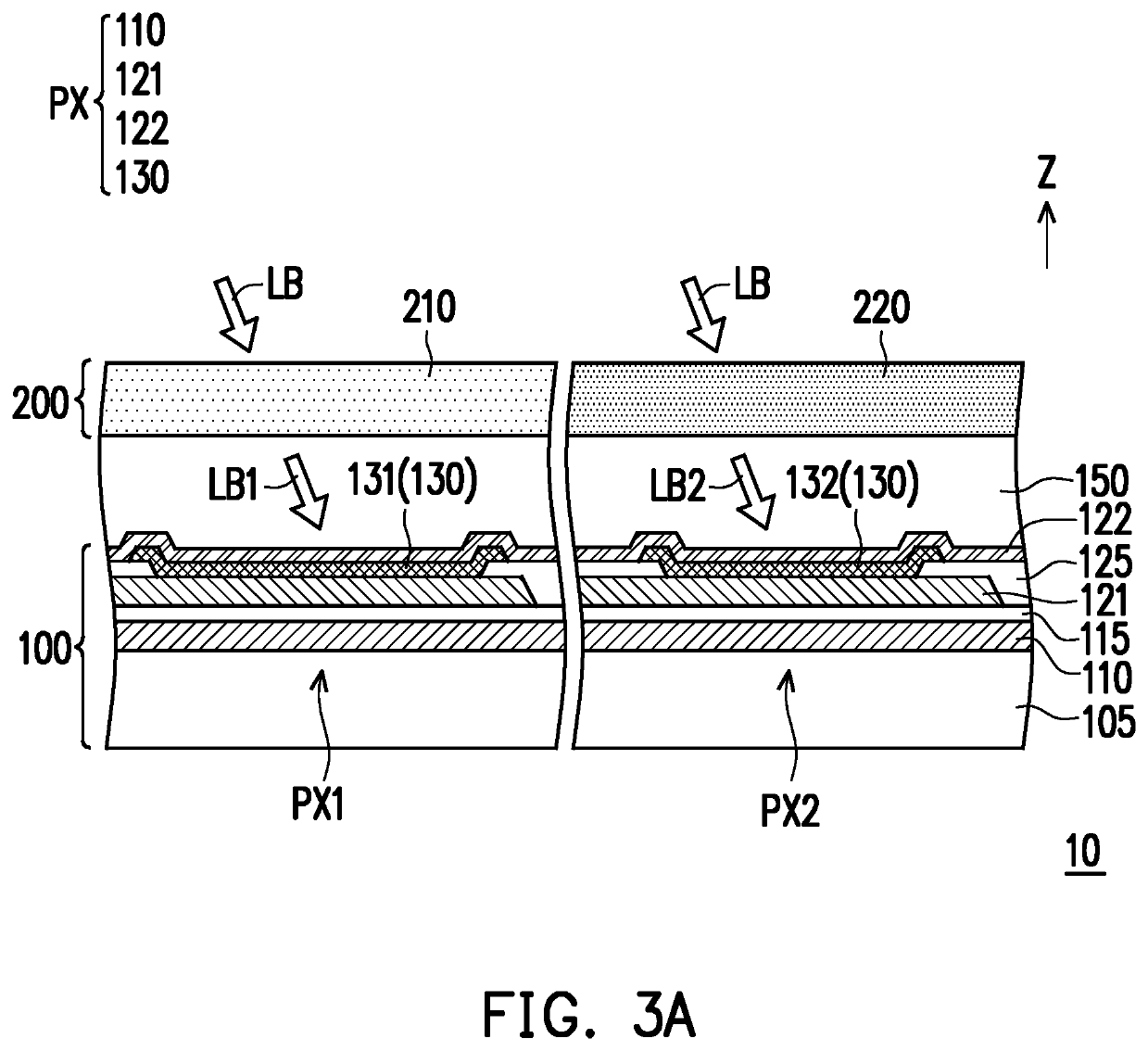
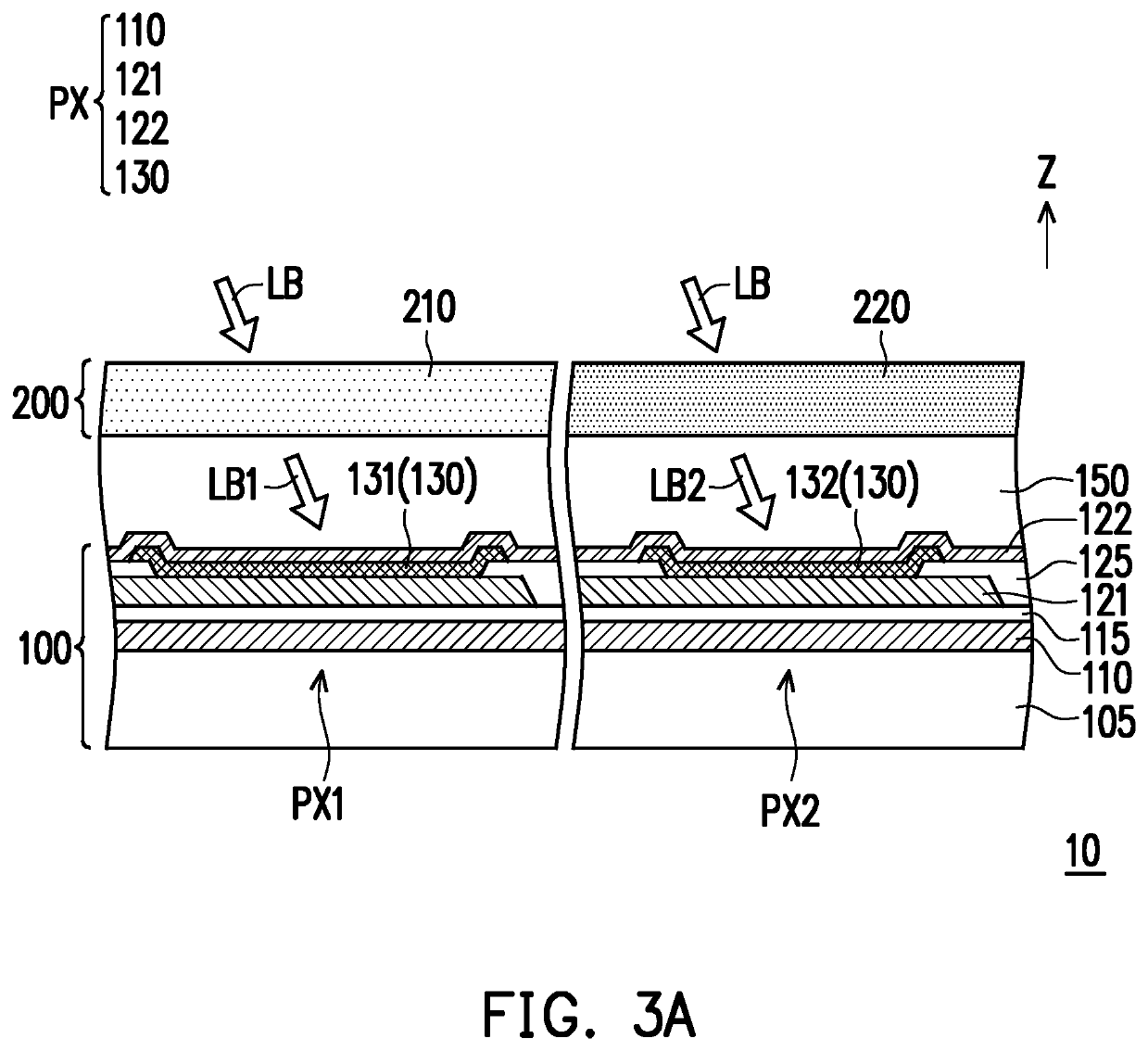
Solid-state image sensor for improving sensing quality and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050202579A1Improve sensing qualitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrolensImage sensor
A method of forming a solid-state image sensor is provided. The method includes the steps of forming a plurality of photosensor elements on a substrate; forming a plurality of color filters on the plurality of photosensors; forming a light blocking member between adjacent color filters; and forming a plurality of microlenses on the plurality of color filters. Each photosensor with each corresponding color filter and microlens is used for receiving an incident light of specific spectrum.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
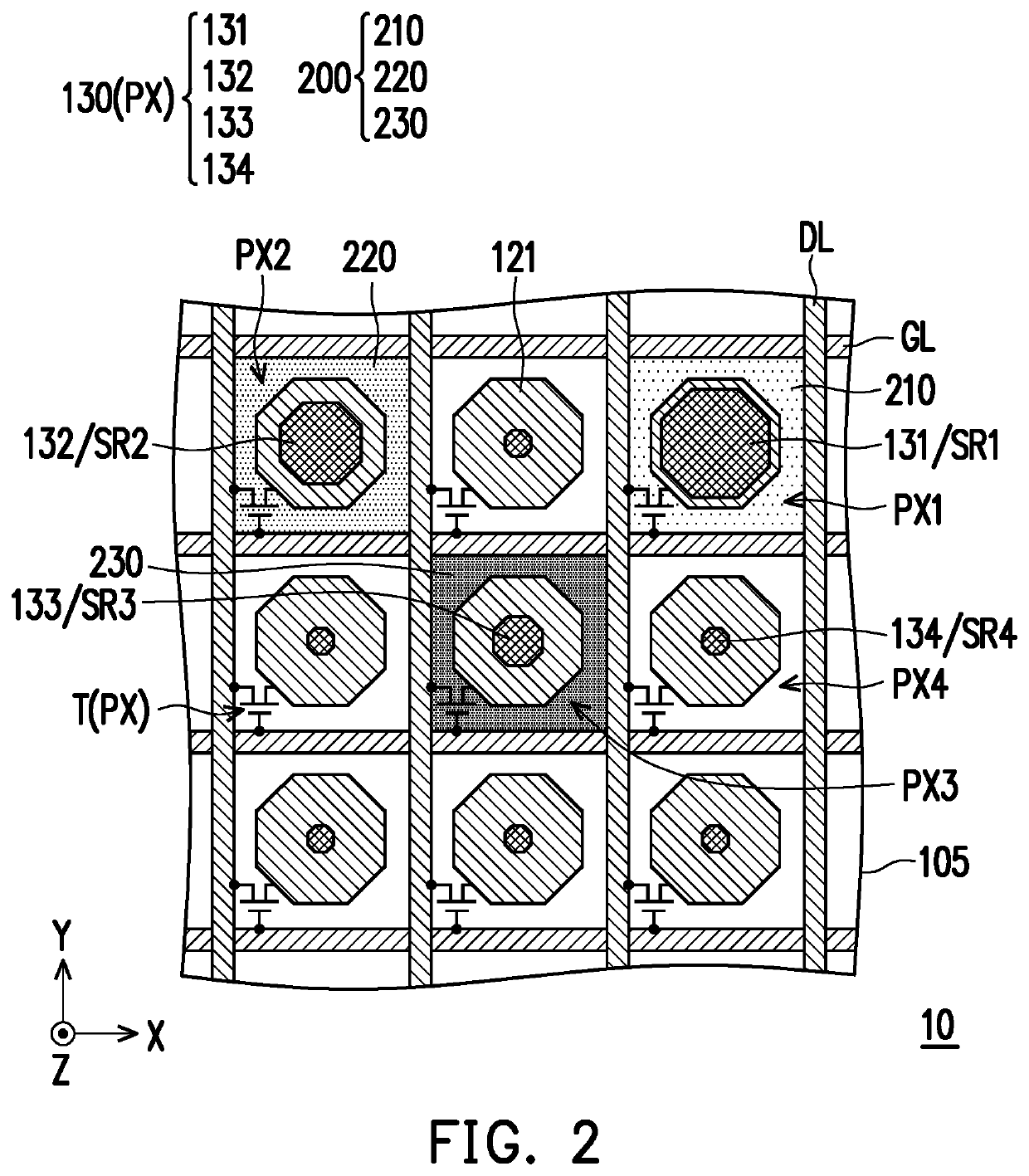
Fingerprint sensing module
ActiveUS20220050990A1Small differenceEnhance the imagePrint image acquisitionNon-linear opticsMaterials scienceOptics
A fingerprint sensing module, including a photosensitive element layer and a color filter layer, is provided. The photosensitive element layer has multiple photosensitive regions, and includes a substrate and multiple photosensitive pixels. The photosensitive pixels have multiple photosensitive patterns overlapping the photosensitive regions. The photosensitive pixels include multiple first photosensitive pixels overlapping multiple first photosensitive regions and multiple second photosensitive pixels overlapping multiple second photosensitive regions. A percentage value of a number of the second photosensitive pixels to a number of the photosensitive pixels is less than 30%. An orthographic projection area of each of the first photosensitive regions is different from an orthographic projection area of each of the second photosensitive regions. The color filter layer has multiple openings overlapping the first photosensitive pixels and multiple first color filter patterns overlapping the second photosensitive pixels.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Cognitive radio sensing method and system
InactiveUS8971911B2Improve Sensing PerformanceImprove sensing qualitySpectral gaps assessmentFrequency-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumEngineering
The cognitive radio system and method uses a wideband chirp signal for characterization of the spectra that a mobile radio may use. A cognitive radio base station broadcasts the low power reference wideband chirp signal with bandwidth covering the sensed spectrum. At the receiver, spectral resolution in the presence of white noise is achieved by cross-correlating the chirp signal with a locally generated copy of itself (i.e., matched filtering). A Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is applied to the output of this matched filtering. The FFT output is fed to a decision circuitry, where a threshold value is set to decide the minimum amplitude of utilized frequencies. This process eases sensing computational complexity and improves the quality of sensing, thereby offering enhanced cognition at the cognitive radio receiver.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
Mutual capacitive touch panel
ActiveUS20200064948A1Improve touch sensing qualityImprove touch accuracyInput/output processes for data processingTouch panelMaterials science
A mutual capacitive touch panel includes a first electrode layer and a second electrode layer. The first electrode layer includes a plurality of first electrode series and a plurality of second electrode series. The second electrode layer includes a plurality of electrode strips, and each electrode strip crosses the first electrode series and the second electrode series. Each first electrode series includes a plurality of first electrodes and a plurality of second electrodes electrically connected with each other, and each first electrode and a corresponding one of the second electrodes are disposed abreast and form an electrode set. Each second electrode series includes a plurality of third electrodes electrically connected with each other, and each electrode set and each third electrode are arranged alternately along a direction.
Owner:ILI TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Capacitive sensing device
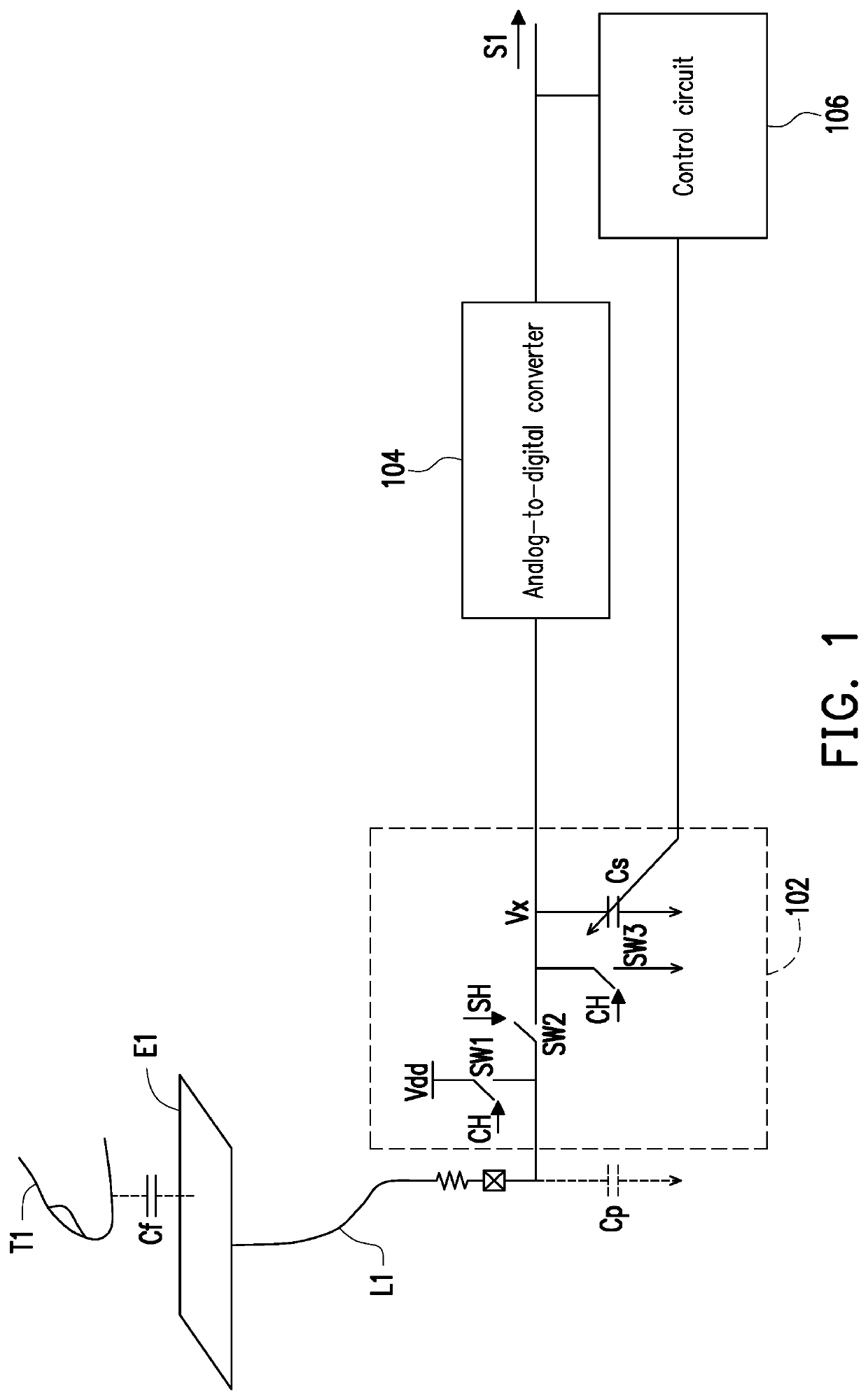
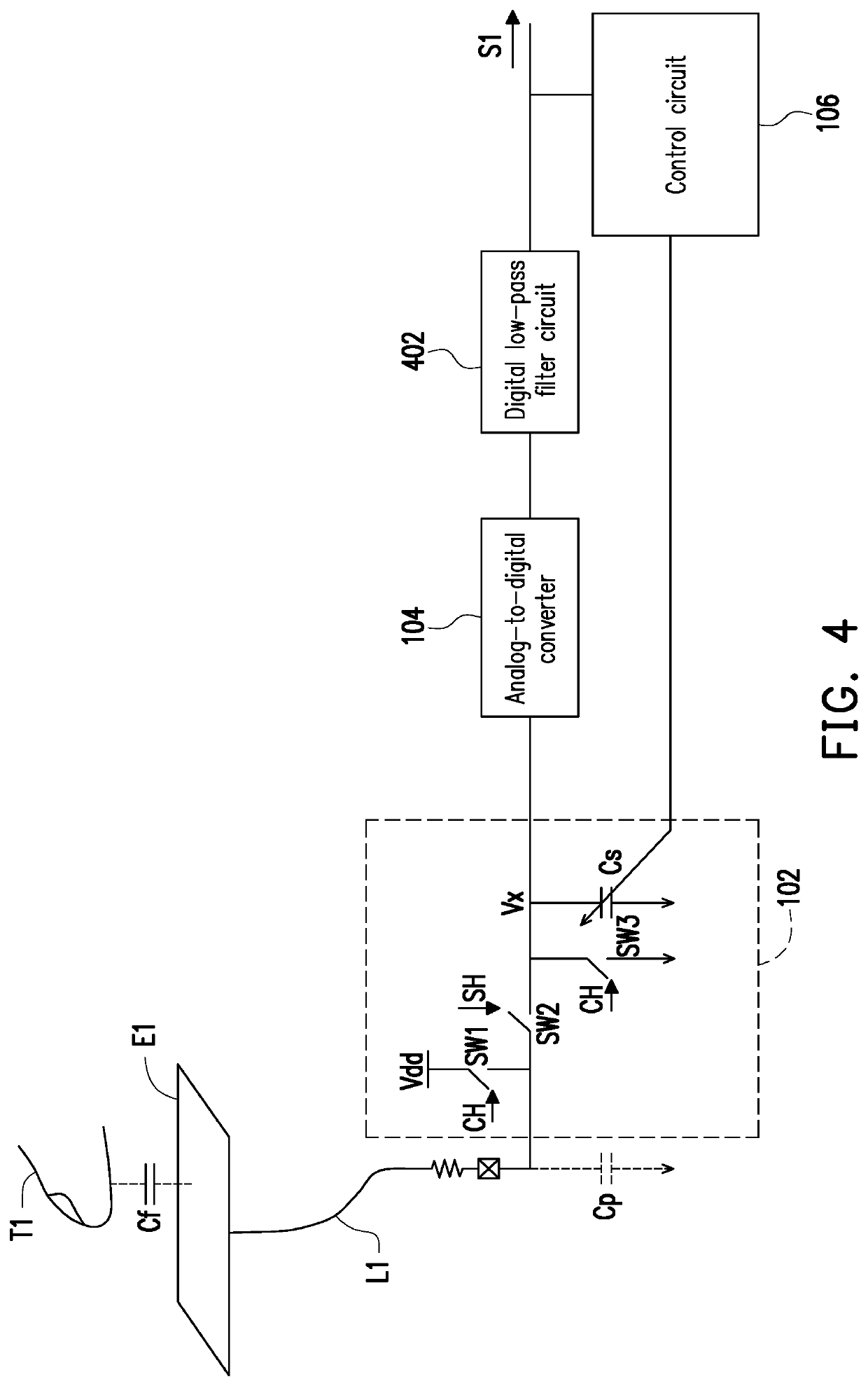
PendingUS20220311441A1Improve the sense of qualityAvoid mistakesCapacitance measurementsElectronic switchingParasitic capacitorCapacitance
A capacitive sensing device is provided. A control circuit adjusts a capacitance value of an adjustable capacitor unit according to a digital sensing signal converted from a sensing signal by an analog-to-digital converter, such that the capacitance value of the adjustable capacitor unit approaches a background parasitic capacitor.
Owner:EGIS TECH
Cognitive radio sensing method and system
InactiveUS20130172030A1Improve Sensing PerformanceImprove the sense of qualitySpectral gaps assessmentRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
The cognitive radio system and method uses a wideband chirp signal for characterization of the spectra that a mobile radio may use. A cognitive radio base station broadcasts the low power reference wideband chirp signal with bandwidth covering the sensed spectrum. At the receiver, spectral resolution in the presence of white noise is achieved by cross-correlating the chirp signal with a locally generated copy of itself (i.e., matched filtering). A Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is applied to the output of this matched filtering. The FFT output is fed to a decision circuitry, where a threshold value is set to decide the minimum amplitude of utilized frequencies. This process eases sensing computational complexity and improves the quality of sensing, thereby offering enhanced cognition at the cognitive radio receiver.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
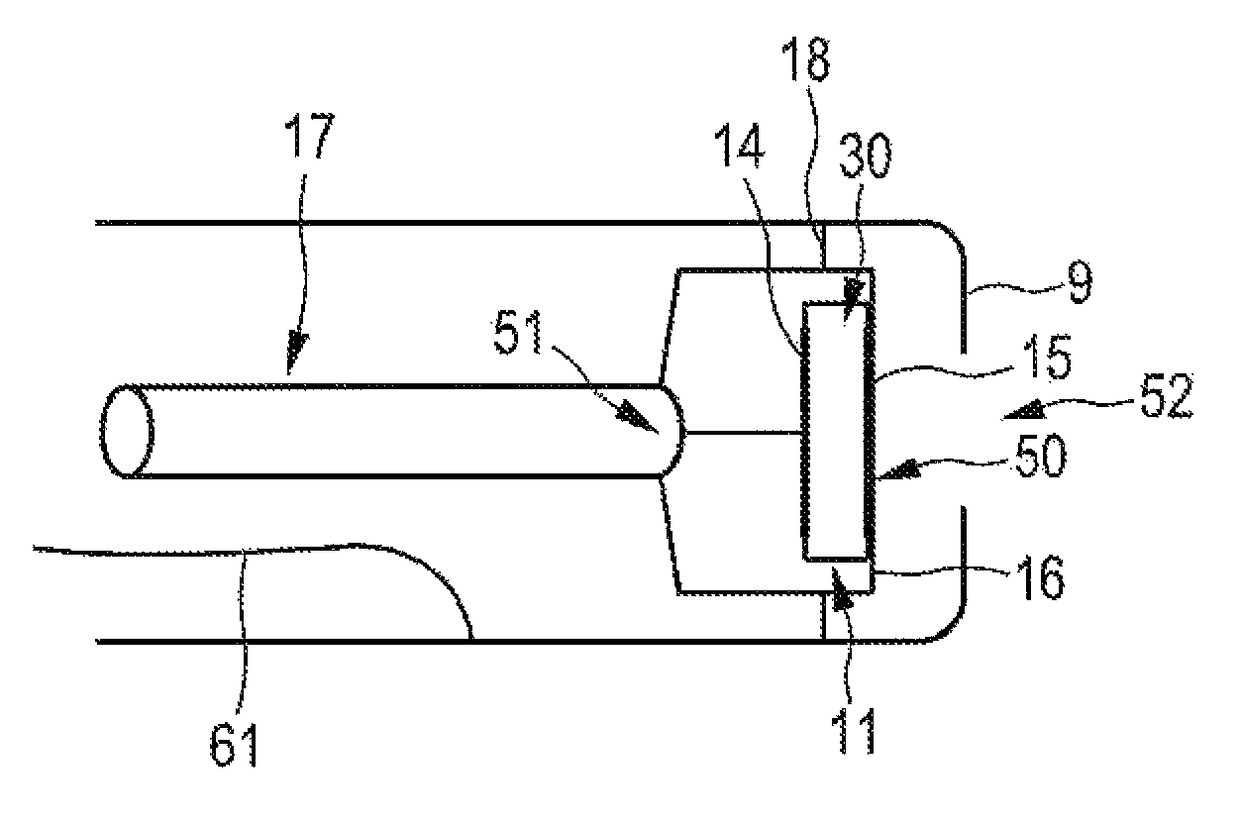
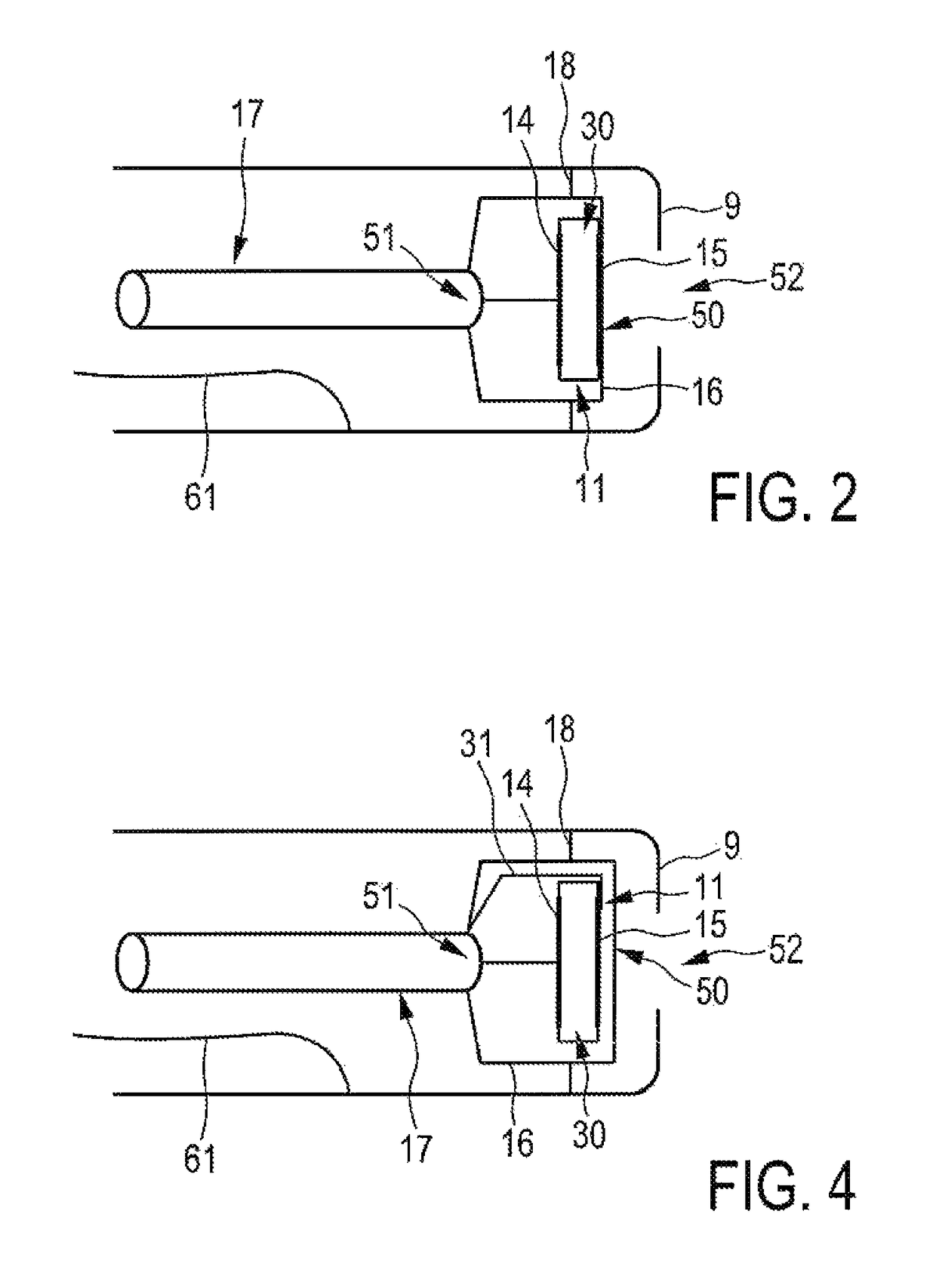
Underwater measurement system
ActiveUS9146331B2Reliably and accurately identifiedImprove sensing qualityTesting dielectric strengthFault location by conductor typesHydrophoneUnderwater explosion
Owner:NAXYS
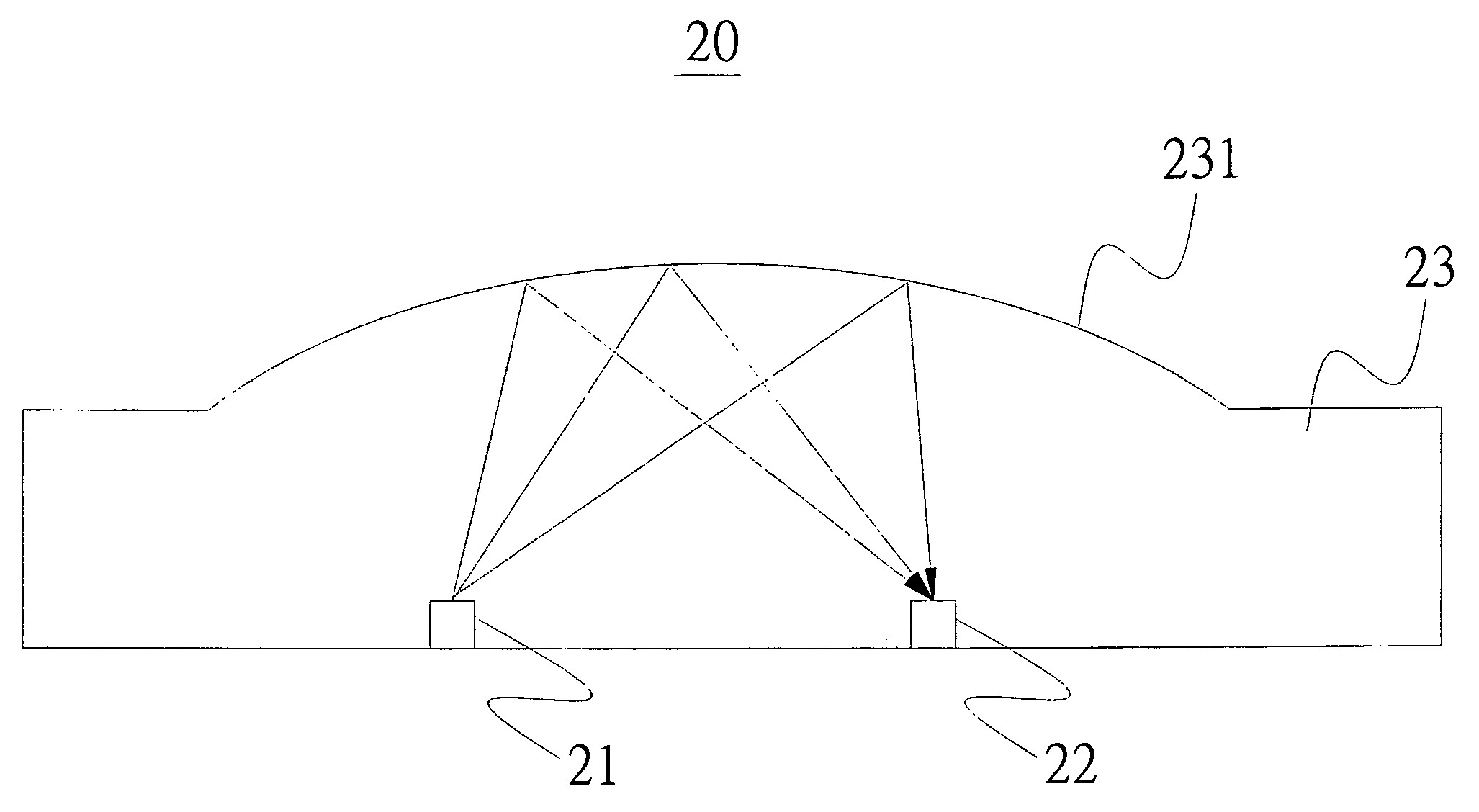
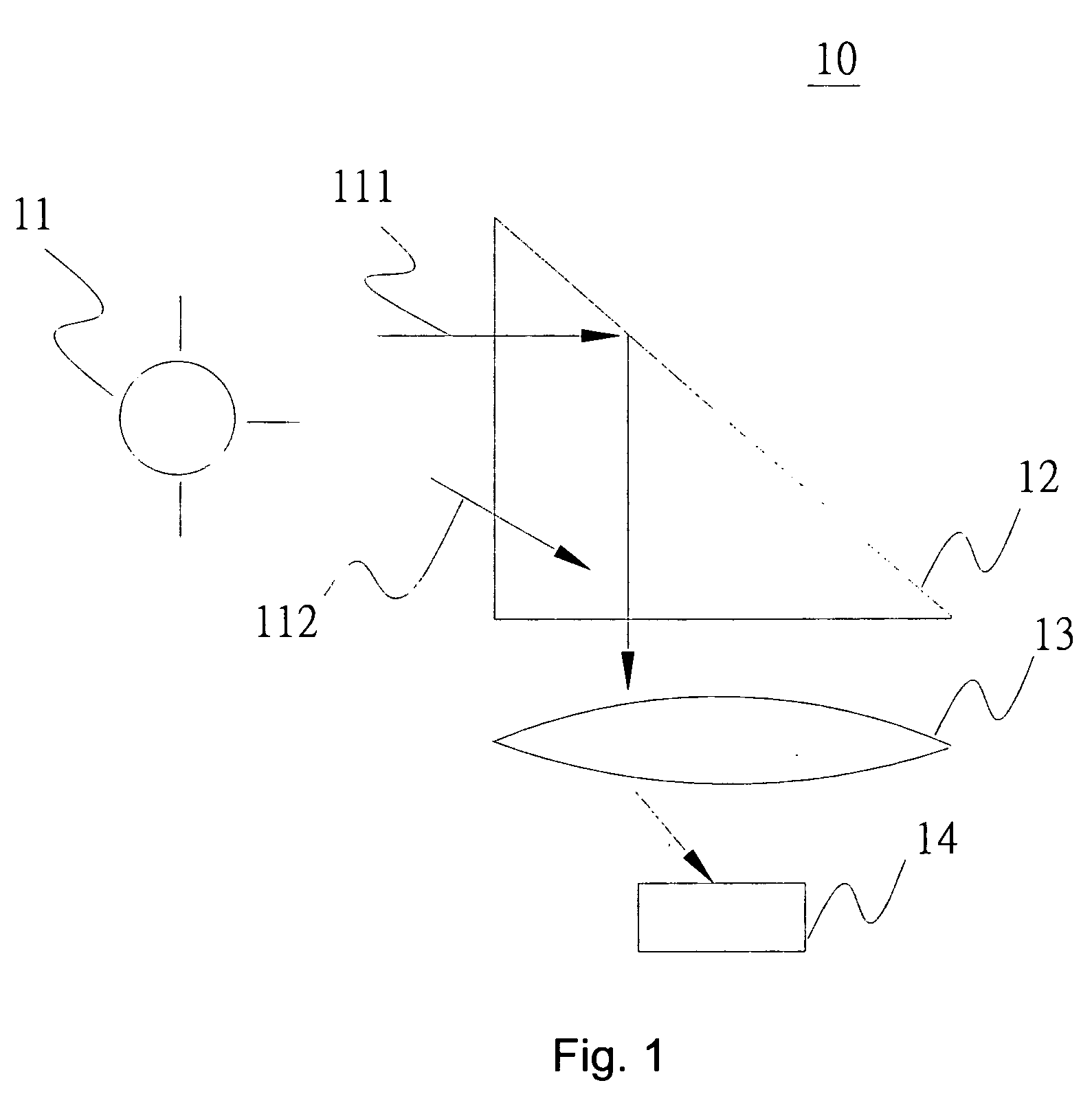
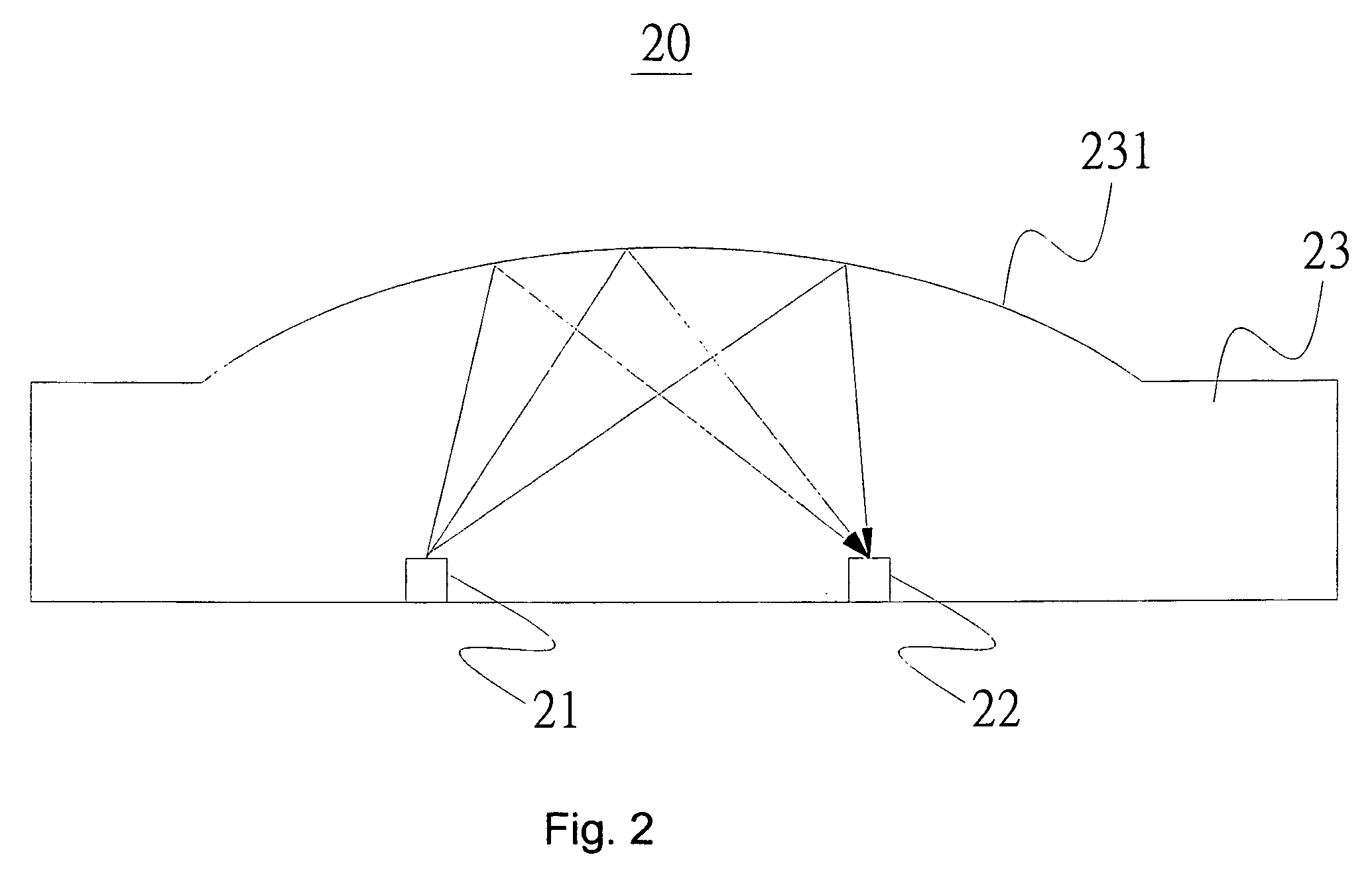
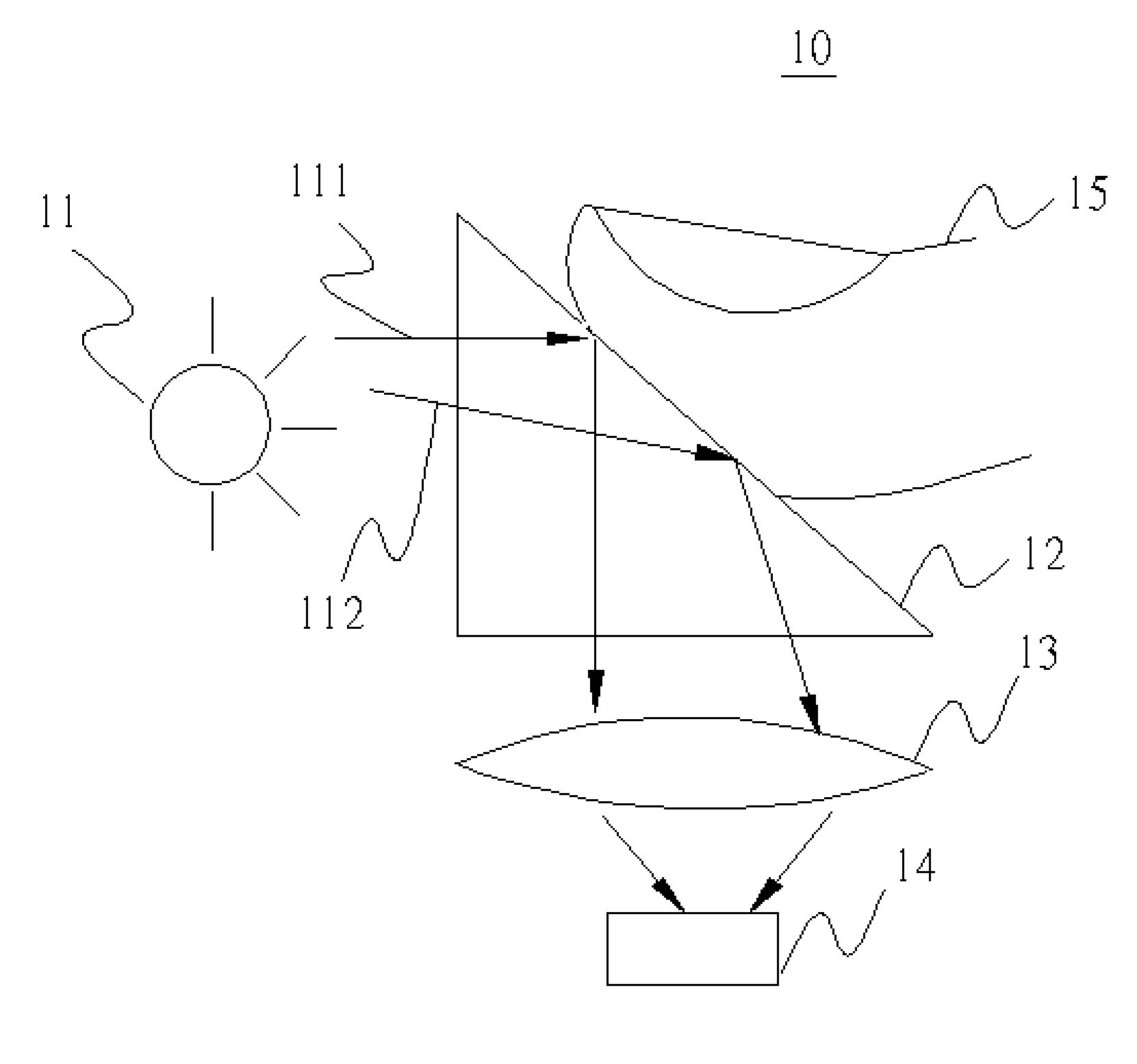
Optical Apparatus and Optical Measurement Method
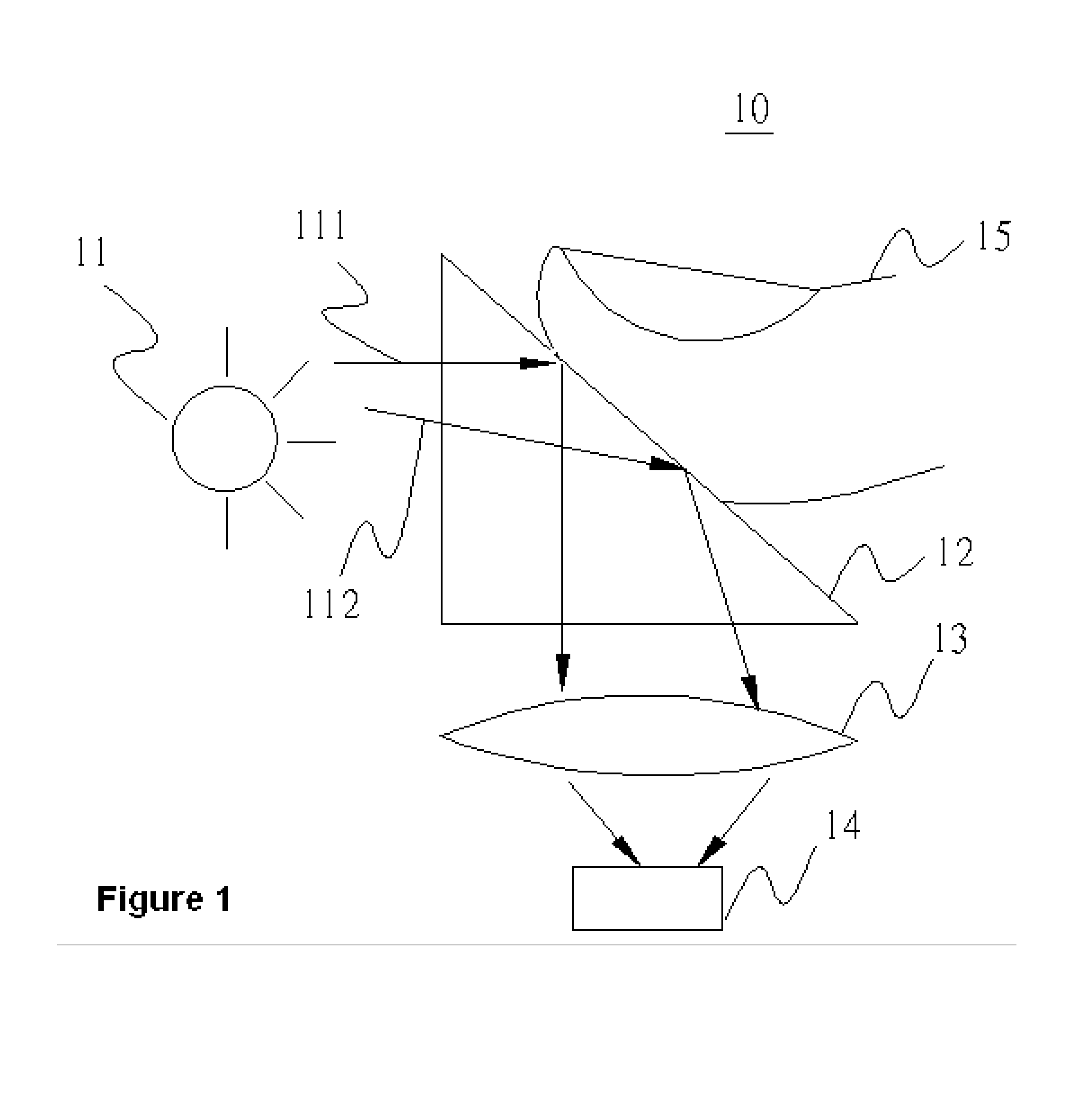
InactiveUS20070153257A1Improve image sensing qualityImprove sensing qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical measurementsOptical sensing
An optical apparatus comprises a light source, an optical sensing device and an optical element. The optical sensing device and the optical element are set at the same side. The optical element includes a reflector which is an arc. A light emitted by the light source can be reflected by the reflector of the optical element to the optical sensing device.
Owner:KUO PENG CHIA
Sensing apparatus for sensing an object
InactiveUS9662170B2Improve sensing qualityQuality improvementOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterCapacitanceElectricity
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
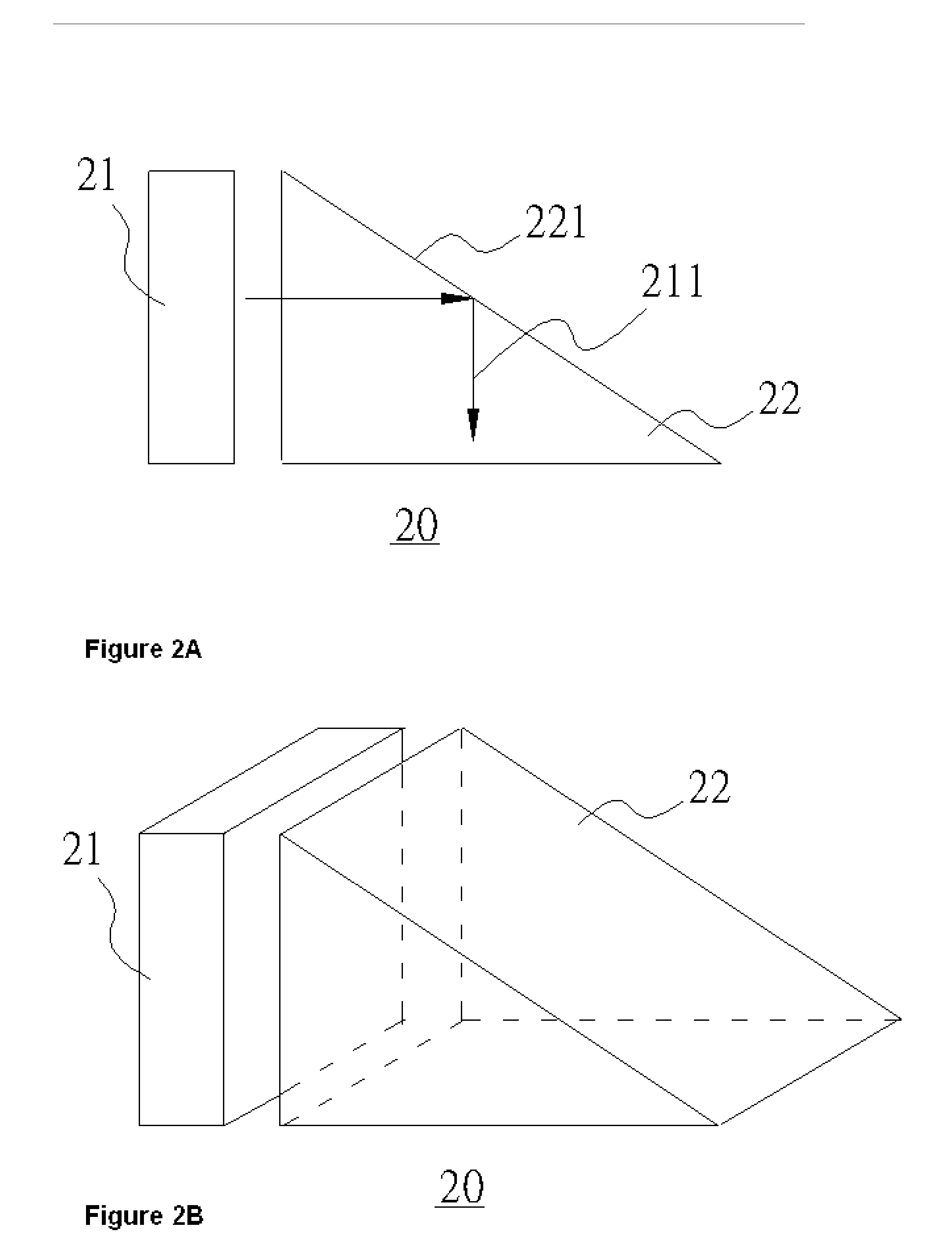
Planar Light Source Module for Fingerprint Recognition Apparatus
InactiveUS20070153346A1Improve image sensing qualityImprove sensing qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical sensingFingerprint recognition
A planar light source module for a fingerprint recognition apparatus is disclosed. A planar light source module comprises a planar light source and an optical element that includes a reflector. A planar incident light emitted by the planar light source can be reflected by the reflector of the optical element to an optical sensing device of the fingerprint recognition apparatus.
Owner:NANOGATE OPTOELECTRONICS ROBOT
Sensor package structure
ActiveUS10868062B2Effectively improve the glare issuesImprove sensing qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A sensor package structure includes a substrate, a sensor chip on the substrate, a ring-shaped support, a light permeable board on the ring-shaped support, and an opaque package body formed on the substrate. A top surface of the sensor chip includes a spacing region and a carrying region surrounding the spacing region. The support is disposed on the carrying region. The light permeable board has a ring-shaped notch recessed from an upper surface thereof, and the notch includes a platform surface at least partially located above the support and a wall surface connected to the platform surface and located above the spacing region. A portion of the opaque package body fills the notch and is defined as a light shielding portion. An inner lateral side of the support is arranged in a projection area formed by orthogonally projecting the platform surface onto the top surface.
Owner:TONG HSING ELECTRONICS IND LTD
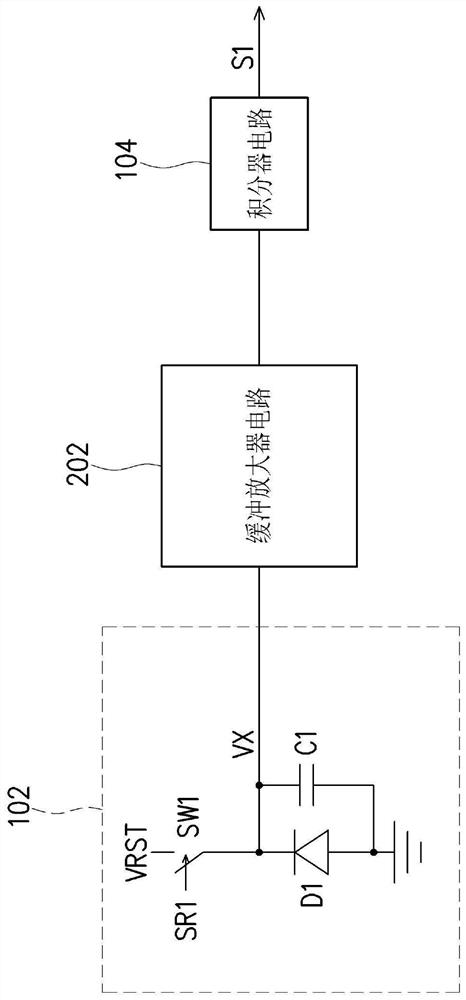
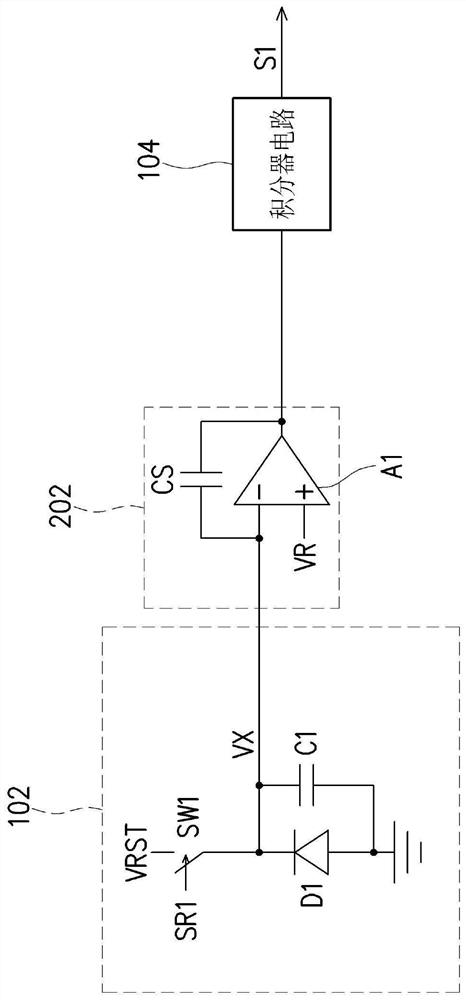
Image sensing device
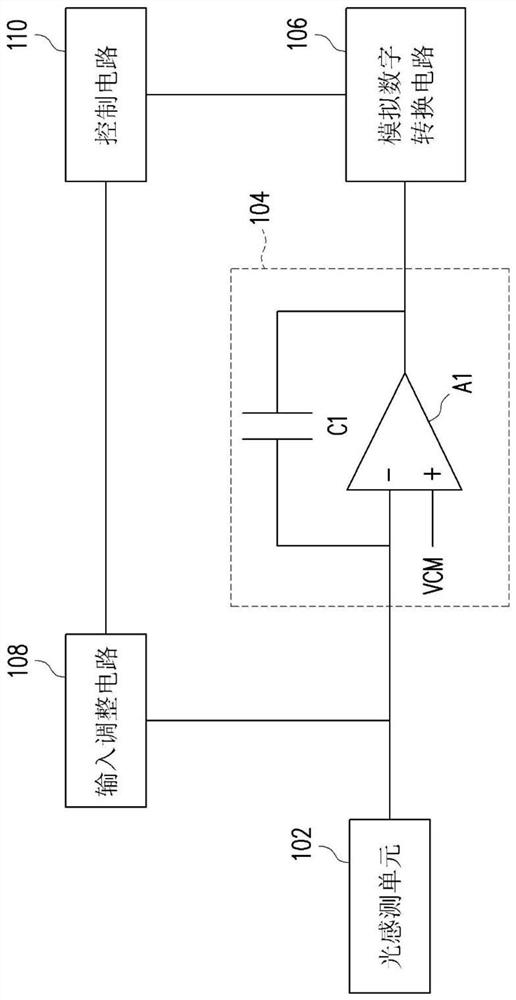
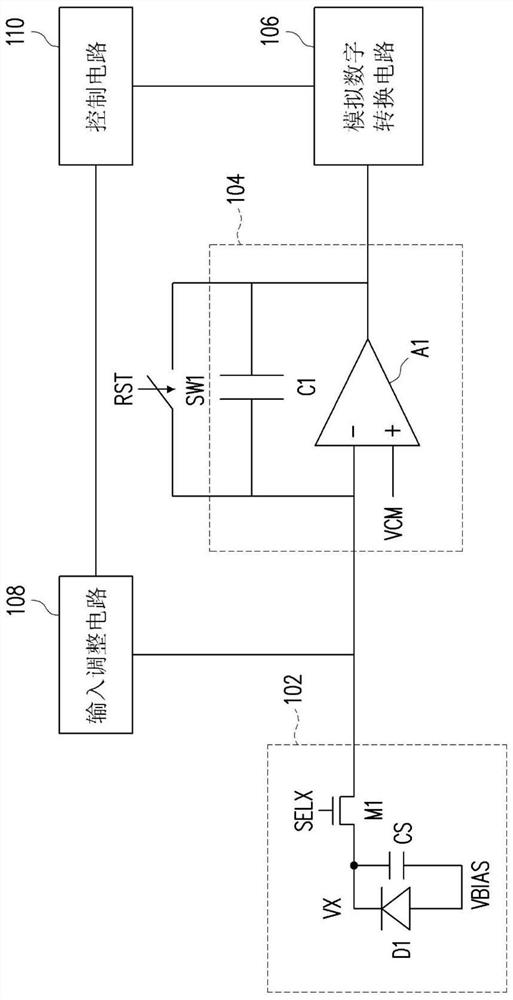
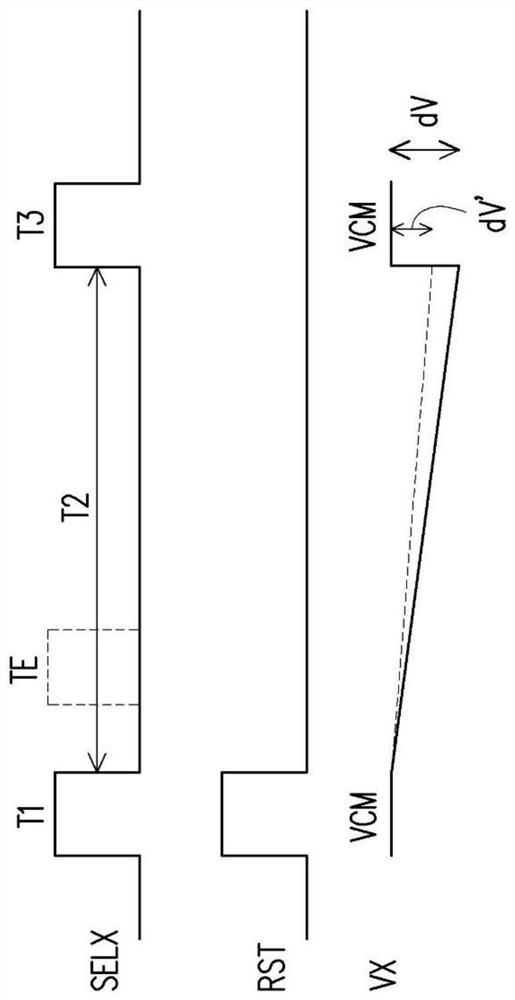
PendingCN112738429AImprove sensing qualityAnalogue/digital conversionTelevision system detailsImage sensingLight sensing
The invention provides an image sensing device. A control circuit determines the voltage change rate of the sensing signal according to the voltage value of the sensing signal generated by the light sensing unit in the estimation period, and controls the input adjusting circuit to provide the input adjusting signal to the negative input end of the operational amplifier in the exposure period according to the voltage change rate. Therefore, the signal value of the amplification signal falls within the preset range during the exposure period.
Owner:EGIS TECH
Sensing apparatus for sensing an object
InactiveUS20130231562A1Improve sensing qualityQuality improvementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterCapacitanceElectricity
The invention relates to a sensing apparatus for sensing an object. The sensing apparatus comprises an ultrasound unit (11) for ultrasonically sensing the object (4), an electrical energy application unit (9) for applying electrical energy to the object (4), and an ultrasound unit shielding element (16) for electrically shielding the ultrasound unit (11), wherein the ultrasound unit shielding element (16) is electrically connected to the electrical energy application unit (9). Since the ultrasound unit shielding element electrically shields the ultrasound unit, the ultrasound sensing of the object is less influenced by a capacitive coupling of the application of electrical energy, in particular, of an RF signal which may be used for applying the electrical energy, into the ultra-sound sensing. A further reduction of this influence is achieved by electrically connecting the ultrasound unit shielding element to the electrical energy application unit.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Photoelectric sensor protection device and protection method
InactiveCN107677297AWith filter functionImprove signal clarityMeasurement apparatus componentsConverting sensor output opticallyStandby powerOpto electronic
The invention discloses a photoelectric sensor protection device. The photoelectric sensor protection device comprises a circuit insertion unit and a stand-by power supply, the circuit insertion unitis arranged on the top of an insulating casing, the insulating casing is inside provided with a transverse stress support bar, a state display screen is arranged under the transverse stress support bar, the bottom of the state display screen is provided with a pluggable connector, the back of the state display screen is provided with a minitype information processor, the upper part of the minitypeinformation processor is connected with the circuit insertion unit through a circuit protection resistor and a filter, and the stand-by power supply is arranged under the minitype information processor. Beneficial effects of the photoelectric sensor protection device are that comprehensive protection of the photoelectric sensor can be carried out in cable fixing, circuit protection, electromagnetic protection, insulation and water proofing ways, the photoelectric sensor protection device has a filtering function at the same time, and therefore the signal clearness and the sensing quality canbe improved.
Owner:广州市康超信息科技有限公司
Sensor package structure
ActiveUS20200105809A1Effectively improve the glare issuesImprove sensing qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A sensor package structure includes a substrate, a sensor chip on the substrate, a ring-shaped support, a light permeable board on the ring-shaped support, and an opaque package body formed on the substrate. A top surface of the sensor chip includes a spacing region and a carrying region surrounding the spacing region. The support is disposed on the carrying region. The light permeable board has a ring-shaped notch recessed from an upper surface thereof, and the notch includes a platform surface at least partially located above the support and a wall surface connected to the platform surface and located above the spacing region. A portion of the opaque package body fills the notch and is defined as a light shielding portion. An inner lateral side of the support is arranged in a projection area formed by orthogonally projecting the platform surface onto the top surface.
Owner:TONG HSING ELECTRONICS IND LTD
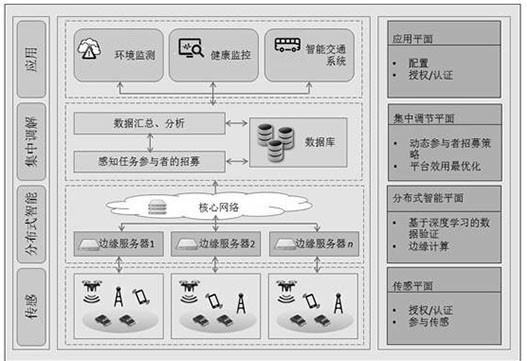
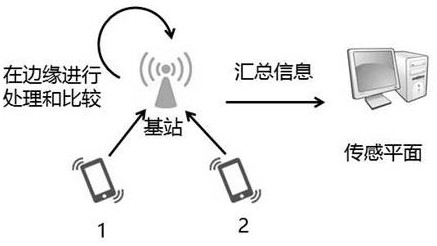
A Robust Mobile Crowd Sensing Algorithm Based on Edge Computing
ActiveCN110072298BImprove sensing qualityReduce data volumeMeasurement devicesNetwork topologiesComputation complexitySource Data Verification
The invention relates to an optimization algorithm based on edge computing that is applied in the MCS (Mobile Crowd Sensing) sensing task scene, and is based on the recruitment of task participants, the judgment of information validity, and the detection and correction of errors. The present invention represents platform utility as a logarithmic function (strictly increasing and sagging) of independent measurement data for each location, and the algorithm aims to maximize total utility under exerting budget constraints. Since the proposed joint optimization problem is a non-deterministic polynomial combinatorial optimization problem, it cannot be solved in polynomial time. Therefore, we design an approximation algorithm that greatly reduces the computational complexity. The present invention uses a deep neural network (DNN) for data verification, thereby increasing the accuracy of predicted data. In addition, the present invention also adopts data redundancy to improve the sensing quality, and when measurement errors are detected near the data source, the amount of data transmitted from the base station to the sensing platform is greatly reduced, the occupied frequency band resource is reduced, and the time delay is reduced.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Statistical analyzing method and statistical quality indicator for reliability improvement of a capacitive touch device
InactiveUS8866794B2Improve sensing qualityTransmission systemsInput/output processes for data processingStatistical analysisStatistical quality
For a capacitive touch device having a capacitive touch sensor to be sensed to generate sensed values, a sensing apparatus and method statistically analyze the sensed values generated in a certain time period to evaluate the sensing quality thereof, discard the poor reliable sensed values, and re-sense the capacitive touch sensor to generate new sensed values, by which the resultant output signal will have improved reliability.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Ultra-violet light sensing device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS8912619B2Low production costSimple manufacturing processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationHigh densityOptoelectronics
The present invention provides an ultra-violet light sensing device. The ultra-violet light sensing device includes a first conductivity type substrate, a second conductivity type region, and a first conductivity type high density region. The first conductivity type substrate includes a light incident surface. The second conductivity type region is disposed in the first conductivity type substrate and adjacent to the light incident surface. The first conductivity type high density region is disposed under the second conductivity type region. The present invention also provides another ultra-violet light sensing device, which further includes a first conductivity type high density shallow region which is sandwiched between the light incident surface and the second conductivity type region. Manufacturing methods for these ultra-violet light sensing devices are also disclosed in the present invention.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Fingerprint sensing module
ActiveUS11495048B2Small differenceEnhance the imageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMaterials scienceOptics
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Mutual capacitive touch panel
ActiveUS11042245B2Reduce capacitanceImprove sensing qualityInput/output processes for data processingTouch panelMaterials science
A mutual capacitive touch panel includes a first electrode layer and a second electrode layer. The first electrode layer includes a plurality of first electrode series and a plurality of second electrode series. The second electrode layer includes a plurality of electrode strips, and each electrode strip crosses the first electrode series and the second electrode series. Each first electrode series includes a plurality of first electrodes and a plurality of second electrodes electrically connected with each other, and each first electrode and a corresponding one of the second electrodes are disposed abreast and form an electrode set. Each second electrode series includes a plurality of third electrodes electrically connected with each other, and each electrode set and each third electrode are arranged alternately along a direction.
Owner:ILI TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Aluminum cabinet
InactiveCN110664123AGuaranteed aestheticsImprove sensing qualityDismountable cabinetsStructural engineeringCupboard
The invention discloses an aluminum cabinet. The aluminum cabinet comprises a plurality of positioning components arranged on upper edges, lower edges and middle parts of the inner surfaces of two side plates. Two external main plates are respectively arranged between the two side plates. An assembly component is installed on each assembly block arranged on each of two sides of the external main plate. The assembly components are installed to the positioning components and connected to the same. An internal partition is arranged between the two side plates. A fixing component is installed on afixing block arranged on each of two sides of the internal partition. A fixing pin installed in the fixing component is installed with the positioning component and connected to the same. Accordingly, connection components are hidden after being assembled. Therefore, the visual appearance of the cabinet is more pleasant, and the sense of worth is also improved.
Owner:江苏广坤铝业有限公司
Image sensing device
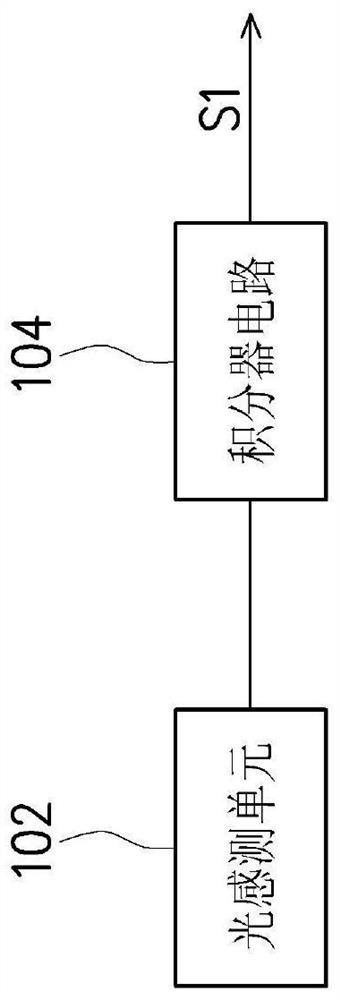
PendingCN112511770AImprove sensing qualityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight sensingLight signal
The invention provides an image sensing device. A light sensing unit receives a light signal including image information to generate a sensing signal. An integrator circuit performs integration operation on the sensing signal in an integration period so as to accumulate the sensing signal and generate an accumulated sensing value falling in a default range.
Owner:EGIS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com