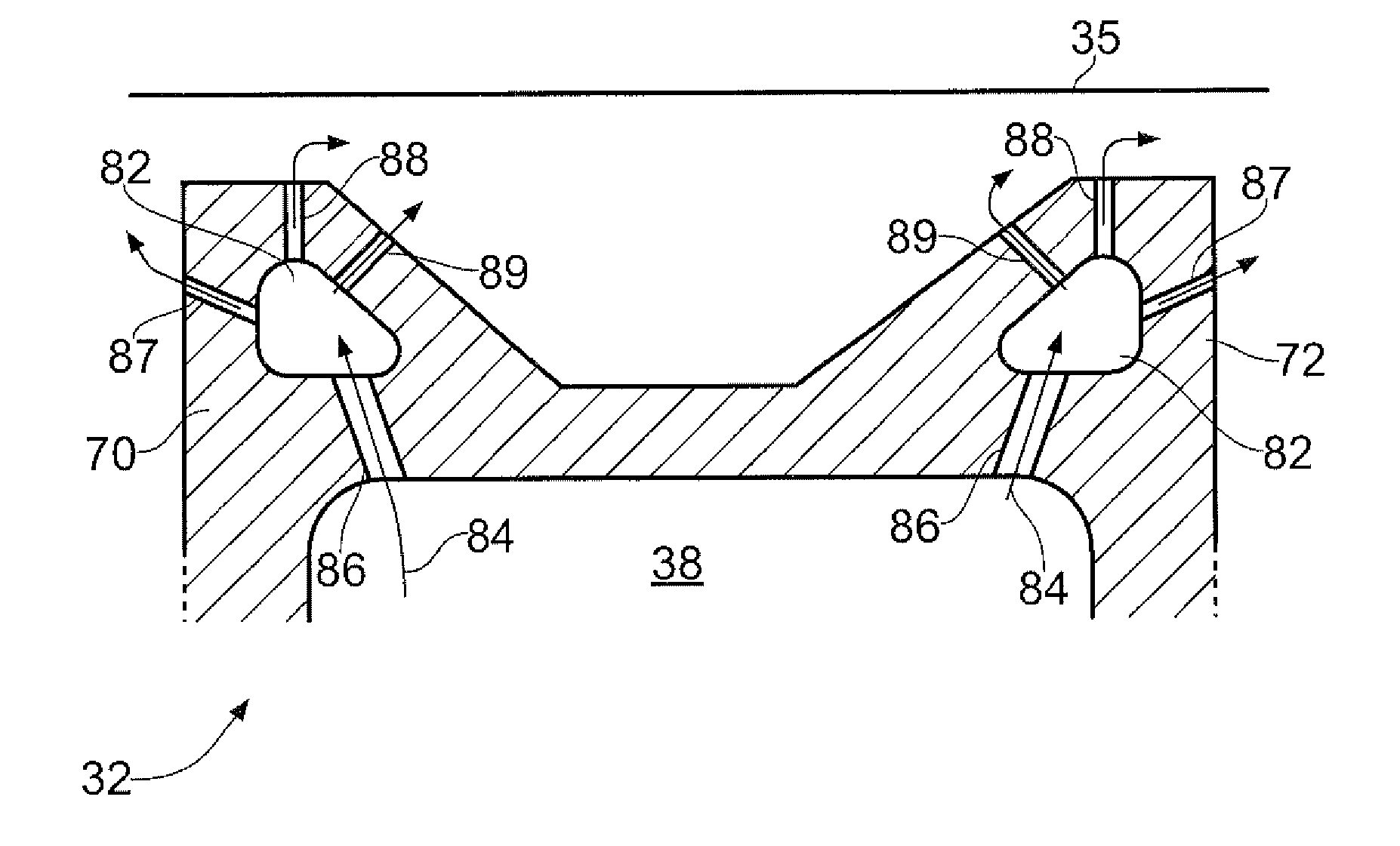
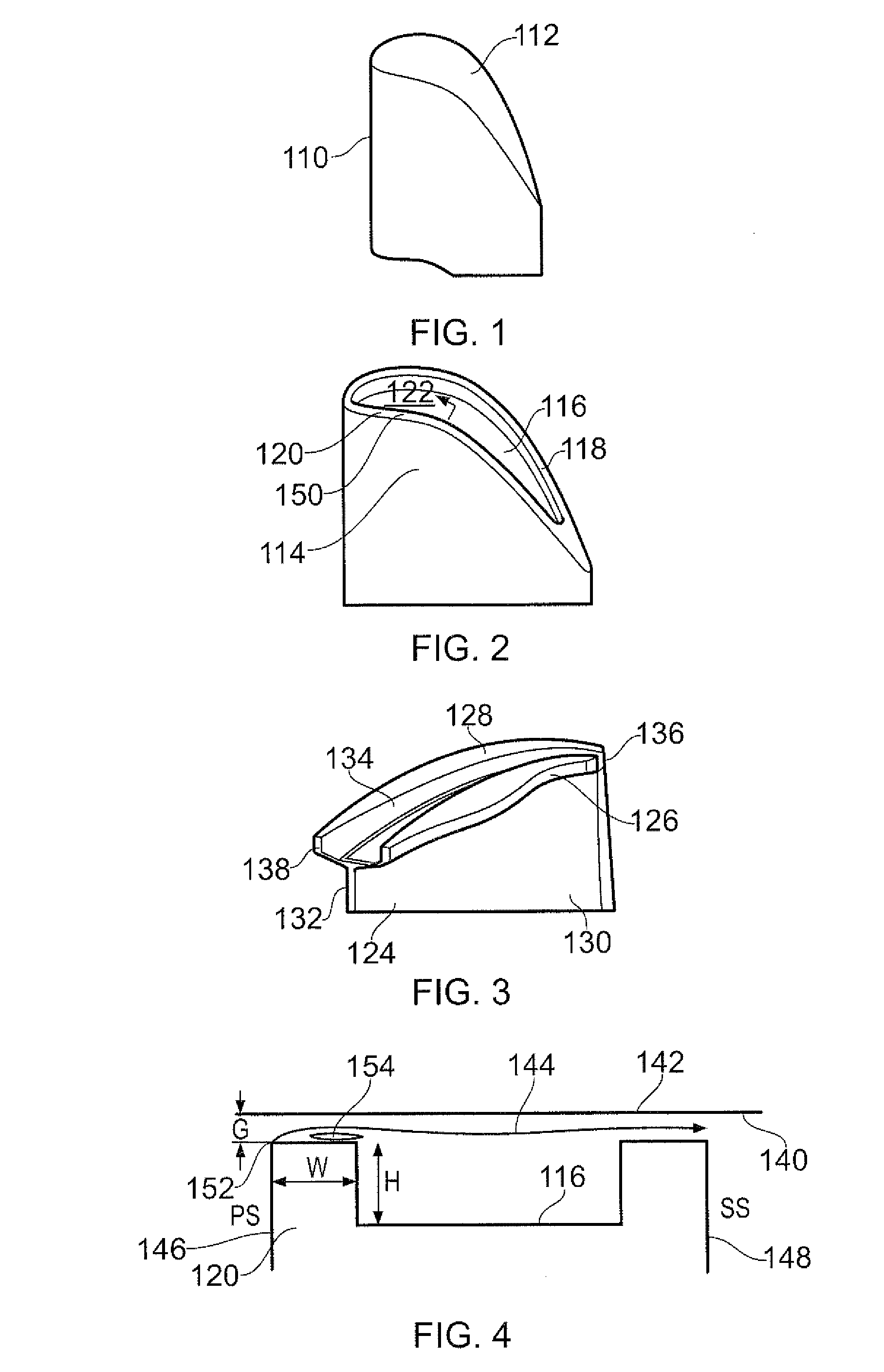
Turbine blade
a turbine blade and blade technology, applied in the field of turbine blades, can solve the problems of conflicting performance characteristics between aerodynamics and heat transfer, current squealer designs are mostly unable to explore the full aerodynamic potential of the squealer working mechanism, etc., to achieve good aerodynamic performance, improve the cooling of the blade tip, and increase the space for cooling chambers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
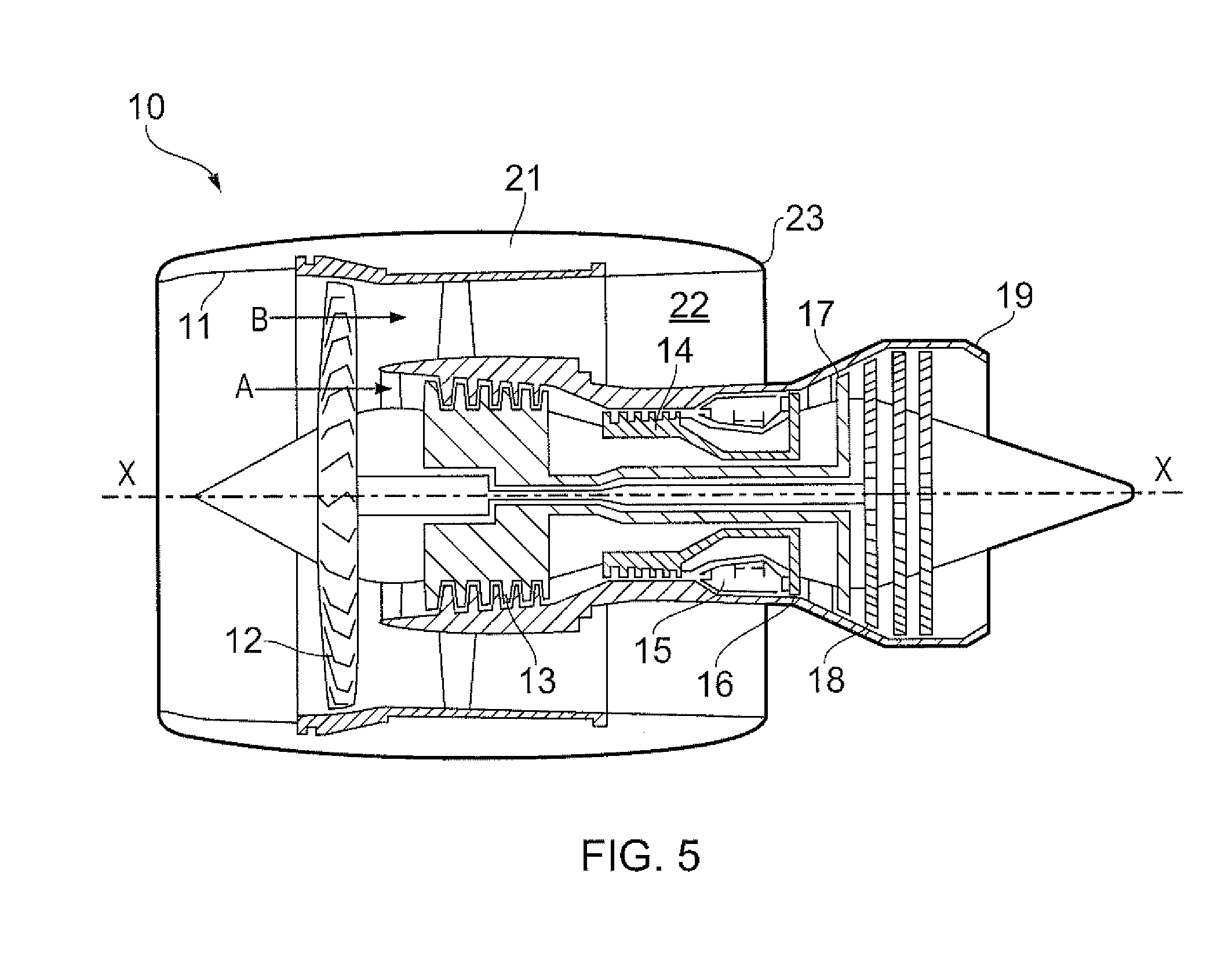
[0050]With reference to FIG. 5, a ducted fan gas turbine engine generally indicated at 10 has a principal and rotational axis X-X. The engine comprises, in axial flow series, an air intake 11, a propulsive fan 12, an intermediate pressure compressor 13, a high-pressure compressor 14, combustion equipment 15, a high-pressure turbine 16, and intermediate pressure turbine 17, a low-pressure turbine 18 and a core engine exhaust nozzle 19. A nacelle 21 generally surrounds the engine 10 and defines the intake 11, a bypass duct 22 and a bypass exhaust nozzle 23.
[0051]The gas turbine engine 10 works in a conventional manner so that air entering the intake 11 is accelerated by the fan 12 to produce two air flows: a first air flow A into the intermediate pressure compressor 13 and a second air flow B which passes through the bypass duct 22 to provide propulsive thrust. The intermediate pressure compressor 13 compresses the air flow A directed into it before delivering that air to the high pre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com