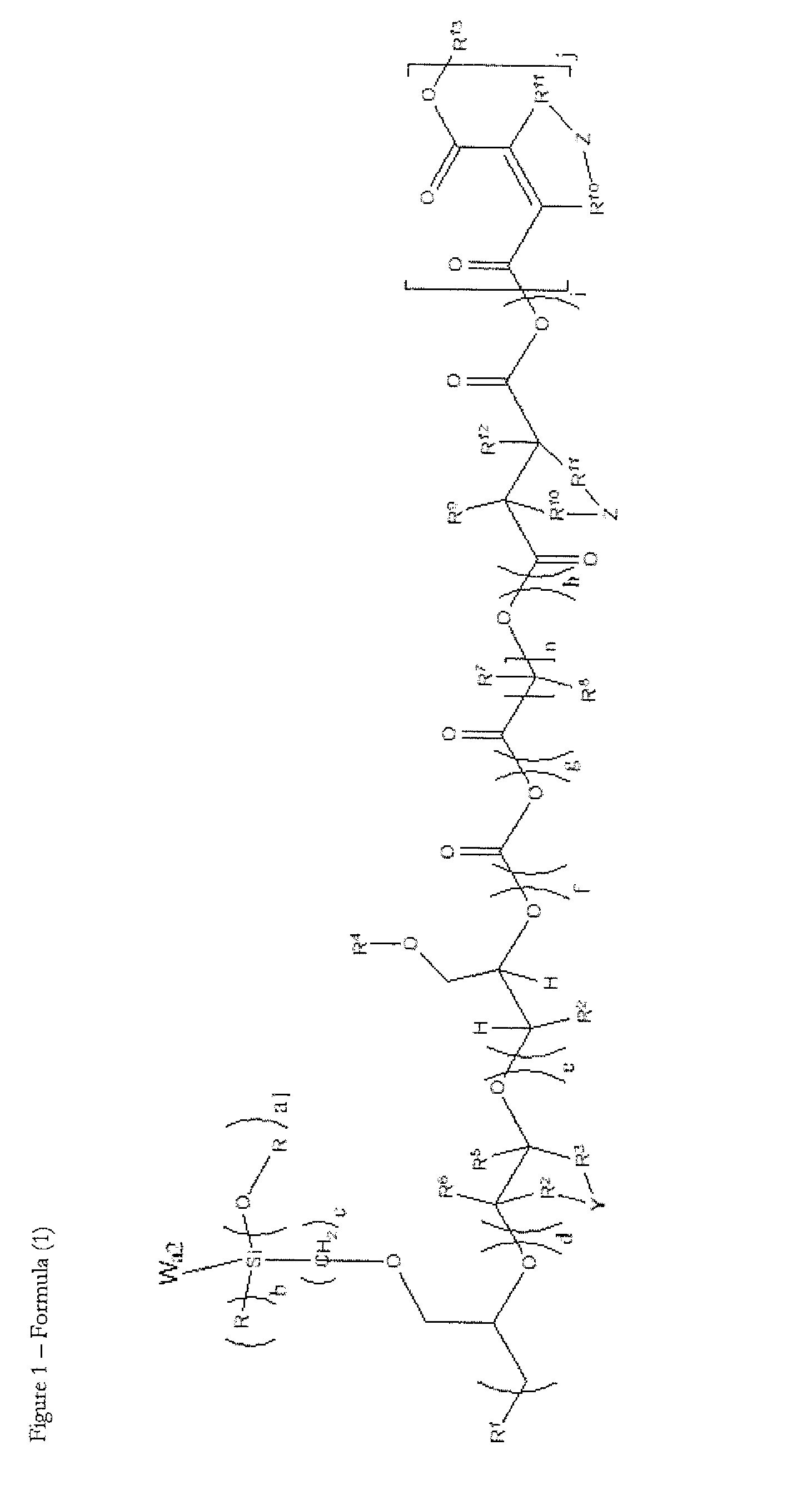
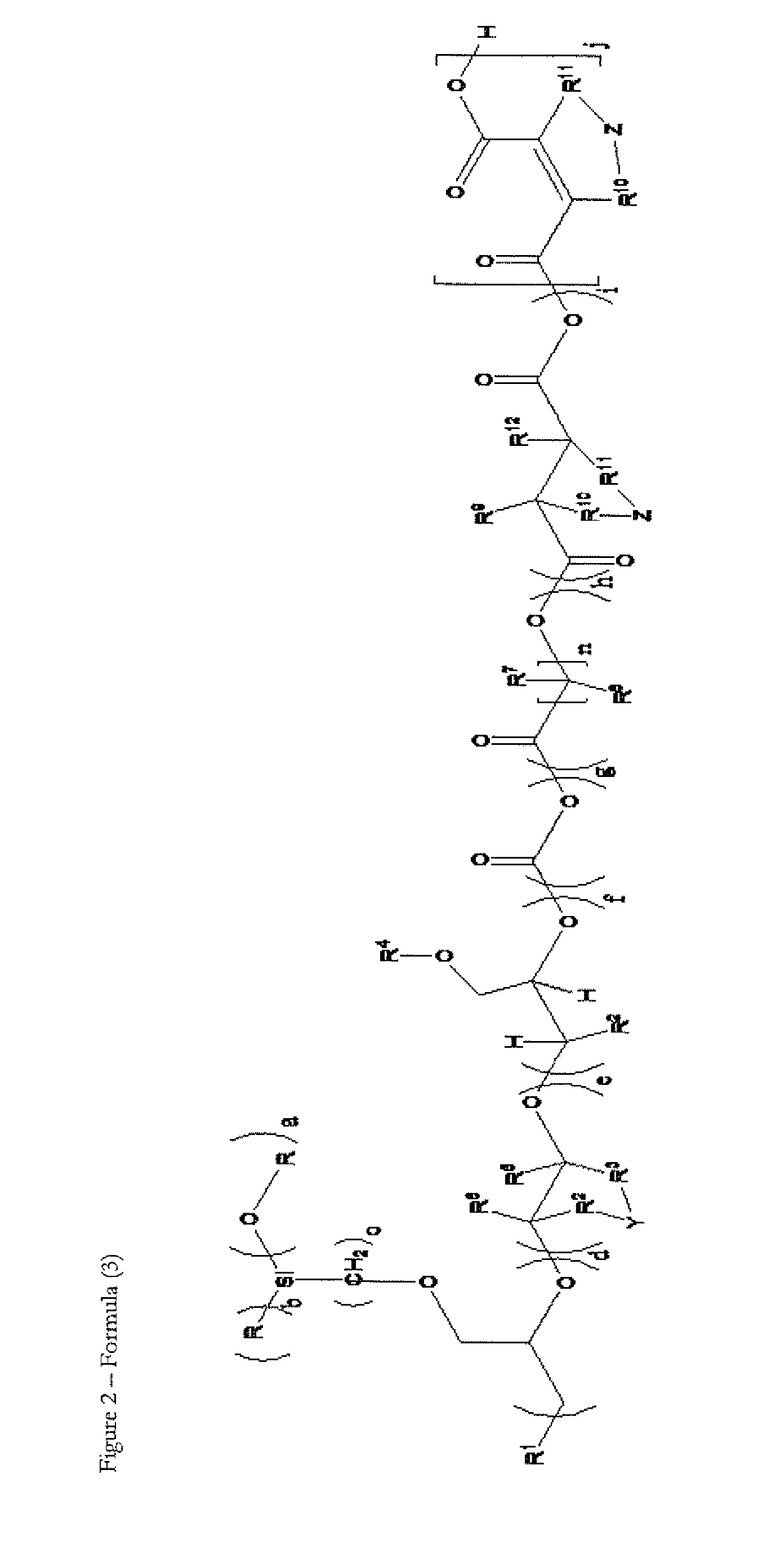
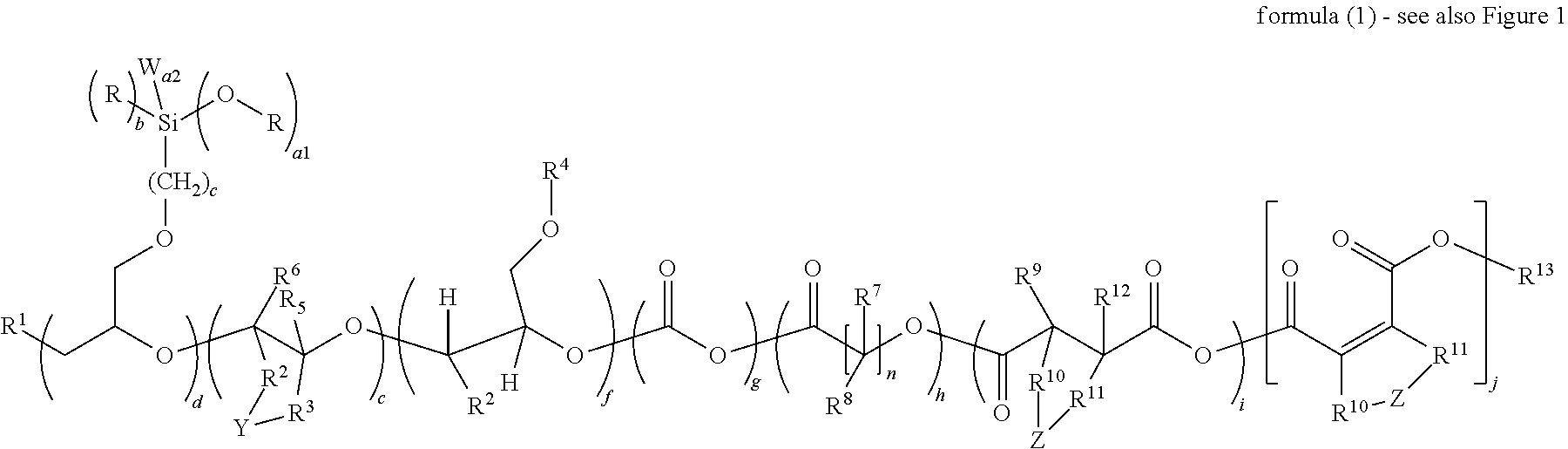
Novel silicone polyether copolymers and process for preparation thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Inventive
[0155]A 250 ml four-neck flask equipped with a precision glass stirrer, an internal thermometer, a dropping funnel and a distillation apparatus is initially charged with 30 g of trimethylethoxysilane at room temperature, and 0.45 ml of trifluoroacetic acid is added with stirring. After heating to 60° C., a mixture of 37.2 g of silyl polyether SP-1 and 20.16 g of demineralized water is added dropwise over a period of one hour. After the metered addition has ended, the cloudy reaction mixture is stirred at 60° C. for 3 hours. 3 g of sodium hydrogencarbonate are added and the mixture is stirred for half an hour at room temperature. After filtering through a fluted filter, a clear solution is obtained. The ethanol formed from the reaction is distilled off at 70° C. and 5 to 15 mbar within 45 minutes. This gives a clear, homogeneous, low-viscosity (29Si NMR spectrum, no signals from the starting compounds are discernible any longer. The ratio of M units to T units is 2.9 to 1 (t...
example 2
Inventive
[0156]A 250 nil four-neck flask equipped with a precision glass stirrer, an internal thermometer, a dropping funnel and a distillation apparatus is initially charged with 31.8 g of trimethylethoxysilane at room temperature, and 0.42 ml of trifluoroacetic acid is added with stirring. After heating to 60° C., a mixture of 30.0 g of silyl polyether SP-2 and 21.4 g of demineralized water is added dropwise over a period of 1.5 hours. After the metered addition has ended, the cloudy reaction mixture is stirred at 60° C. for 3 hours. The ethanol formed during the reaction is distilled off at 60° C. and 50 mbar within one hour. 1.7 g of sodium hydrogencarbonate are added and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for half an hour. After filtering through a fluted filter, a clear, homogeneous, yellowish product with a viscosity of 204 mPa*s at 25° C. is obtained. In the 29Si NMR spectrum, no signals of the starting compounds are discernible any longer. The ratio of M units to T ...
example 3
Inventive
[0157]A 250 ml four-neck flask equipped with a precision glass stirrer, an internal thermometer, a dropping funnel and a distillation apparatus is initially charged with 21.8 g of hexamethyldisiloxane at room temperature, and 0.42 ml of trifluoroacetic acid is added with stirring. After stirring at 70° C. for 1 hour, a mixture of 30.0 g of silyl polyether SP-2 and 21.4 g of demineralized water is added dropwise over a period of one hour. After the metered addition has ended, the cloudy reaction mixture is stirred at 70° C. for 3 hours. The ethanol formed during the reaction is distilled off at 70° C. and 20 mbar within one hour. 1.7 g of sodium hydrogencarbonate are added and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for half an hour. After filtering through a fluted filter, a clear, homogeneous, yellowish product with a viscosity of 294.2 mPa*s at 25° C. is obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com