Scanning electrochemical microscopy
a microscopy and electrochemical technology, applied in the field of scanning microscopy, can solve the problems of difficult to find appropriate redox-active species, general unresolved, etc., and achieve the effects of enhancing the electrochemical information content, inexpensive and simple methods, and robust and simple methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
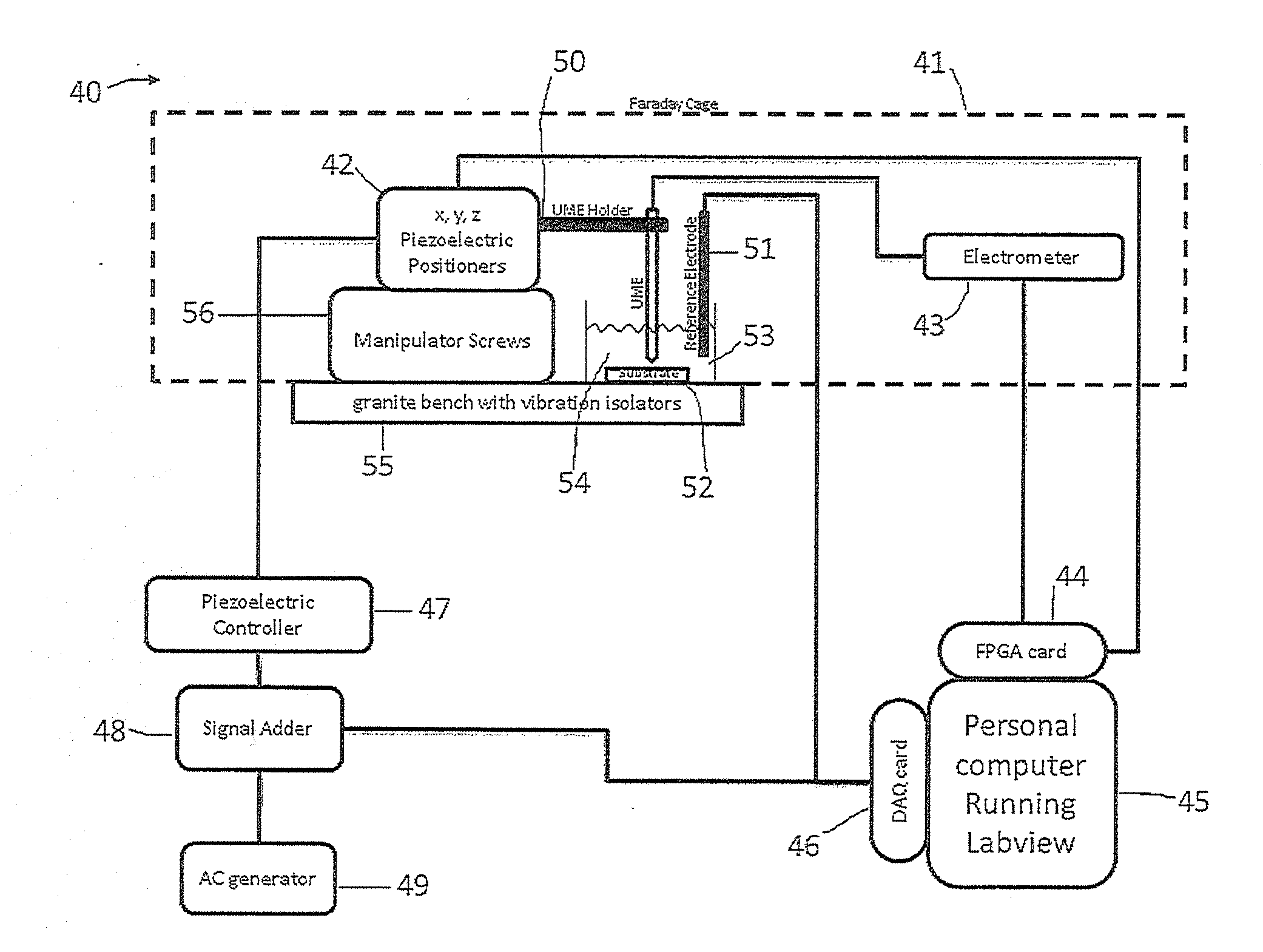
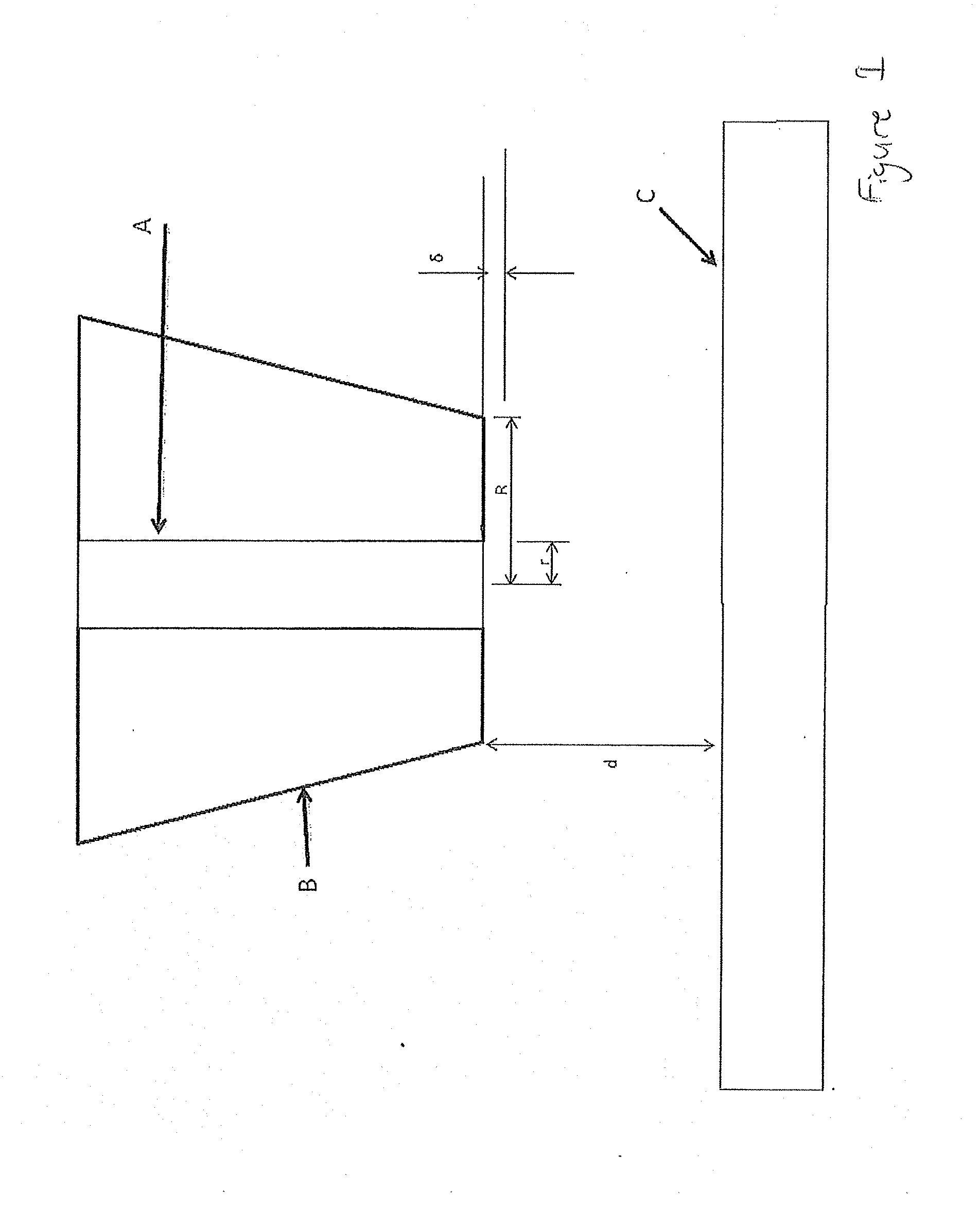
[0046]Embodiments of the invention involve the application of an oscillatory perturbation of typically 0.1 nm to 1 μm at typically 5 to 100 000 Hz to a SECM tip. The SECM tip may be a UME, for instance in the form of a metal wire A, with a radius of 0.002 to 12.5 μm, sealed in a glass capillary B relative, typically normal, to a surface of interest C. With this oscillation the amplitude of the oscillation becomes damped as the tip encounters the surface. The oscillation is typically sinusoidal, though other oscillation types can be used
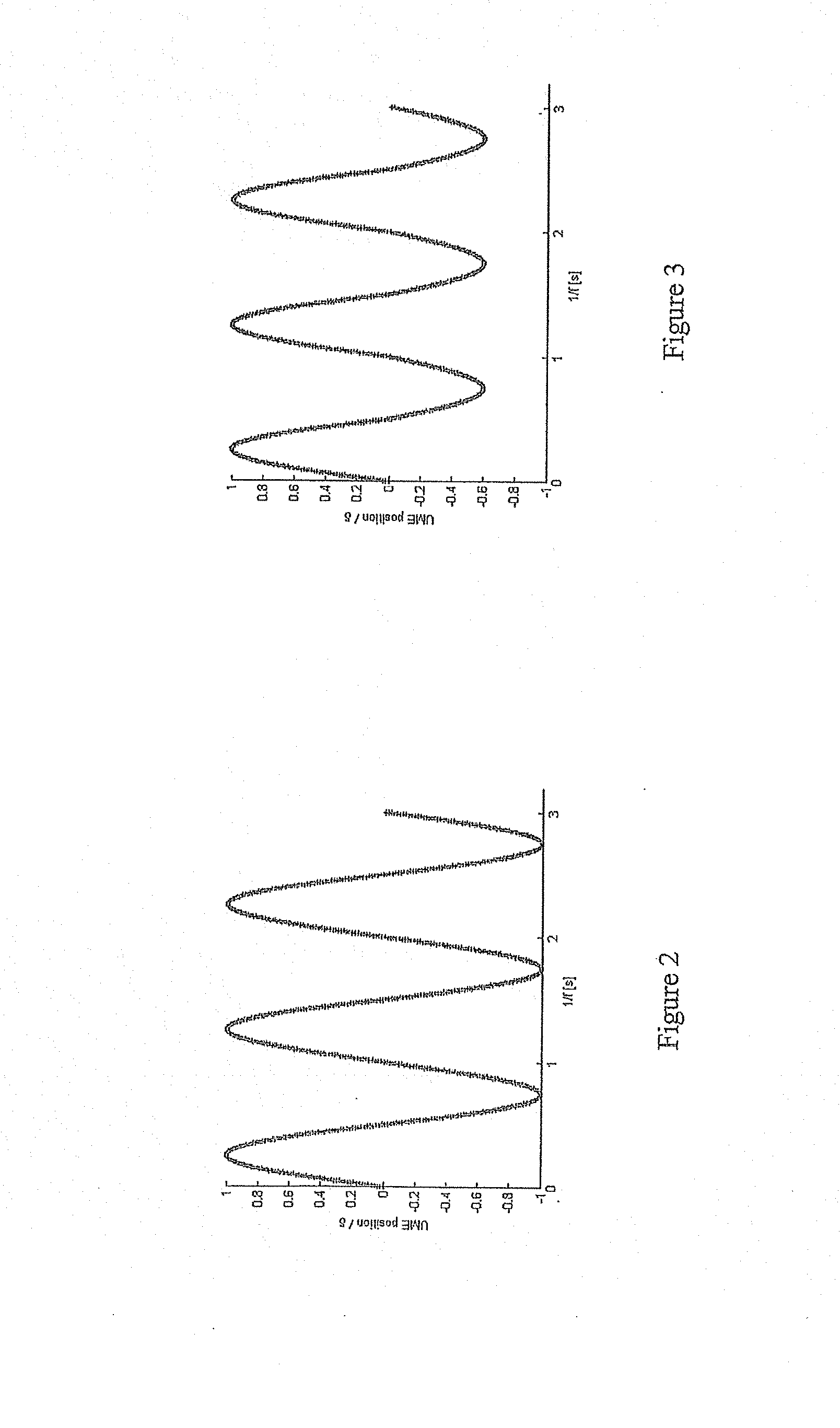
[0047]FIG. 1 shows a cross section of an UME and the oscillation of the UME. FIG. 2 shows the movement of the SECM tip when in bulk solution (i.e. not in contact with the surface). FIG. 3 shows the movement of the SECM tip when in intermittent contact with the substrate surface. Here, it can be seen that the uppermost half of the waveform, i.e. the parts above position 0, are substantially the same as for FIG. 2, however the lowermost half of the wave...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| scanning microscopy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com