Electrochemical separators with inserted conductive layers
a technology of conductive layer and separator, which is applied in the direction of secondary cell servicing/maintenance, cell components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of thermal runaway in batteries, and achieve the effects of enhancing the safety of the cell, limiting or preventing hot spots and/or thermal runaway, and prolonging the cycle li
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Multilayer Separators Made of Materials that Upon Electronic Contact with an Electrode Result in an Observable Change in Voltage
[0149]The electrochemical cells in this disclosure include, but are not limited to, batteries, fuel cells, flow batteries and semi-solid batteries. Any of the electrode active materials can be solid, liquid, gas, flowable semi-solid or condensed liquid composition. A flowable anodic semi-solid (also referred to herein as “anolyte”) and / or a flowable cathodic semi-solid (also referred to herein as “catholyte”) are / is comprised of a suspension of electrochemically-active agents (anode particulates and / or cathode particulates) and, optionally, electronically conductive particles (e.g., carbon). The cathodic particles and conductive particles are co-suspended in an electrolyte to produce a catholyte semi-solid. The anodic particles and conductive particles are co-suspended in an electrolyte to produce an anolyte semi-solid. All voltages are wrt Li+ / Li.
[0150]Saf...
example 2
Electrochemical Systems with Inserted Conductive Layers
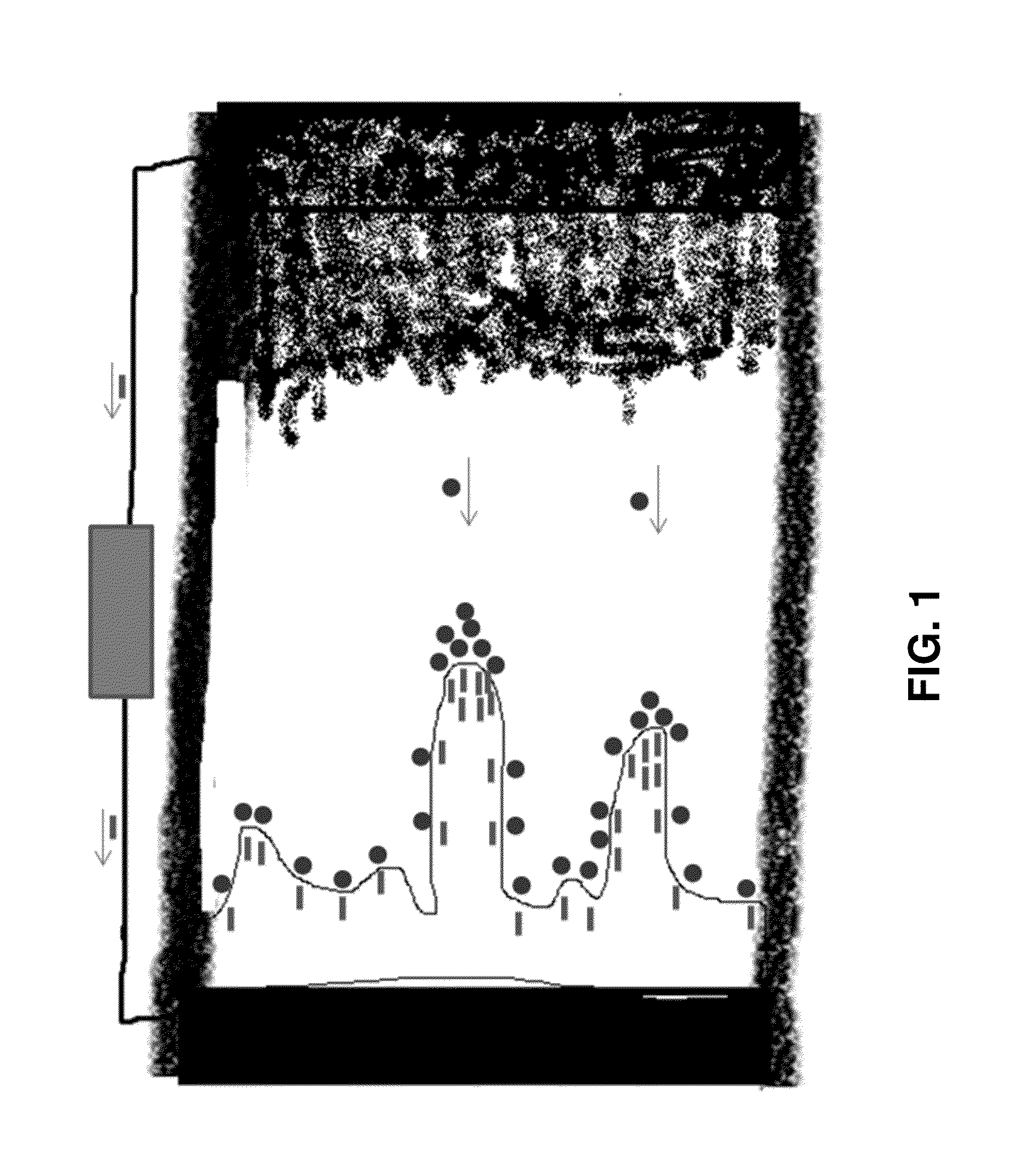
[0156]This example relates to methods in order to stop, slow down or control the dendrite formation in electrochemical plating such as in rechargeable electrochemical cells with lithium metal, zinc metal or aluminum metal anodes, for example in Li-air, Zn-air and Al-air batteries. This disclosure enables high energy, high rate and high cycle life (high performance) rechargeable batteries. Other applications such as electroplating gold or other materials of interest such as other metals can also benefit from this disclosure.
[0157]Different methods are suggested for this purpose. One method is based on manipulating the electric filed near the electrode of interest. In any electroplating, the electric field plays a role in the morphology and speed of the deposition. As an example, there may be some inhomogeneities or impurities (existing such as those from the substrate material or in situ forming such as those from the reactions b...
example 3
Electrochemical Cells with Improved Safety and Performance
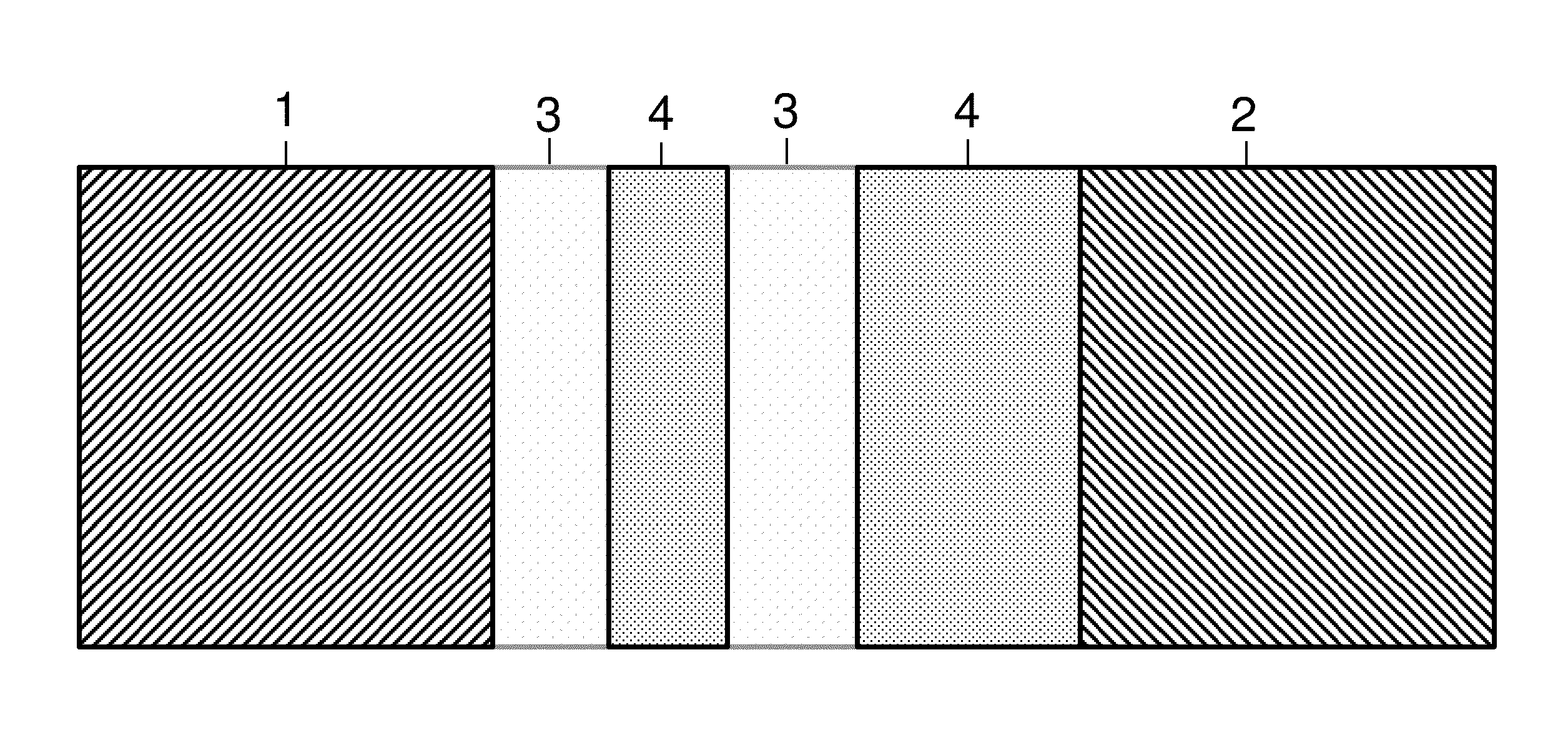
[0167]An electrochemical cell is introduced, consisting of an anode, a cathode, an electrolyte, one or more separator layer(s) and an electronically conductive layer.
[0168]The electronically conductive layer may have no electronic connections with one of the electrodes or may have no electronic connections with any of the electrodes.
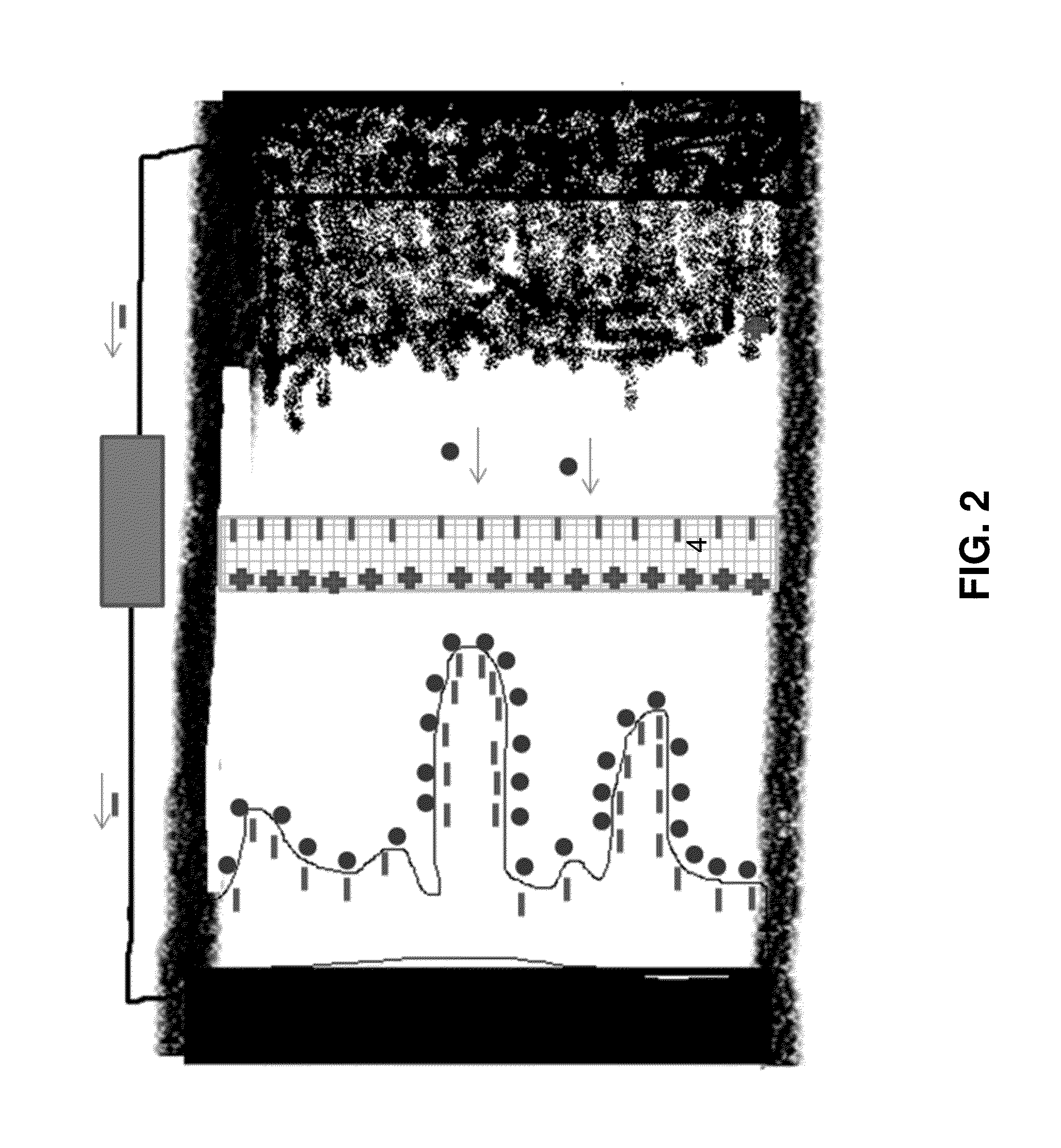
[0169]The electronically conductive layer can be porous, perforated, nonwoven or thin coating. The size of the holes can be from 10 nm to 1 cm, depending on the chemistry of the cell. For example in a lithium ion battery it can be about 0.2 mm. In an alkaline battery (Zinc anode based or Nickel cathode based) it can be about 0.5 mm. The thickness of the layer can be less than 1 mm, preferably less than 0.1 mm depending on the chemistry. For example in li-ion battery it can be about 0.01 mm. In an alkaline battery (Zinc anode based or Nickel cathode based) it can be about 0.1 mm. The layer itself c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com